Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray spectral data of uranium-bearing waste drums
-ray spectral data of uranium-bearing waste drumsHata, Haruhi; Ishimori, Yuu
Radioisotopes, 66(4), p.149 - 158, 2017/04
For the estimation of radioactive inventory, the radioactive waste drums should be classified based on their radioactive composition. We compared the classification performances between random forests and support vector machine, both of which are machine learning methods. The tested uranium in waste drums included natural uranium from uranium ore, reprocessed uranium from nuclear fuel, and natural uranium with rich radium from the impurities in yellow cake. A total of 75 data in 1037  -ray spectral data of these drums were trained, and 962 data were applied in the classification models. It was found that the random forests were advantageous in the shift of the channels.
-ray spectral data of these drums were trained, and 962 data were applied in the classification models. It was found that the random forests were advantageous in the shift of the channels.
Ishimori, Yuu; Yokoyama, Kaoru*; Hayakawa, Tomoya; Hata, Haruhi; Sakoda, Akihiro; Naganuma, Masaki
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (55), p.36 - 44, 2017/03
This paper gives an outline of the current status of uranium measurements and their related techniques at the Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The JAWAS-N and the Q system have been adopted to evaluate uranium contents in the wastes. About 10 g or more of uranium in a 200
system have been adopted to evaluate uranium contents in the wastes. About 10 g or more of uranium in a 200  drum can be evaluated by these systems. The equivalent model developed to correct the evaluation results with Q
drum can be evaluated by these systems. The equivalent model developed to correct the evaluation results with Q system is not available to less than dozens of grams of uranium in a 200 L drum. The paper illustrates the advantage of use of the improved equivalent model which evaluates uranium content from full energy peak of 1001 keV and its Compton spectrum in order to correct the inhomogeneous distribution of uranium in measuring objects. The use of model achieved the limit of uranium quantitative determination under one tenth of those of previous evaluation methods. To determine
system is not available to less than dozens of grams of uranium in a 200 L drum. The paper illustrates the advantage of use of the improved equivalent model which evaluates uranium content from full energy peak of 1001 keV and its Compton spectrum in order to correct the inhomogeneous distribution of uranium in measuring objects. The use of model achieved the limit of uranium quantitative determination under one tenth of those of previous evaluation methods. To determine  U, it was demonstrated that the shielding factor,
U, it was demonstrated that the shielding factor, 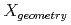 for evaluation of 1001 keV
for evaluation of 1001 keV  -ray is also possible to use for evaluation of 186 keV
-ray is also possible to use for evaluation of 186 keV  -ray. The measurement systems adopting the model have been introduced to other nuclear operators in Japan. In addition, it is also examined to use for clearance. As a related technique, feasibility studies on machine learning algorithms have been performed to classify the waste drums depending on their
-ray. The measurement systems adopting the model have been introduced to other nuclear operators in Japan. In addition, it is also examined to use for clearance. As a related technique, feasibility studies on machine learning algorithms have been performed to classify the waste drums depending on their  -ray spectrum.
-ray spectrum.
 -ray spectra
-ray spectraHata, Haruhi; Ishimori, Yuu
Radioisotopes, 66(1), p.1 - 10, 2017/01
The feasibility of Random Forests, one of machine learning methods was examined for the classification of radioactive waste drums. It was carried out using 954  -ray spectra of drums which were already classified to natural or reprocessed uranium. After 300 spectra were selected at random to reassemble training datasets, the percentages of correct classification by Random Forests were evaluated with another 654 spectra. When the counts of spectra were reprocessed as the difference of their logarithm, Random Forests accurately classified 654 drums.
-ray spectra of drums which were already classified to natural or reprocessed uranium. After 300 spectra were selected at random to reassemble training datasets, the percentages of correct classification by Random Forests were evaluated with another 654 spectra. When the counts of spectra were reprocessed as the difference of their logarithm, Random Forests accurately classified 654 drums.
Yokoyama, Kaoru; Hata, Haruhi; Naganuma, Masaki; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Ishimori, Yuu
Radioisotopes, 64(11), p.687 - 696, 2015/11
Authors developed the new analysis technique (hereinafter referred to as the equivalent model) which calculates the amount of uranium by correcting the influence of uneven distribution of the uranium. Two  rays different in the shelter effect are used in the equivalent model. The
rays different in the shelter effect are used in the equivalent model. The  rays (766 keV, 1001 keV) released from
rays (766 keV, 1001 keV) released from 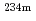 Pa are used for uranium quantitative determination. The quantity error is decided by the
Pa are used for uranium quantitative determination. The quantity error is decided by the  ray with the small calculation rate. The way to get the high calculation rate is considered to reduce the quantity error. Many
ray with the small calculation rate. The way to get the high calculation rate is considered to reduce the quantity error. Many  rays are scattered by the Compton effect in radioactive waste, and scattered photons occur. We applied the scattered photon with the big count rate to equivalent model. It was effective to apply the count rate of the scattered photon by the Compton effect to equivalent model.
rays are scattered by the Compton effect in radioactive waste, and scattered photons occur. We applied the scattered photon with the big count rate to equivalent model. It was effective to apply the count rate of the scattered photon by the Compton effect to equivalent model.
 -ray spectra
-ray spectraHata, Haruhi; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Ishimori, Yuu; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Yoshio; Sugitsue, Noritake
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 104, p.143 - 146, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.70(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We investigated the feasibility of using support vector machine (SVM), a computer learning method, to classify uranium waste drums as natural uranium or reprocessed uranium based on their origins. The method was trained using 12 training datasets were used and tested on 955 datasets of  -ray spectra obtained with NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors. The results showed that only 4 out of 955 test datasets were different from the original labels-one of them was mislabeled and the other three were misclassified by SVM. These findings suggest that SVM is an effective method to classify a large quantity of data within a short period of time. Consequently, SVM is a feasible method for supporting the scaling factor method and as a supplemental tool to check original labels.
-ray spectra obtained with NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors. The results showed that only 4 out of 955 test datasets were different from the original labels-one of them was mislabeled and the other three were misclassified by SVM. These findings suggest that SVM is an effective method to classify a large quantity of data within a short period of time. Consequently, SVM is a feasible method for supporting the scaling factor method and as a supplemental tool to check original labels.
Yokoyama, Kaoru; Hata, Haruhi; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Naganuma, Masaki; Sugitsue, Noritake
Radioisotopes, 63(12), p.559 - 566, 2014/12
The amount of  U in uranium-contaminated waste drums generated in the decommissioning of nuclear facilities is evaluated using
U in uranium-contaminated waste drums generated in the decommissioning of nuclear facilities is evaluated using  ray measurement. We used the
ray measurement. We used the  -ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q
-ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q ) Low Level Waste Assay Systems and measured the waste drum. This equipment assumes uniform distribution of the uranium radiation source. But, homogeneity is not checked with a real waste drum. Authors developed the new analysis technique which calculates the amount of uranium by correcting the influence of uneven distribution of the uranium radiation source. As a result of evaluating using the new analysis technique, the error which the radiation source uneven distribution in a drum gives to
) Low Level Waste Assay Systems and measured the waste drum. This equipment assumes uniform distribution of the uranium radiation source. But, homogeneity is not checked with a real waste drum. Authors developed the new analysis technique which calculates the amount of uranium by correcting the influence of uneven distribution of the uranium radiation source. As a result of evaluating using the new analysis technique, the error which the radiation source uneven distribution in a drum gives to  U quantitative value of this equipment has been evaluated.
U quantitative value of this equipment has been evaluated.
Saito, Tatsuo; Sakai, Akihiro; Sato, Kazuhiko; Yagi, Naoto; Hata, Haruhi; Fumoto, Hiromichi*; Kawagoshi, Hiroshi; Hasegawa, Makoto
JAEA-Review 2014-021, 30 Pages, 2014/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency surveyed the reference cases for the disposal of uranium bearing waste in low activity concentration as the contents of their own category 2 waste disposal facility for the Research and Development Activities. We reviewed the concepts mentioned in IAEA and ICRP documents, reference cases of uranium bearing waste disposal in selected countries (USA, Canada, UK, France and Sweden), and the disposal styles of long-lived radioactive waste were summarized, and the action items for application to the disposal system of our country was arranged. The disposal facilities in selected countries can be classified into 2 types with the length of performance assessment period for intruder scenario. They are long term assessment type and short term assessment type. It seems that the disposal system construction in category 2 waste disposal is the most realistic since there are many precedence examples of each country. Correspondence of 2 types of these disposal facilities is useful as a reference case.
Sato, Kazuhiko; Sakai, Akihiro; Hata, Haruhi; Fumoto, Hiromichi*; Kawagoshi, Hiroshi; Saito, Tatsuo; Hasegawa, Makoto
JAEA-Review 2014-006, 78 Pages, 2014/03
In this paper, we report the result of survey for basic principle of safety assessment for long-lived low-level (LL-LL) waste disposal and experience of the industrial waste disposal sites for uranium bearing waste in France, UK and Sweden, following the report of survey for U.S.A. and Canada published in December 2013.
 low level waste assay systems
low level waste assay systemsYokoyama, Kaoru; Hata, Haruhi; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake
Radioisotopes, 62(11), p.833 - 840, 2013/11
We have proposed a new theory on passive  assay for
assay for  U determination of uranium-contaminated waste drums. According to this theory, regardless of the inhomogeneity of waste matrix density or uranium source distribution, we can accurately determine the amount of
U determination of uranium-contaminated waste drums. According to this theory, regardless of the inhomogeneity of waste matrix density or uranium source distribution, we can accurately determine the amount of  U contained in drums nondestructively using count rates of rays of two energies (1001 keV and 766 keV) emitted from
U contained in drums nondestructively using count rates of rays of two energies (1001 keV and 766 keV) emitted from  U progeny nuclide
U progeny nuclide 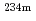 Pa. This technique is aimed final at introducing into the existing
Pa. This technique is aimed final at introducing into the existing  ray measuring device. In this paper, we have verified the theory using the existing
ray measuring device. In this paper, we have verified the theory using the existing  ray measuring device by tests under various simulated waste drums conditions. We used the
ray measuring device by tests under various simulated waste drums conditions. We used the  -ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q
-ray measurement system made from CANBERRA: Qualitative and Quantitative (Q ) Low Level Waste Assay Systems. The application validity of this evaluation technique was shown.
) Low Level Waste Assay Systems. The application validity of this evaluation technique was shown.
 gas
gasHata, Haruhi; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Sugitsue, Noritake
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2012/07
The uranium enrichment facilities, located at Ningyo-toge in Japan, are contaminated by uranium fluorides. There is the risk of exposing the HF gas when the equipments will be dismantled. Therefore, we performed the systematic chemical decontamination by using IF gas. This paper reports the actual results of the decontamination by using IF
gas. This paper reports the actual results of the decontamination by using IF gas. The result shows that the decontamination factor is approximately 100 or more. In addition, we performed the simulation of the reactions with IF
gas. The result shows that the decontamination factor is approximately 100 or more. In addition, we performed the simulation of the reactions with IF gas and uranium fluorides.
gas and uranium fluorides.
Hyakutake, Toru*; Muto, Akinori*; Sasakura, Mariko*; Minowa, Hirotsugu*; Suzuki, Kazuhiko*; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Takahashi, Nobuo; Hata, Haruhi; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Research 2011-035, 53 Pages, 2012/01
System decontamination has been generally carried out with the aim of reducing the amount of radioactive waste generated and minimizing exposure to radiation released from nuclear fuel facilities. At the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center, metal surfaces that are contaminated by uranium are dry decontaminated by using iodine heptafluoride (IF ) as a system decontaminator. Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination techniques is required. In the present study, the efficiency of a dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of uranium hexafluoride.
) as a system decontaminator. Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination techniques is required. In the present study, the efficiency of a dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of uranium hexafluoride.
Hata, Haruhi; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Ohashi, Yusuke; Koga, Osamu; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Research 2011-022, 35 Pages, 2011/09
For disposal of Very low-level radioactive Waste (VLLW) from nuclear related facilities, one of important factors for safety assessment is the characteristics of elution. As for VLLW from the nuclear power plant, concrete pit and trench disposals have been performed and the evaluation methods for the characteristics have been established. On the other hand, as for the uranium waste, the concept on how to test the elution characteristics is not shown yet. Based on these circumstances, preliminary tests have been conducted to study elution characteristics of uranium waste. The results show that the important factors for the uranium elution are how uranium exists in waste. In addition, the elution characteristics also depend on the precipitation amount on the disposal site. Therefore, to assess the elution rate from uranium waste, these factors must be considered.
 gas
gasHata, Haruhi; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Sugitsue, Noritake
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2011) (CD-ROM), p.105 - 110, 2011/09
IF treatment technique belongs to the system decontamination technology. It has the high performance decontamination technique for the plant that deposits the uranium intermediate fluoride, for example, UF
treatment technique belongs to the system decontamination technology. It has the high performance decontamination technique for the plant that deposits the uranium intermediate fluoride, for example, UF , UF
, UF , U
, U F
F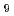 , and U
, and U F
F , which exist in the uranium enrichment plant by the Gas Centrifuge. The characteristics of IF
, which exist in the uranium enrichment plant by the Gas Centrifuge. The characteristics of IF treatment, the secondary waste is just an IF
treatment, the secondary waste is just an IF and little adsorbent. In addition, this IF
and little adsorbent. In addition, this IF is possible to reuse as a materials for makings new IF
is possible to reuse as a materials for makings new IF gas. According to that IF
gas. According to that IF treatment is the simple method using chemical reaction, we hardly need to care about secondary reaction with the exception of the reaction with IF
treatment is the simple method using chemical reaction, we hardly need to care about secondary reaction with the exception of the reaction with IF gas and the uranium intermediate fluoride. This is very important feature when applying to a large-scale plant.
gas and the uranium intermediate fluoride. This is very important feature when applying to a large-scale plant.
Hyakutake, Toru*; Muto, Akinori*; Sasakura, Mariko*; Minowa, Hirotsugu*; Suzuki, Kazuhiko*; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Takahashi, Nobuo; Hata, Haruhi; Sugitsue, Noritake
JAEA-Research 2010-032, 32 Pages, 2010/10
System decontamination has been generally carried out with the aim of reducing the amount of radioactive waste generated and minimizing human exposure to radiation released from nuclear fuel facilities. At the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center, metal surfaces that are contaminated by uranium are dry decontaminated by using iodine heptafluoride (IF ) as a system decontaminator. In this dry decontamination technique, a chemical reaction occurs between the uranium compound attached to the metal surface and IF
) as a system decontaminator. In this dry decontamination technique, a chemical reaction occurs between the uranium compound attached to the metal surface and IF . Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of Uranium Hexafluoride.
. Only a few studies have been carried out on the decontamination efficiency, mechanism, level, etc. of dry decontamination techniques that use a decontamination gas. Therefore, the generalization of dry decontamination technique was assessed by a numerical method using decontamination data obtained at the Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center. A concrete analytical content is a depositing of Uranium Hexafluoride.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 200, p.012059_1 - 012059_4, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We studied Fe-dopant effects on spin correlations in Bi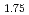 Pb
Pb Sr
Sr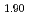 CuO
CuO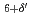 . Magnetic neutron elastic scattering, which is absent in a pristine sample, has been observed at incommensurate positions with an incommensurability of
. Magnetic neutron elastic scattering, which is absent in a pristine sample, has been observed at incommensurate positions with an incommensurability of 
 0.2. Surprisingly, this anomalously large
0.2. Surprisingly, this anomalously large  follows a linear relation
follows a linear relation 

 even in the overdoped region, unlike for La
even in the overdoped region, unlike for La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO . We discuss this specific feature observed in the overdoped phase from a dynamical stripe viewpoint.
. We discuss this specific feature observed in the overdoped phase from a dynamical stripe viewpoint.
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO cuprate superconductor
cuprate superconductorHiraka, Haruhiro*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Physical Review Letters, 102(3), p.037002_1 - 037002_4, 2009/01
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:76.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Local distortions around a Ni dopant in the hole-type La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO superconductor system were studied by X-ray-absorption fine structure (XAFS) using single crystals over a wide hole-doping range. Two distinct interatomic distances between Ni and in-plane oxygen appear in the Ni K-edge extended XAFS. Combined with previous results on hole-localization effects by Ni doping, two types of charge states are strongly indicated for Ni. This duality disqualifies a magnetic-impurity picture for Ni dopant in the superconducting phase of cuprates.
superconductor system were studied by X-ray-absorption fine structure (XAFS) using single crystals over a wide hole-doping range. Two distinct interatomic distances between Ni and in-plane oxygen appear in the Ni K-edge extended XAFS. Combined with previous results on hole-localization effects by Ni doping, two types of charge states are strongly indicated for Ni. This duality disqualifies a magnetic-impurity picture for Ni dopant in the superconducting phase of cuprates.
 cuprates studied by neutron scattering and XAFS spectroscopy
cuprates studied by neutron scattering and XAFS spectroscopyHiraka, Haruhiro*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Matsuda, Masaaki; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 69(12), p.3136 - 3138, 2008/12
 cuprates studied by neutron scattering and XAFS spectroscopy
cuprates studied by neutron scattering and XAFS spectroscopyHiraka, Haruhiro*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Matsuda, Masaaki; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 69(12), p.3136 - 3138, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.73(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Neutron scattering experiments using La Sr
Sr Cu
Cu Ni
Ni O
O clarified that the parallel spin-density modulations (SDMs) in the superconducting phase are susceptible to Ni, in the same way as the diagonal SDMs in the insulating spin-glass phase. Ni substitution reduces the mobile hole concentration from
clarified that the parallel spin-density modulations (SDMs) in the superconducting phase are susceptible to Ni, in the same way as the diagonal SDMs in the insulating spin-glass phase. Ni substitution reduces the mobile hole concentration from  down to
down to  -
-  . Polarized XAFS measurements using Ni
. Polarized XAFS measurements using Ni  -edge probe two types of Ni valence states; Ni
-edge probe two types of Ni valence states; Ni and Ni
and Ni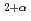 . It indicates that a strong hole localization occurs around Ni, resulting in an effective spin-
. It indicates that a strong hole localization occurs around Ni, resulting in an effective spin- value at Ni sites. Therefore, a charge impurity nature of Ni is most likely realized when
value at Ni sites. Therefore, a charge impurity nature of Ni is most likely realized when 
 .
.
Sakata, Osami*; Furukawa, Yukito*; Goto, Shunji*; Mochizuki, Tetsuro*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Takeshita, Kunikazu*; Ohashi, Haruhiko*; Ohata, Toru*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Takahashi, Sunao*; et al.
Surface Review and Letters, 10(2&3), p.543 - 547, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:143 Percentile:96.26(Chemistry, Physical)The main components of a new beamline for surface and interface crystal structure determination at SPring-8 are briefly described. Stages for the beamline monochromator are modified for making an incident X-ray intensity more stable for surface X-ray experiments. Absolute photon flux densities were measured with an incident photon energy. A new ultrahigh vacuum system is introduced with preliminary X-ray measurements from an ordered oxygen on Pt(111) surface.
Hata, Haruhi; Yokoyama, Kaoru; Tanaka, Yoshio; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake
no journal, ,
For decommission of uranium handling facilities, it is important to characterize the details of the facilities, which are the distribution of nuclide, the existence of hazardous waste and so on. The report suggests classification method based on the nuclide composition by using principal component analysis.