Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Pshenichnikov, A.; Zubekhina, B.; 多木 寛; Pham, V. H.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
The CLADS-MADE-05 is the next test in the series of large-scale tests performed in JAEA with a purpose of understanding of mock-up assembly degradation and melt propagation behaviour accompanied by Cs and B containing aerosol release. A possibility of Cs and B aerosols interactions in RPV and formation of a new Cs bearing contaminating phase has been shown. This paper analyses the data on aerosol behaviour of Cs and B bearing aerosols when they interact in the gas line, and concentrates on the phenomenon of possible reactions on the liquid-liquid and liquid-gas interface when aerosols are interacting during the large-scale bundle degradation test.
Nguyen, T. H.*; Le Ba, T.*; Tran, C. T.*; Nguyen, T. T.*; Doan, T. T. T.*; Do, V. K.; 渡邉 雅之; Pham, Q. M.*; Hoang, S. T.*; Nguyen, D. V.*; et al.
Hydrometallurgy, 213, p.105933_1 - 105933_11, 2022/08
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:80.29(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)ベトナム・イェンフー希土類精鉱浸出液からトリウム(Th)とウラン(U)を選択的に回収するための連続向流抽出法を系統的に研究した。抽出剤としては、イソパラフィンIP-2028希釈液で調製した一級アミンN1923を用いた。トリウムとウランは、連続ミキサーセトラエクストラクション,スクラビング,逆エクストラクションによって確立された湿式製錬サイクルで選択的に回収され、ラボスケールで実施された。有機相と水相の体積比(O/A比)を管理することにより、ThとUの所望の純度を達成することができる。逆抽出液とラフィネートからそれぞれ高純度のThとUを回収することができ、その後の核物質処理に十分な特性を有している。
Pham, V. H.; 倉田 正輝; Steinbrueck, M.*
Thermo (Internet), 1(2), p.151 - 167, 2021/09
Since the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011, a considerable number of studies have been conducted to develop accident tolerant fuel (ATF) claddings for safety enhancement of light water reactors. Among many potential ATF claddings, silicon carbide is one of the most promising candidates with many superior features suitable for nuclear applications. In spite of many potential benefits of SiC cladding, there are some concerns over the oxidation/corrosion resistance of the cladding, especially at extreme temperatures (up to 2000 C) in severe accidents. However, the study of SiC steam oxidation in conventional test facilities in water vapor atmospheres at temperatures above 1600
C) in severe accidents. However, the study of SiC steam oxidation in conventional test facilities in water vapor atmospheres at temperatures above 1600 C is very challenging. In recent years, several efforts have been made to modify existing or to develop new advanced test facilities to perform material oxidation tests in steam environments typical of severe accident conditions. In this article, the authors outline the features of SiC oxidation/corrosion at high temperatures, as well as the developments of advanced test facilities in their laboratories, and, finally, give some of the current advances in understanding based on recent data obtained from those advanced test facilities.
C is very challenging. In recent years, several efforts have been made to modify existing or to develop new advanced test facilities to perform material oxidation tests in steam environments typical of severe accident conditions. In this article, the authors outline the features of SiC oxidation/corrosion at high temperatures, as well as the developments of advanced test facilities in their laboratories, and, finally, give some of the current advances in understanding based on recent data obtained from those advanced test facilities.
 C studied by laser heating
C studied by laser heatingPham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝; Bottomley, D.; 古本 健一郎*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 529, p.151939_1 - 151939_8, 2020/02
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:87.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)As expected for accident tolerant fuels, investigation of steam oxidation for silicon carbide under the conditions beyond design basis accident scenarios is needed. Many studies focused on steam oxidation of SiC at temperatures up 1600 C have been conducted and reported in the literature. However, behavior of SiC in steam at temperatures above 1600
C have been conducted and reported in the literature. However, behavior of SiC in steam at temperatures above 1600 C still remains unclear. To complete this task, we have designed and manufactured a laser heating facility for steam oxidation at extreme temperatures. With the facility, we report the first results on the steam oxidation behavior of SiC at temperatures range of 1400-1800
C still remains unclear. To complete this task, we have designed and manufactured a laser heating facility for steam oxidation at extreme temperatures. With the facility, we report the first results on the steam oxidation behavior of SiC at temperatures range of 1400-1800 C for short term exposure of 1-7 h under atmospheric pressure. Based on the mass change of SiC samples, parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate were calculated. The oxidation layer appears to be maintained at 1800
C for short term exposure of 1-7 h under atmospheric pressure. Based on the mass change of SiC samples, parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate were calculated. The oxidation layer appears to be maintained at 1800 C in steam, but the bubble formation phenomenon suggests other volatilization reactions may limit its life.
C in steam, but the bubble formation phenomenon suggests other volatilization reactions may limit its life.
Pham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝; 古本 健一郎*; 佐藤 寿樹*; 石橋 良*; 山下 真一郎
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.670 - 674, 2019/09
Silicon carbide (SiC) has recently attracted much attention as a potential material for accident tolerant fuel cladding. To investigate the performance of SiC in severe accident conditions, study of steam oxidation at high temperatures is necessary. However, the study focusing on steam oxidation of SiC at temperatures above 1600 C is still certainly limited due to lack of test facilities. With the extreme oxidation/corrosion environment in steam at high temperatures, current refractory materials such as alumina and zirconia would not survive during the tests. Application of laser heating technique could be a great solution for this problem. Using laser heating technique, we can localize the heat and focus them on the test sample only. In this study, we developed a laser heating facility to investigate high-temperature oxidation of SiC in steam at temperature range of 1400-1800
C is still certainly limited due to lack of test facilities. With the extreme oxidation/corrosion environment in steam at high temperatures, current refractory materials such as alumina and zirconia would not survive during the tests. Application of laser heating technique could be a great solution for this problem. Using laser heating technique, we can localize the heat and focus them on the test sample only. In this study, we developed a laser heating facility to investigate high-temperature oxidation of SiC in steam at temperature range of 1400-1800 C for 1-7 h. The oxidation kinetics is then being studied based on the weight gain and observation on cross-sectioned surface of tested sample using field emission scanning electron microscope. Off-gas measurement of hydrogen (H
C for 1-7 h. The oxidation kinetics is then being studied based on the weight gain and observation on cross-sectioned surface of tested sample using field emission scanning electron microscope. Off-gas measurement of hydrogen (H ) and carbon monoxide (CO) generated during the test is also being conducted via a sensor gas chromatography. Current results showed that the SiC sample experienced a mass loss process which obeyed paralinear laws. Parabolic oxidation rate constant and linear volatilization rate constant of the process were calculated from the mass change of the samples. The apparent activation energy of the parabolic oxidation process was calculated to be 85 kJ.mol
) and carbon monoxide (CO) generated during the test is also being conducted via a sensor gas chromatography. Current results showed that the SiC sample experienced a mass loss process which obeyed paralinear laws. Parabolic oxidation rate constant and linear volatilization rate constant of the process were calculated from the mass change of the samples. The apparent activation energy of the parabolic oxidation process was calculated to be 85 kJ.mol . The data of the study also indicated that the mass change of SiC under the investigated conditions reached to its steady stage where hydrogen generation became stable. Above 1800
. The data of the study also indicated that the mass change of SiC under the investigated conditions reached to its steady stage where hydrogen generation became stable. Above 1800 C, a unique bubble formation on sample surface was recorded.
C, a unique bubble formation on sample surface was recorded.
 C
CPham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
Proceedings of Annual Topical Meeting on Reactor Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2018) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/10
High temperature interaction of chemical vapor deposition SiC with steam was investigated at 1700-1800 C for 0.1-3 h in a mixture of steam and argon gas containing 98% of steam at 1 atm. At the investigated conditions, although a dense oxide layer was observed on sample surface, significant mass loss of SiC occurred. Below 1700
C for 0.1-3 h in a mixture of steam and argon gas containing 98% of steam at 1 atm. At the investigated conditions, although a dense oxide layer was observed on sample surface, significant mass loss of SiC occurred. Below 1700 C, the oxidation kinetics seems to follow the para-linear laws. The apparent activation calculated based on the data of this study is to be 370 kJ/mol. Rapid degradation and bubbling of SiC at 1800
C, the oxidation kinetics seems to follow the para-linear laws. The apparent activation calculated based on the data of this study is to be 370 kJ/mol. Rapid degradation and bubbling of SiC at 1800 C were observed after 1 h oxidation. This suggested that chemical interaction behaviours above 1700
C were observed after 1 h oxidation. This suggested that chemical interaction behaviours above 1700 C might be changed due to the liquefaction of silica.
C might be changed due to the liquefaction of silica.
山崎 宰春; Pshenichnikov, A.; Pham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝; 徳島 二之*; 青見 雅樹*; 坂本 寛*
Proceedings of Annual Topical Meeting on Reactor Fuel Performance (TopFuel 2018) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/10
燃料集合体の酸化及び水素吸収はその後の事故進展挙動に影響を与えることから、PWR燃料集合体では、実効的な水蒸気流量としてg-H O/sec/rodという単位が導入されており、事故進展評価の重要なパラメータといて用いられている。一方BWRにおいては、燃料集合体の構成がPWRとは異なることにより、PWRで用いられている規格化された水蒸気流量ではチャンネルボックスの内外での酸化及び水素吸収の差が正確に評価できない。そのため、PWRで用いられているg-H
O/sec/rodという単位が導入されており、事故進展評価の重要なパラメータといて用いられている。一方BWRにおいては、燃料集合体の構成がPWRとは異なることにより、PWRで用いられている規格化された水蒸気流量ではチャンネルボックスの内外での酸化及び水素吸収の差が正確に評価できない。そのため、PWRで用いられているg-H O/sec/rodという規格化された水蒸気流量に代わる、適切な評価パラメータがBWRでも必要である。そこで、ジルカロイの水蒸気枯渇条件での酸化及び水素吸収データを取得するため、実機を模擬したBWRバンドル試験体を用いて高温酸化試験を行なった。BWRにおける水蒸気流量を規格化するため、水蒸気流路断面積を考慮したパラメータを検討した。
O/sec/rodという規格化された水蒸気流量に代わる、適切な評価パラメータがBWRでも必要である。そこで、ジルカロイの水蒸気枯渇条件での酸化及び水素吸収データを取得するため、実機を模擬したBWRバンドル試験体を用いて高温酸化試験を行なった。BWRにおける水蒸気流量を規格化するため、水蒸気流路断面積を考慮したパラメータを検討した。
Pham, V. H.; 根本 義之; 山下 真一郎
no journal, ,
Various coatings ranging from ceramics to metals and alloys have been proposed to enhance the performance of Zry as accident tolerant fuel cladding. Ceramic coatings that formed Al O
O or SiO
or SiO tend to show better steam oxidation resistance, but exhibit poor performance in long-term corrosion resistance due to their dissolutions of cations in aqueous environments. In the meantime, metals and alloys coatings seemed to have improvements in steam oxidation resistance as well as corrosion resistance in water. Nevertheless, the interdiffusion and eutectic reactions of the metallic coatings and Zry substrate at high temperatures may become a serious concern in the event of severe accident conditions. Multilayer coatings on Zry could be a good solution to achieve maximum benefits of each individual coating layer. In attempt to search for alternative coating solutions to improve the performance of Zry4 cladding, in this study, multi-coating of TiN and TiAlN layers on Zry4 was proposed and fabricated by physical vapor deposition coating technique. After the coating works, oxidation tests of coated Zry4 and uncoated-Zry4 in steam via a thermogravimetric system were conducted at 800-1000
tend to show better steam oxidation resistance, but exhibit poor performance in long-term corrosion resistance due to their dissolutions of cations in aqueous environments. In the meantime, metals and alloys coatings seemed to have improvements in steam oxidation resistance as well as corrosion resistance in water. Nevertheless, the interdiffusion and eutectic reactions of the metallic coatings and Zry substrate at high temperatures may become a serious concern in the event of severe accident conditions. Multilayer coatings on Zry could be a good solution to achieve maximum benefits of each individual coating layer. In attempt to search for alternative coating solutions to improve the performance of Zry4 cladding, in this study, multi-coating of TiN and TiAlN layers on Zry4 was proposed and fabricated by physical vapor deposition coating technique. After the coating works, oxidation tests of coated Zry4 and uncoated-Zry4 in steam via a thermogravimetric system were conducted at 800-1000 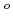 C to evaluate the protection effectiveness of the coating layers. Post-test analysis of the oxidized samples was carried out with X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope. The results of this investigation showed that oxidation kinetics of TiN/TiAlN coated Zry4 followed linear laws. The coating layers only showed some positive effects on oxidation resistance in steam at 800
C to evaluate the protection effectiveness of the coating layers. Post-test analysis of the oxidized samples was carried out with X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope. The results of this investigation showed that oxidation kinetics of TiN/TiAlN coated Zry4 followed linear laws. The coating layers only showed some positive effects on oxidation resistance in steam at 800 C. At higher temperatures, the samples with coating layers even exhibited faster oxidation rate than that of the uncoated-Zry4. Horizontal cracking at ZrO
C. At higher temperatures, the samples with coating layers even exhibited faster oxidation rate than that of the uncoated-Zry4. Horizontal cracking at ZrO zone due to the formation of ZrN is attributed to the main cause of this degradation. Multilayer coating on Zry4 remained under discussion. However, nitrides coatings on Zry4 therefore should be avoid for this application.
zone due to the formation of ZrN is attributed to the main cause of this degradation. Multilayer coating on Zry4 remained under discussion. However, nitrides coatings on Zry4 therefore should be avoid for this application.
Pham, V. H.; 石橋 良*; 佐々木 政名*; 根本 義之; 山下 真一郎
no journal, ,
SiCは高温水蒸気中での耐酸化性と被覆管の健全性の点で、事故耐性燃料被覆管の有力な候補の一つである。しかし、炉内での適用を考えた場合、長期間の腐食環境下での水中へのSiO の溶出が懸念される。そこで、通常運転時の耐食性を向上させるために、SiC上にTi層を被覆することが提案された。本研究では、1200-1500
の溶出が懸念される。そこで、通常運転時の耐食性を向上させるために、SiC上にTi層を被覆することが提案された。本研究では、1200-1500 CにおけるTi被覆SiCの酸化挙動と酸化速度論を熱天秤装置を用いて調べた。その結果に基づき、SiCの酸化速度論と挙動に対するTi被覆層の影響について議論し、報告する。
CにおけるTi被覆SiCの酸化挙動と酸化速度論を熱天秤装置を用いて調べた。その結果に基づき、SiCの酸化速度論と挙動に対するTi被覆層の影響について議論し、報告する。
河合 慶人*; 根本 義之; 藤村 由希; 近藤 啓悦; 阿部 陽介; Mohamad, A. B.; Pham, V. H.; 石川 法人; 石島 暖大; 井岡 郁夫; et al.
no journal, ,
現行のジルカロイ被覆管よりも事故耐性に優れた事故耐性燃料(ATF)被覆管の開発が進められている。その一つに被覆管外面にCrをコーティングしたコーティング被覆管があり、高温水蒸気中での耐酸化性の向上が見込まれている。しかし、冷却水損失事故(LOCA)時には被覆管が破裂し、コーティングされていない被覆管内面も酸化することが予想される。そこで、本研究ではジルカロイ4被覆管及びその外面にCrコーティングを施したコーティング被覆管を用いて高温水蒸気中での酸化試験を行い、酸化挙動、水素吸収挙動及び機械特性の違いを検討した。
 C at elevated temperatures
C at elevated temperaturesPham, V. H.; 松浦 傑*; 南口 誠*; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
no journal, ,
In this study, soaking experiments of Zry plates in molten SS-B C were conducted to investigate the recession rate of Zry plates in molten SS-B
C were conducted to investigate the recession rate of Zry plates in molten SS-B C at 1175-1225
C at 1175-1225 C. The molten SS-B
C. The molten SS-B C mixture was prepared by heat-treatment at 1400
C mixture was prepared by heat-treatment at 1400 C for 12 h of a powder mixture containing 5 mol% B
C for 12 h of a powder mixture containing 5 mol% B C and stainless steel. After decreasing temperature to the testing temperatures, Zry plates were soaked in the molten mixture for 0-60 min. After soaking tests, the Zry plates were pulled out of the molten mixture. The remaining thickness of Zry plates after the tests were measured by using optical microscope. To understand the influences of alloying elements in Zry and SS, three other sets of experiments (Zr plates in Fe-B
C and stainless steel. After decreasing temperature to the testing temperatures, Zry plates were soaked in the molten mixture for 0-60 min. After soaking tests, the Zry plates were pulled out of the molten mixture. The remaining thickness of Zry plates after the tests were measured by using optical microscope. To understand the influences of alloying elements in Zry and SS, three other sets of experiments (Zr plates in Fe-B C, Zr plates in SS-B
C, Zr plates in SS-B C and Zry plates in Fe-B
C and Zry plates in Fe-B C) were also conducted. Results of the study indicated that the thickness of Zry plates decreased linearly with increase of soaking duration. The recession rate of Zry plates was increase with increase of testing temperatures. The value of apparent activation energy on the thickness recession rate of Zry plates was determined to be 333 kJ/mol. The alloying elements in SS showed a positive effect on suppression of Zry corrosion. In contrast, the alloying elements in Zry showed a negative effect on the process.
C) were also conducted. Results of the study indicated that the thickness of Zry plates decreased linearly with increase of soaking duration. The recession rate of Zry plates was increase with increase of testing temperatures. The value of apparent activation energy on the thickness recession rate of Zry plates was determined to be 333 kJ/mol. The alloying elements in SS showed a positive effect on suppression of Zry corrosion. In contrast, the alloying elements in Zry showed a negative effect on the process.
 scale on fuel tube cladding by the melt of control rod assemble
scale on fuel tube cladding by the melt of control rod assemble中島 正太郎*; 松浦 傑*; 南口 誠*; 倉田 正輝; Pham, V. H.
no journal, ,
For a better understanding of the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, a reaction model of core melting process is very important. In this study, oxidized Zry plates were soaked into molten SS-B C mixture and heated into Ar gas at 1200
C mixture and heated into Ar gas at 1200 C. Recession of ZrO
C. Recession of ZrO scale was observed in the both cases. An oxygen solid solution region in the Zry sample was observed below ZrO
scale was observed in the both cases. An oxygen solid solution region in the Zry sample was observed below ZrO scale, although it was not observed in Zry oxidized at 600
scale, although it was not observed in Zry oxidized at 600 C in high temperature steam conditions. When oxygen supply from the surrounding was halted, ZrO
C in high temperature steam conditions. When oxygen supply from the surrounding was halted, ZrO scale can be reduced at high temperature such as 1200
scale can be reduced at high temperature such as 1200 C by oxygen dissolution into Zry inside.
C by oxygen dissolution into Zry inside.
Pham, V. H.; 松浦 傑*; 中島 正太郎*; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
no journal, ,
In this study, soaking experiments of pre-oxidized zry plates in molten mixture of stainless steel and 5 mol% boron carbide were conducted at 1200-1250 C. Thickness of oxide layer, ZrO
C. Thickness of oxide layer, ZrO was measured before and after the soaking test to investigate the ZrO
was measured before and after the soaking test to investigate the ZrO thickness recession in the molten mixture. Results of the study indicated that the thickness recession of ZrO
thickness recession in the molten mixture. Results of the study indicated that the thickness recession of ZrO was mainly caused by the diffusion of oxygen from oxide layer to metallic-Zr region.
was mainly caused by the diffusion of oxygen from oxide layer to metallic-Zr region.
倉田 正輝; Pham, V. H.; 永江 勇二
no journal, ,
Since the disaster at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, development of accident tolerant fuel to manage severe accidents has been proposed. As temperature of fuel rods could reach to temperatures above 2000 C during the accident, investigation of oxidation behavior at such temperatures for fuel claddings must be conducted. Nevertheless, there is no test facility capable for operating at such conditions. In this study, we developed a laser heating facility for steam oxidation of cladding materials at extreme temperatures. Main features of the facility are controlled environment, in situ observation, extreme fast heating and cooling rate and off gas analysis. As the heat is focused on the test sample only, the facility can be operated at temperatures above 2000
C during the accident, investigation of oxidation behavior at such temperatures for fuel claddings must be conducted. Nevertheless, there is no test facility capable for operating at such conditions. In this study, we developed a laser heating facility for steam oxidation of cladding materials at extreme temperatures. Main features of the facility are controlled environment, in situ observation, extreme fast heating and cooling rate and off gas analysis. As the heat is focused on the test sample only, the facility can be operated at temperatures above 2000 C. Preliminary tests have been conducted for monolithic SiC at 1400-1800
C. Preliminary tests have been conducted for monolithic SiC at 1400-1800 C for 1-7 h under 0.96 atm steam partial pressure. Results of the investigation showed that SiC underwent a mass loss which obeyed paralinear laws. Based on the mass change data, parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate of the process were obtained. The apparent activation energy of the oxidation process was calculated to be 96 kJmol
C for 1-7 h under 0.96 atm steam partial pressure. Results of the investigation showed that SiC underwent a mass loss which obeyed paralinear laws. Based on the mass change data, parabolic oxidation rate and linear volatilization rate of the process were obtained. The apparent activation energy of the oxidation process was calculated to be 96 kJmol  . Bubbling phenomenon was observed on SiC sample surface at 1800
. Bubbling phenomenon was observed on SiC sample surface at 1800 C.
C.
Pham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝; 石橋 良*; 山下 真一郎
no journal, ,
In this study, oxidation of SiC under various flow rates of steam was investigated at 1400 C using laser heating. Results of the investigation indicated that the mass evolution of SiC underwent a mass gain with 0.1 g/min of steam flow rate. Whereas, the mass evolution experienced a mass loss with 3 g/min of steam. Based on the data of mass change under the investigated conditions, the parabolic and linear rate constants were calculated and reported.
C using laser heating. Results of the investigation indicated that the mass evolution of SiC underwent a mass gain with 0.1 g/min of steam flow rate. Whereas, the mass evolution experienced a mass loss with 3 g/min of steam. Based on the data of mass change under the investigated conditions, the parabolic and linear rate constants were calculated and reported.
Mohamad, A. B.; 山下 真一郎; 相馬 康孝; 根本 義之; Pham, V. H.; 阿部 陽介; 井岡 郁夫; 佐藤 智徳; 石島 暖大; 三輪 周平; et al.
no journal, ,
Accident tolerant fuel, ATF, development has become one of the interest topics in the nuclear field recently. In the 4th ATF Workshop, the purpose is to have a technical discussion with a view to domestic readiness by obtaining suggestions among nuclear related organisations including NRA in domestic ATF development. JAEA, as the project coordinator in Japan, will provide an overview of the ATF development currently underway overseas, e.g. the readiness of Cr-coated Zry cladding developed by Framatome and Westinghouse, where the lead test assembly has been completed. An overview of the Japanese ATF development will be given, highlighting the current status and the issues we are currently facing in the development such as the readiness of irradiation testing at Japan. In addition, JAEA, a part of the project coordinator, JAEA also conducted research and development with the cooperation of stakeholders. An overview of R&D under different phenomena with a final goal of transferring experimental data into modelling will be an example of the ongoing work at JAEA. Finally, JAEA hopes to accelerate the development of ATF in Japan with the full cooperation of all members.
 スケールにおける酸素供給が絶たれた際の減肉挙動
スケールにおける酸素供給が絶たれた際の減肉挙動中島 正太郎*; 松浦 傑*; 南口 誠*; 倉田 正輝; Pham, V. H.
no journal, ,
沸騰型軽水炉(BWR)では、核燃料ペレット(UO )をZr合金(Zry)製被覆管で構成した燃料棒および炭化ホウ素(B
)をZr合金(Zry)製被覆管で構成した燃料棒および炭化ホウ素(B C)製中性子吸収材料をステンレス鋼(SS)製管で構成された制御棒が隣接して格納されている。全電力喪失時においては、冷却水の供給停止によって核燃料が冷却されず、核燃料の温度が上昇し続けると、冷却水が蒸発して反応炉内が高温水蒸気環境となり、Zry中のZrと反応し燃料棒表面にZrO
C)製中性子吸収材料をステンレス鋼(SS)製管で構成された制御棒が隣接して格納されている。全電力喪失時においては、冷却水の供給停止によって核燃料が冷却されず、核燃料の温度が上昇し続けると、冷却水が蒸発して反応炉内が高温水蒸気環境となり、Zry中のZrと反応し燃料棒表面にZrO スケールを形成するとされている。また、制御棒を構成しているSSおよびB
スケールを形成するとされている。また、制御棒を構成しているSSおよびB Cが共晶反応を起こし、液相が形成される。この液相が燃料被覆管と接触することで燃料被覆管が腐食され、核燃料の暴露に繋がったと考えられている。しかしながら、燃料棒表面に形成されたZrO
Cが共晶反応を起こし、液相が形成される。この液相が燃料被覆管と接触することで燃料被覆管が腐食され、核燃料の暴露に繋がったと考えられている。しかしながら、燃料棒表面に形成されたZrO スケールと液相の腐食プロセスの理解は十分にはされていないのが現状である。そこで本研究では、Ar雰囲気気流下においてZrO
スケールと液相の腐食プロセスの理解は十分にはされていないのが現状である。そこで本研究では、Ar雰囲気気流下においてZrO スケールを形成したZry板に熱処理を加えることで、液相化したSS-B
スケールを形成したZry板に熱処理を加えることで、液相化したSS-B Cに接触して水蒸気の供給が遮断された状況を熱力学的に模擬した実験を行い、シビアアクシデント時の腐食プロセスの解明を行った。
Cに接触して水蒸気の供給が遮断された状況を熱力学的に模擬した実験を行い、シビアアクシデント時の腐食プロセスの解明を行った。
Mohamad, A. B.; 根本 義之; 相馬 康孝; 石島 暖大; 佐藤 智徳; 井岡 郁夫; Pham, V. H.; 三輪 周平; 中島 邦久; 加治 芳行; et al.
no journal, ,
ATF等の新型燃料実用化においては、関連技術開発やそれらの基となる科学的知見の取得及び拡充が不可欠である。原子力機構は、照射試験実施による燃料ふるまい解析技術基盤の構築のための研究開発を行い、長期を要する開発において、開発内容やスケジュールの予見性向上に貢献していくべきと認識している。このため、実装化が最も早いCrコーティング被覆管に関して、燃料ふるまいのメカニズムに立ち返り、「長期照射時の影響」「事故時影響」に関する科学的知見を拡充することを目的とした基礎基盤研究計画を立案し、研究をすすめている。本発表では各研究項目の内容や期待される成果、これまでに得られた結果等を紹介する。
Mohamad, A. B.; 根本 義之; 相馬 康孝; 石島 暖大; 佐藤 智徳; 井岡 郁夫; Pham, V. H.; 三輪 周平; 中島 邦久; 加治 芳行; et al.
no journal, ,
原子力機構(JAEA)では事故耐性の向上を目指した燃料被覆管の実用化に資する基礎研究の一環として、各種コーティング被覆管の特性評価を進めている。講演では全体概要の他、特性評価試験に用いることを目的としたJAEAでの新規装置開発の状況、高温水蒸気酸化特性評価試験の結果等について紹介する。
 C
CPham, V. H.; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
no journal, ,
Silicon carbide (SiC) has recently attracted much attention as a potential material for accident tolerant fuel cladding. High-temperature interaction of SiC at temperature range below 1600 C has been studied by various authors. As expected for enhanced accident tolerant fuel cladding, high-temperature interaction of SiC must be also investigated at temperatures above 1600
C has been studied by various authors. As expected for enhanced accident tolerant fuel cladding, high-temperature interaction of SiC must be also investigated at temperatures above 1600 C. In this study, we investigate high-temperature interaction of SiC in steam at temperature range of 1700
C. In this study, we investigate high-temperature interaction of SiC in steam at temperature range of 1700 1800
1800 C using laser heating furnace. The oxidation kinetics is then studied based on the weight change and observation on cross-sectioned surface of tested sample using field emission scanning electron microscope. Off-gas measurement of hydrogen (H
C using laser heating furnace. The oxidation kinetics is then studied based on the weight change and observation on cross-sectioned surface of tested sample using field emission scanning electron microscope. Off-gas measurement of hydrogen (H ) and carbon monoxide (CO) generated during the test was also conducted via sensor gas chromatography.
) and carbon monoxide (CO) generated during the test was also conducted via sensor gas chromatography.