Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 experiment using a
experiment using a  Cf calibration source
Cf calibration sourceLee, D. H.*; 百々 拓; 羽賀 勝洋; 原田 正英; 長谷川 勝一; 春日井 好己; 木下 秀孝; 増田 志歩; 明午 伸一郎; 酒井 健二; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170216_1 - 170216_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:94.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)JSNS investigates short-baseline neutrino oscillations using a 24-meter baseline and a 17-tonne Gd-loaded liquid scintillator target. Accurate event-reconstruction algorithms are crucial for analyzing experimental data. The algorithms undergo meticulous validation through calibration with a
investigates short-baseline neutrino oscillations using a 24-meter baseline and a 17-tonne Gd-loaded liquid scintillator target. Accurate event-reconstruction algorithms are crucial for analyzing experimental data. The algorithms undergo meticulous validation through calibration with a  Cf source. This paper outlines the methodology and evaluates the reconstruction performance, focusing on neutrino interactions up to approximately 50 MeV for sterile neutrino searches. Both
Cf source. This paper outlines the methodology and evaluates the reconstruction performance, focusing on neutrino interactions up to approximately 50 MeV for sterile neutrino searches. Both  Cf and Michel electron events are studied to evaluate reconstruction accuracy. The analysis concludes that the uncertainty of the fiducial volume, with an appropriate correction, is much less than the requirement of JSNS
Cf and Michel electron events are studied to evaluate reconstruction accuracy. The analysis concludes that the uncertainty of the fiducial volume, with an appropriate correction, is much less than the requirement of JSNS requirement (10%). Furthermore, the energy resolution is measured to be 3.3
requirement (10%). Furthermore, the energy resolution is measured to be 3.3  0.1% for the Michel electron endpoint and 4.3
0.1% for the Michel electron endpoint and 4.3  0.1% for the n-Gd peak in the central region.
0.1% for the n-Gd peak in the central region.

百々 拓; 羽賀 勝洋; 原田 正英; 長谷川 勝一; 春日井 好己; 木下 秀孝; 増田 志歩; 明午 伸一郎; 酒井 健二; 鈴谷 賢太郎; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2025(2), p.023H02_1 - 023H02_8, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)JSNS (J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search a t J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment that is searching for sterile neutrinos via the observation of
(J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search a t J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment that is searching for sterile neutrinos via the observation of 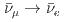 appearance oscillations using neutrinos from muon decay-at-rest. For this search, rejecting cosmic-ray-induced neutron events by Pulse Shape Discrimination (PSD) is essential because the JSNS
appearance oscillations using neutrinos from muon decay-at-rest. For this search, rejecting cosmic-ray-induced neutron events by Pulse Shape Discrimination (PSD) is essential because the JSNS detector is located above ground, on the third floor of the building. We have achieved 94.95
detector is located above ground, on the third floor of the building. We have achieved 94.95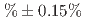 rejection of neutron events while keeping 92.82
rejection of neutron events while keeping 92.82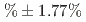 of signal, electron-like events using a data-driven likelihood method. This article will report the PSD technique using the full fiducial volume of the JSNS
of signal, electron-like events using a data-driven likelihood method. This article will report the PSD technique using the full fiducial volume of the JSNS detector.
detector.
Marzec, E.*; 百々 拓; 羽賀 勝洋; 原田 正英; 長谷川 勝一; 春日井 好己; 木下 秀孝; 増田 志歩; 明午 伸一郎; 酒井 健二; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 134, p.081801_1 - 081801_9, 2025/00
被引用回数:0We present the first measurement of the missing energy due to nuclear effects in monoenergetic, muon neutrino charged-current interactions on carbon, originating from 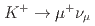 decay at rest (
decay at rest (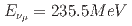 ), performed with the J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at the J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source liquid scintillator based experiment. Toward characterizing the neutrino interaction, ostensibly
), performed with the J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at the J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source liquid scintillator based experiment. Toward characterizing the neutrino interaction, ostensibly 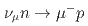 or
or 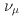
 C
C 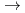
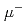
 N, we define the missing energy as the energy transferred to the nucleus (
N, we define the missing energy as the energy transferred to the nucleus ( ) minus the kinetic energy of the outgoing proton(s),
) minus the kinetic energy of the outgoing proton(s), 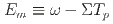 , and relate this to visible energy in the detector,
, and relate this to visible energy in the detector, ![$$E_m = E_{nu_{mu}} (235.5 MeV) - m_{mu}(105.7 MeV) + [m_n - m_p(1.3 MeV)] - E_{vis}$$](/search/images/ERCV41JAHUQEKX11LRXHKX11LRWXK5L3EAUDEMZVFY0SATLFKYUSALJANVPXWXDNOV4SQMJQGUXDOICNMVLCSIBLEBNW0X1OEAWSA1K5OAUDCLRTEBGWKVRJLUQC0ICFL33XM0LTPUSA.gif) . The missing energy, which is naively expected to be zero in the absence of nuclear effects (e.g., nucleon separation energy, Fermi momenta, and final-state interactions), is uniquely sensitive to many aspects of the interaction, and has previously been inaccessible with neutrinos. The shape-only, differential cross section measurement reported, based on a
. The missing energy, which is naively expected to be zero in the absence of nuclear effects (e.g., nucleon separation energy, Fermi momenta, and final-state interactions), is uniquely sensitive to many aspects of the interaction, and has previously been inaccessible with neutrinos. The shape-only, differential cross section measurement reported, based on a 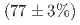 pure double-coincidence kaon decay-at-rest signal (621 total events), provides detailed insight into neutrino-nucleus interactions, allowing even the nuclear orbital shell of the struck nucleon to be inferred. The measurement provides an important benchmark for models and event generators at hundreds of MeV neutrino energies, characterized by the difficult-to-model transition region between neutrino-nucleus and neutrino-nucleon scattering, and relevant for applications in nuclear physics, neutrino oscillation measurements, and Type-II supernova studies.
pure double-coincidence kaon decay-at-rest signal (621 total events), provides detailed insight into neutrino-nucleus interactions, allowing even the nuclear orbital shell of the struck nucleon to be inferred. The measurement provides an important benchmark for models and event generators at hundreds of MeV neutrino energies, characterized by the difficult-to-model transition region between neutrino-nucleus and neutrino-nucleon scattering, and relevant for applications in nuclear physics, neutrino oscillation measurements, and Type-II supernova studies.
 C
C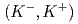 reaction at 1.8 GeV/
reaction at 1.8 GeV/ with the Superconducting Kaon spectrometer
with the Superconducting Kaon spectrometer市川 裕大; 藤田 真奈美; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 七村 拓野; 成木 恵; 佐藤 進; 佐甲 博之; 田村 裕和; 谷田 聖; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2024(9), p.091D01_1 - 091D01_13, 2024/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We conducted a measurement of the inclusive missing-mass spectrum in the  C
C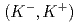 reaction at an incident beam momentum of 1.8 GeV/
reaction at an incident beam momentum of 1.8 GeV/ . This measurement was carried out utilizing the Superconducting Kaon Spectrometer (SKS) and the K1.8 beamline spectrometer at the Hadron Experimental Hall in J-PARC. Remarkably, our experimental setup yielded an exceptionaly good energy resolution of 8.2 MeV (FWHM), enabling us to observe significant enhancements in the vicinity of the
. This measurement was carried out utilizing the Superconducting Kaon Spectrometer (SKS) and the K1.8 beamline spectrometer at the Hadron Experimental Hall in J-PARC. Remarkably, our experimental setup yielded an exceptionaly good energy resolution of 8.2 MeV (FWHM), enabling us to observe significant enhancements in the vicinity of the 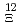 Be threshold region. In order to estimate the spectrum information, we employed several fitting parameters assumptions. The best agreement with the spectrum shape was obtained with combining quasi-free (QF) component and two-Gaussian functions, with the experimental resolution
Be threshold region. In order to estimate the spectrum information, we employed several fitting parameters assumptions. The best agreement with the spectrum shape was obtained with combining quasi-free (QF) component and two-Gaussian functions, with the experimental resolution  being held constant. The peak positions were obtained to be
being held constant. The peak positions were obtained to be 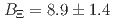 (stat.)
(stat.) 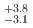 (syst.) MeV and
(syst.) MeV and 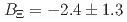 (stat.)
(stat.) 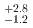 (syst.) MeV. Another model assumption, utilizing quasi-free (QF) and one Breit-Wigner function with
(syst.) MeV. Another model assumption, utilizing quasi-free (QF) and one Breit-Wigner function with 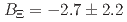 (stat.)
(stat.) 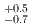 (syst.) MeV and
(syst.) MeV and 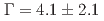 (stat.)
(stat.) 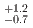 (syst.) MeV, also yielded a similar
(syst.) MeV, also yielded a similar 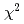 value.
value.
 experiment
experimentLee, D. H.*; 百々 拓; 羽賀 勝洋; 原田 正英; 長谷川 勝一; 春日井 好己; 木下 秀孝; 増田 志歩; 明午 伸一郎; 酒井 健二; et al.
European Physical Journal C, 84, p.409_1 - 409_6, 2024/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.24(Physics, Particles & Fields)JSNS (J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment that searches for sterile neutrinos via the observation of
(J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment that searches for sterile neutrinos via the observation of 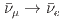 appearance oscillations using muon decay-at-rest neutrinos. The JSNS
appearance oscillations using muon decay-at-rest neutrinos. The JSNS experiment performed data taking from 2021. In this manuscript, a study of the accidental background is presented. The rate of the accidental background is (9.29
experiment performed data taking from 2021. In this manuscript, a study of the accidental background is presented. The rate of the accidental background is (9.29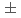 0.39)
0.39)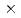 10
10 / spill with 0.75 MW beam power and comparable to the expected number of signal events.
/ spill with 0.75 MW beam power and comparable to the expected number of signal events.
 -II neutrino target
-II neutrino targetShin, C. D.*; 百々 拓; 羽賀 勝洋; 原田 正英; 長谷川 勝一; 春日井 好己; 木下 秀孝; 増田 志歩; 明午 伸一郎; 酒井 健二; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 18(12), p.T12001_1 - T12001_9, 2023/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JSNS (J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment designed for the search for sterile neutrinos. The experiment is currently at the stage of the second phase named JSNS
(J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) is an experiment designed for the search for sterile neutrinos. The experiment is currently at the stage of the second phase named JSNS -II with two detectors at near and far locations from the neutrino source. One of the key components of the experiment is an acrylic vessel, that is used for the target volume for the detection of the anti-neutrinos. The specifications, design, and measured properties of the acrylic vessel are described.
-II with two detectors at near and far locations from the neutrino source. One of the key components of the experiment is an acrylic vessel, that is used for the target volume for the detection of the anti-neutrinos. The specifications, design, and measured properties of the acrylic vessel are described.
Ahn, J. K.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; 他10名*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1047, p.167775_1 - 167775_13, 2023/02
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:18.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have constructed a conduction-cooled superconducting dipole magnet for the Hyperon spectrometer at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The magnet is a Helmholtz-type dipole magnet with two circular coils with a radius of 500 mm separated by 500 mm. It provides a uniform magnetic field of 1.0 T or higher in a volume of  mm
mm  600 mm, covering the drift region of a time projection chamber (TPC). Owing to the target location inside the TPC, the Hyperon spectrometer has a broad angular coverage with a nearly
600 mm, covering the drift region of a time projection chamber (TPC). Owing to the target location inside the TPC, the Hyperon spectrometer has a broad angular coverage with a nearly 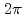 solid angle. We have successfully excited the magnet up to 1.3 T. At 1.0 T, we operated it stably for more than 1 week in single-magnet configuration and double-magnet configuration with a normal-conducting 0.7-T dipole magnet located 30 cm apart. The measured magnetic field distribution in the TPC volume is consistent with the calculated field map.
solid angle. We have successfully excited the magnet up to 1.3 T. At 1.0 T, we operated it stably for more than 1 week in single-magnet configuration and double-magnet configuration with a normal-conducting 0.7-T dipole magnet located 30 cm apart. The measured magnetic field distribution in the TPC volume is consistent with the calculated field map.
 atomic X-ray spectroscopy using a counter-emulsion hybrid method
atomic X-ray spectroscopy using a counter-emulsion hybrid method藤田 真奈美; 長谷川 勝一; 細見 健二; 市川 真也; 市川 裕大; Kim, S.; 七村 拓野; 佐甲 博之; 田村 裕和; 山本 剛史; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(12), p.123D01_1 - 123D01_17, 2022/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:15.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary) atomic X-ray spectroscopy is one of the most useful methods for investigation of the
atomic X-ray spectroscopy is one of the most useful methods for investigation of the  -nucleus strong interaction. Since the X-ray energy is shifted and/or broadened due to the
-nucleus strong interaction. Since the X-ray energy is shifted and/or broadened due to the  -nucleus strong interaction compared to those calculated from electromagnetic interaction alone, the measurement of the energy shift,
-nucleus strong interaction compared to those calculated from electromagnetic interaction alone, the measurement of the energy shift,  E, and the width,
E, and the width,  , give us information on the
, give us information on the  -nucleus potential. A serious problem in the measurement is the significant background derived from in-flight
-nucleus potential. A serious problem in the measurement is the significant background derived from in-flight  decay. A novel method of identifying stopped
decay. A novel method of identifying stopped  events using the nuclear emulsion was developed to realize the first
events using the nuclear emulsion was developed to realize the first  atomic X-ray spectroscopy experiment as the J-PARC E07 experiment, which also aimed at searching for
atomic X-ray spectroscopy experiment as the J-PARC E07 experiment, which also aimed at searching for 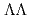 and
and 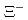 hypernuclei in the emulsion. The X-rays emitted from
hypernuclei in the emulsion. The X-rays emitted from 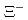 Br and
Br and 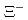 Ag atoms were measured using germanium detectors. No clear peaks were observed in the obtained spectra. However, we succeeded in reducing the background to 1/170 by this method employing coincidence measurements using nuclear emulsion and X-ray detectors.
Ag atoms were measured using germanium detectors. No clear peaks were observed in the obtained spectra. However, we succeeded in reducing the background to 1/170 by this method employing coincidence measurements using nuclear emulsion and X-ray detectors.
三輪 浩司*; 藤田 真奈美; 原田 健志; 長谷川 勝一; 細見 健二; 市川 真也; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 田村 裕和; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.04001_1 - 04001_7, 2022/11
A new hyperon-proton scattering experiment, dubbed J-PARC E40, was performed to measure differential cross sections of the 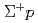 ,
, 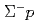 elastic scatterings and the
elastic scatterings and the 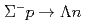 scattering by identifying a lot of
scattering by identifying a lot of 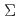 particles in the momentum ranging from 0.4 to 0.8 GeV/
particles in the momentum ranging from 0.4 to 0.8 GeV/ produced by the
produced by the 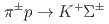 reactions. We successfully measured the differential cross sections of these three channels with a drastically improved accuracy with a fine angular step. These new data will become important experimental constraints to improve the theories of the two-body baryon-baryon interactions. Following this success, we proposed a new experiment to measure the differential cross sections and spin observables by using a highly polarized
reactions. We successfully measured the differential cross sections of these three channels with a drastically improved accuracy with a fine angular step. These new data will become important experimental constraints to improve the theories of the two-body baryon-baryon interactions. Following this success, we proposed a new experiment to measure the differential cross sections and spin observables by using a highly polarized  beam for providing quantitative information on the
beam for providing quantitative information on the 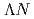 interaction. The results of three
interaction. The results of three 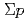 channels and future prospects of the
channels and future prospects of the 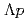 scattering experiment are described.
scattering experiment are described.
後神 利志*; 江端 健悟; 藤田 真奈美; 原田 健志; 長谷川 勝一; 細見 健二; 市川 裕大; 今井 憲一*; Kim, S.; 七村 拓野; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.11002_1 - 11002_7, 2022/11
In the K1.8 beam-line at Hadron Experimental Facility of J-PARC, a new magnetic spectrometer S-2S is being installed. S-2S was designed to achieve a high momentum resolution of 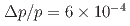 in FWHM. Several strangeness-physics programs which require the high resolution will be realized by S-2S. The present article introduces J-PARC E70 (missing-mass spectroscopy of
in FWHM. Several strangeness-physics programs which require the high resolution will be realized by S-2S. The present article introduces J-PARC E70 (missing-mass spectroscopy of 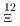 Be) and E94 (missing-mass spectroscopy of
Be) and E94 (missing-mass spectroscopy of 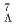 Li,
Li, 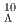 B, and
B, and 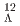 C) experiments.
C) experiments.
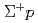 elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/c
elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/c七村 拓野; 藤田 真奈美; 長谷川 勝一; 市川 真也; 市川 裕大; 今井 憲一*; 成木 恵; 佐藤 進; 佐甲 博之; 田村 裕和; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(9), p.093D01_1 - 093D01_35, 2022/09
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:83.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We performed a novel 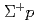 scattering experiment at the J-PARC Hadron Experimental Facility. Approximately 2400
scattering experiment at the J-PARC Hadron Experimental Facility. Approximately 2400 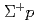 elastic scattering events were identified from
elastic scattering events were identified from 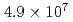 tagged
tagged 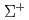 particles in the
particles in the 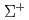 momentum range 0.44 - 0.80 GeV/c. The differential cross sections of the
momentum range 0.44 - 0.80 GeV/c. The differential cross sections of the 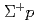 elastic scattering were derived with much better precision than in previous experiments. The obtained differential cross sections were approximately 2 mb/sr or less, which were not as large as those predicted by the fss2 and FSS models based on the quark cluster model in the short-range region. By performing phase-shift analyses for the obtained differential cross sections, we experimentally derived the phase shifts of the
elastic scattering were derived with much better precision than in previous experiments. The obtained differential cross sections were approximately 2 mb/sr or less, which were not as large as those predicted by the fss2 and FSS models based on the quark cluster model in the short-range region. By performing phase-shift analyses for the obtained differential cross sections, we experimentally derived the phase shifts of the 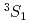 and
and 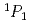 channels for the first time. The phase shift of the 3S1 channel, where a large repulsive core was predicted owing to the Pauli effect between quarks, was evaluated to be
channels for the first time. The phase shift of the 3S1 channel, where a large repulsive core was predicted owing to the Pauli effect between quarks, was evaluated to be 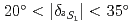 . If the sign of
. If the sign of 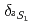 is assumed to be negative, the interaction in this channel is moderately repulsive, as the Nijmegen extended-sort-core models predicted.
is assumed to be negative, the interaction in this channel is moderately repulsive, as the Nijmegen extended-sort-core models predicted.
 meson production in
meson production in 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他365名*
Physical Review C, 106(1), p.014908_1 - 014908_13, 2022/07
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:67.20(Physics, Nuclear)Small nuclear collisions are mainly sensitive to cold-nuclear-matter effects; however, the collective behavior observed in these collisions shows a hint of hot-nuclear-matter effects. The identified-particle spectra, especially the  mesons which contain strange and antistrange quarks and have a relatively small hadronic-interaction cross section, are a good tool to study these effects. The PHENIX experiment has measured
mesons which contain strange and antistrange quarks and have a relatively small hadronic-interaction cross section, are a good tool to study these effects. The PHENIX experiment has measured  mesons in a specific set of small collision systems
mesons in a specific set of small collision systems 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au, as well as
Au, as well as 
 Au, at
Au, at  GeV. The transverse-momentum spectra and nuclear-modification factors are presented and compared to theoretical-model predictions. The comparisons with different calculations suggest that quark-gluon plasma may be formed in these small collision systems at
GeV. The transverse-momentum spectra and nuclear-modification factors are presented and compared to theoretical-model predictions. The comparisons with different calculations suggest that quark-gluon plasma may be formed in these small collision systems at  GeV. However, the volume and the lifetime of the produced medium may be insufficient for observing strangeness-enhancement and jet-quenching effects. Comparison with calculations suggests that the main production mechanisms of
GeV. However, the volume and the lifetime of the produced medium may be insufficient for observing strangeness-enhancement and jet-quenching effects. Comparison with calculations suggests that the main production mechanisms of  mesons at midrapidity may be different in
mesons at midrapidity may be different in 
 Al versus
Al versus 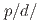
 He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV. While thermal quark recombination seems to dominate in
GeV. While thermal quark recombination seems to dominate in 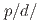
 He
He Au collisions, fragmentation seems to be the main production mechanism in
Au collisions, fragmentation seems to be the main production mechanism in 
 Al collisions.
Al collisions.
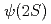 nuclear modification at backward and forward rapidity in
nuclear modification at backward and forward rapidity in 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他310名*
Physical Review C, 105(6), p.064912_1 - 064912_15, 2022/06
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:91.22(Physics, Nuclear)Suppression of the 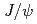 nuclear-modification factor has been seen as a trademark signature of final-state effects in large collision systems for decades. In small systems, the nuclear modification was attributed to cold-nuclear-matter effects until the observation of strong differential suppression of the
nuclear-modification factor has been seen as a trademark signature of final-state effects in large collision systems for decades. In small systems, the nuclear modification was attributed to cold-nuclear-matter effects until the observation of strong differential suppression of the 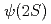 state in
state in 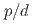

 collisions suggested the presence of final-state effects. Results of
collisions suggested the presence of final-state effects. Results of 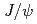 and
and 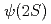 measurements in the dimuon decay channel are presented here for
measurements in the dimuon decay channel are presented here for 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collision systems at
Au collision systems at  GeV. The results are predominantly shown in the form of the nuclear-modification factor,
GeV. The results are predominantly shown in the form of the nuclear-modification factor, 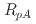 , the ratio of the
, the ratio of the 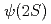 invariant yield per nucleon-nucleon collision in collisions of proton on target nucleus to that in
invariant yield per nucleon-nucleon collision in collisions of proton on target nucleus to that in 

 collisions. Measurements of the
collisions. Measurements of the 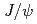 and
and 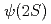 nuclear-modification factor are compared with shadowing and transport-model predictions, as well as to complementary measurements at Large-Hadron-Collider energies.
nuclear-modification factor are compared with shadowing and transport-model predictions, as well as to complementary measurements at Large-Hadron-Collider energies.

 Al,
Al, 
 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV using
GeV using 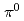 production
productionAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他547名*
Physical Review C, 105(6), p.064902_1 - 064902_19, 2022/06
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:94.22(Physics, Nuclear)The PHENIX collaboration presents a systematic study of 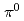 production from
production from 

 ,
, 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV. Measurements were performed with different centrality selections as well as the total inelastic, 0% - 100%, selection for all collision systems. For 0% - 100% collisions, the nuclear modification factors,
GeV. Measurements were performed with different centrality selections as well as the total inelastic, 0% - 100%, selection for all collision systems. For 0% - 100% collisions, the nuclear modification factors, 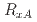 , are consistent with unity for
, are consistent with unity for  above 8 GeV/
above 8 GeV/ , but exhibit an enhancement in peripheral collisions and a suppression in central collisions. The enhancement and suppression characteristics are similar for all systems for the same centrality class. It is shown that for high-
, but exhibit an enhancement in peripheral collisions and a suppression in central collisions. The enhancement and suppression characteristics are similar for all systems for the same centrality class. It is shown that for high- -
-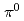 production, the nucleons in the
production, the nucleons in the  and
and  He interact mostly independently with the Au nucleus and that the counter intuitive centrality dependence is likely due to a physical correlation between multiplicity and the presence of a hard scattering process. These observations disfavor models where parton energy loss has a significant contribution to nuclear modifications in small systems. Nuclear modifications at lower
He interact mostly independently with the Au nucleus and that the counter intuitive centrality dependence is likely due to a physical correlation between multiplicity and the presence of a hard scattering process. These observations disfavor models where parton energy loss has a significant contribution to nuclear modifications in small systems. Nuclear modifications at lower  resemble the Cronin effect - an increase followed by a peak in central or inelastic collisions and a plateau in peripheral collisions. The peak height has a characteristic ordering by system size as
resemble the Cronin effect - an increase followed by a peak in central or inelastic collisions and a plateau in peripheral collisions. The peak height has a characteristic ordering by system size as 
 Au
Au 

 Au
Au 
 He
He Au
Au 

 Al. For collisions with Au ions, current calculations based on initial state cold nuclear matter effects result in the opposite order, suggesting the presence of other contributions to nuclear modifications, in particular at lower
Al. For collisions with Au ions, current calculations based on initial state cold nuclear matter effects result in the opposite order, suggesting the presence of other contributions to nuclear modifications, in particular at lower  .
.

 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He+Au at
He+Au at 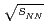 = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他378名*
Physical Review C, 105(2), p.024901_1 - 024901_13, 2022/02
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:87.03(Physics, Nuclear)There is strong evidence for the formation of small droplets of quark-gluon plasma in 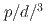 He+Au collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) and in
He+Au collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) and in  +
+ /Pb collisions at the Large Hadron Collider. In particular, the analysis of data at RHIC for different geometries obtained by varying the projectile size and shape has proven insightful. In the present analysis, we find excellent agreement with the previously published PHENIX at RHIC results on elliptical and triangular flow with an independent analysis via the two-particle correlation method, which has quite different systematic uncertainties and an independent code base. In addition, the results are extended to other detector combinations with different kinematic (pseudorapidity) coverage. These results provide additional constraints on contributions from nonflow and longitudinal decorrelations.
/Pb collisions at the Large Hadron Collider. In particular, the analysis of data at RHIC for different geometries obtained by varying the projectile size and shape has proven insightful. In the present analysis, we find excellent agreement with the previously published PHENIX at RHIC results on elliptical and triangular flow with an independent analysis via the two-particle correlation method, which has quite different systematic uncertainties and an independent code base. In addition, the results are extended to other detector combinations with different kinematic (pseudorapidity) coverage. These results provide additional constraints on contributions from nonflow and longitudinal decorrelations.
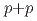 collisions at
collisions at 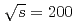 GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他306名*
Physical Review D, 105(3), p.032003_1 - 032003_8, 2022/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:20.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)In 2015, the PHENIX collaboration has measured single-spin asymmetries for charged pions in transversely polarized proton-proton collisions at the center of mass energy of 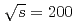 GeV. The pions were detected at central rapidities of
GeV. The pions were detected at central rapidities of 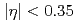 . The single-spin asymmetries are consistent with zero for each charge individually, as well as consistent with the previously published neutral-pion asymmetries in the same rapidity range. However, they show a slight indication of charge-dependent differences which may suggest a flavor dependence in the underlying mechanisms that create these asymmetries.
. The single-spin asymmetries are consistent with zero for each charge individually, as well as consistent with the previously published neutral-pion asymmetries in the same rapidity range. However, they show a slight indication of charge-dependent differences which may suggest a flavor dependence in the underlying mechanisms that create these asymmetries.


 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collisions at
Au collisions at 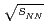 = 200 GeV as a function of transverse and longitudinal momenta
= 200 GeV as a function of transverse and longitudinal momentaAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他305名*
Physical Review D, 105(3), p.032004_1 - 032004_13, 2022/02
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:37.56(Astronomy & Astrophysics)In 2015 the PHENIX collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider recorded 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collision data at center of mass energies of
Au collision data at center of mass energies of  GeV with the proton beam(s) transversely polarized. At very forward rapidities
GeV with the proton beam(s) transversely polarized. At very forward rapidities 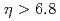 relative to the polarized proton beam, neutrons were detected either inclusively or in (anti)correlation with detector activity related to hard collisions. The resulting single spin asymmetries, that were previously reported, have now been extracted as a function of the transverse momentum of the neutron as well as its longitudinal momentum fraction
relative to the polarized proton beam, neutrons were detected either inclusively or in (anti)correlation with detector activity related to hard collisions. The resulting single spin asymmetries, that were previously reported, have now been extracted as a function of the transverse momentum of the neutron as well as its longitudinal momentum fraction 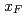 . The explicit kinematic dependence, combined with the correlation information allows for a closer look at the interplay of different mechanisms suggested to describe these asymmetries, such as hadronic interactions or electromagnetic interactions in ultra-peripheral collisions, UPC. Events that are correlated with a hard collision indeed display a mostly negative asymmetry that increases in magnitude as a function of transverse momentum with only little dependence on
. The explicit kinematic dependence, combined with the correlation information allows for a closer look at the interplay of different mechanisms suggested to describe these asymmetries, such as hadronic interactions or electromagnetic interactions in ultra-peripheral collisions, UPC. Events that are correlated with a hard collision indeed display a mostly negative asymmetry that increases in magnitude as a function of transverse momentum with only little dependence on 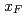 . In contrast, events that are not likely to have emerged from a hard collision display positive asymmetries for the nuclear collisions with a kinematic dependence that resembles that of a UPC based model. Because the UPC interaction depends strongly on the charge of the nucleus, those effects are very small for
. In contrast, events that are not likely to have emerged from a hard collision display positive asymmetries for the nuclear collisions with a kinematic dependence that resembles that of a UPC based model. Because the UPC interaction depends strongly on the charge of the nucleus, those effects are very small for 

 collisions, moderate for
collisions, moderate for 
 Al collisions, and large for
Al collisions, and large for 
 Au collisions.
Au collisions.
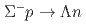 reaction in momentum range 470-650 MeV/
reaction in momentum range 470-650 MeV/
三輪 浩司*; 藤田 真奈美; 長谷川 勝一; 細見 健二; 市川 裕大*; 今井 憲一*; 七村 拓野; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 田村 裕和; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 128(7), p.072501_1 - 072501_6, 2022/02
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:86.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The differential cross sections of the 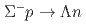 reaction were measured accurately for the
reaction were measured accurately for the 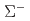 momentum
momentum 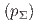 ranging from 470 to 650 MeV/
ranging from 470 to 650 MeV/ at the J-PARC Hadron Experimental Facility. Precise angular information about the
at the J-PARC Hadron Experimental Facility. Precise angular information about the 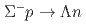 reaction was obtained for the first time by detecting approximately 100 reaction events at each angular step of
reaction was obtained for the first time by detecting approximately 100 reaction events at each angular step of 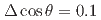 . The obtained differential cross sections show slightly forward-peaking structure in the measured momentum regions. The cross sections integrated for
. The obtained differential cross sections show slightly forward-peaking structure in the measured momentum regions. The cross sections integrated for 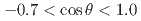 were obtained as
were obtained as 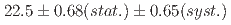 mb and
mb and 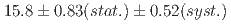 mb for
mb for 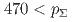 (MeV/c)
(MeV/c) 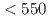 and
and 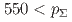 (MeV/c)
(MeV/c)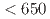 , respectively. These results show a drastic improvement compared to past measurements of the hyperon-proton scattering experiments. They will play essential roles in updating the theoretical models of the baryon-baryon interactions.
, respectively. These results show a drastic improvement compared to past measurements of the hyperon-proton scattering experiments. They will play essential roles in updating the theoretical models of the baryon-baryon interactions.
 detector
detector味村 周平*; 羽賀 勝洋; 原田 正英; 長谷川 勝一; 春日井 好己; 木下 秀孝; 増田 志歩; 明午 伸一郎; 酒井 健二; 鈴谷 賢太郎; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1014, p.165742_1 - 165742_15, 2021/10
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:94.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)The JSNS (J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) experiment aims to search for oscillations involving a sterile neutrino in the eV
(J-PARC Sterile Neutrino Search at J-PARC Spallation Neutron Source) experiment aims to search for oscillations involving a sterile neutrino in the eV mass-splitting range. The experiment will search for the appearance of electron antineutrinos oscillated from muon antineutrinos. The electron antineutrinos are detected via the inverse beta decay process using a liquid scintillator detector. A 1MW beam of 3 GeV protons incident on a spallation neutron target produces an intense and pulsed neutrino source from pion, muon, and kaon decay at rest. The JSNS
mass-splitting range. The experiment will search for the appearance of electron antineutrinos oscillated from muon antineutrinos. The electron antineutrinos are detected via the inverse beta decay process using a liquid scintillator detector. A 1MW beam of 3 GeV protons incident on a spallation neutron target produces an intense and pulsed neutrino source from pion, muon, and kaon decay at rest. The JSNS detector is located 24m away from the neutrino source and began operation from June 2020. The detector contains 17 tonnes of gadolinium (Gd) loaded liquid scintillator (LS) in an acrylic vessel, as a neutrino target. It is surrounded by 31 tonnes of unloaded LS in a stainless steel tank. Optical photons produced in LS are viewed by 120 R7081 Hamamatsu 10-inch Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs). In this paper, we describe the JSNS
detector is located 24m away from the neutrino source and began operation from June 2020. The detector contains 17 tonnes of gadolinium (Gd) loaded liquid scintillator (LS) in an acrylic vessel, as a neutrino target. It is surrounded by 31 tonnes of unloaded LS in a stainless steel tank. Optical photons produced in LS are viewed by 120 R7081 Hamamatsu 10-inch Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs). In this paper, we describe the JSNS detector design, construction, and operation.
detector design, construction, and operation.
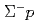 elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
三輪 浩司*; 藤田 真奈美; 長谷川 勝一; 細見 健二; 市川 裕大; 今井 憲一*; 七村 拓野; 成木 恵; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(4), p.045204_1 - 045204_20, 2021/10
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:89.84(Physics, Nuclear)A high statistics 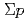 scattering experiment is performed at the J-PARC Hadron Experimental Facility. Momentum-tagged
scattering experiment is performed at the J-PARC Hadron Experimental Facility. Momentum-tagged 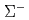 s running in a liquid hydrogen target are accumulated by detecting the reaction with a high intensity
s running in a liquid hydrogen target are accumulated by detecting the reaction with a high intensity 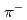 beam of 20 M/spill. The differential cross sections of the
beam of 20 M/spill. The differential cross sections of the 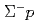 elastic scattering were derived with a drastically improved accuracy by identifying approximately 4,500 events from 1.72
elastic scattering were derived with a drastically improved accuracy by identifying approximately 4,500 events from 1.72  10
10
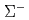 . The derived differential cross section shows a clear forward-peaking angular distribution for a
. The derived differential cross section shows a clear forward-peaking angular distribution for a 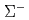 momentum range from 470 to 850 MeV/
momentum range from 470 to 850 MeV/ . The accurate data will impose a strong constraint on the theoretical models of the baryon-baryon interactions.
. The accurate data will impose a strong constraint on the theoretical models of the baryon-baryon interactions.