Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 stress measurement in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, Japan
stress measurement in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory, JapanSato, Toshinori; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Harumi*
Proceedings of 6th International Symposium on In-situ Rock Stress (RS 2013) (CD-ROM), p.354 - 359, 2013/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is operating underground research laboratory projects in order to establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal of HLW. One of these is the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project focused on crystalline rock. Rock mechanical studies, including  stress measurements, are being conducted as part of the projects. This paper describes the current status of in situ stress studies conducted in the MIU. Applicability of high-compliance system for hydraulic fracturing was evaluated and the maximum stress values were revised. Core disking was observed with groundwater flow in galleries at the depth of GL.-200m, during the Compact Conical-ended Borehole Overcoring (CCBO) test was adopted. To simultaneously estimate regional stress fields and the elastic modulus of rock mass from in situ stress measurements, back analysis methods based on three-dimensional finite element analysis and the boundary element method were developed.
stress measurements, are being conducted as part of the projects. This paper describes the current status of in situ stress studies conducted in the MIU. Applicability of high-compliance system for hydraulic fracturing was evaluated and the maximum stress values were revised. Core disking was observed with groundwater flow in galleries at the depth of GL.-200m, during the Compact Conical-ended Borehole Overcoring (CCBO) test was adopted. To simultaneously estimate regional stress fields and the elastic modulus of rock mass from in situ stress measurements, back analysis methods based on three-dimensional finite element analysis and the boundary element method were developed.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Kondo, Keiji; Inagaki, Daisuke; Kato, Harumi*
Proceedings of 6th International Symposium on In-situ Rock Stress (RS 2013) (CD-ROM), p.331 - 338, 2013/08
In a high-level radioactive waste disposal, initial stress state is important for designing support and layout of repository. Based on the background, objectives of this paper is to investigate the state of regional stress in detail and change of initial stress state along construction of the Underground Research Laboratory (URL). Hydraulic fracturing tests and observation of the borehole breakouts through borehole televiewer logging have been conducted in the boreholes around the Horonobe URL and in the galleries of the URL. As a result, the values of the stress measured in the boreholes around the URL increased along depth and the orientations of the maximum horizontal stress were different between a map scale fault. In addition, values of initial stresses measured in the galleries were less than those of boreholes around the URL and orientation of the maximum horizontal stress were different in each depth of the gallery. These results suggest that measurements of the stress in the galleries are important for modification of the layout designed before construction of the URL.
Sato, Toshinori; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Harumi*
Journal of MMIJ, 129(2,3), p.59 - 64, 2013/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting  stress measurements by overcoring method, to aiming establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal. Core disking is observed where rock stress measurements are performed by compact conical-ended borehole overcoring technique in the depth of 300 m from the surface at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In this report, failure initiation of core disking is discussed.
stress measurements by overcoring method, to aiming establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal. Core disking is observed where rock stress measurements are performed by compact conical-ended borehole overcoring technique in the depth of 300 m from the surface at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In this report, failure initiation of core disking is discussed.
Kondo, Keiji; Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Inagaki, Daisuke; Sugita, Yutaka; Kato, Harumi*; Niunoya, Sumio*
Dai-13-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.583 - 588, 2013/01
no abstracts in English
Sato, Toshinori; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Harumi*
Heisei-24 Nendo (2012 Nen) Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Shuki Taikai Koenshu, p.221 - 222, 2012/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting  stress measurements by overcoring method, to aiming establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal. Core disking is observed where rock stress measurements are performed by compact conical-ended borehole overcoring technique in the depth of 300m from the surface at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In this report, failure initiation of core disking is discussed.
stress measurements by overcoring method, to aiming establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal. Core disking is observed where rock stress measurements are performed by compact conical-ended borehole overcoring technique in the depth of 300m from the surface at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In this report, failure initiation of core disking is discussed.
Sato, Toshinori; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Harumi*
Journal of MMIJ, 128(7), p.449 - 454, 2012/07
Hydraulic fracturing has provided many determinations of in situ stress, but also include many errors in data obtained, as the ISRM suggested. This report provides a comparison of the data obtained by the conventional hydraulic fracturing method with those of a new high-compliance system. Analysis of the results of 57 hydraulic fracturing tests in granite to a maximum depth of 1000m, indicated that 35% of the data obtained using the conventional system is low quality. In addition, the maximum horizontal stresses calculated using the conventional equation is overestimated by about 23%. In contrast, the data obtained with the new system is better quality compared with the conventional system, because flow rate of pressurization is measured in the borehole near the test section rather than at surface, thus reducing compliance in the system and the inherent errors introduced in the stress calculations.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Matsui, Hiroya; Sato, Toshinori; Kato, Harumi*
JAEA-Research 2011-038, 26 Pages, 2012/01
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project has been implemented to establish the techniques for investigation, analysis and assessment of the deep geological environment and to develop a range of engineering techniques for application deep underground. In this paper, results of differential strain curve analysis (DSCA) and elastic wave measurements using polyhedral specimens at the 08MI13 and 09MI20 boreholes in -300 m stage are described. The objectives of this work are to evaluate in situ stress condition on the -300 m stage.
Sato, Toshinori; Tanno, Takeo; Hikima, Ryoichi; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Harumi*
Heisei-23 Nendo (2011 Nen) Shigen, Sozai Gakkai Shuki Taikai Koenshu, p.175 - 176, 2011/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting in-situ stress measurements by hydraulic fracturing method to aiming establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal. Hydraulic fracturing method has many results, but including many errors in data as International Rock Mechanics Society suggested. This report describes results compared with the data obtained by ordinary system and that of new type of system.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Kato, Harumi*
JAEA-Research 2011-012, 217 Pages, 2011/06
For the purpose of studying the in situ state of stress around Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, hydraulic fracturing technique was carried out three boreholes drilled from the 250m gallery located near the bottom of the ventilation shaft. The results of the measurements are summarized as follows. Shut-in pressure of inclined transverse cracks and the circumferential position of longitudinal cracks on the wellbore surface were used to determine the magnitude and orientation of principal stress around the 250m gallery on the assumption that all of the target zones of hydraulic fracturing were in a uniform stress state. The determined in situ stress state showed a little difference of magnitude between intermediate stress and minimum stress. The vertical component of the in situ stress was evaluated to be about a half of the overburden at the test site. The maximum principal stress was inclined to about 40 degrees from the level with azimuth of NE orientation.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Kato, Harumi*
Doboku Gakkai Heisei-22-Nendo Zenkoku Taikai Dai-65-Kai Nenji Gakujutsu Koenkai Koen Gaiyoshu (DVD-ROM), p.129 - 130, 2010/09
Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) project aims at improvement of the reliability of technologies for geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes. In investigation during construction of the underground facilities, the updating and check of the validity of initial stress estimations made during surface-based investigations is one of the main issues. Thus, three boreholes were made from the niche (GL-140 m) of ventilation and east shaft, and a three-dimensional evaluation of the initial stress in Koetoi Formation was done by the method called hydraulic fracturing technique and the analysis of the borehole breakout. Moreover, the direction of the maximum horizontal principal stress had been found to be east/west in general. However, the present test showed that the direction was 26 or 46 degrees counterclockwise from east/west.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Kato, Harumi*
JAEA-Research 2010-017, 105 Pages, 2010/07
For the purpose of studying the in situ state of stress around Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, hydraulic fracturing technique was carried out three boreholes drilled from the 140m niche located near the bottom of the east shaft. The results of the measurements are summarized as follows. Evaluation of stress in a plane perpendicular to the borehole axis was impossible because transverse fractures which developed along a pre-existing plane of weakness were created at eleven depths. Therefore, the relation between the shut-in pressure of a transverse fracture and the in situ stress was used to obtain the in situ stress state on the assumption that all of the target zones of hydraulic fracturing were in a uniform stress state. The determined in situ stress state showed that none of the principal stress axis was coaxial with respect to E-N-V coordinate system where E, N and V represent east, north and vertical direction.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Kato, Harumi*
JAEA-Research 2009-004, 165 Pages, 2009/05
Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) project aims at improvement of the reliability of technologies for geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes. In investigation during construction of the underground facilities, the updating and check of the validity of initial stress estimations made during surface-based investigations is one of the main issues. Thus, three boreholes were made from the niche (GL-140 m) of ventilation shaft, and a three-dimensional evaluation of the initial stress in Koetoi Formation was done by the method called hydraulic fracturing technique and the analysis of the borehole breakout. Moreover, the direction of the maximum horizontal principal stress had been found to be east/west in general. However, the present test showed that the direction was 25 or 43 degrees counterclockwise from east/west.
Nakamura, Takahiro; Kato, Harumi*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka
Dai-12-Kai Iwa No Rikigaku Kokunai Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.297 - 303, 2008/09
This paper shows the results of initial stress obtained from stress relief method, hydraulic fracturing technique and breakout analysis which have been carried out at 140 m niche as a part of the investigation of Horonobe Underground Research Project. The results of investigations are summarized as follows. Initial stress measuring has been tried by stress relief method, but none of the gluing of the gage plugs was successful because clayish slime stuck over the end of the borehole. The direction and value of initial stress obtained from hydraulic fracturing technique and breakout analysis was closely similar.
Maekawa, Yasunari; Yuasa, Kanako*; Enomoto, Kazuyuki; Matsushita, Harumi*; Kato, Jun*; Yamashita, Takashi*; Ito, Kazuo*; Yoshida, Masaru
Chemistry of Materials, 20(16), p.5320 - 5324, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.94(Chemistry, Physical)Polymer films with acid-responsive chromic dyes and acid generators have been designed for an electron beam (EB)-induced color imaging system. Arylsulfonic acid esters and triphenylsulfonium salts were used as an EB-sensitive acid generator; the acid (H ) allows a chromic reaction with rhodamine B base (RB) and 4,4'-bis(dimethylamino)benzhydrol (BH) to be triggered. Upon EB irradiation, poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) films consisting of RB or BH and acid generators exhibited a characteristic absorption band with
) allows a chromic reaction with rhodamine B base (RB) and 4,4'-bis(dimethylamino)benzhydrol (BH) to be triggered. Upon EB irradiation, poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) films consisting of RB or BH and acid generators exhibited a characteristic absorption band with  max at 560 and at 612 nm, respectively, and an isosbestic point. These spectral changes clearly indicate that colorless chromic dyes in PMMA are transformed selectively to the colored form. The color imaging of these films was performed by electron beam direct writing (EBDW) with a 50 nm diameter beam to form 100 - 1000 nm line and space patterns and was evaluated by optical and confocal laser microscopy. EBDW on the acid chromic polymer films, especially for BH, yielded clear color imaging of 100 - 200 nm line and space patterns with a dose of only 10
max at 560 and at 612 nm, respectively, and an isosbestic point. These spectral changes clearly indicate that colorless chromic dyes in PMMA are transformed selectively to the colored form. The color imaging of these films was performed by electron beam direct writing (EBDW) with a 50 nm diameter beam to form 100 - 1000 nm line and space patterns and was evaluated by optical and confocal laser microscopy. EBDW on the acid chromic polymer films, especially for BH, yielded clear color imaging of 100 - 200 nm line and space patterns with a dose of only 10  C/cm
C/cm . The confocal laser microscopy gave thinner lines than the laser wavelength (632.8 nm), probably because of the large change in refractive index of the patterned film induced by EB irradiation even with a low energy dose.
. The confocal laser microscopy gave thinner lines than the laser wavelength (632.8 nm), probably because of the large change in refractive index of the patterned film induced by EB irradiation even with a low energy dose.
Kato, Jun; Yuasa, Kanako; Matsushita, Harumi*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Enomoto, Kazuyuki; Ishii, Tatsuhito*; Ito, Kazuo*; Yamashita, Takashi*
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 19(1), p.105 - 110, 2006/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.32(Polymer Science)The novel electron beam (EB)-induced color imaging system, consisting of polymer films with acid-responsive chromic molecules (chromic dyes) and EB-acid generators (EBAGs) was proposed. EB irradiation of the acid-chromic polymer films induced acid generation from EBAG, resulting in color formation of the acid-chromic molecules (protonated forms). Nanoscale color imaging on the acid- chromic polymer films was carried out using EB scanning direct drawing. Clear color imaging of 200 nm square and 100 nm line/space patterns could be observed with a dose of only 50  C cm
C cm . Furthermore, the large EB-induced refractive index change of these films (0.013 at 632.8 nm) was observed in both TE and TM modes by an m-line method, which is sufficient to create an optical circuit.
. Furthermore, the large EB-induced refractive index change of these films (0.013 at 632.8 nm) was observed in both TE and TM modes by an m-line method, which is sufficient to create an optical circuit.
 stress in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project
stress in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory ProjectNakama, Shigeo; Sato, Toshinori; Kato, Harumi*
Proceedings of 40th U.S. Rock Mechanics Symposium (Alaska Rocks 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/06
 stress is an important factor for design and construction of deep, large underground structures, such as underground power stations and geological disposal facilities for high-level radioactive waste. In-situ stress is recognized as a primary factor for development of an excavation disturbed zone (EDZ). An EDZ will be less stable and essentially will be a highly permeable groundwater flow path, so an EDZ is recognized as a key issue not only for the design and construction of disposal facilities but also for safety assessment. Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) is conducting underground research laboratory projects to establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal; one is the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project for crystalline rock, the other is the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (Hnb-URL) project for sedimentary rock. Rock mechanical studies including in-situ stress measurements are performed in these projects. The main elements of these studies are: (1) hydraulic fracturing tests in 1000 m deep boreholes and utilization of several laboratory core testing methods; (2) development of overcoring methods for vertical 1000 m deep boreholes; and (3) development of numerical techniques for estimation of regional stress state. This paper describes the current state of in-situ stress studies in the MIU project, especially hydraulic fracturing tests in 1000 m deep boreholes, and development of overcoring techniques for vertical 1000 m deep boreholes in saturated conditions.
stress is an important factor for design and construction of deep, large underground structures, such as underground power stations and geological disposal facilities for high-level radioactive waste. In-situ stress is recognized as a primary factor for development of an excavation disturbed zone (EDZ). An EDZ will be less stable and essentially will be a highly permeable groundwater flow path, so an EDZ is recognized as a key issue not only for the design and construction of disposal facilities but also for safety assessment. Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) is conducting underground research laboratory projects to establish a firm scientific basis for safe geological disposal; one is the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project for crystalline rock, the other is the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (Hnb-URL) project for sedimentary rock. Rock mechanical studies including in-situ stress measurements are performed in these projects. The main elements of these studies are: (1) hydraulic fracturing tests in 1000 m deep boreholes and utilization of several laboratory core testing methods; (2) development of overcoring methods for vertical 1000 m deep boreholes; and (3) development of numerical techniques for estimation of regional stress state. This paper describes the current state of in-situ stress studies in the MIU project, especially hydraulic fracturing tests in 1000 m deep boreholes, and development of overcoring techniques for vertical 1000 m deep boreholes in saturated conditions.
Kato, Harumi*
JNC TJ7430 2005-006, 68 Pages, 2004/03
Ten overcoring tests wewe made in the vertical borehole 02SE-04 by using an automatic probe developed by JNC.
Kato, Harumi*
JNC TJ7400 2004-018, 97 Pages, 2004/03
In situ stress measurements (AE/DRA method, ASR method, DSCA method) were carried out using cores taken from MIZ-1 borehole in order to evaluate in situ state of stress from surface down to 1000m. AE/DRA method was carried out using cores taken from the depths of 291.0mabh, 455.0 mabh and 494.0 mabh. The in situ stress variation with depth obtained from AE/DRA method was different from the results of hydraulic fracturing test at Shobasama Site. The direction of principal stresses determined by AE/DRA method showed extreme dispersions, and systematic variation of the direction was not found. ASR method was carried out using cores taken from the depths of 462.7 mabh, 462.8 mabh, 502.5 mabh and 502.6 mabh. Quantitative evaluation of in situ stress was difficult because the anelastic strain recovery of cores were less than ten micro strains. DSCA method was carried out using cores taken from the depths of 298.86 mabh, 455.78 mabh and 494.09 mabh for evaluating anisotropic property and three dimensional micro crack property of Toki granite. The intrinsic linear compressibility of Toki granite showed moderate degree of anisotropy ranging between 20% and 27%. The ratio of principal stress magnitude estimated from (
 /
/
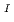 ) revealed that (
) revealed that (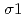 /
/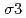 ) varied between 1.5 to 2.7 and (
) varied between 1.5 to 2.7 and (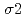 /
/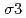 ) varied between 1.2 to 2.0 although considerable dispersions were found. The direction of the maximum principal value of (
) varied between 1.2 to 2.0 although considerable dispersions were found. The direction of the maximum principal value of (
 /
/
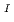 )
)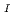 , (
, (

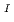 ) and (
) and (
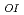 ) were NNW orientation in two cores taken from shallower depths (298.86 mabh and 455.78 mabh), and WNW orientation in the core taken from the deepest depth (494.09 mabh).
) were NNW orientation in two cores taken from shallower depths (298.86 mabh and 455.78 mabh), and WNW orientation in the core taken from the deepest depth (494.09 mabh).
Kato, Harumi*
JNC TJ7410 2003-003, 83 Pages, 2003/03
The overcoring tests in the vertical borehole 02SE-04 (a standard HQ-WL) were made at depths of 122.7m, 142.7m, 157.0m, 173.5m and 192.0m by using modified equipments and an automatic probe developed by Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). By adopting a newly developed wire line type probe carrier and pilot hole drilling tool, it was ensured that quick accomplishment of steps followed during overcoring at great depth was possible. Modifications to a glue capsule were carried out to achieve successful grouting of the SI cell in the pilot hole at great depths. Since cracks developed along the planes of weakness during the overcoring, none of the tests at the five depths provided valid measurement. In order to determine the elastic properties of the overcore and epoxy cement, cyclic loading test was made. The test reviled that the core taken down to a depth of 160m possessed plastic property. It was also found that long periods of up to three days were required for the epoxy cement extruded in the pilot hole to change into elastic material. Hydraulic fracturing tests were also conducted in the borehole 02SE-04 at depths ranging from 125.8m to 168.0m. At two depths, fractures parallel to the borehole axis were induced. The test results indicated that the stress regime at the two depths was reverse faulting tectonic environment (Sv Sh
Sh SH+) and the orientation of the hydraulic fracture trace in 02SE-04 was found to give an average azimuth for the maximum horizontal stress SH of N60°E.
SH+) and the orientation of the hydraulic fracture trace in 02SE-04 was found to give an average azimuth for the maximum horizontal stress SH of N60°E.
Kato, Harumi*
JNC TJ7400 2003-001, 44 Pages, 2003/03
no abstracts in English