Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 meson production in
meson production in 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他365名*
Physical Review C, 106(1), p.014908_1 - 014908_13, 2022/07
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:67.20(Physics, Nuclear)Small nuclear collisions are mainly sensitive to cold-nuclear-matter effects; however, the collective behavior observed in these collisions shows a hint of hot-nuclear-matter effects. The identified-particle spectra, especially the  mesons which contain strange and antistrange quarks and have a relatively small hadronic-interaction cross section, are a good tool to study these effects. The PHENIX experiment has measured
mesons which contain strange and antistrange quarks and have a relatively small hadronic-interaction cross section, are a good tool to study these effects. The PHENIX experiment has measured  mesons in a specific set of small collision systems
mesons in a specific set of small collision systems 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au, as well as
Au, as well as 
 Au, at
Au, at  GeV. The transverse-momentum spectra and nuclear-modification factors are presented and compared to theoretical-model predictions. The comparisons with different calculations suggest that quark-gluon plasma may be formed in these small collision systems at
GeV. The transverse-momentum spectra and nuclear-modification factors are presented and compared to theoretical-model predictions. The comparisons with different calculations suggest that quark-gluon plasma may be formed in these small collision systems at  GeV. However, the volume and the lifetime of the produced medium may be insufficient for observing strangeness-enhancement and jet-quenching effects. Comparison with calculations suggests that the main production mechanisms of
GeV. However, the volume and the lifetime of the produced medium may be insufficient for observing strangeness-enhancement and jet-quenching effects. Comparison with calculations suggests that the main production mechanisms of  mesons at midrapidity may be different in
mesons at midrapidity may be different in 
 Al versus
Al versus 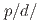
 He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV. While thermal quark recombination seems to dominate in
GeV. While thermal quark recombination seems to dominate in 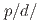
 He
He Au collisions, fragmentation seems to be the main production mechanism in
Au collisions, fragmentation seems to be the main production mechanism in 
 Al collisions.
Al collisions.

 Al,
Al, 
 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV using
GeV using 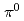 production
productionAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他547名*
Physical Review C, 105(6), p.064902_1 - 064902_19, 2022/06
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:94.22(Physics, Nuclear)The PHENIX collaboration presents a systematic study of 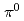 production from
production from 

 ,
, 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He
He Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV. Measurements were performed with different centrality selections as well as the total inelastic, 0% - 100%, selection for all collision systems. For 0% - 100% collisions, the nuclear modification factors,
GeV. Measurements were performed with different centrality selections as well as the total inelastic, 0% - 100%, selection for all collision systems. For 0% - 100% collisions, the nuclear modification factors, 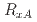 , are consistent with unity for
, are consistent with unity for  above 8 GeV/
above 8 GeV/ , but exhibit an enhancement in peripheral collisions and a suppression in central collisions. The enhancement and suppression characteristics are similar for all systems for the same centrality class. It is shown that for high-
, but exhibit an enhancement in peripheral collisions and a suppression in central collisions. The enhancement and suppression characteristics are similar for all systems for the same centrality class. It is shown that for high- -
-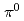 production, the nucleons in the
production, the nucleons in the  and
and  He interact mostly independently with the Au nucleus and that the counter intuitive centrality dependence is likely due to a physical correlation between multiplicity and the presence of a hard scattering process. These observations disfavor models where parton energy loss has a significant contribution to nuclear modifications in small systems. Nuclear modifications at lower
He interact mostly independently with the Au nucleus and that the counter intuitive centrality dependence is likely due to a physical correlation between multiplicity and the presence of a hard scattering process. These observations disfavor models where parton energy loss has a significant contribution to nuclear modifications in small systems. Nuclear modifications at lower  resemble the Cronin effect - an increase followed by a peak in central or inelastic collisions and a plateau in peripheral collisions. The peak height has a characteristic ordering by system size as
resemble the Cronin effect - an increase followed by a peak in central or inelastic collisions and a plateau in peripheral collisions. The peak height has a characteristic ordering by system size as 
 Au
Au 

 Au
Au 
 He
He Au
Au 

 Al. For collisions with Au ions, current calculations based on initial state cold nuclear matter effects result in the opposite order, suggesting the presence of other contributions to nuclear modifications, in particular at lower
Al. For collisions with Au ions, current calculations based on initial state cold nuclear matter effects result in the opposite order, suggesting the presence of other contributions to nuclear modifications, in particular at lower  .
.
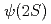 nuclear modification at backward and forward rapidity in
nuclear modification at backward and forward rapidity in 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他310名*
Physical Review C, 105(6), p.064912_1 - 064912_15, 2022/06
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:91.22(Physics, Nuclear)Suppression of the 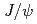 nuclear-modification factor has been seen as a trademark signature of final-state effects in large collision systems for decades. In small systems, the nuclear modification was attributed to cold-nuclear-matter effects until the observation of strong differential suppression of the
nuclear-modification factor has been seen as a trademark signature of final-state effects in large collision systems for decades. In small systems, the nuclear modification was attributed to cold-nuclear-matter effects until the observation of strong differential suppression of the 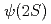 state in
state in 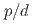

 collisions suggested the presence of final-state effects. Results of
collisions suggested the presence of final-state effects. Results of 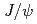 and
and 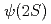 measurements in the dimuon decay channel are presented here for
measurements in the dimuon decay channel are presented here for 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collision systems at
Au collision systems at  GeV. The results are predominantly shown in the form of the nuclear-modification factor,
GeV. The results are predominantly shown in the form of the nuclear-modification factor, 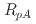 , the ratio of the
, the ratio of the 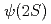 invariant yield per nucleon-nucleon collision in collisions of proton on target nucleus to that in
invariant yield per nucleon-nucleon collision in collisions of proton on target nucleus to that in 

 collisions. Measurements of the
collisions. Measurements of the 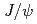 and
and 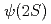 nuclear-modification factor are compared with shadowing and transport-model predictions, as well as to complementary measurements at Large-Hadron-Collider energies.
nuclear-modification factor are compared with shadowing and transport-model predictions, as well as to complementary measurements at Large-Hadron-Collider energies.

 Au,
Au, 
 Au, and
Au, and  He+Au at
He+Au at 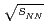 = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他378名*
Physical Review C, 105(2), p.024901_1 - 024901_13, 2022/02
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:87.03(Physics, Nuclear)There is strong evidence for the formation of small droplets of quark-gluon plasma in 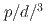 He+Au collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) and in
He+Au collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) and in  +
+ /Pb collisions at the Large Hadron Collider. In particular, the analysis of data at RHIC for different geometries obtained by varying the projectile size and shape has proven insightful. In the present analysis, we find excellent agreement with the previously published PHENIX at RHIC results on elliptical and triangular flow with an independent analysis via the two-particle correlation method, which has quite different systematic uncertainties and an independent code base. In addition, the results are extended to other detector combinations with different kinematic (pseudorapidity) coverage. These results provide additional constraints on contributions from nonflow and longitudinal decorrelations.
/Pb collisions at the Large Hadron Collider. In particular, the analysis of data at RHIC for different geometries obtained by varying the projectile size and shape has proven insightful. In the present analysis, we find excellent agreement with the previously published PHENIX at RHIC results on elliptical and triangular flow with an independent analysis via the two-particle correlation method, which has quite different systematic uncertainties and an independent code base. In addition, the results are extended to other detector combinations with different kinematic (pseudorapidity) coverage. These results provide additional constraints on contributions from nonflow and longitudinal decorrelations.
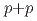 collisions at
collisions at 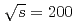 GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他306名*
Physical Review D, 105(3), p.032003_1 - 032003_8, 2022/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:20.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)In 2015, the PHENIX collaboration has measured single-spin asymmetries for charged pions in transversely polarized proton-proton collisions at the center of mass energy of 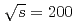 GeV. The pions were detected at central rapidities of
GeV. The pions were detected at central rapidities of 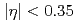 . The single-spin asymmetries are consistent with zero for each charge individually, as well as consistent with the previously published neutral-pion asymmetries in the same rapidity range. However, they show a slight indication of charge-dependent differences which may suggest a flavor dependence in the underlying mechanisms that create these asymmetries.
. The single-spin asymmetries are consistent with zero for each charge individually, as well as consistent with the previously published neutral-pion asymmetries in the same rapidity range. However, they show a slight indication of charge-dependent differences which may suggest a flavor dependence in the underlying mechanisms that create these asymmetries.


 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collisions at
Au collisions at 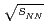 = 200 GeV as a function of transverse and longitudinal momenta
= 200 GeV as a function of transverse and longitudinal momentaAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他305名*
Physical Review D, 105(3), p.032004_1 - 032004_13, 2022/02
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:37.56(Astronomy & Astrophysics)In 2015 the PHENIX collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider recorded 

 ,
, 
 Al, and
Al, and 
 Au collision data at center of mass energies of
Au collision data at center of mass energies of  GeV with the proton beam(s) transversely polarized. At very forward rapidities
GeV with the proton beam(s) transversely polarized. At very forward rapidities 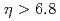 relative to the polarized proton beam, neutrons were detected either inclusively or in (anti)correlation with detector activity related to hard collisions. The resulting single spin asymmetries, that were previously reported, have now been extracted as a function of the transverse momentum of the neutron as well as its longitudinal momentum fraction
relative to the polarized proton beam, neutrons were detected either inclusively or in (anti)correlation with detector activity related to hard collisions. The resulting single spin asymmetries, that were previously reported, have now been extracted as a function of the transverse momentum of the neutron as well as its longitudinal momentum fraction 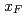 . The explicit kinematic dependence, combined with the correlation information allows for a closer look at the interplay of different mechanisms suggested to describe these asymmetries, such as hadronic interactions or electromagnetic interactions in ultra-peripheral collisions, UPC. Events that are correlated with a hard collision indeed display a mostly negative asymmetry that increases in magnitude as a function of transverse momentum with only little dependence on
. The explicit kinematic dependence, combined with the correlation information allows for a closer look at the interplay of different mechanisms suggested to describe these asymmetries, such as hadronic interactions or electromagnetic interactions in ultra-peripheral collisions, UPC. Events that are correlated with a hard collision indeed display a mostly negative asymmetry that increases in magnitude as a function of transverse momentum with only little dependence on 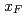 . In contrast, events that are not likely to have emerged from a hard collision display positive asymmetries for the nuclear collisions with a kinematic dependence that resembles that of a UPC based model. Because the UPC interaction depends strongly on the charge of the nucleus, those effects are very small for
. In contrast, events that are not likely to have emerged from a hard collision display positive asymmetries for the nuclear collisions with a kinematic dependence that resembles that of a UPC based model. Because the UPC interaction depends strongly on the charge of the nucleus, those effects are very small for 

 collisions, moderate for
collisions, moderate for 
 Al collisions, and large for
Al collisions, and large for 
 Au collisions.
Au collisions.
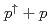 collisions at
collisions at  =200 GeV
=200 GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他306名*
Physical Review Letters, 127(16), p.162001_1 - 162001_8, 2021/10
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:61.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Studying spin-momentum correlations in hadronic collisions offers a glimpse into a three-dimensional picture of proton structure. The transverse single-spin asymmetry for midrapidity isolated direct photons in 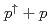 collisions at
collisions at  =200 GeV is measured with the PHENIX detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC). Because direct photons in particular are produced from the hard scattering and do not interact via the strong force, this measurement is a clean probe of initial-state spin-momentum correlations inside the proton and is in particular sensitive to gluon interference effects within the proton. This is the first time direct photons have been used as a probe of spin-momentum correlations at RHIC. The uncertainties on the results are a fifty-fold improvement with respect to those of the one prior measurement for the same observable, from the Fermilab E704 experiment. These results constrain gluon spin-momentum correlations in transversely polarized protons.
=200 GeV is measured with the PHENIX detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC). Because direct photons in particular are produced from the hard scattering and do not interact via the strong force, this measurement is a clean probe of initial-state spin-momentum correlations inside the proton and is in particular sensitive to gluon interference effects within the proton. This is the first time direct photons have been used as a probe of spin-momentum correlations at RHIC. The uncertainties on the results are a fifty-fold improvement with respect to those of the one prior measurement for the same observable, from the Fermilab E704 experiment. These results constrain gluon spin-momentum correlations in transversely polarized protons.
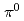 and
and  mesons in polarized
mesons in polarized 

 collisions at
collisions at 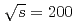 GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他309名*
Physical Review D, 103(5), p.052009_1 - 052009_10, 2021/03
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:33.21(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We present a measurement of the transverse single-spin asymmetry for 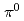 and
and  mesons in
mesons in 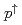

 collisions in the pseudorapidity range
collisions in the pseudorapidity range 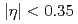 and at a center-of-mass energy of 200 GeV with the PHENIX detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. In comparison with previous measurements in this kinematic region, these results have a factor of 3 smaller uncertainties. As hadrons,
and at a center-of-mass energy of 200 GeV with the PHENIX detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. In comparison with previous measurements in this kinematic region, these results have a factor of 3 smaller uncertainties. As hadrons, 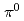 and
and  mesons are sensitive to both initial- and final-state nonperturbative effects for a mix of parton flavors. Comparisons of the differences in their transverse single-spin asymmetries have the potential to disentangle the possible effects of strangeness, isospin, or mass. These results can constrain the twist-3 trigluon collinear correlation function as well as the gluon Sivers function.
mesons are sensitive to both initial- and final-state nonperturbative effects for a mix of parton flavors. Comparisons of the differences in their transverse single-spin asymmetries have the potential to disentangle the possible effects of strangeness, isospin, or mass. These results can constrain the twist-3 trigluon collinear correlation function as well as the gluon Sivers function.


 collisions at
collisions at 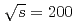 GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他308名*
Physical Review D, 103(3), p.032007_1 - 032007_8, 2021/02
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:20.82(Astronomy & Astrophysics)In 2015, the PHENIX collaboration has measured very forward (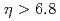 ) single-spin asymmetries of inclusive neutrons in transversely polarized proton-proton and proton-nucleus collisions at a center of mass energy of 200 GeV. A previous publication from this data set concentrated on the nuclear dependence of such asymmetries. In this measurement the explicit transverse-momentum dependence of inclusive neutron single spin asymmetries for proton-proton collisions is extracted using a bootstrapping-unfolding technique on the transverse momenta. This explicit transverse-momentum dependence will help improve the understanding of the mechanisms that create these asymmetries.
) single-spin asymmetries of inclusive neutrons in transversely polarized proton-proton and proton-nucleus collisions at a center of mass energy of 200 GeV. A previous publication from this data set concentrated on the nuclear dependence of such asymmetries. In this measurement the explicit transverse-momentum dependence of inclusive neutron single spin asymmetries for proton-proton collisions is extracted using a bootstrapping-unfolding technique on the transverse momenta. This explicit transverse-momentum dependence will help improve the understanding of the mechanisms that create these asymmetries.
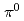 and
and  mesons in U
mesons in U U collisions at
U collisions at 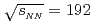 GeV
GeVAcharya, U.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 永宮 正治*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他397名*
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064905_1 - 064905_13, 2020/12
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:50.34(Physics, Nuclear)The PHENIX experiment at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider measured 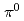 and
and  mesons at midrapidity in U
mesons at midrapidity in U U collisions at
U collisions at 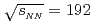 GeV in a wide transverse momentum range. Measurements were performed in the
GeV in a wide transverse momentum range. Measurements were performed in the 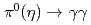 decay modes. A strong suppression of
decay modes. A strong suppression of 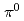 and
and  meson production at high transverse momentum was observed in central U
meson production at high transverse momentum was observed in central U U collisions relative to binary scaled
U collisions relative to binary scaled 

 results. Yields of
results. Yields of 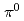 and
and  mesons measured in U
mesons measured in U U collisions show similar suppression pattern to the ones measured in Au
U collisions show similar suppression pattern to the ones measured in Au Au collisions at
Au collisions at  GeV for similar numbers of participant nucleons. The
GeV for similar numbers of participant nucleons. The  /
/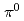 ratios do not show dependence on centrality or transverse momentum, and are consistent with previously measured values in hadron-hadron, hadron-nucleus, nucleus-nucleus, and
ratios do not show dependence on centrality or transverse momentum, and are consistent with previously measured values in hadron-hadron, hadron-nucleus, nucleus-nucleus, and 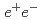 collisions.
collisions.
 +Au collisions at
+Au collisions at  GeV
GeVAcharya, U.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 永宮 正治*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他572名*
Physical Review C, 102(5), p.054910_1 - 054910_11, 2020/11
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:44.30(Physics, Nuclear)We present direct photon-hadron correlations in 200 GeV/A Au Au,
Au, 
 Au and
Au and 

 collisions, for direct photon
collisions, for direct photon  from 5 - 12 GeV/
from 5 - 12 GeV/ , collected by the PHENIX Collaboration in the years from 2006 to 2011. We observe no significant modification of jet fragmentation in
, collected by the PHENIX Collaboration in the years from 2006 to 2011. We observe no significant modification of jet fragmentation in 
 Au collisions, indicating that cold nuclear matter effects are small or absent. Hadrons carrying a large fraction of the quark's momentum are suppressed in Au
Au collisions, indicating that cold nuclear matter effects are small or absent. Hadrons carrying a large fraction of the quark's momentum are suppressed in Au Au compared to
Au compared to 

 and
and 
 Au. As the momentum fraction decreases, the yield of hadrons in Au
Au. As the momentum fraction decreases, the yield of hadrons in Au Au increases to an excess over the yield in
Au increases to an excess over the yield in 

 collisions. The excess is at large angles and at low hadron
collisions. The excess is at large angles and at low hadron  and is most pronounced for hadrons associated with lower momentum direct photons. Comparison to theoretical calculations suggests that the hadron excess arises from medium response to energy deposited by jets.
and is most pronounced for hadrons associated with lower momentum direct photons. Comparison to theoretical calculations suggests that the hadron excess arises from medium response to energy deposited by jets.
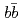 at forward rapidity in
at forward rapidity in  collisions at
collisions at 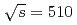 GeV
GeVAcharya, U.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 永宮 正治*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他344名*
Physical Review D, 102(9), p.092002_1 - 092002_14, 2020/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The cross section of bottom quark-antiquark (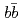 ) production in
) production in  collisions at
collisions at 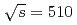 GeV is measured with the PHENIX detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. The results are based on the yield of high mass, like-sign muon pairs measured within the PHENIX muon arm acceptance (
GeV is measured with the PHENIX detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. The results are based on the yield of high mass, like-sign muon pairs measured within the PHENIX muon arm acceptance (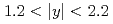 ). The
). The 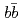 signal is extracted from like-sign dimuons by utilizing the unique properties of neutral
signal is extracted from like-sign dimuons by utilizing the unique properties of neutral  meson oscillation. We report a differential cross section of
meson oscillation. We report a differential cross section of  nb for like-sign muons in the rapidity and
nb for like-sign muons in the rapidity and  ranges
ranges 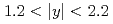 and
and 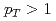 GeV/
GeV/ , and dimuon mass of 5 - 10 GeV/
, and dimuon mass of 5 - 10 GeV/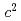 . The extrapolated total cross section at this energy for
. The extrapolated total cross section at this energy for 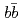 production is
production is 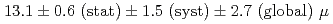 b. The total cross section is compared to a perturbative quantum chromodynamics calculation and is consistent within uncertainties. The azimuthal opening angle between muon pairs from
b. The total cross section is compared to a perturbative quantum chromodynamics calculation and is consistent within uncertainties. The azimuthal opening angle between muon pairs from 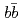 decays and their
decays and their  distributions are compared to distributions generated using
distributions are compared to distributions generated using 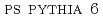 , which includes next-to-leading order processes. The azimuthal correlations and pair
, which includes next-to-leading order processes. The azimuthal correlations and pair  distribution are not very well described by
distribution are not very well described by 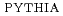 calculations, but are still consistent within uncertainties. Flavor creation and flavor excitation subprocesses are favored over gluon splitting.
calculations, but are still consistent within uncertainties. Flavor creation and flavor excitation subprocesses are favored over gluon splitting.
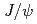 production in
production in  collisions at
collisions at 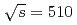 GeV
GeVAcharya, U.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 永宮 正治*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他344名*
Physical Review D, 102(7), p.072008_1 - 072008_13, 2020/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:12.65(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment has measured the spin alignment for inclusive 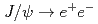 decays in
decays in  collisions at
collisions at 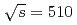 GeV at midrapidity. The angular distributions have been measured in three different polarization frames, and the three decay angular coefficients have been extracted in a full two-dimensional analysis. Previously, PHENIX saw large longitudinal net polarization at forward rapidity at the same collision energy. This analysis at midrapidity, complementary to the previous PHENIX results, sees no sizable polarization in the measured transverse momentum range of
GeV at midrapidity. The angular distributions have been measured in three different polarization frames, and the three decay angular coefficients have been extracted in a full two-dimensional analysis. Previously, PHENIX saw large longitudinal net polarization at forward rapidity at the same collision energy. This analysis at midrapidity, complementary to the previous PHENIX results, sees no sizable polarization in the measured transverse momentum range of 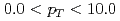 GeV/
GeV/ . The results are consistent with a previous one-dimensional analysis at midrapidity at
. The results are consistent with a previous one-dimensional analysis at midrapidity at 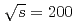 GeV. The transverse-momentum-dependent cross section for midrapidity
GeV. The transverse-momentum-dependent cross section for midrapidity 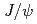 production has additionally been measured, and after comparison to world data we find a simple logarithmic dependence of the cross section on
production has additionally been measured, and after comparison to world data we find a simple logarithmic dependence of the cross section on  .
.


 collisions at
collisions at 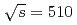 GeV
GeVAcharya, U.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 永宮 正治*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他354名*
Physical Review D, 102(3), p.032001_1 - 032001_9, 2020/08
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:53.65(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider has measured the longitudinal double spin asymmetries,  , for charged pions at midrapidity (
, for charged pions at midrapidity (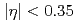 ) in longitudinally polarized
) in longitudinally polarized 

 collisions at
collisions at 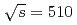 GeV. These measurements are sensitive to the gluon spin contribution to the total spin of the proton in the parton momentum fraction
GeV. These measurements are sensitive to the gluon spin contribution to the total spin of the proton in the parton momentum fraction  range between 0.04 and 0.09. One can infer the sign of the gluon polarization from the ordering of pion asymmetries with charge alone. The asymmetries are found to be consistent with global quantum-chromodynamics fits of deep-inelastic scattering and data at
range between 0.04 and 0.09. One can infer the sign of the gluon polarization from the ordering of pion asymmetries with charge alone. The asymmetries are found to be consistent with global quantum-chromodynamics fits of deep-inelastic scattering and data at 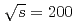 GeV, which show a nonzero positive contribution of gluon spin to the proton spin.
GeV, which show a nonzero positive contribution of gluon spin to the proton spin.
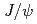 at forward and backward rapidity in
at forward and backward rapidity in  +
+ ,
, 
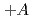 l,
l, 
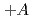 u, and
u, and  He+Au collisions at
He+Au collisions at 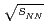 = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAcharya, U.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他358名*
Physical Review C, 102(1), p.014902_1 - 014902_23, 2020/07
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:84.76(Physics, Nuclear)Charmonium is a valuable probe in heavy-ion collisions to study the properties of the quark gluon plasma, and is also an interesting probe in small collision systems to study cold nuclear matter effects, which are also present in large collision systems. With the recent observations of collective behavior of produced particles in small system collisions, measurements of the modification of harmonium in small systems have become increasingly relevant. We present the results of 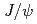 measurements at forward and backward rapidity in various small collision systems,
measurements at forward and backward rapidity in various small collision systems, 

 ,
, 
 Al,
Al, 
 Au and
Au and  He
He Au, at
Au, at 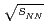 =200 GeV. The results are presented in the form of the observable
=200 GeV. The results are presented in the form of the observable 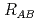 , the nuclear modification factor, a measure of the ratio of the
, the nuclear modification factor, a measure of the ratio of the 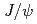 invariant yield compared to the scaled yield in
invariant yield compared to the scaled yield in 

 collisions. We examine the rapidity, transverse momentum, and collision centrality dependence of nuclear effects on
collisions. We examine the rapidity, transverse momentum, and collision centrality dependence of nuclear effects on 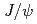 production with different projectile sizes
production with different projectile sizes  and
and  He, and different target sizes Al and Au. The modification is found to be strongly dependent on the target size, but to be very similar for
He, and different target sizes Al and Au. The modification is found to be strongly dependent on the target size, but to be very similar for 
 Au and
Au and  He
He Au. However, for 0% - 20% central collisions at backward rapidity, the modification for
Au. However, for 0% - 20% central collisions at backward rapidity, the modification for  He
He Au is found to be smaller than that for
Au is found to be smaller than that for 
 Au, with a mean fit to the ratio of
Au, with a mean fit to the ratio of 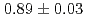 (stat)
(stat)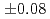 (syst), possibly indicating final state effects due to the larger projectile size.
(syst), possibly indicating final state effects due to the larger projectile size.
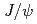 and
and 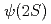 production at forward rapidity in
production at forward rapidity in  +
+ collisions at
collisions at 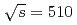 GeV
GeVAcharya, U. A.*; 長谷川 勝一; 今井 憲一*; 永宮 正治*; 佐甲 博之; 佐藤 進; 谷田 聖; PHENIX Collaboration*; 他353名*
Physical Review D, 101(5), p.052006_1 - 052006_13, 2020/03
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:39.04(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider has measured the differential cross section, mean transverse momentum, mean transverse momentum squared of inclusive 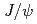 and cross-section ratio of
and cross-section ratio of 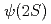 to
to 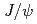 at forward rapidity in
at forward rapidity in 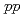 collisions at
collisions at 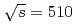 GeV via the dimuon decay channel. Comparison is made to inclusive
GeV via the dimuon decay channel. Comparison is made to inclusive 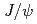 cross sections measured at
cross sections measured at 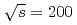 GeV and 2.76 - 13 TeV. The result is also compared to leading-order nonrelativistic QCD calculations coupled to a color-glass-condensate description of the low-
GeV and 2.76 - 13 TeV. The result is also compared to leading-order nonrelativistic QCD calculations coupled to a color-glass-condensate description of the low- gluons in the proton at low transverse momentum (
gluons in the proton at low transverse momentum ( ) and to next-to-leading order nonrelativistic QCD calculations for the rest of the
) and to next-to-leading order nonrelativistic QCD calculations for the rest of the  range. These calculations overestimate the data at low
range. These calculations overestimate the data at low  . While consistent with the data within uncertainties above
. While consistent with the data within uncertainties above 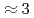 GeV/
GeV/ , the calculations are systematically below the data. The total cross section times the branching ratio is BR
, the calculations are systematically below the data. The total cross section times the branching ratio is BR 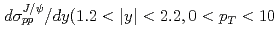 GeV/
GeV/ ) = 54.3
) = 54.3  0.5 (stat)
0.5 (stat)  5.5 (syst) nb.
5.5 (syst) nb.