Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
深津 勇太; 小栗 朋美*; 浜本 貴史*; 石田 圭輔*; Martin, A.*; 舘 幸男
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 277, p.104865_1 - 104865_12, 2026/02
被引用回数:0For long-term safety assessments of deep geological disposal, evaluating effective diffusion coefficients (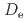 ) and distribution coefficients (
) and distribution coefficients ( ) under in-situ conditions remains a critical yet challenging task due to practical limitations. This study aims to establish a methodology for evaluating these parameters under realistic geological conditions through an integrated analysis of a long-term in-situ diffusion (LTD-II) experiment and complementary laboratory through-diffusion experiments in Grimsel granodiorite. The proposed approach combines (i) post analysis of cored samples to characterize spatial variations in pore connectivity and anisotropic transport, (ii) numerical modeling that accounts for the borehole disturbed zone (BDZ), and (iii) laboratory diffusion experiments to verify the consistency and reliability of in-situ parameter estimation. The modeling reproduced both the depletion curves and the tracer concentration profiles observed in the LTD-II experiment, particularly the sharp gradients within a few millimeters from the injection hole, which were attributed to BDZ. The derived
) under in-situ conditions remains a critical yet challenging task due to practical limitations. This study aims to establish a methodology for evaluating these parameters under realistic geological conditions through an integrated analysis of a long-term in-situ diffusion (LTD-II) experiment and complementary laboratory through-diffusion experiments in Grimsel granodiorite. The proposed approach combines (i) post analysis of cored samples to characterize spatial variations in pore connectivity and anisotropic transport, (ii) numerical modeling that accounts for the borehole disturbed zone (BDZ), and (iii) laboratory diffusion experiments to verify the consistency and reliability of in-situ parameter estimation. The modeling reproduced both the depletion curves and the tracer concentration profiles observed in the LTD-II experiment, particularly the sharp gradients within a few millimeters from the injection hole, which were attributed to BDZ. The derived 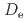 and K
and K values for sorbing tracers (Na
values for sorbing tracers (Na , Cs
, Cs , and Ba
, and Ba ) were consistent between laboratory and in-situ conditions for transport distances up to several centimeters, confirming the reliability of the parameter derivation approach for sorbing species over short distances. In contrast, non-sorbing tracers (HTO and
) were consistent between laboratory and in-situ conditions for transport distances up to several centimeters, confirming the reliability of the parameter derivation approach for sorbing species over short distances. In contrast, non-sorbing tracers (HTO and  Cl
Cl ) exhibited depth-dependent concentration variations extending
) exhibited depth-dependent concentration variations extending  50 cm from the injection hole. The D
50 cm from the injection hole. The D values of non-sorbing tracers were two to three times higher than those obtained in laboratory tests, yet remained within the same order of magnitude. These variations of non-sorbing tracers could be qualitatively explained by anisotropic transport along foliation and minor advection over several tens of centimeters, highlighting the importance of accounting for local structural and hydraulic variations when interpreting in-situ diffusion data. These results demonstrate that integrating in-situ diffusion data with laboratory verification and spatial profiling provides a methodology for deriving diffusion and sorption parameters representative of in-situ conditions, and clarifies the practical limitations and applicable range of transport modeling in crystalline rocks.
values of non-sorbing tracers were two to three times higher than those obtained in laboratory tests, yet remained within the same order of magnitude. These variations of non-sorbing tracers could be qualitatively explained by anisotropic transport along foliation and minor advection over several tens of centimeters, highlighting the importance of accounting for local structural and hydraulic variations when interpreting in-situ diffusion data. These results demonstrate that integrating in-situ diffusion data with laboratory verification and spatial profiling provides a methodology for deriving diffusion and sorption parameters representative of in-situ conditions, and clarifies the practical limitations and applicable range of transport modeling in crystalline rocks.
深津 勇太; Hu, Q.*; 舘 幸男
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 276, p.104789_1 - 104789_12, 2026/01
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)This study investigated the diffusion and sorption behavior of Cs in granitic rocks by conducting through-diffusion experiments using tonalite, granodiorite, and granite samples. The effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Cs
in granitic rocks by conducting through-diffusion experiments using tonalite, granodiorite, and granite samples. The effective diffusion coefficients (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of Cs were evaluated under various KCl concentrations, as potassium is a key competing cation for Cs
were evaluated under various KCl concentrations, as potassium is a key competing cation for Cs sorption. In addition, elemental mapping and mineralogical characterization of solid samples were conducted using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and X-ray diffraction, to support the interpretation of Cs
sorption. In addition, elemental mapping and mineralogical characterization of solid samples were conducted using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and X-ray diffraction, to support the interpretation of Cs transport. The results showed that rocks with higher biotite content exhibited higher De values and, in some cases, higher Kd values under high KCl conditions (1
transport. The results showed that rocks with higher biotite content exhibited higher De values and, in some cases, higher Kd values under high KCl conditions (1 10
10 mol L
mol L ). At this concentration, formation of a dual profile, characterized by localized Cs enrichment near the inlet boundary, was suppressed. This suppression may be explained by the disappearance of a hydrobiotite peak observed in XRD spectra, suggesting that structural modification of biotite to hydrobiotite was inhibited. As a result, the number of high affinity of Cs
). At this concentration, formation of a dual profile, characterized by localized Cs enrichment near the inlet boundary, was suppressed. This suppression may be explained by the disappearance of a hydrobiotite peak observed in XRD spectra, suggesting that structural modification of biotite to hydrobiotite was inhibited. As a result, the number of high affinity of Cs sorption sites near the sample boundaries was reduced. Furthermore, in all rock types, the De values for Cs
sorption sites near the sample boundaries was reduced. Furthermore, in all rock types, the De values for Cs exceeded those of deuterated water as a neutral tracer. This trend indicates cation excess diffusion, in which Cs
exceeded those of deuterated water as a neutral tracer. This trend indicates cation excess diffusion, in which Cs diffusivity is enhanced by its accumulation in the electrical double layer adjacent to negatively charged surfaces of biotite, occur. Although structural modifications of biotite depending on KCl concentration may have influenced Cs
diffusivity is enhanced by its accumulation in the electrical double layer adjacent to negatively charged surfaces of biotite, occur. Although structural modifications of biotite depending on KCl concentration may have influenced Cs transport, the systematic correlation between biotite content and Cs
transport, the systematic correlation between biotite content and Cs diffusivity provides a consistent explanation in the understanding of matrix diffusion and sorption behaviors among various granitic rock types. These findings demonstrate that cation excess diffusion associated with biotite is a critical mechanism in the control of Cs
diffusivity provides a consistent explanation in the understanding of matrix diffusion and sorption behaviors among various granitic rock types. These findings demonstrate that cation excess diffusion associated with biotite is a critical mechanism in the control of Cs transport in the matrix of crystalline rocks and should be considered in predictive models for repository safety assessments.
transport in the matrix of crystalline rocks and should be considered in predictive models for repository safety assessments.
中山 雅; 石井 英一; 青柳 和平; 早野 明; 村上 裕晃; 大野 宏和; 武田 匡樹; 深津 勇太; 望月 陽人; 尾崎 裕介; et al.
JAEA-Review 2025-042, 136 Pages, 2025/12
幌延深地層研究計画は、日本原子力研究開発機構(以下、原子力機構)が堆積岩を対象に北海道幌延町で実施しているプロジェクトである。令和6年度は、「令和2年度以降の幌延深地層研究計画」で示した、「実際の地質環境における人工バリアの適用性確認」、「処分概念オプションの実証」および「地殻変動に対する堆積岩の緩衝能力の検証」の3つの研究課題を対象に調査研究を実施した。具体的には、「実際の地質環境における人工バリアの適用性確認」では、人工バリア性能確認試験および物質移行試験を、「処分概念オプションの実証」では、人工バリアの定置・品質確認などの方法論に関する実証試験および高温度等の限界条件下での人工バリア性能確認試験を実施した。また、「地殻変動に対する堆積岩の緩衝能力の検証」では、ダクティリティインデックスを用いた透水性評価手法の検証および水圧擾乱試験から原位置の地圧の状態を推定する手法の検討などを実施した。地下施設整備を継続し、東立坑および換気立坑が深度500mまでの掘削を完了するとともに、西立坑および500m調査坑道の掘削を開始した。令和6年度末現在の掘削進捗は、東立坑および換気立坑が深度500m、西立坑が深度472m、500m調査坑道が112.9mである。幌延国際共同プロジェクト(Horonobe International Project: HIP)では、令和6年6月には合同タスク会合を幌延深地層研究センター国際交流施設にて開催し、坑道の整備状況や試験の準備状況について確認した。また、管理委員会やタスク会合を通じて参加機関との議論を行った。HIPは令和4年度後半から令和6年度までをフェーズ1、令和7年度から令和10年度までをフェーズ2に分けて実施することとしており、令和6年度はフェーズ1の研究成果を取りまとめた。
 , I
, I and HDO onto pre-Neogene sedimentary rocks
and HDO onto pre-Neogene sedimentary rocksHou, L.*; 深津 勇太; 岡本 駿一*; 戸田 賀奈子*; 中田 弘太郎*; 野原 慎太郎*; 石寺 孝充; 斉藤 拓巳*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(11), p.1121 - 1134, 2025/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:68.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigates the diffusion behaviors of Cs , I
, I , and HDO in a pre-Neogene sedimentary rock as a potential host rock for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal in Japan. Through-diffusion experiments were conducted to reveal distinct patterns in their breakthrough curves. Cs
, and HDO in a pre-Neogene sedimentary rock as a potential host rock for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal in Japan. Through-diffusion experiments were conducted to reveal distinct patterns in their breakthrough curves. Cs exhibited the fastest diffusion among the tracers, significantly influenced by fractures, surface diffusion mechanisms, and aragonite formation. In contrast, the anion exclusion effect notably hindered the diffusion behavior of I
exhibited the fastest diffusion among the tracers, significantly influenced by fractures, surface diffusion mechanisms, and aragonite formation. In contrast, the anion exclusion effect notably hindered the diffusion behavior of I . The results highlight the diverse diffusion and retardation properties of pre-Neogene sedimentary rocks, showing that the effective diffusion coefficient of HDO is more similar to that of crystalline rocks. These findings contribute to the understanding of the suitability of pre-Neogene sedimentary rocks as a potential natural barrier for HLW repositories.
. The results highlight the diverse diffusion and retardation properties of pre-Neogene sedimentary rocks, showing that the effective diffusion coefficient of HDO is more similar to that of crystalline rocks. These findings contribute to the understanding of the suitability of pre-Neogene sedimentary rocks as a potential natural barrier for HLW repositories.
小池 彩華*; 上野 吹佳*; 石寺 孝充; 岩田 孟; 深津 勇太; 種市 やよい; 野中 麻衣
NUMO-TR-25-03; 技術開発成果概要2024, p.124 - 126, 2025/10
地層処分事業の実施主体である原子力発電環境整備機構(NUMO)が、日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)をはじめとする関係研究機関及び大学との共同研究等により実施した2024年度の技術開発成果の概要を取りまとめ、報告する。本報告は、NUMOとJAEAの共同研究「ニアフィールドシステムの状態変遷に伴うバリア材及び核種の長期挙動評価のための研究」で2024年度に実施したサイト調査を反映した核種移行パラメータ設定の方法論の検討及びデータ拡充に関する成果についての概要をまとめたものである。
浜本 貴史*; 小池 彩華*; 石寺 孝充; 岩田 孟; 深津 勇太; 種市 やよい
NUMO-TR-24-03; 技術開発成果概要2023, p.85 - 86, 2024/10
地層処分事業の実施主体である原子力発電環境整備機構(NUMO)が、日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)をはじめとする関係研究機関及び大学との共同研究等により実施した2023年度の技術開発成果の概要を取りまとめ、報告する。本報告は、NUMOとJAEAの共同研究「ニアフィールドシステムの状態変遷に伴うバリア材及び核種の長期挙動評価のための研究」で2023年度に実施したサイト調査を反映した核種移行パラメータ設定の方法論の検討及びデータ拡充に関する成果についての概要をまとめたものである。
浜本 貴史*; 深津 勇太
NUMO-TR-24-01; 技術開発成果概要2022, p.95 - 97, 2024/05
地層処分事業の実施主体である原子力発電環境整備機構(NUMO)が、日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)をはじめとする関係研究機関及び大学との共同研究等により実施した2022年度の技術開発成果の概要を取りまとめ、報告する。本報告は、NUMOとJAEAの共同研究「ニアフィールドシステムの状態変遷に伴うバリア材及び核種の長期挙動評価のための研究」で2022年度に実施した割れ目が卓越した母岩中の核種移行モデルに関する原位置試験データを用いた妥当性確認に関する成果についての概要をまとめたものである。
Soler, J. M.*; Jurado, D.*; Saaltink, M. W.*; Mart nez, L.*; Hidalgo, J. J.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Heule, M.*; 深津 勇太; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Havlov
nez, L.*; Hidalgo, J. J.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Heule, M.*; 深津 勇太; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Havlov , V.*; et al.
, V.*; et al.
Applied Geochemistry, 162, p.105927_1 - 105927_12, 2024/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:36.73(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Within the framework of the GTS-LTD project (Grimsel Test Site, Long-Term Diffusion), a radionuclide transport experiment in unfractured granitic rock matrix was performed. Grimsel groundwater containing several radionuclide tracers ( H as HTO,
H as HTO,  Cl
Cl ,
,  Na
Na ,
,  Cs
Cs ,
,  Ba
Ba ) was continuously circulated through a packed-off borehole interval. The decrease in tracer concentrations in the solution was monitored for a period of 1266 days (March 05, 2014-August 22, 2017). Additionally, tracer breakthrough was monitored in an observation borehole at a distance of 18.6 cm. Core samples from new boreholes were collected immediately after the end of the experiment, allowing the measurement of tracer distributions in the rock. The observed patterns for the non-sorbing tracers (HTO,
) was continuously circulated through a packed-off borehole interval. The decrease in tracer concentrations in the solution was monitored for a period of 1266 days (March 05, 2014-August 22, 2017). Additionally, tracer breakthrough was monitored in an observation borehole at a distance of 18.6 cm. Core samples from new boreholes were collected immediately after the end of the experiment, allowing the measurement of tracer distributions in the rock. The observed patterns for the non-sorbing tracers (HTO,  Cl
Cl ) showed clear preferential transport directions, consistent with advective flow towards the gallery from which the boreholes were drilled. Final 3D modeling of the experiment can explain the measured concentrations in the boreholes and in the rock. Tracer transport for the conservative tracers (HTO,
) showed clear preferential transport directions, consistent with advective flow towards the gallery from which the boreholes were drilled. Final 3D modeling of the experiment can explain the measured concentrations in the boreholes and in the rock. Tracer transport for the conservative tracers (HTO,  Cl
Cl ) is affected by both diffusion and advection through the granitic rock matrix. Also, in situ accessible porosities deduced from the modeling (0.0014) are smaller than those measured in rock samples (about 0.009), pointing to unloading and destressing of the rock samples after drilling. At the spatial and temporal scales of the experiment, the effect of advection for the weakly sorbing
) is affected by both diffusion and advection through the granitic rock matrix. Also, in situ accessible porosities deduced from the modeling (0.0014) are smaller than those measured in rock samples (about 0.009), pointing to unloading and destressing of the rock samples after drilling. At the spatial and temporal scales of the experiment, the effect of advection for the weakly sorbing  Na
Na is only minor, and it is practically negligible for the strongly sorbing tracers (
is only minor, and it is practically negligible for the strongly sorbing tracers ( Cs
Cs ,
,  Ba
Ba ).
).
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Zhang, T.*; Zhao, C.*; Iltaf, K. H.*; Liu, S. Q.*; 深津 勇太
Energy Reports (Internet), 9, p.3661 - 3682, 2023/12
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:65.04(Energy & Fuels)This study evaluates petrophysical properties of representative geological rocks in the context of injectivity, storage space, and caprock integrity for effective utilization and long-term storage of carbon dioxide. A total of 10 geological rocks were selected as representative storage media for consideration as saline aquifers & depleted oil and gas reservoirs, basalts, and cap rocks, as well as utilization in organic-rich shale and coal seams. An integrated suite of laboratory tests, including liquid immersion porosimetry, gas expansion porosimetry, grain size distribution, mercury intrusion porosimetry, and gas diffusion, were performed on these various rock samples. The results exhibit a disparity of petrophysical properties among two broad groups of rocks: rocks selected for possible storage of CO have porosities of
have porosities of  10-25%, permeabilities of
10-25%, permeabilities of  10
10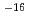 -10
-10 m
m ,
,  m-sized pore-throat size distribution, and mostly good pore connectivity; in contrast, the potential caprocks have porosities of
m-sized pore-throat size distribution, and mostly good pore connectivity; in contrast, the potential caprocks have porosities of  0.5-5%, permeabilities of
0.5-5%, permeabilities of  10
10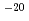 -10
-10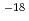 m
m , pore throat sizes of
, pore throat sizes of  50 nm, and probably poorly connected pore networks. An understanding of the measured facets of pore structure and contribution of fractures is also critical in the context of different testing principles and data interpretation of petrophysical analyses, as well as observational scales in the laboratory and field, and therefore reliable confidence of CO
50 nm, and probably poorly connected pore networks. An understanding of the measured facets of pore structure and contribution of fractures is also critical in the context of different testing principles and data interpretation of petrophysical analyses, as well as observational scales in the laboratory and field, and therefore reliable confidence of CO storage and utilization performance. Our work further illustrates the controlling influence of grain size distribution and geological processes on pore size distribution and pore connectivity for a wide range of rock types and lithologies, and particularly presents the extent and behavior of CO
storage and utilization performance. Our work further illustrates the controlling influence of grain size distribution and geological processes on pore size distribution and pore connectivity for a wide range of rock types and lithologies, and particularly presents the extent and behavior of CO gas diffusion with a custom-designed apparatus for a holistic understanding of various petrophysical attributes of widely different geological rocks.
gas diffusion with a custom-designed apparatus for a holistic understanding of various petrophysical attributes of widely different geological rocks.
Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 209(11), p.1765 - 1784, 2023/11
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:66.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)The REPRO-TDE test was performed at a depth of about 400 m in the ONKALO underground research facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing radionuclide tracers (HTO, Cl-36, Na-22, Ba-133, Cs-134) was circulated for about four years in a packed-off interval of the injection borehole. Tracer activities were additionally monitored in two observation boreholes. The test was the subject of a modelling exercise by the SKB GWFTS Task Force. Eleven teams participated in the exercise, using different model concepts and approaches. Predictive model calculations were based on laboratory-based information concerning porosities, diffusion coefficients and sorption partition coefficients. After the experimental results were made available, the teams were able to revise their models to reproduce the observations. General conclusions from these back-analysis calculations include the need for reduced effective diffusion coefficients for Cl-36 compared to those applicable to HTO (anion exclusion), the need to implement weaker sorption for Na-22, compared to results from laboratory batch-sorption experiments, and the observation of large differences between the theoretical initial concentrations for the strongly-sorbing Ba-133 and Cs-134 and the first measured values a few hours after tracer injection. Different teams applied different concepts, concerning mainly the implementation of isotropic vs. anisotropic diffusion, or the possible existence of Borehole Disturbed Zones around the different boreholes. The role of microstructure was also addressed in two of the models.
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; 舘 幸男; 深津 勇太; 濱本 昌一郎*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:66.38(Engineering, Civil)Mass transport in geomedia as influenced by the pore structure is an important phenomenon. Six rocks (granodiorite, limestone, two chalks, mudstone, and dolostone) with different extents of heterogeneity at six different particle sizes were studied to describe the effects of pore connectivity on mass transport. The multiple methods applied were porosity measurement, gas diffusion test, and batch sorption test of multiple ions. Porosity measurement results reveal that with decreasing particle sizes, the effective porosities for the "heterogenous" group (granodiorite and limestone) increase, whereas the porosities of "homogeneous" group (chalks, mudstone, and dolostone) roughly remain constant. Gas diffusion results show that the intraparticle gas diffusion coefficient among these two groups, varying in the magnitude of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /s. The batch sorption work displays a different affinity of these rocks for tracers, which are related to their mineral components. For granodiorite, mudstone, and dolostone, the adsorption capacity increases as the particle size decreases, due to higher specific surface area in smaller particle-size. In general, this integrated research of grain size distribution, rock porosity, intraparticle diffusivity, and ionic sorption capacity gives insights into the pore connectivity effect on both gas diffusion and chemical transport behaviors for different lithologies and/or different particle sizes.
/s. The batch sorption work displays a different affinity of these rocks for tracers, which are related to their mineral components. For granodiorite, mudstone, and dolostone, the adsorption capacity increases as the particle size decreases, due to higher specific surface area in smaller particle-size. In general, this integrated research of grain size distribution, rock porosity, intraparticle diffusivity, and ionic sorption capacity gives insights into the pore connectivity effect on both gas diffusion and chemical transport behaviors for different lithologies and/or different particle sizes.
 Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations
Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations大窪 貴洋*; 武井 滉洋*; 舘 幸男; 深津 勇太; 出口 健三*; 大木 忍*; 清水 禎*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 127(4), p.973 - 986, 2023/02
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:61.51(Chemistry, Physical)粘土鉱物へのCsの吸着サイトの特定は、環境化学の分野で研究されてきた。核磁気共鳴(NMR)実験によって、吸着されたCsの局所構造を直接観察することが可能である。固体NMR実験から得られた CsのNMRパラメータは、吸着されたCsの局所的な構造に敏感である。しかしながら、NMRデータだけからCsの吸着位置を決定することは困難であった。本研究では、機械学習と実験的に観察されたケミカルシフトを組み合わせることにより、粘土鉱物に吸着されたCsの吸着位置を特定するためのアプローチについて提示する。原子配置の記述子とNMRによるケミカルシフトの第一原理計算結果を関連付けて評価する機械学習の線形リッジ回帰モデルを構築した。これにより、原子配置の構造データから
CsのNMRパラメータは、吸着されたCsの局所的な構造に敏感である。しかしながら、NMRデータだけからCsの吸着位置を決定することは困難であった。本研究では、機械学習と実験的に観察されたケミカルシフトを組み合わせることにより、粘土鉱物に吸着されたCsの吸着位置を特定するためのアプローチについて提示する。原子配置の記述子とNMRによるケミカルシフトの第一原理計算結果を関連付けて評価する機械学習の線形リッジ回帰モデルを構築した。これにより、原子配置の構造データから Csのケミカルシフトを高速で計算することが可能となった。機械学習モデルによって、実験的に観察された化学シフトから逆解析を行うことにより、Cs吸着位置を導き出すことが可能になる。
Csのケミカルシフトを高速で計算することが可能となった。機械学習モデルによって、実験的に観察された化学シフトから逆解析を行うことにより、Cs吸着位置を導き出すことが可能になる。
Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-21-09, 204 Pages, 2021/11
Task 9C of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes (Task Force GWFTS) was the third subtask within Task 9 and focused on (1) predictive and (2) back-analysis modelling of experimental results from the REPRO-TDE in situ diffusion experiment. The test was performed at a depth of about 400 m in the ONKALO underground research facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing radionuclide tracers (HTO, Cl-36, Na-22, Ba-133, Cs-134) was circulated for about four years in a packed-off interval of the so-called injection borehole. Tracer activities were additionally monitored in two observation boreholes arranged as a right-angled triangle and located at about 0.1 m wall-to-wall from the injection borehole. Eleven modelling teams participated in the modelling exercise, using different model concepts and approaches. Three main types of models were applied: (1) An analytical solution to the diffusion-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium-type numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models. The predictive model calculations were based on laboratory-based information concerning porosities, diffusion coefficients and sorption partition coefficients available in the task description. Microstructural characterisation of rock samples was also available and used by the teams using microstructure-based models.
 Cs
Cs , and
, and  I
I in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approaches
in compacted Ca-montmorillonite; Experimental and modeling approaches深津 勇太; 四辻 健治*; 大窪 貴洋*; 舘 幸男
Applied Clay Science, 211, p.106176_1 - 106176_10, 2021/09
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:87.47(Chemistry, Physical)Mechanistic understanding and predictive modeling of radionuclide diffusion in Na- and Ca-montmorillonite are essential to evaluate the long-term evolution of the bentonite barrier and their impact on radionuclide migration during geological disposal of radioactive wastes. Thus, the diffusion behavior of  Cs
Cs ,
,  I
I , and tritiated water (HTO) in compacted Ca-montmorillonite was investigated as a function of porewater salinity and dry density via both experiments and models. The effective diffusion coefficient (De) followed in the order of
, and tritiated water (HTO) in compacted Ca-montmorillonite was investigated as a function of porewater salinity and dry density via both experiments and models. The effective diffusion coefficient (De) followed in the order of  Cs
Cs
 HTO
HTO 
 I
I . The De of
. The De of  Cs
Cs decreased with increasing salinity, whereas the dependence of De of
decreased with increasing salinity, whereas the dependence of De of  I
I on salinity was uncertain. The cation excess and anion exclusion effects for Ca-montmorillonite were lower than those for Na-montmorillonite. The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model, assuming the homogeneous pore structure and the electrical double layer (EDL) theory for 2:1 electrolyte (CaCl
on salinity was uncertain. The cation excess and anion exclusion effects for Ca-montmorillonite were lower than those for Na-montmorillonite. The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model, assuming the homogeneous pore structure and the electrical double layer (EDL) theory for 2:1 electrolyte (CaCl ), could account for the observed trends for De in Ca-montmorillonite. The lower dependence of De on the porewater salinity in Ca-montmorillonite was caused by the reduction of the EDL thickness for divalent cations (Ca
), could account for the observed trends for De in Ca-montmorillonite. The lower dependence of De on the porewater salinity in Ca-montmorillonite was caused by the reduction of the EDL thickness for divalent cations (Ca ) in comparison with that for monovalent cations (Na
) in comparison with that for monovalent cations (Na ). The multipore model could improve the fit for De of
). The multipore model could improve the fit for De of  I
I at low salinity due to the reduction of interlayer pore volumes and anion exclusion effect, however, the disparity at higher densities was considerably larger. From these results, cation diffusion for compacted Ca-montmorillonite could be mainly explained by the electrostatic interactions in the homogeneous pore model; in contrast, anion diffusion was sensitive to both electrostatic interactions and heterogeneous pore structures. The proposed ISD model is an effective tool to evaluate the radionuclide diffusion and sorption behavior in both compacted Ca-montmorillonite and Na-montmorillonite.
at low salinity due to the reduction of interlayer pore volumes and anion exclusion effect, however, the disparity at higher densities was considerably larger. From these results, cation diffusion for compacted Ca-montmorillonite could be mainly explained by the electrostatic interactions in the homogeneous pore model; in contrast, anion diffusion was sensitive to both electrostatic interactions and heterogeneous pore structures. The proposed ISD model is an effective tool to evaluate the radionuclide diffusion and sorption behavior in both compacted Ca-montmorillonite and Na-montmorillonite.
大窪 貴洋*; 山崎 秋雄*; 深津 勇太; 舘 幸男
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 313, p.110841_1 - 110841_11, 2021/01
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:51.63(Chemistry, Applied)Ca型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布が、乾燥密度(0.8-1.6g/cm ),間隙水塩濃度(脱イオン水、0.1及び1M CaCl
),間隙水塩濃度(脱イオン水、0.1及び1M CaCl ),温度(233-303K)の条件下で、
),温度(233-303K)の条件下で、 H NMR測定によって調査された。圧縮Ca型モンモリロナイト中の2層及び3層水和を含む層間間隙と層間外間隙の体積割合が、緩和時間
H NMR測定によって調査された。圧縮Ca型モンモリロナイト中の2層及び3層水和を含む層間間隙と層間外間隙の体積割合が、緩和時間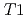 及び
及び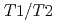 分布の分析に基づくNMR緩和時間測定法によって定量評価され、さらに、NMR凍結間隙測定法及びX線回折法による結果と比較された。これらの分析によって、Na型モンモリロナイトと比較可能な、Ca型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布の状態を把握することができた。圧縮Ca型及びNa型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布に影響を及ぼす主要な因子は圧縮密度であり、間隙水塩濃度の影響は相対的に小さい結果となった。CaとNaの層間陽イオンの影響は高密度条件では小さいが、低密度ではその影響は顕著であった。
分布の分析に基づくNMR緩和時間測定法によって定量評価され、さらに、NMR凍結間隙測定法及びX線回折法による結果と比較された。これらの分析によって、Na型モンモリロナイトと比較可能な、Ca型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布の状態を把握することができた。圧縮Ca型及びNa型モンモリロナイト中の間隙分布に影響を及ぼす主要な因子は圧縮密度であり、間隙水塩濃度の影響は相対的に小さい結果となった。CaとNaの層間陽イオンの影響は高密度条件では小さいが、低密度ではその影響は顕著であった。
舘 幸男; 四辻 健治*; 深津 勇太; 杉浦 佑樹; 大窪 貴洋*
no journal, ,
放射性廃棄物の地層処分の安全評価において、ベントナイト緩衝材や岩石中に含まれる粘土鉱物中の核種移行現象の理解が重要となる。粘土鉱物中の核種移行モデルを構築するうえで、中核となるのは層状構造をもつ粘土鉱物によって形成される間隙構造と粘土鉱物表面での静電的な相互作用である。本報告では、セメント系材料の共存によるベントナイトの状態変遷(Na型からCa型への変化)の影響を評価するため、圧縮ベントナイト中の間隙構造と静電的な相互作用の双方の効果を考慮した核種の拡散・収着モデルの開発成果を報告する。
Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q.*; Zhao, C.*; Zhang, T.*; 舘 幸男; 深津 勇太
no journal, ,
Fine-grained and clay-rich mudrocks play an important role in the long-term performance of a geological repository for storing high-level nuclear wastes and petroleum production in shale formations. However, low-permeability mudrocks whose pores are poorly interconnected are known to have anomalous diffusion properties that strongly impact long-term net diffusion. The complex pore structure involving predominantly nano-sized pore space is related to compaction and diagenesis from the maturation process of organic matter-rich mudrocks at deep depths, leading to a much smaller effective porosity which could be further partitioned by water- or oil-wet pore networks. Working with shallow clayey sediments of Wakkanai formation around Horonobe underground research center in Hokkaido of Japan and Opalinus clay of Mt. Terri Underground Research Laboratory in Switzerland, as well as various deep shales (Barnett, Eagle Ford and Wolfcamp from Texas, Bakken from North Dakota), using a wide range of sample sizes, this multi-approach and -scale work utilizes a complementary suite of approaches for pore structure characterization (e.g., helium pycnometry, mercury intrusion porosimetry, small angle/X-ray neutron scattering, field emission-scanning electron microscopy), gas diffusion and liquid (including water-, oil-, and bi-wetting) imbibition involving custom-designed tracer recipe followed with micro-scale mapping with laser ablation-ICP-MS. The experimental results show that deep mudrocks has a much smaller effective porosity than the total porosity (as a result of poor pore connectivity) and associated diffusion coefficient, and the effective porosity and diffusion coefficients are also dependent upon the sample sizes used in the measurement.
Martin, A.*; 深津 勇太; 舘 幸男; 石田 圭輔*; Muuri, E.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Havlov , V.*; Vokal, A.*
, V.*; Vokal, A.*
no journal, ,
Diffusion and sorption parameters used in performance assessment calculations for assessing the long term safety of future radioactive waste repositories are typically derived from rock samples that are de-stressed once removed from the host rock. This can lead to an over-estimation of matrix diffusion and sorption from lab based experiments primarily due to sample preparation in comparison with actual conditions in crystalline rocks. Despite this, there have been very few long-term field-scale experiments to realistically evaluate matrix diffusion and sorption of radionuclides in fractured rock with minimal disturbance to in-situ conditions. These issues have formed the basis for the design of the Long Term Diffusion (LTD) project at the Grimsel Test Site (GTS) in Switzerland. The results and comparison to diffusion and sorption models, with a particular focus on scaling from lab to in situ conditions and process understanding will be overviewed in this paper.
深津 勇太; 石寺 孝充; 舘 幸男
no journal, ,
放射性廃棄物の地層処分において、核種漏えいを抑制するためのバリア材として、Na型モンモリロナイトを主成分とした圧縮ベントナイトの使用が検討されている。これまでに、圧縮ベントナイトのバリア性能を評価するため、核種の移行度を示す実効拡散係数(De)及び収着分配係数(Kd)が取得され、圧縮ベントナイト中の拡散及び収着挙動の理解が進められてきた。しかしながら、対象とされてきた核種はCs やI
やI などの一価の陽イオン及び陰イオンがほとんどであり、多価イオン核種の拡散及び収着挙動は十分に明らかになっていない。多価イオンは水溶液中で水酸化物イオンと錯体を形成することに加えて、地下水中に含まれる炭酸イオン(CO
などの一価の陽イオン及び陰イオンがほとんどであり、多価イオン核種の拡散及び収着挙動は十分に明らかになっていない。多価イオンは水溶液中で水酸化物イオンと錯体を形成することに加えて、地下水中に含まれる炭酸イオン(CO
 )と錯体を形成する。したがって、多価イオンの拡散及び収着挙動の理解には、錯体形成による複数化学種共存下での拡散と収着を考慮するとともに、平衡反応による各化学種の存在割合の変化と拡散及び収着挙動の関係を評価することが重要である。Np(V)は、溶液中でNpO
)と錯体を形成する。したがって、多価イオンの拡散及び収着挙動の理解には、錯体形成による複数化学種共存下での拡散と収着を考慮するとともに、平衡反応による各化学種の存在割合の変化と拡散及び収着挙動の関係を評価することが重要である。Np(V)は、溶液中でNpO
 として存在し、CO
として存在し、CO
 濃度の増加に伴いNpO
濃度の増加に伴いNpO CO
CO
 の割合が高くなる。したがって、CO
の割合が高くなる。したがって、CO
 濃度を制御した拡散試験により、NpO
濃度を制御した拡散試験により、NpO
 とNpO
とNpO CO
CO
 の存在割合の変化による拡散及び収着挙動への影響を評価することが可能となる。本研究では、CO
の存在割合の変化による拡散及び収着挙動への影響を評価することが可能となる。本研究では、CO
 を含む溶液で飽和した圧縮ベントナイトを対象に、Np(V)の透過拡散試験を実施した。また、平衡反応によるNpO
を含む溶液で飽和した圧縮ベントナイトを対象に、Np(V)の透過拡散試験を実施した。また、平衡反応によるNpO
 とNpO
とNpO CO
CO
 の存在割合の変化と拡散及び収着を考慮したシミュレーションを行い、実験データとの回帰分析から、圧縮ベントナイト中のNpO
の存在割合の変化と拡散及び収着を考慮したシミュレーションを行い、実験データとの回帰分析から、圧縮ベントナイト中のNpO
 とNpO
とNpO CO
CO
 のDe及びKdを評価した。
のDe及びKdを評価した。
深津 勇太; 伊藤 剛志*; 舘 幸男; 石田 圭輔*; Martin, A.*
no journal, ,
In the safety assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, it is an important task to confirm applicability of the models and parameters to quantify the radionuclide migration based on laboratory diffusion and sorption tests to the actual underground environment. In this study, the second Long-Term Diffusion (LTD-II) test at the GTS using tritiated water (HTO), Cl-36, Na-22, Cs-134 and Ba-133 as tracers were analysed focusing borehole disturbed zone (BDZ) effect near borehole and diffusion anisotropy by the foliation effect. We measured the detailed depth profile of the cations and wide-range distributions of HTO and Cl-36 around an injection hole by additional laboratory analysis, and in situ LTD-II test results were predicted by the scaling approach from laboratory to in situ condition.