Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, F.*; Tang, X.*; Fei, Y.*; Zhang, J.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Che, G.*; Zhao, Z.*; Zheng, Y.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(17), p.14054 - 14059, 2025/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)2,2'-ビピラジン(BPZ)の圧力誘起重合により結晶性グラファンナノリボン(GANR)を合成した。中性子回折データのリートベルト精密化,核磁気共鳴スペクトル,赤外スペクトル,理論計算を行った結果、BPZは

 積層した芳香環の間でディールス・アルダー重合し、並外れた長距離秩序を持つ伸びたボート型GANR構造を形成することがわかった。未反応の-C=N-基がボートの両端を橋渡ししており、さらなる機能化の余地がある。このGANRのバンドギャップは2.25eVであり、光電応答は良好である(I
積層した芳香環の間でディールス・アルダー重合し、並外れた長距離秩序を持つ伸びたボート型GANR構造を形成することがわかった。未反応の-C=N-基がボートの両端を橋渡ししており、さらなる機能化の余地がある。このGANRのバンドギャップは2.25eVであり、光電応答は良好である(I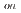 /I
/I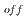 =18.8)。われわれの研究は、高圧トポケミカル重合法が、特定の構造と望んだ特性を持つグラファンの精密な合成に有望な方法であることを強調している。
=18.8)。われわれの研究は、高圧トポケミカル重合法が、特定の構造と望んだ特性を持つグラファンの精密な合成に有望な方法であることを強調している。
Zhang, X.-T.*; Xing, Y.-H.*; Yao, X.-P.*; 大湊 友也*; Zhang, L.*; 松尾 衛
Communications Physics (Internet), 8, p.103_1 - 103_8, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Spin pumping effect is a sensitive and well-established experimental method in two-dimensional (2D) magnetic materials. We propose that spin pumping effect can be a valuable probe for non-Fermi liquid (NFL) behaviors at the 2D interface of magnetic heterostructures. We show that the modulations of ferromagnetic resonance exhibit power-law scalings in frequency and temperature for NFL metals induced near a quantum critical point (QCP). At the Ising nematic QCP, we demonstrate that the enhanced Gilbert damping coefficient 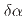 acquires negative power-law exponents in distinct frequency regimes. The exponents convey universal parameters inherited from the QCP and reflect the non- quasiparticle nature of the spin carriers in the NFL metal. At finite temperature, we show that the Gilbert damping mechanism is restored in the quantum critical regime and
acquires negative power-law exponents in distinct frequency regimes. The exponents convey universal parameters inherited from the QCP and reflect the non- quasiparticle nature of the spin carriers in the NFL metal. At finite temperature, we show that the Gilbert damping mechanism is restored in the quantum critical regime and 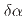 measures the temperature dependence of the correlation length.
measures the temperature dependence of the correlation length.
Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs) have emerged as promising materials for light-emitting diode applications. In this study, by using time-of-flight neutron spectroscopy we identified and quantitatively separated the lattice vibrational and molecular rotational dynamics of two perovskites, butylammonium lead iodide (BA) PbI
PbI and phenethyl-ammonium lead iodide (PEA)
and phenethyl-ammonium lead iodide (PEA) PbI
PbI . By examining the corresponding temperature dependence, we found that the lattice vibrations, as evidenced by neutron spectra, are consistent with the lattice dynamics obtained from Raman scattering. We revealed that the rotational dynamics of organic molecules in these materials tend to suppress their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) while the vibrational dynamics did not show predominant correlations with the same. Additionally, we observed photoluminescence emission peak splitting for both systems, which becomes prominent above certain critical temperatures where the suppression of PLQY begins. This study suggests that the rotational motions of polarized molecules may lead to a reduction in exciton binding energy or the breaking of degeneracy in exciton binding energy levels, enhancing non-radiative recombination rates, and consequently reducing photoluminescence yield. These findings offer a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions in 2D HOIPs and could guide the design of more efficient light-emitting materials for advanced technological applications.
. By examining the corresponding temperature dependence, we found that the lattice vibrations, as evidenced by neutron spectra, are consistent with the lattice dynamics obtained from Raman scattering. We revealed that the rotational dynamics of organic molecules in these materials tend to suppress their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) while the vibrational dynamics did not show predominant correlations with the same. Additionally, we observed photoluminescence emission peak splitting for both systems, which becomes prominent above certain critical temperatures where the suppression of PLQY begins. This study suggests that the rotational motions of polarized molecules may lead to a reduction in exciton binding energy or the breaking of degeneracy in exciton binding energy levels, enhancing non-radiative recombination rates, and consequently reducing photoluminescence yield. These findings offer a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions in 2D HOIPs and could guide the design of more efficient light-emitting materials for advanced technological applications.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez Espinoza, V.*; Stakhanova, A.*; Groudev, P.*; Petrova, P.*; Vryashkova, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.110962_1 - 110962_16, 2025/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:94.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The completed Horizon-2020 project on "Management and Uncertainties of Severe Accidents (MUSA)" has reviewed uncertainty sources and Uncertainty Quantification methodology for the purpose of assessing Severe Accidents (SA). The key motivation of the project has been to bring the advantages of the Best Estimate Plus Uncertainty approach to the field of Severe Accident. The applications brought together a large group of participants that set out to apply uncertainty analysis (UA) within their field of SA modelling expertise, in particular reactor types, but also SA code used (ASTEC, MELCOR, etc.), uncertainty quantification tools used (DAKOTA, RAVEN, etc.), detailed accident scenarios, and in some cases SAM actions. This paper synthesizes the reactor-application work at the end of the project. Analyses of 23 partners are sorted into different categories, depending on whether their main goal is/are (i) uncertainty bands of simulation results; (ii) the understanding of dominating uncertainties in specific sub-models of the SA code; (iii) improving the understanding of specific accident scenarios, with or without the application of SAM actions; or, (iv) a demonstration of the tools used and developed, and of the capability to carry out an uncertainty analysis in the presence of the challenges faced. The partners' experiences made during the project have been evaluated and are presented as good practice recommendations. The paper ends with conclusions on the level of readiness of UA in SA modelling, on the determination of governing uncertainties, and on the analysis of SAM actions.
 neutron imaging and diffraction analysis revealing spatial lithiation phase evolution in an ultra-thick graphite electrode
neutron imaging and diffraction analysis revealing spatial lithiation phase evolution in an ultra-thick graphite electrodeStrobl, M.*; Baur, M. E.*; Samothrakitis, S.*; Molamud, F.*; Zhang, X.*; Tung, P. K. M.*; Schmidt, S.*; Woracek, R.*; Lee, J.*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; et al.
Advanced Energy Materials, p.2405238_1 - 2405238_9, 2025/01
被引用回数:0Energy-efficient, safe, and reliable Li-ion batteries (LIBs) are required for a wide range of applications. The introduction of ultra-thick graphite anodes, desired for high energy densities, meets limitations in internal electrode transport properties, leading to detrimental consequences. Yet, there is a lack of experimental tools capable of providing a complete view of local processes. Here, a multi-modal  measurement approach is introduced, enabling quantitative spatio-temporal observations of Li concentrations and intercalation phases in ultra-thick graphite electrodes. Neutron imaging and diffraction concurrently provide correlated multiscale information from the scale of the cell down to the crystallographic scale. In particular, the evolving formation of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI), observation of gradients in total lithium content, as well as in the formation of ordered Li
measurement approach is introduced, enabling quantitative spatio-temporal observations of Li concentrations and intercalation phases in ultra-thick graphite electrodes. Neutron imaging and diffraction concurrently provide correlated multiscale information from the scale of the cell down to the crystallographic scale. In particular, the evolving formation of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI), observation of gradients in total lithium content, as well as in the formation of ordered Li C
C phases and trapped lithium are mapped throughout the first charge-discharge cycle of the cell. Different lithiation stages co-exist during charging and discharging; delayed lithiation and delithiation processes are observed in central regions of the electrode, while the SEI formation, potential plating, and dead lithium are predominantly found closer to the interface with the separator. The study emphasizes the potential to investigate Li-ion diffusion and the kinetics of lithiation phase formation in thick electrodes.
phases and trapped lithium are mapped throughout the first charge-discharge cycle of the cell. Different lithiation stages co-exist during charging and discharging; delayed lithiation and delithiation processes are observed in central regions of the electrode, while the SEI formation, potential plating, and dead lithium are predominantly found closer to the interface with the separator. The study emphasizes the potential to investigate Li-ion diffusion and the kinetics of lithiation phase formation in thick electrodes.
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; 服部 高典; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:84.76(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)飽和sp -カーボンナノスレッド(CNTh)は、その高いヤング率と熱伝導率が予測され、大きな関心を集めている。中心環へのヘテロ原子の導入がCNThの形成に影響を与え、化学的に均質な生成物が得られることが示されているが、ペンダント基が重合プロセスに与える影響については、まだ未解明である。本研究では、フェノールの圧力誘起重合を調べ、0.5GPaと4GPa以下で起こる2つの相転移を明らかにした。20GPa以上では、フェノールは水酸基とカルボニル基を持つ重合度4のCNTに重合する。ヒドロキシル基の水素移動は、重合度6のナノスレッドの形成を妨げることがわかった。この発見は、さらなるカラム内重合を阻止する水酸基の重要な役割を浮き彫りにし、今後のメカニズム研究やナノ材料合成に貴重な示唆を与えるものである。
-カーボンナノスレッド(CNTh)は、その高いヤング率と熱伝導率が予測され、大きな関心を集めている。中心環へのヘテロ原子の導入がCNThの形成に影響を与え、化学的に均質な生成物が得られることが示されているが、ペンダント基が重合プロセスに与える影響については、まだ未解明である。本研究では、フェノールの圧力誘起重合を調べ、0.5GPaと4GPa以下で起こる2つの相転移を明らかにした。20GPa以上では、フェノールは水酸基とカルボニル基を持つ重合度4のCNTに重合する。ヒドロキシル基の水素移動は、重合度6のナノスレッドの形成を妨げることがわかった。この発見は、さらなるカラム内重合を阻止する水酸基の重要な役割を浮き彫りにし、今後のメカニズム研究やナノ材料合成に貴重な示唆を与えるものである。
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; 服部 高典; 阿部 淳*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)アルダー-エン反応は、アルケンとアリル水素との化学反応であり、C-C結合を構築する効率的な方法である。従来、この反応には触媒、高温、あるいは光触媒が必要であった。本研究では、触媒を用いずに室温下で加圧することで成功した1-ヘキセンのアルダー-エン反応を報告する。1-ヘキセンは4.3GPaで結晶化し、18GPaで重合してオレフィンを形成する。ガスクロマトグラフィー-質量分析法により、1-ヘキセンが高圧下でのアルダー-エン反応により二量体を生成することを発見した。その場中性子回折から、この反応過程はトポケミカル則に従わないことがわかった。理論計算により、1つのC-H  結合と2つのアルケン
結合と2つのアルケン 結合を含む6員環遷移状態が示され、そのエネルギーは20GPaまで圧縮すると明らかに減少した。本研究は、触媒を用いずに室温でアルダー-エン反応を実現する新規かつ有望な方法を提供し、この重要な反応の応用を拡大するものである。
結合を含む6員環遷移状態が示され、そのエネルギーは20GPaまで圧縮すると明らかに減少した。本研究は、触媒を用いずに室温でアルダー-エン反応を実現する新規かつ有望な方法を提供し、この重要な反応の応用を拡大するものである。
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 楡井 真実; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Crystalline solids exhibiting inherently low lattice thermal conductivity ( ) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,
) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,  cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg
cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg Te
Te , which exhibits an extremely low
, which exhibits an extremely low  value of
value of  0.18 Wm
0.18 Wm K
K . On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at
. On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at  3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low
3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low  , which is heavily deviated from the
, which is heavily deviated from the 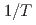 temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg
temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg Te
Te . These factors synergistically account for the ultralow
. These factors synergistically account for the ultralow  value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
Ying, H.*; Yang, X.*; He, H.*; Yan, A.*; An, K.*; Ke, Y.*; Wu, Z.*; Tang, S.*; Zhang, Z.*; Dong, H.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 250, p.116181_1 - 116181_7, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:36.18(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Nanoscale chemical fluctuations and their effect on the deformation behavior of CrFeCoNi-based high-entropy alloys (HEAs) were investigated using small-angle scattering and in situ neutron diffraction measurements. Small-angle scattering results demonstrated the presence of nano ( 10 nm) chemical fluctuations in the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEAs, which was attributed to the negative mixing of enthalpy and the significant atomic radius difference between Pd and the constituent elements in the CrFeCoNi-based alloys. Subsequent tensile tests demonstrated that the yield and tensile strengths of the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEA surpass those of the as-prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEA. Neutron diffraction data analysis revealed an anomalous response of dislocation evolution with the strain.
10 nm) chemical fluctuations in the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEAs, which was attributed to the negative mixing of enthalpy and the significant atomic radius difference between Pd and the constituent elements in the CrFeCoNi-based alloys. Subsequent tensile tests demonstrated that the yield and tensile strengths of the as-prepared CrFeCoNiPd HEA surpass those of the as-prepared CrMnFeCoNi HEA. Neutron diffraction data analysis revealed an anomalous response of dislocation evolution with the strain.
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(7), p.2175 - 2185, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:70.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-speed railway S38C axles undergo surface induction hardening for durability, but are susceptible to fatigue cracks from foreign object impact. The neutron diffraction method was employed to measure the residual strain in S38C axles, obtaining microscopic lattice distortion data, for the gradient layer at a depth of 8 mm under the surface. The results showed that after induction-hardening, the microscopic lattice distortion had a gradient distribution, decreasing with the distance from the surface. However, in the case of impacting speed of 600 km/m, the average microscopic lattice distortion increased with the distance from the surface, reaching a maximum augmentation of 55 pct. These findings indicate a strong experimental basis, and improve our understanding of the relationship between macroscopic residual stress and decision-making, in regard to operation and maintenance.
Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:98.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanoprecipitates and nanoscale retained austenite (RA) with suitable stability play crucial roles in determining the yield strength (YS) and ductility of ultrahigh strength steels (UHSSs). However, owing to the kinetics incompatibility between nanoprecipitation and austenite reversion, it is highly challenging to simultaneously introduce high-density nanoprecipitates and optimized RA in UHSSs. In this work, through the combination of austenite reversion treatment (ART) and subsequent flash austenitizing (FA), nanoscale chemical heterogeneity was successfully introduced into a low-cost UHSS prior to the aging process. This chemical heterogeneity involved the enrichment of Mn and Ni in the austenite phase. The resulting UHSS exhibited dual-nanoprecipitation of Ni(Al,Mn) and (Mo,Cr) C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:96.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Best-Estimate Plus Uncertainty (BEPU) framework, the use of best-estimate code requires to go through a Verification, Validation and Uncertainty Quantification process (VVUQ). The relevance of the experimental data in relation to the physical phenomena of interest in the VVUQ process is crucial. Adequacy analysis of selected experimental databases addresses this problem. The outcomes of the analysis can be used to select a subset of relevant experimental data, to encourage designing new experiments or to drop some experiments from a database because of their substantial lack of adequacy. The development of a specific transparent and reproducible approach to analyze the relevance of experimental data for VVUQ still remains open and is the topic of this contribution. In this paper, the concept of adequacy initially introduced in the OECD/NEA SAPIUM (Systematic APproach for model Input Uncertainty quantification Methodology) activity is formalized. It is defined through two key properties, called representativeness and completeness, that allows considering the multifactorial dimension of the adequacy problem. A new systematic approach is then proposed to analyze the adequacy of a set of experimental databases. It relies on the introduction of two sets of criteria to characterize representativeness and completeness and on the use of multi-criteria decision analysis method to perform the analysis. Finally, the approach is applied in the framework of the new OECD/NEA ATRIUM activity which includes a set of practical IUQ exercises in thermal-hydraulics to test the SAPIUM guideline in determining input uncertainties and forward propagating them on an application case. It allows evaluating the adequacy of eight experimental databases coming from the Super Moby-dick, Sozzi-Sutherland and Marviken experiments and identifying the most adequate ones.
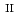 complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transition
complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transitionJi, T.*; Su, S.*; Wu, S.*; 堀 優太*; 重田 育照*; Huang, Y.*; Zheng, W.*; Xu, W.*; Zhang, X.*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 63(25), p.e202404843_1 - e202404843_6, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we investigated reversible intermolecular proton shifting (IPS) coupled with spin transition (ST) in a novel Fe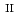 complex. The host Fe
complex. The host Fe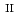 complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
 -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; 古府 麻衣子; 中島 健次; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:89.71(Physics, Applied)The desire for intrinsically low lattice thermal conductivity (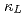 ) in thermoelectrics motivates numerous efforts on understanding the microscopic mechanisms of heat transport in solids. Here, based on theoretical calculations, we demonstrate that
) in thermoelectrics motivates numerous efforts on understanding the microscopic mechanisms of heat transport in solids. Here, based on theoretical calculations, we demonstrate that  -MgAgSb hosts low-energy localized phonon bands and avoided crossing of the rattler modes, which coincides with the inelastic neutron scattering result. Using the two-channel lattice dynamical approach, we find, besides the conventional contribution (
-MgAgSb hosts low-energy localized phonon bands and avoided crossing of the rattler modes, which coincides with the inelastic neutron scattering result. Using the two-channel lattice dynamical approach, we find, besides the conventional contribution ( 70% at 300 K) from particlelike phonons propagating, the coherence contribution dominated by the wavelike tunneling of phonons accounts for
70% at 300 K) from particlelike phonons propagating, the coherence contribution dominated by the wavelike tunneling of phonons accounts for  30% of total
30% of total 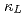 at 300 K. By considering dual contributions, our calculated room-temperature
at 300 K. By considering dual contributions, our calculated room-temperature 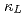 of 0.64 Wm
of 0.64 Wm K
K well agrees with the experimental value of 0.63 Wm
well agrees with the experimental value of 0.63 Wm K
K . More importantly, our computations give a nonstandard
. More importantly, our computations give a nonstandard 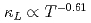 dependence, perfectly explaining the abnormal temperature-trend of
dependence, perfectly explaining the abnormal temperature-trend of 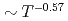 in experiment for
in experiment for  -MgAgSb. By molecular dynamics simulation, we reveal that the structure simultaneously has soft crystalline sublattices with the metavalent bonding and fluctuating liquid-like sublattices with thermally induced large amplitude vibrations. These diverse forms of chemical bonding arouse mixed part-crystal part-liquid state, scatter strongly heat-carrying phonons, and finally produce extremely low
-MgAgSb. By molecular dynamics simulation, we reveal that the structure simultaneously has soft crystalline sublattices with the metavalent bonding and fluctuating liquid-like sublattices with thermally induced large amplitude vibrations. These diverse forms of chemical bonding arouse mixed part-crystal part-liquid state, scatter strongly heat-carrying phonons, and finally produce extremely low 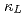 . The fundamental research from this study will accelerate the design of ultralow-
. The fundamental research from this study will accelerate the design of ultralow-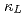 materials for energy-conversion applications.
materials for energy-conversion applications.
Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; 舟越 賢一*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; 肥後 祐司*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Thermodynamics)The phase transformations and pressure-volume dependencies of the Ti-45Al alloy with respect to pressure have been investigated by means of in-situ observation using multi anvil-type high-pressure devices and synchrotron radiation. Under hydrostatic compression from 0 to 10.1 GPa, about 2.3 vol. % of  transforms continuously to
transforms continuously to  2. Lattice parameters as well as volume fractions of these two phases have been determined as a function of pressure. Bulk moduli estimated using Birch-Murnaghan's equation of state are 148 GPa for the
2. Lattice parameters as well as volume fractions of these two phases have been determined as a function of pressure. Bulk moduli estimated using Birch-Murnaghan's equation of state are 148 GPa for the  phase, 138 GPa for the
phase, 138 GPa for the  2 phase, and 149 GPa for their two-phase mixture of Ti-45Al alloy. First-principles have also applied to investigate bulk moduli of two single phases, and the deviation between calculations and measurements is discussed and attributed to mainly phase transformation. The presently study provides useful insights into thermodynamics of
2 phase, and 149 GPa for their two-phase mixture of Ti-45Al alloy. First-principles have also applied to investigate bulk moduli of two single phases, and the deviation between calculations and measurements is discussed and attributed to mainly phase transformation. The presently study provides useful insights into thermodynamics of  2 and
2 and  phases under high pressure.
phases under high pressure.
Zhang, X.*; Gong, W.; 他8名*
International Journal of Plasticity, 173, p.103896_1 - 103896_24, 2024/02
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:99.08(Engineering, Mechanical)The distribution and partitioning of solute atoms in age-hardenable aluminum (Al) alloys markedly impact strength, ductility and failure of alloy materials, thus rendering the understanding of dislocation-obstacle (solute-rich features) interactions crucial in the development of a new class of heat-treatable Al alloys. Here, we investigate the slip mechanisms, strain localization and strain hardening of a high Mg-content lightweight AlMgZn-based crossover alloy aged to different conditions with the focus on the dislocation-obstacle interactions. It is found that due to different elemental partitioning between matrix and solute-rich features the interaction of dislocations with obstacles can be drastically different for samples with varying precipitates. The dislocations in the under-aged and near peak-aged samples show predominantly planar slip, which produces strain localization. Whereas in the over-aged sample, gliding dislocations initially bend between adjacent precipitates lying in the slip planes, and subsequently surmount them by local cross slip processes, giving rise to homogeneous slip. It is discovered that strain localization in the form of coarse slip bands induces strain hardening in the under-aged material. To understand the enhanced strain hardening observed in the under-aged sample, four key influencing factors are proposed. In addition, the predicted yield strengths for the solution-treated and artificially aged materials match well with those experimentally measured values.
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; 徐 平光; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:79.11(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The quasi-static superelastic responses and hierarchical martensite transformation from body-centered cubic (BCC) to face-centered cubic (FCC) under dynamic impact in Fe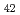 Mn
Mn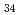 Al
Al Ni
Ni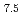 Ti
Ti alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC
alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC  FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:23.52(Chemistry, Physical)The grain orientation-dependent lattice strain evolution of a (TiZrHfNb)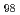
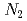 refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using
refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using  neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary
neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary 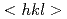 -oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
-oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
Lloveras, P.*; Zhang, Z.*; Zeng, M.*; Barrio, M.*; 川北 至信; Yu, D.*; Lin, S.*; Li, K.*; Moya, X.*; Tamarit, J.-L.*; et al.
Barocaloric Effects in the Solid State; Materials and methods, p.7_1 - 7_30, 2023/10
被引用回数:232 パーセンタイル:99.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)「固体状態における圧力熱量効果」と題する電子ブックの第一章として、様々な柔粘性結晶が紹介されている。柔粘性結晶における圧力熱量反応を決定する方法、その熱力学的な起源、中性子準弾性散乱からの分光学的洞察、柔粘性結晶の応用などが解説されている。
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:92.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnon polarons are novel elementary excitations possessing hybrid magnonic and phononic signatures, and are responsible for many exotic spintronic and magnonic phenomena. Despite long-term sustained experimental efforts in chasing for magnon polarons, direct spectroscopic evidence of their existence is hardly observed. Here, we report the direct observation of magnon polarons using neutron spectroscopy on a multiferroic Fe Mo
Mo O
O possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.