Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

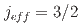 insulator Sr
insulator Sr OsO
OsO
Wakabayashi, Yuki*; Krockenberger, Y.*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Wadachi, Hiroki*; Shibata, Goro; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Taniyasu, Yoshitaka*; Yamamoto, Hideki*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 12(5), p.291 - 293, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
 -Fe
-FeSuzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(7), p.075102_1 - 075102_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:62.71(Physics, Applied)Fracture of body centred cubic (bcc) metals and alloys below the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature is brittle. This is theoretically explained by the notion that the critical stress intensity factor of a given crack front for brittle fracture is smaller than that for plastic deformation; hence, brittle fracture is chosen over plastic deformation. Although this view is true from a macroscopic point of view, such brittle fracture is always accompanied by small-scale plastic deformation in the vicinity of the crack tip, i.e. crack tip plasticity. This short paper investigates the origin of this plasticity using atomistic modeling with a recently developed machine-learning interatomic potential of  -Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
-Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Zairyo, 73(2), p.129 - 135, 2024/02
Body-centered-cubic transition metals, such as Fe and W, cleave along the {100} plane. To find out the mechanism of this response, atomistic simulations of curved crack-fronts of bcc Fe were conducted at 0 K using an interatomic potential created by an artificial neural network (ANN) technique. We discovered that dislocations can be emitted from the curved crack fronts along the {110} crack plane, and this phenomenon explains why the cleavage is observed only along the {100} plane. In addition, the cleavage simulations along {100} at the elevated temperature were found to be accompanied by plasticity; namely, they represented more realistic fracture.
Mori, Hideki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsunaka, Daisuke*; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(6), p.063605_1 - 063605_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The introduction of obstacles (e.g., precipitates) for controlling dislocation motion in molecular structures is a prevalent method for designing the mechanical strength of metals. Owing to the nanoscale size of the dislocation core ( 1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the
1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the 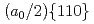 edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
Suzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 12, p.19701_1 - 19701_10, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:62.47(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Body-centered-cubic (bcc) transition metals, such as  -Fe and W, cleave along the {100} plane, even though the surface energy is the lowest along the {110} plane. To unravel the mechanism of this odd response, large-scale atomistic simulations of curved cleavage cracks of
-Fe and W, cleave along the {100} plane, even though the surface energy is the lowest along the {110} plane. To unravel the mechanism of this odd response, large-scale atomistic simulations of curved cleavage cracks of  -Fe were conducted in association with stress intensity factor analyses of straight crack fronts using an interatomic potential created by an artificial neural network technique. The study provides novel findings: Dislocations are emitted from the crack fronts along the {110} cleavage plane, and this phenomenon explains why the {100} plane can be the cleavage plane. However, the simple straight crack-front analyses did not yield the same conclusion. It is suggested that atomistic modeling, at sufficiently large scales to capture the inherent complexities of materials using highly accurate potentials, is necessary to correctly predict the mechanical strength. The method adopted in this study is generally applicable to the cleavage problem of bcc transition metals and alloys.
-Fe were conducted in association with stress intensity factor analyses of straight crack fronts using an interatomic potential created by an artificial neural network technique. The study provides novel findings: Dislocations are emitted from the crack fronts along the {110} cleavage plane, and this phenomenon explains why the {100} plane can be the cleavage plane. However, the simple straight crack-front analyses did not yield the same conclusion. It is suggested that atomistic modeling, at sufficiently large scales to capture the inherent complexities of materials using highly accurate potentials, is necessary to correctly predict the mechanical strength. The method adopted in this study is generally applicable to the cleavage problem of bcc transition metals and alloys.
Kitamura, Akihisa*; Okazaki, Sota*; Kondo, Mitsuru*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Hori, Rie*; Ikeda, Masayuki*; Ichimura, Koji*; Nakagawa, Yuki*; Mori, Hideki*
Shizuoka Daigaku Chikyu Kagaku Kenkyu Hokoku, (49), p.73 - 86, 2022/07
On July 3 2021, a debris flow caused by a landslide from a landfill occurred along the Aizome River in the Izusan area of Atami City, Shizuoka. In this study, debris flow deposits and soil samples were characterized in terms of their sedimentology and geochemically analyzed.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Kanazawa, Ryosuke*; Matsunaka, Daisuke*; Lobzenko, I.; Tsuru, Tomohito; Koyama, Masanori*; Mori, Hideki*
Scripta Materialia, 207, p.114268_1 - 114268_4, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:79.97(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)This study reports grain boundary (GB) energy calculations for 46 symmetric-tilt GBs in  -iron using molecular mechanics based on an artificial neural network (ANN) potential and compares the results with calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT), the embedded atom method (EAM), and the modified EAM (MEAM). The results by the ANN potential are in excellent agreement with those of the DFT (5% on average), while the EAM and MEAM significantly differ from the DFT results (about 27% on average). In a uniaxial tensile calculation of GB, the ANN potential reproduced the brittle fracture tendency of the GB observed in the DFT while the EAM and MEAM mistakenly showed ductile behaviors. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the ANN potential in calculating grain boundaries of iron, which is in high demand in modern industry.
-iron using molecular mechanics based on an artificial neural network (ANN) potential and compares the results with calculations based on the density functional theory (DFT), the embedded atom method (EAM), and the modified EAM (MEAM). The results by the ANN potential are in excellent agreement with those of the DFT (5% on average), while the EAM and MEAM significantly differ from the DFT results (about 27% on average). In a uniaxial tensile calculation of GB, the ANN potential reproduced the brittle fracture tendency of the GB observed in the DFT while the EAM and MEAM mistakenly showed ductile behaviors. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the ANN potential in calculating grain boundaries of iron, which is in high demand in modern industry.
Kurihara, Momo*; Yasutaka, Tetsuo*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Ashikawa, Nobuo*; Ebina, Hiroyuki*; Iijima, Takeshi*; Ishimaru, Kei*; Kanai, Ramon*; Karube, Jinichi*; Konnai, Yae*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 322(2), p.477 - 485, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.09(Chemistry, Analytical)We assessed the repeatability and reproducibility of methods for determining low dissolved radiocesium concentrations in freshwater in Fukushima. Twenty-one laboratories pre-concentrated three of 10 L samples by five different pre-concentration methods (prussian-blue-impregnated filter cartridges, coprecipitation with ammonium phosphomolybdate, evaporation, solid-phase extraction disks, and ion-exchange resin columns), and activity of radiocesium was measured. The z-scores for all of the  Cs results were within
Cs results were within  2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
Aso, Tomokazu; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Otsu, Kiichi*; Kawakami, Yoshihiko*; Komori, Shinji*; Muto, Hideki*; Takada, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2019-013, 77 Pages, 2019/09
At Materials and Life Science experimental Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), a 1-MW pulsed spallation neutron source is equipped with a cryogenic hydrogen system which circulates liquid hydrogen (20 K and 1.5 MPa) to convert high energy neutrons generated at a mercury target to cold neutrons at three moderators with removing nuclear heat of 3.8 kW deposited there. The cryogenic system includes an accumulator with a bellows structure in order to absorb pressure fluctuations generated by the nuclear heat deposition in the system. Welded inner bellows of the first accumulator was failured during operation, forcing us to improve the accumulator to have sufficient pressure resistance and longer life-time. We have developed elemental technologies for manufacturing welded bellows of the accumulator by a thick plate with high pressure resistance, succeeding to find optimum welding conditions. We fabricated a prototype bellows block and carried out an endurance test by adding a pressure change of 2 MPa repeatedly. As a result, the prototype bellows was successfully in use exceeding the design life of 10,000 times. Since distortions given during welding and assembling affect functionality and lifetime of the bellows, we set the levelness of each element of the bellows as within 0.1 . The improved accumulator has already been in operation for about 25,000 hours as of January 2019, resulting that the number of strokes reached to 16,000. In July 2018, we demonstrated that the accumulator could suppress the pressure fluctuation generated by the 932 kW beam injection as designed. As current operational beam power is 500 kW, the current cryogenic hydrogen system could be applicable for stable operation at higher power in the future.
. The improved accumulator has already been in operation for about 25,000 hours as of January 2019, resulting that the number of strokes reached to 16,000. In July 2018, we demonstrated that the accumulator could suppress the pressure fluctuation generated by the 932 kW beam injection as designed. As current operational beam power is 500 kW, the current cryogenic hydrogen system could be applicable for stable operation at higher power in the future.
Haraga, Tomoko; Ouchi, Kazuki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Hoshino, Hitoshi*; Tanana, Rei*; Fujihara, Takashi*; Kurokawa, Hideki*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1032, p.188 - 196, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:46.22(Chemistry, Analytical)The development of safe, rapid and highly sensitive analytical methods for radioactive samples, especially actinide (An) ions, represents an important challenge. Here we propose a methodology for selecting appropriate emissive probes for An ions with very low consumption and emission of radioactivity by capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence detection (CE-LIF), using a small chemical library of probes with eight different chelating moieties. It was found that the emissive probe, which possesses the tetradentate chelating moiety, was suitable for detecting uranyl ions. The detection limit for the uranyl-probe complex using CE-LIF combined with dynamic ternary complexation and on-capillary concentration techniques was determined to be 0.7 ppt. This method was successfully applied to real radioactive liquid samples collected from nuclear facilities.
 promoter on Pt electro-catalyst
promoter on Pt electro-catalystFugane, Keisuke*; Mori, Toshiyuki*; Yan, P.*; Masuda, Takuya*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Ye, F.*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Auchterlonie, G.*; Drennan, J.*
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7(4), p.2698 - 2707, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:65.07(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)no abstracts in English
Negi, Tateyuki*; Mizunaga, Hideki*; Asamori, Koichi; Umeda, Koji
Exploration Geophysics, 44(3), p.145 - 155, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:4.67(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This paper presents a fast algorithm for electromagnetic inversion. The algorithm is distinct for the level of accuracy it attains when bypassing the sensitivity matrix update. A common sensitivity matrix for homogeneous half-space is used in all of the iterations. Instead of a fixed sensitivity matrix, the Laplace filter coefficients at each element are updated based on the spatial differences of resistivity calculated by a reconstructed structure derived from the former iteration. This substitution is expected not only to reduce the computation time required for large-scale inversions, such as those for three-dimensional surveys, but also to allow reconstruction for sharp boundaries in resistivity structures. This algorithm was applied to three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion in order to confirm the effectiveness. This paper reports the results of several synthetic examples using different resistivity models and conditions.
 nanocomposite electrocatalyst; An in situ electrochemical X-ray absorption fine structure study
nanocomposite electrocatalyst; An in situ electrochemical X-ray absorption fine structure studyMasuda, Takuya*; Fukumitsu, Hitoshi*; Fugane, Keisuke*; Togasaki, Hirotaka*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Nishihata, Yasuo; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Kobayashi, Keisuke*; Mori, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 116(18), p.10098 - 10102, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:127 Percentile:93.68(Chemistry, Physical)In situ electrochemical X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements were performed at the Pt L and Ce L
and Ce L edges of the Pt-CeO
edges of the Pt-CeO /C catalyst, which was prepared by a combined process of precipitation and coimpregnation methods, as well as at the Pt L
/C catalyst, which was prepared by a combined process of precipitation and coimpregnation methods, as well as at the Pt L edge of the conventional Pt/C catalyst in oxygen-saturated H
edge of the conventional Pt/C catalyst in oxygen-saturated H SO
SO solution to clarify the role of CeO
solution to clarify the role of CeO in the reduction of the overpotential for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) at the Pt-CeO
in the reduction of the overpotential for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) at the Pt-CeO nanocomposite compared with the conventional Pt/C catalyst. XAFS measurements clearly show that the enhancement of ORR activity is attributed to the inhibition of Pt oxide formation by the CeO
nanocomposite compared with the conventional Pt/C catalyst. XAFS measurements clearly show that the enhancement of ORR activity is attributed to the inhibition of Pt oxide formation by the CeO layer, of which Ce
layer, of which Ce was oxidized to Ce
was oxidized to Ce instead of Pt at the Pt oxide formation potential.
instead of Pt at the Pt oxide formation potential.
Otani, Hiroshi; Matsushima, Akira; Mori, Naoto; Kutsuna, Hideki; Higashiura, Norikazu
JAEA-Review 2011-041, 55 Pages, 2012/01
In planning and carrying out decommissioning technical development of Fugen, "Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning", which consists of the members well-informed, is established, aiming to make good use of Fugen as a place for technological development which is opened inside and outside the country, as the central point in the energy research and development base making project of Fukui prefecture, and to utilize the outcome in our decommissioning to the technical development effectively. This report compiles presentation materials "Current Situation of Fugen Decommissioning", "Radioactive Corrosion Products Decontamination Experiment with using Heavy Water System Equipment", "Laser Cutting Test on Dust Behavior in Cutting Work in Air", "Preparatory Situation for Operation of Clearance System" of this committee.
 studied by photoemission and soft X-ray absorption spectroscopies
studied by photoemission and soft X-ray absorption spectroscopiesUtsumi, Yuki*; Sato, Hitoshi*; Kurihara, Hidenao*; Maso, Hiroyuki*; Hiraoka, Koichi*; Kojima, Kenichi*; Tobimatsu, Komei*; Okochi, Takuo*; Fujimori, Shinichi; Takeda, Yukiharu; et al.
Physical Review B, 84(11), p.115143_1 - 115143_7, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:47.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied conduction-band (CB) electronic states of a typical valence-transition compound YbInCu by means of temperature-dependent hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES), soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (SX-PES) of the valence band. We have described the valence transition in YbInCu
by means of temperature-dependent hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES), soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (SX-PES) of the valence band. We have described the valence transition in YbInCu in terms of the charge transfer from the CB to Yb 4
in terms of the charge transfer from the CB to Yb 4 states.
states.
Kutsuna, Hideki; Matsumori, Akira*; Izumi, Masanori; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Higashiura, Norikazu
JAEA-Review 2011-025, 43 Pages, 2011/07
In planning and carrying out our decommissioning technical development, "Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning", which consists of the members well-informed, is established, aiming to make good use of Fugen as a place for technological development which is opened inside and outside the country, as the central point in the energy research and development base making project of Fukui prefecture, and to utilize the outcome in our decommissioning to the technical development effectively. This report compiles presentation materials "Current Situation of Fugen Decommissioning", "Radioactive Corrosion Products (CP) Decontamination Experiment with Heavy Water System Equipment", "Application of management data evaluation system to Fugen", "Preparatory Situation for Operation of Clearance System" of the 22nd Technical special committee on Fugen decommissioning which held on September 14, 2010.
Kusano, Tomohiro; Asamori, Koichi; Kurosawa, Hideki; Kokubu, Yoko; Tanikawa, Shinichi; Negi, Tateyuki; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yasue, Kenichi; Yamasaki, Seiko; Yamada, Kunimi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-044, 153 Pages, 2011/01
This progress report (H22 report) documents progress made during JAEA 1st Midterm Plan (FY 2005 - 2009) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. For the current 5-year R&D programme, three major goals have been defined as follows: (1) development and synthesis of investigation techniques for selecting suitable sites in geosphere stability, (2) development, application, and evaluation of prediction models for evaluating the changes of geological environment in thermal, hydraulic, mechanical and geochemical conditions for a long period of time, and (3) development of new dating techniques for providing information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Asamori, Koichi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Matsuura, Yuki*; Kosaka, Hideki*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.407 - 413, 2010/10
In this study, we present the preliminary results for the estimation of a horizontal crustal movement by using geodetic and geological approach in the Horonobe area, northern Hokkaido, Japan. The estimations have been carried out by using a GPS data and a geological cross section obtained by applying balanced-section method. As results of this study, both of the shortening rates estimated by GPS data and balanced-section method indicate several millimeters per year. Namely, there is no contradiction between geodetic and geological data, and it is considered that Horonobe area is still situated similar tendency and magnitude of a crustal movement. Geodetic data is not usually used to evaluate the long-term crustal movement. However, the results of this study indicate that geodetic data provide valuable information for estimating the long-term crustal movement in the area.
Yasue, Kenichi; Asamori, Koichi; Yamada, Kunimi; Kokubu, Yoko; Yamasaki, Seiko; Kurosawa, Hideki; Tanikawa, Shinichi; Negi, Tateyuki; Kusano, Tomohiro; Hanamuro, Takahiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-034, 42 Pages, 2010/09
The concept of geological disposal of HLW in Japan is based on a multibarrier system which combines a stable geological environment with an engineered barrier system. Potential geological host formations and their surroundings are chosen, in particular, for their long-term stability, taking into account the fact that Japan is located in a tectonically active zone. This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) for geosphere stability for long-term isolation of HLW in JAEA, in fiscal year 2010. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2010 are described in detail based on the outline of 5 years plan (fiscal years 2010-2014). In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.