Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*; 伊東 達矢; 山下 享介*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)An ultrafine-grained 304 austenitic stainless steel exhibited pronounced serrated Luders deformation at 20 K, with stress and temperature oscillations reaching 200 MPa and 20 K.  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation revealed discontinuous Luders band propagation and burst martensite formation. During deformation, austenite phase stress remained lower than at upper yielding, indicating elastic behavior. Notably, martensite phase stress stayed lower than austenite until fracture, likely due to stress relaxation from burst martensitic transformation at 20 K. The low martensite stress delayed brittle fracture until austenite plastically yielded during uniform deformation.
Go, J.*; Park, M.-H.*; Gao, S.*; 松宮 久*; Gong, W.; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1014, p.178749_1 - 178749_10, 2025/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:95.66(Chemistry, Physical)In Mg alloys, basal dislocation slip is the preferential slip system that is activated at room temperature, while non-basal slips are typically difficult to activate owing to their high critical resolved shear stress. Until now, minimal focus has been directed towards the influence of loading direction on slip behavior in pre-twinned AZ31 alloys. This study employed transmission electron microscopy to demonstrate that non-basal slips, specifically prismatic and pyramidal I slips, are activated under deformation conditions where de-twinning is difficult in a pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy. When the tensile loading direction is parallel to the precompression direction, de-twinning and basal slip are the primary deformation modes. Conversely, when the tensile loading direction is perpendicular to the precompression direction, where de-twinning is challenging to activate, both basal and non-basal slips, such as prismatic and pyramidal I slips, emerge as the primary deformation modes. These results indicate that the pre-twinned AZ31 Mg alloy cannot deform solely through basal slips, and the activation of either de-twinning or non-basal slips is necessary to satisfy the von Mises criterion. Our findings in this study demonstrate the impact of non-basal slip activity on macroscopic yield stress and overall deformation, hence enhancing the understanding of magnesium alloy deformation mechanisms.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; 伊東 達矢; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:96.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using a hybrid method of in situ neutron diffraction and digital image correlation, we found that ultrafine-grained 304 stainless steel exhibits Luders deformation after yielding, in which the deformation behavior changes from a cooperation mechanism involving dislocation slip and martensitic transformation to one primarily governed by martensitic transformation, as the temperature decreases from 295 K to 77 K. Such martensitic transformation-governed Luders deformation delays the activation of plastic deformation in both the austenite parent and martensite product, resulting in delayed strain hardening. This preserves the strain-hardening capability for the later stage of deformation, thereby maintaining a remarkable elongation of 29% while achieving a high tensile strength of 1.87 GPa at 77 K.
 neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinement
neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinementMao, W.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 諸岡 聡; Gao, S.*; 川崎 卓郎; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 176, p.69 - 82, 2024/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:59.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-24Ni-0.3C(wt.%)準安定オーステナイト鋼の降伏応力は、平均結晶粒径が35 m(粗粒[CG])から0.5
m(粗粒[CG])から0.5 m(超微細粒[UFG])に減少すると3.5倍(158
m(超微細粒[UFG])に減少すると3.5倍(158 551MPa)に増加したが、引張伸びは大きく維持された(0.87
551MPa)に増加したが、引張伸びは大きく維持された(0.87 0.82)。結晶粒径が力学特性と変形機構に及ぼす影響を定量的に明らかにするため、室温での引張変形中にCGとUFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C鋼のその場中性子回折測定を行った。CGとUFG試料における塑性変形の初期段階は転位すべりによって支配され、変形後期には変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)も生じた。結晶粒の微細化により、DIMTの開始応力が大きく増加し、ひずみに関するDIMTの速度が抑制されることがわかった。結果として、(i)結晶粒微細化によりオー ステナイトが安定化し、DIMTに対して最も安定な結晶粒である
0.82)。結晶粒径が力学特性と変形機構に及ぼす影響を定量的に明らかにするため、室温での引張変形中にCGとUFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C鋼のその場中性子回折測定を行った。CGとUFG試料における塑性変形の初期段階は転位すべりによって支配され、変形後期には変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)も生じた。結晶粒の微細化により、DIMTの開始応力が大きく増加し、ひずみに関するDIMTの速度が抑制されることがわかった。結果として、(i)結晶粒微細化によりオー ステナイトが安定化し、DIMTに対して最も安定な結晶粒である 111
111 //LD(LD:負荷方向)オーステナイト粒でのDIMTの開始が大幅に遅れた。その結果、UFG試験片の
//LD(LD:負荷方向)オーステナイト粒でのDIMTの開始が大幅に遅れた。その結果、UFG試験片の 111
111 //LDオーステナイト粒のほとんどはマルテンサイトに変態しなかった。(ii)結晶粒の微細化は、マルテンサイト変態の自己促進効果も抑制した。それにもかかわらず、UFG試験片の変態速度が低いDIMTは、CG試験片のより応力を増加させるのに効率がよく、変形中に均一な変形を維持するのに適していた。以上の現象は、UFG準安定オーステナイト鋼の優れた強度と延性の両立に相互に寄与している。
//LDオーステナイト粒のほとんどはマルテンサイトに変態しなかった。(ii)結晶粒の微細化は、マルテンサイト変態の自己促進効果も抑制した。それにもかかわらず、UFG試験片の変態速度が低いDIMTは、CG試験片のより応力を増加させるのに効率がよく、変形中に均一な変形を維持するのに適していた。以上の現象は、UFG準安定オーステナイト鋼の優れた強度と延性の両立に相互に寄与している。
 ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining
ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysis
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysisMao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 235, p.115642_1 - 115642_6, 2023/10
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:86.78(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)本研究では、巨大なリューダースバンド変形を示す超微細粒(UFG)ステンレス鋼の引張その場中性子回折とデジタル画像相関測定を行い、バンド伝播中の歪硬化に対するオーステナイト母相と変形誘起マルテンサイトの個々の寄与を評価した。定量的解析の結果、UFG構造によって流動応力が大幅に増加した場合、オーステナイト母相のひずみ硬化は均一な変形を維持するには不十分であることがわかった。リューダースバンドの伝播に必要なひずみ硬化は、マルテンサイトの形成とその内部の高い内部応力によってもたらされた。
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Bai, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 256, p.119139_1 - 119139_16, 2023/09
被引用回数:36 パーセンタイル:98.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)変形誘起塑性(TRIP)鋼は、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態(DIMT)に伴う加工硬化率の向上により、強度と延性の優れた組み合わせを示す。TRIP鋼や合金の加工硬化挙動におけるDIMTの役割を定量的に評価することは、強度と延性の両立を可能にする先進材料を設計するための指針を与えるが、変形中に相組成が変化し続け、応力と塑性ひずみの両方が構成相間で動的に分配されるため、その評価は困難である。本研究では、Fe-24Ni-0.3C(wt.%)TRIPオーステナイト鋼の引張変形とその場中性子回折測定を行った。中性子回折測定による応力分割と相分割に基づく解析手法を提案し、試験片の引張流動応力と加工硬化率を、オーステナイト母相,変形誘起マルテンサイト、DIMT変態速度に関連する因子に分解し、試料の加工硬化挙動における各因子の役割を考察した。さらに、回折プロファイル解析により測定した転位密度を用いてオーステナイトとマルテンサイト間の塑性ひずみ分配を間接的に推定し、材料中のオーステナイトとマルテンサイト間の応力・ひずみ分配の全体像を構築した。その結果、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態速度とマルテンサイトが負担する相応力の両方が、材料の全体的な引張特性に重要な役割を果たしていることが示唆された。提案した分解解析法は、TRIP現象を示す多相合金の機械的挙動を調べるために広く適用できる可能性がある。
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetization of a quantum magnet can be pinned at a fraction of its saturated value by collective effects. One example of such a plateau phase is found in spin-1/2 triangular-lattice antiferromagnets. They feature strong geometrical frustration and the plateau phase therein is often interpreted as arising from an order-by-disorder mechanism driven by quantum fluctuations. Here we observe a one-third magnetization plateau under an applied magnetic field in the spin-1 antiferromagnet Na Ni
Ni BiO
BiO with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
Chong, Y.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; 都留 智仁; Zhang, R.*; 井上 耕治*; Gao, W.*; Godfrey, A.*; 光原 昌寿*; Morris, J. W. Jr.*; Minor, A. M.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.404_1 - 404_11, 2023/02
被引用回数:49 パーセンタイル:96.50(Multidisciplinary Sciences)チタンは格子間酸素によって脆化する。特に極低温では顕著な脆化挙動を示すため、チタンやその合金の製造において酸素含有量を厳しく管理する必要がある。この問題を解決するために、我々は結晶粒の微細化という構造戦略を提案した。77Kで非常に脆い粗粒の組織と比較して、Ti-0.3wt.%Oの超微細粒(UFG)組織(粒径 2.0
2.0 m)は、UFG組織特有の超高降伏強度を維持したまま均一延びを1桁上昇させることに成功した。UFG Ti-0.3wt.%Oにおけるこの特異な強度-延性相乗効果は、粒界凝集エネルギー向上に寄与する希薄な酸素の粒界偏析と優れたひずみ硬化能に寄与する
m)は、UFG組織特有の超高降伏強度を維持したまま均一延びを1桁上昇させることに成功した。UFG Ti-0.3wt.%Oにおけるこの特異な強度-延性相乗効果は、粒界凝集エネルギー向上に寄与する希薄な酸素の粒界偏析と優れたひずみ硬化能に寄与する 転位の活性化の複合効果によって達成された。この方法は、低温での高強度Ti-O合金の応用の可能性を高めるだけでなく、格子間固溶硬化による延性の低下を生じる他の合金系にも適用できる可能性がある。
転位の活性化の複合効果によって達成された。この方法は、低温での高強度Ti-O合金の応用の可能性を高めるだけでなく、格子間固溶硬化による延性の低下を生じる他の合金系にも適用できる可能性がある。
Chen, J.*; 山本 慧; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; Yu, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:62.75(Physics, Applied)Coherent coupling in magnon based hybrid system has many potential applications in quantum information processing. Magnons can propagate in magnetically ordered materials without any motion of electrons, offering a unique method to build low-power-consumption devices and information channels free of heat dissipation. In this article, we demonstrate the coherent propagation of hybridized modes between spin waves and Love surface acoustic waves in a multiferroic BiFeO and ferromagnetic La
and ferromagnetic La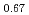 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO based heterostructure. The magneto-elastic coupling enables a giant enhancement of strength of the hybridized mode by a factor of 26 compared to that of the pure spin waves. A short wavelength down to 250 nm is demonstrated for the hybridized mode, which is desirable for nanoscale acousto-magnonic applications. Our combined experimental and theoretical analyses represent an important step towards the coherent control in hybrid magnonics, which may inspire the study of magnon-phonon hybrid systems for coherent information processing and manipulation.
based heterostructure. The magneto-elastic coupling enables a giant enhancement of strength of the hybridized mode by a factor of 26 compared to that of the pure spin waves. A short wavelength down to 250 nm is demonstrated for the hybridized mode, which is desirable for nanoscale acousto-magnonic applications. Our combined experimental and theoretical analyses represent an important step towards the coherent control in hybrid magnonics, which may inspire the study of magnon-phonon hybrid systems for coherent information processing and manipulation.
 neutron diffraction and electron microscopy study
neutron diffraction and electron microscopy studyZheng, R.*; Gong, W.; Du, J.-P.*; Gao, S.*; Liu, M.*; Li, G.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Ma, C.*; 尾方 成信*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 238, p.118243_1 - 118243_15, 2022/10
被引用回数:44 パーセンタイル:97.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Grain refinement can lead to the strengthening of metallic materials according to the Hall-Petch relationship. However, our recent results suggested that grain boundary sliding is the dominant deformation mode in bulk ultrafine grained (UFG) pure Mg at room temperature, leading to softening. Here, for the first time, we report that the Hall-Petch strengthening can be regained in bulk UFG pure Mg at cryogenic temperature. At 77K, the UFG pure Mg with a mean grain size of 0.6  m exhibited ultrahigh tensile yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of 309 MPa and 380 MPa, respectively. Combined
m exhibited ultrahigh tensile yield strength and ultimate tensile strength of 309 MPa and 380 MPa, respectively. Combined  neutron diffraction and electron microscopy investigation indicated that residual dislocation structures and deformation twins hardly formed in the UFG specimen during tensile test at 298K. In contrast, fast accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable reorientation were evident at 77K, suggesting that the grain-boundary-mediated process was suppressed and the plastic deformation was dominated by dislocation slip and deformation twinning. In addition, all the pure Mg specimens exhibited pronounced strain hardening at 77 K, which was mainly attributed to the suppressed grain boundary sliding and dynamic recovery. The mean dislocation density and relative fractions of dislocations with various Burgers vectors of the UFG specimen deformed at 77K were determined quantitatively from neutron diffraction data.
neutron diffraction and electron microscopy investigation indicated that residual dislocation structures and deformation twins hardly formed in the UFG specimen during tensile test at 298K. In contrast, fast accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable reorientation were evident at 77K, suggesting that the grain-boundary-mediated process was suppressed and the plastic deformation was dominated by dislocation slip and deformation twinning. In addition, all the pure Mg specimens exhibited pronounced strain hardening at 77 K, which was mainly attributed to the suppressed grain boundary sliding and dynamic recovery. The mean dislocation density and relative fractions of dislocations with various Burgers vectors of the UFG specimen deformed at 77K were determined quantitatively from neutron diffraction data.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez-Espinoza, V.*; Groudev, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; Bocanegra, R.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Berda , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2022) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/05
The current HORIZON-2020 project on "Management and Uncertainties of Severe Accidents (MUSA)" aims at applying Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) in the modeling of Severe Accidents (SA), particularly in predicting the radiological source term of mitigated and unmitigated accident scenarios. Within its application part, the project is devoted to the uncertainty quantification of different severe accident codes when predicting the radiological source term of selected severe accident sequences of different nuclear power plant designs, e.g. PWR, VVER, and BWR. Key steps for this investigation are, (a) the selection of severe accident sequences for each reactor design, (b) the development of a reference input model for the specific design and SA-code, (c) the selection of a list of uncertain model parameters to be investigated, (d) the choice of an UQ-tool e.g. DAKOTA, SUSA, URANIE, etc., (e) the definition of the figures of merit for the UA-analysis, (f) the performance of the simulations with the SA-codes, and, (g) the statistical evaluation of the results using the capabilities, i.e. methods and tools offered by the UQ-tools. This paper describes the project status of the UQ of different SA codes for the selected SA sequences, and the technical challenges and lessons learnt from the preparatory and exploratory investigations performed.
Liu, M.*; Gong, W.; Zheng, R.*; Li, J.*; Zhang, Z.*; Gao, S.*; Ma, C.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 226, p.117629_1 - 117629_13, 2022/03
被引用回数:85 パーセンタイル:99.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One hopeful path to realize good comprehensive mechanical properties in metallic materials is to accomplish homogeneous nanocrystalline (NC) or ultrafine grained (UFG) structure with low dislocation density. In this work, high pressure torsion deformation followed by appropriate annealing was performed on 316 stainless steel (SS). For the first time, we successfully obtained NC/UFG 316 SS having uniform microstructures with various average grain sizes ranging from 46 nm to 2.54  m and low dislocation densities. Among the series, an un-precedentedly high yield strength (2.34 GPa) was achieved at the smallest grain size of 46 nm, in which dislocation scarcity induced hardening accounting for 57% of the strength. On the other hand, exceptional strength-ductility synergy with high yield strength (900 MPa) and large uniform elongation (27%) was obtained in the fully recrystallized specimen having the grain size of 0.38
m and low dislocation densities. Among the series, an un-precedentedly high yield strength (2.34 GPa) was achieved at the smallest grain size of 46 nm, in which dislocation scarcity induced hardening accounting for 57% of the strength. On the other hand, exceptional strength-ductility synergy with high yield strength (900 MPa) and large uniform elongation (27%) was obtained in the fully recrystallized specimen having the grain size of 0.38  m. The high yield stress and scarcity of dislocation sources in recrystallized UFGs activated stacking faults and deformation twins nucleating from grain boundaries during straining, and their interaction with dislocations allowed for sustainable strain hardening, which also agreed with the plaston concept recently proposed. The multiple deformation modes activated, together with the effective strengthening mechanisms, were responsible for the outstanding comprehensive mechanical performance of the material.
m. The high yield stress and scarcity of dislocation sources in recrystallized UFGs activated stacking faults and deformation twins nucleating from grain boundaries during straining, and their interaction with dislocations allowed for sustainable strain hardening, which also agreed with the plaston concept recently proposed. The multiple deformation modes activated, together with the effective strengthening mechanisms, were responsible for the outstanding comprehensive mechanical performance of the material.
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Bai, Y.*; Park, M.-H.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 辻 伸泰*
Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 17, p.2690 - 2700, 2022/03
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:80.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)超微細結晶粒(UFG)組織を有する準安定オーステナイト鋼は、冷間圧延中の変形誘起マルテンサイト変態と焼鈍時のオーステナイトへの逆変態を利用することにより、従来の冷間圧延および焼鈍プロセスで製造することができる。しかし、変形誘起マルテンサイト変態に対するオーステナイトの機械的安定性が高い場合には、冷間圧延中に十分な量のマルテンサイトが生成しないため、このようなプロセスは適用できない。本研究では、高い機械的安定性を有するFe-24Ni-0.3C準安定オーステナイト鋼に対して、冷間圧延と焼鈍の2段階プロセスを適用した。冷間圧延に先立ち、繰り返しサブゼロ処理と逆焼鈍処理を施した。このような処理により、オーステナイトの機械的安定性が劇的に低下し、その後の冷間圧延工程で変形誘起マルテンサイトの生成が大幅に促進された。その結果、結晶粒の微細化が著しく促進され、平均オーステナイト粒径0.5mmの完全再結晶試験片の作製に成功し、高強度と高延性を両立させた。
 /La
/La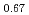 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO heterostructures
heterostructuresZhang, J.*; Chen, M.*; Chen, J.*; 山本 慧; Wang, H.*; Hamdi, M.*; Sun, Y.*; Wagner, K.*; He, W.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.7258_1 - 7258_8, 2021/12
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:77.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnons can transfer information in metals and insulators without Joule heating, and therefore are promising for low-power computation. The on-chip magnonics however suffers from high losses due to limited magnon decay length. In metallic thin films, it is typically on the tens of micrometre length scale. Here, we demonstrate an ultra-long magnon decay length of up to one millimetre in multiferroic/ferromagnetic BiFeO (BFO)/La
(BFO)/La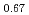 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (LSMO) heterostructures at room temperature. This decay length is attributed to a magnon-phonon hybridization and is more than two orders of magnitude longer than that of bare metallic LSMO. The long-distance modes have high group velocities of 2.5 km
(LSMO) heterostructures at room temperature. This decay length is attributed to a magnon-phonon hybridization and is more than two orders of magnitude longer than that of bare metallic LSMO. The long-distance modes have high group velocities of 2.5 km as detected by time-resolved Brillouin light scattering. Numerical simulations suggest that magnetoelastic coupling via the BFO/LSMO interface hybridizes phonons in BFO with magnons in LSMO. Our results provide a solution to the long-standing issue on magnon decay lengths in metallic magnets and advance the bourgeoning field of hybrid magnonics.
as detected by time-resolved Brillouin light scattering. Numerical simulations suggest that magnetoelastic coupling via the BFO/LSMO interface hybridizes phonons in BFO with magnons in LSMO. Our results provide a solution to the long-standing issue on magnon decay lengths in metallic magnets and advance the bourgeoning field of hybrid magnonics.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; 西尾 勝久; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; 牧井 宏之; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; 廣瀬 健太郎; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:33.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The long-lived  Fe (with a half-life of 2.62 Myr) is a crucial diagnostic of active nucleosynthesis in the Milky Way galaxy and in supernovae near the solar system. The neutron-capture reaction
Fe (with a half-life of 2.62 Myr) is a crucial diagnostic of active nucleosynthesis in the Milky Way galaxy and in supernovae near the solar system. The neutron-capture reaction  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe on
Fe on  Fe (half-life=44.5 days) is the key reaction for the production of
Fe (half-life=44.5 days) is the key reaction for the production of  Fe in massive stars. This reaction cross section has been previously constrained by the Coulomb dissociation experiment, which offered partial constraint on the E1
Fe in massive stars. This reaction cross section has been previously constrained by the Coulomb dissociation experiment, which offered partial constraint on the E1  -ray strength function but a negligible constraint on the M1 and E2 components. In this work, for the first time, we use the surrogate ratio method to experimentally determine the
-ray strength function but a negligible constraint on the M1 and E2 components. In this work, for the first time, we use the surrogate ratio method to experimentally determine the  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross sections in which all the components are included. We derived a Maxwellian-averaged cross section of 27.5
Fe cross sections in which all the components are included. We derived a Maxwellian-averaged cross section of 27.5 3.5 mb at
3.5 mb at 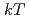 = 30 keV and 13.4
= 30 keV and 13.4 1.7 mb at
1.7 mb at 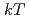 = 90 keV, roughly 10%-20% higher than previous estimates. We analyzed the impact of our new reaction rates in nucleosynthesis models of massive stars and found that uncertainties in the production of
= 90 keV, roughly 10%-20% higher than previous estimates. We analyzed the impact of our new reaction rates in nucleosynthesis models of massive stars and found that uncertainties in the production of  Fe from the
Fe from the  Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe rate are at most 25
Fe rate are at most 25 . We conclude that stellar physics uncertainties now play a major role in the accurate evaluation of the stellar production of
. We conclude that stellar physics uncertainties now play a major role in the accurate evaluation of the stellar production of  Fe.
Fe.
Harjo, S.; 窪田 哲*; Gong, W.*; 川崎 卓郎; Gao, S.*
Acta Materialia, 196, p.584 - 594, 2020/09
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:58.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To understand work hardening behavior during low-cycle loading, ductile cast iron containing spheroidal graphite, pearlite, and ferrite matrix was investigated in an in situ neutron diffraction study of up to four cycles of tensile-compressive loading with applied strains of  0.01. The amplitudes of applied stress, Bauschinger stress, and Bauschinger strain were found to increase with increasing cycle number, indicating work hardening as cyclic loading progressed. Absolute values of ferrite lattice strain at maximum and minimum applied strains increased with increasing cycle number, indicating an increase in ferrite strength. Consequently, the stress contribution to the strength from ferrite increased as cyclic loading progressed. The increase in ferrite strength, caused by dislocation accumulation in ferrite during cyclic loading, played an important role in the work hardening of the ductile cast iron.
0.01. The amplitudes of applied stress, Bauschinger stress, and Bauschinger strain were found to increase with increasing cycle number, indicating work hardening as cyclic loading progressed. Absolute values of ferrite lattice strain at maximum and minimum applied strains increased with increasing cycle number, indicating an increase in ferrite strength. Consequently, the stress contribution to the strength from ferrite increased as cyclic loading progressed. The increase in ferrite strength, caused by dislocation accumulation in ferrite during cyclic loading, played an important role in the work hardening of the ductile cast iron.
 neutron diffraction study on the deformation of a TRIP-assisted multi-phase steel composed of ferrite, austenite and martensite
neutron diffraction study on the deformation of a TRIP-assisted multi-phase steel composed of ferrite, austenite and martensiteLavakumar, A.*; Park, M. H.*; Gao, S.*; 柴田 曉伸*; 興津 貴隆*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 580, p.012036_1 - 012036_6, 2019/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:81.43(Engineering, Mechanical)Multi-phase steels showing transformation induced plasticity (TRIP), can exhibit an excellent combination of high strength and good ductility by the aid of martensitic transformation during deformation. Even though TRIP-assisted multi-phase steels have been widely used in industry, the role of each phase in the enhancement of mechanical properties is still unclear given their complicated microstructures. In order to understand better the nature of the TRIP effect, the mechanical interaction between different phases at the micro-scale should be clarified. In the present study, the mechanical behavior of a transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) assisted multi-phase steel, has been characterized by  neutron diffraction during tensile testing. The result of strain partitioning between the different phases obtained from the
neutron diffraction during tensile testing. The result of strain partitioning between the different phases obtained from the  neutron analysis revealed that the martensite phase took much more elastic strain than the ferrite and retained austenite phases, which suggests that the work hardening behavior in the present steel is affected by the higher load borne by deformation-induced martensite.
neutron analysis revealed that the martensite phase took much more elastic strain than the ferrite and retained austenite phases, which suggests that the work hardening behavior in the present steel is affected by the higher load borne by deformation-induced martensite.
元川 竜平; 小林 徹; 遠藤 仁; Mu, J.*; Williams, C. D.*; Masters, A. J.*; Antonio, M. R.*; Heller, W. T.*; 長尾 道弘*
ACS Central Science, 5(1), p.85 - 96, 2019/01
被引用回数:56 パーセンタイル:85.91(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We present a hierarchical aggregate model of an organic phase containing a coordination species that acts as a fundamental building unit of higher-order structures formed in the organic phase. We aimed to elucidate the fundamental aspects of the microscopic structure and phase separation occurring in ionic separation and recovery systems during solvent extraction. The coordination species aggregate through a hydrogen-bonding network formed by interaction between the hydrophilic part of the coordination species with extracted water and acid molecules. This reduces the hydrophilic surface area, resulting in subsequent formation of small primal clusters of 2 to 3 nm in diameter. The primal clusters further aggregate due to van der Waals interaction to form large aggregates of  10 nm in diameter. The size of the primal cluster does not depend on the concentration of the coordination species, whereas the size of the large aggregate increases as the aggregation number of the primal clusters increases. We conclude that hybrid interaction is a key driving force in the formation and growth of the hierarchical aggregate and the induction of phase separation of the organic phase.
10 nm in diameter. The size of the primal cluster does not depend on the concentration of the coordination species, whereas the size of the large aggregate increases as the aggregation number of the primal clusters increases. We conclude that hybrid interaction is a key driving force in the formation and growth of the hierarchical aggregate and the induction of phase separation of the organic phase.
元川 竜平; 遠藤 仁*; 長尾 道弘*; Heller, W. T.*
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 34(5), p.399 - 406, 2016/07
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:17.92(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We performed neutron polarization analysis (NPA) of extracted organic phases containing complexes, comprised of Zr(NO )
) and tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP), which enabled decomposition of the intensity distribution of small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) into the coherent and incoherent scattering components. The coherent scattering intensity, containing structural information, and the incoherent scattering compete over a wide range of magnitude of scattering vector,
and tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP), which enabled decomposition of the intensity distribution of small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) into the coherent and incoherent scattering components. The coherent scattering intensity, containing structural information, and the incoherent scattering compete over a wide range of magnitude of scattering vector,  , specifically when
, specifically when  is larger than
is larger than 
 1/
1/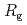 , where
, where 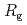 is the radius of gyration of scatterer. Therefore, it is important to determine the incoherent scattering intensity exactly to perform an accurate structural analysis from SANS data when
is the radius of gyration of scatterer. Therefore, it is important to determine the incoherent scattering intensity exactly to perform an accurate structural analysis from SANS data when 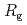 is small, such as the aforementioned extracted coordination species. Although NPA is the best method for evaluating the incoherent scattering component for accurately determining the coherent scattering in SANS, this method is not used frequently in SANS data analysis because it is technically challenging. In this study, we successfully demonstrated that experimental determination of the incoherent scattering using NPA is suitable for sample systems containing a small scatterer with a weak coherent scattering intensity, such as extracted complexes in biphasic solvent extraction system.
is small, such as the aforementioned extracted coordination species. Although NPA is the best method for evaluating the incoherent scattering component for accurately determining the coherent scattering in SANS, this method is not used frequently in SANS data analysis because it is technically challenging. In this study, we successfully demonstrated that experimental determination of the incoherent scattering using NPA is suitable for sample systems containing a small scatterer with a weak coherent scattering intensity, such as extracted complexes in biphasic solvent extraction system.
Schaffer, M. J.*; Snipes, J. A.*; Gohil, P.*; de Vries, P.*; Evans, T. E.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Gao, X.*; Garofalo, A. M.*; Gates, D. A.*; Greenfield, C. M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103028_1 - 103028_11, 2011/10
被引用回数:42 パーセンタイル:82.79(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)ITERのテストブランケットモジュールが作ると思われる誤差磁場の影響を調べる実験をDIII-Dにおいて実施した。プラズマ回転とモードロッキング,閉じ込め,LH遷移,ELM安定化,ELMとHモードペデスタル特性,高エネルギー粒子損失等を調べた。実験では、ITERの1つの赤道面ポートを模擬する3つ組のコイルを1セット使用した。その結果、ITERのTBMが作る誤差磁場のためにITERの運転が妨げられるような結果は得られなかった。一番大きな変化はプラズマ回転を減速させるものであり、非共鳴ブレーキング効果によってプラズマ全体の回転が50%程度減少した。密度や閉じ込めへの影響は、回転の影響の1/3程度である。これらの影響は、プラズマ圧力の高いプラズマや回転の低いプラズマで顕著である。それ以外の影響は軽微であった。