Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometry
by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometryNakajima, Kunihisa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 491, p.183 - 189, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:70.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)One of the main chemical forms of cesium in the gas phase during severe accidents of light water reactor is expected to be cesium metaborate, CsBO , by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO
, by thermodynamic equilibrium calculation considering reaction with boron. But accuracy of the thermodynamic data of gaseous metaborate, CsBO (g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO
(g), has been judged as poor quality. Thus, Knudsen effusion mass spectrometric measurement of CsBO was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO
was carried out to obtain reliable thermodynamic data. The evaluated values of standard enthalpy of formation of CsBO (g),
(g), 
 H
H
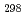 (CsBO
(CsBO ,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7
,g), by the 2nd and 3rd law treatments are -700.7 10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0
10.7 kJ/mol and -697.0 10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
10.6 kJ/mol, respectively, and agree with each other within the errors, which suggests our data are reliable. Further, it was found that the existing data of the Gibbs energy function and the standard enthalpy of formation agreed well with the values evaluated in this study, which indicates the existing thermodynamic data are also reliable.
Takai, Toshihide; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Furukawa, Tomohiro
JAEA-Technology 2015-002, 20 Pages, 2015/03
To improve the evaluation technique of source term, the measurement technique of the equilibrium vapor pressure using a high temperature mass spectrometer is required to expand the thermodynamic database of the simulated FPs. Existing test apparatus was adapted for this purpose. A mass spectrometer capable of measuring a wide mass number range and glove box for handling simulated FPs were installed for analyzing heavy FPs and preventing deterioration of simulated FPs in an air atmosphere, respectively. Function verification using standard sample and precision investigation using simulated FP sample were carried out. The oxygen dissociation pressure and standard enthalpy of formation of RuO (s) were evaluated, and it was confirmed these evaluated values were agreed with the calculated value from existing thermodynamic data and evaluation value written in the literature. Consequently, it was proven that high precision thermodynamic data was able to obtain by using this apparatus.
(s) were evaluated, and it was confirmed these evaluated values were agreed with the calculated value from existing thermodynamic data and evaluation value written in the literature. Consequently, it was proven that high precision thermodynamic data was able to obtain by using this apparatus.
Sato, Isamu; Miwa, Shuhei; Tanaka, Kosuke; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Hirosawa, Takashi; Iwasaki, Maho; Onishi, Takashi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takai, Toshihide; Amaya, Masaki; et al.
Proceedings of 2014 Water Reactor Fuel Performance Meeting/ Top Fuel / LWR Fuel Performance Meeting (WRFPM 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2014/09
A new research program on severe accidents is lunched for the evaluation of FP release and transport behavior in BWR system. The purpose of the program is to improve the FP release and transport model using experimental database about FP chemistry focusing on Cs and I chemistry. In this program, effects of B including in control rod materials, B C for the Cs and I chemistry are paid attention. The experimental database used for the improvement will consist of results to obtain with newly-prepared test device under atmosphere with broad-ranging oxygen and/or steam partial pressure simulated those in BWR. The state of preparation for these experimental studies and analyses is introduced. In addition, the preliminary test was moved into action to show B chemical effect on Cs and I transport under one of the processes, which is deposited Cs compounds and B vapor and aerosol interaction. In this experiment, a "B stripping effect" to deposited CsI was observed.
C for the Cs and I chemistry are paid attention. The experimental database used for the improvement will consist of results to obtain with newly-prepared test device under atmosphere with broad-ranging oxygen and/or steam partial pressure simulated those in BWR. The state of preparation for these experimental studies and analyses is introduced. In addition, the preliminary test was moved into action to show B chemical effect on Cs and I transport under one of the processes, which is deposited Cs compounds and B vapor and aerosol interaction. In this experiment, a "B stripping effect" to deposited CsI was observed.
Imai, Suguru*; Nakajima, Yuki*; Taguchi, Kenji*; Kashiwa, Tatsuya*; Kitazawa, Toshihide*; Suzuki, Masahiro; Segawa, Tomoomi; Fujii, Kanichi
Proceedings of 2011 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP 2011) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2011/10
As a part of the nuclear fuel cycle in Japan, the mixed oxide (MOX) fuels are produced through the microwave heating of the Pu/U mixed nitrate solution obtained from spent fuels. This paper investigated the electric power absorption of the solid Pu/U mixed nitrate medium in a cylindrical oven cavity and the effect of the input polarized waves. The numerical simulations have revealed that the incidence of the circularly polarized wave improves the uniformity of the absorbed power of the medium placed in the cylindrical cavity.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-066, 99 Pages, 2000/03
The active fault survey tunnel across the Mozumi-Sukenobu Fault is located at the Kamioka Mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. At present, the comprehensive studies of the active fault are being carried out in this tunnel. In this report, the results of the laboratory test using steel pipes and numerical simulation for the new ground stress measuring instrument were presented in order to inspect the stress state around the active fault.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-063, 242 Pages, 1999/03
The active fault survey tunnel across the Mozumi-Sukenobu Fault is located at the Kamioka Mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. At present, The comprehensive studies of the active fault are being carried out in this tunnel. The results of the laboratory test and numerical simulation for the new ground stress measuring instrument were presented in order to inspect the stress state around the active fault.
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Sakogaichi, Kaoru*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Takebe, Akimitsu*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*; Yamanouchi, Hirofumi*
JNC TJ7420 2005-041, 129 Pages, 1999/03
The active fault survey tunnel that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (a member of the Atotsugawa fault system) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault such as the earthquake mechanism is done by using this tunnel. The purpose of this investigation is to define the hydrological characteristics inside and around the Mozumi - Sukenobu fault crush zones. The investigation is mainly Lugeon test and simple permeability test inside and around the crush zones.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-038, 39 Pages, 1998/03
The active fault study drift that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (a member of the Atotsugawa fault system) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault is done in this drift. The purpose of this investigation is to obtain the data of the basis to clear the hydro-geological structure around the active fault. From December 1, 1997 to March 13, 1998, the pore pressure was measured using the hole.
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Shingu, Kazuki*; Sakogaichi, Kaoru*; Nishikawa, Yuji*; Okada, Yoichi*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*
JNC TJ7420 2005-035, 152 Pages, 1998/03
The active fault survey tunnel that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (MSF) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault, such as the study of the earthquake mechanism and the development of the new initial stress measurement method is done by using this tunnel. One of the purposes of this investigation is to define the three-dimensional distribution of the MSF by geological survey, on the basis of the seismic and geophysical studies on this fault. The other purpose is to develop the new initial stress measurement method.
Takemura, Tomoyuki*; Shingu, Kazuki*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Okada, Yoichi*; Takebe, Akimitsu*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Inoue, Toshio*
JNC TJ7420 2005-033, 128 Pages, 1998/03
The active fault survey tunnel that crossed the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault (a member of the Atotsugawa fault system) is located at the Kamioka mine, northern Gifu prefecture, Central Japan. The comprehensive study of the active fault is done by using this tunnel. The purpose of this investigation is to define the hydrological characteristics of the Mozumi-Sukenobu fault crush zones. The permeability of the crush zones is measured by the Lugeon test and the simple injection test.
; Shingu, Kazuki*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Yamashita, Mitsugu*; ;
PNC TJ7187 97-002, 586 Pages, 1997/11
None
Shingu, Kazuki*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Nakajima, Toshihide*
PNC TJ7187 97-001, 170 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
Hama, Hiroshi*; Yamada, Tsuyoshi*; Ide, Mitsuyoshi*; Takahashi, Eiichiro*; Yamamoto, Katsuya*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Watabe, Takeo*
JNC TJ7440 2005-074, 270 Pages, 1995/05
In 1997, DH-5 hole was drilled at P.N.C.(present J.N.C.) Toki Branch of Tono Geoscience Centr in Gifu prefecture. The borehole was drilled to a depth of 502.3 meters in Toki granite in order to investigate the deep groundwater. This report describes the investigation of the groundwater conducted at depth from 323.8 to 330.8 meters to make clear geological, hydrogeological and geochemical characteristics of study area. The investigation includes the following items;i) Sampling of the groundwaterii) Measurement of physical chemistry parameters of the groundwater in the borehole iii) Chemicaal analysis of the main composition of the groundwater during the continuous samplingiv) Chemical analysis of the groundwater It has become clear the following points;* The physical chemistry parameters of groundwater was alkalic, low deoxidize and buffer ability. There were few total ions and sulfide ions in the groundwater.* The isotopic analysis showed that the groundwater was regarded as rainwater in origin on the side of the Pacific Ocean and was relatively young with the age of a few decades.* According to the tri-linear diagram, the groundwater was classified into Ca(HCO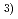
 type. Based on hydrochemical facies, the groundwater was classified into Ca
type. Based on hydrochemical facies, the groundwater was classified into Ca sup+ Na
sup+ Na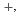 and HCO
and HCO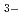 Cl
Cl SO
SO

 in the cation and anion facies, respectively.* Nitrite oxidizing bacteria, nitrite reducing bacteria and nitrate reducing bacteria were detected in the groundwater by the bacteria analysis.
in the cation and anion facies, respectively.* Nitrite oxidizing bacteria, nitrite reducing bacteria and nitrate reducing bacteria were detected in the groundwater by the bacteria analysis.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Sato, Eitaro*; Adachi, Kazuhiro*; Kudo, Masakatsu*; Ishizuka, Yoshiaki*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Nakajima, Toshihide*
JNC TJ7400 2005-007, 214 Pages, 1995/03
The objective of this study is to prove the long-term geoscientific stability of the geological environment. The survey will clarify the extent and degree of mechanical change influenced by fault movement deep underground as well as the surface. The study was conducted in Mozumi of the Kamioka mining district, located in the Atotsu active fault system zone. This year, a study was carried out by measuring stress state and rock properties around the active fault. At first, stress measurement by double fracturing was conducted at Nagato No.1 borehole in order to compare a newly measured stress state with the one done last year. The difference between them was very little. Secondly, the first stress measurement was carried out on the Nagato No.3 borehole.
Shingu, Kazuki*; Horinokuchi, Kenji*; Nakajima, Toshihide*; Furumori, Hisayoshi*
JNC TJ7400 2005-005, 250 Pages, 1994/03
The objective of this study is to prove the long-term geoscientific stability of a geological environment. This was accomplished by measurement of stress and study of rock properties around an active fault in the Atotsu fault system near Mozumi in the Kamioka mining district. A future goal of the project is to clarify the areal extent and degree to which fault movement at the surface and at depth affects mechanical changes.
Takai, Toshihide; Takada, Juntaro; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Fundamental knowledge of the characteristics of the Cs-chemisorbed deposits was important for decommissioning of the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F). Some important information was obtained from foregoing experiments results. Nevertheless, it was not enough for covering 1F accident conditions. Purpose of this study was to confirm the Cs-chemisorption mechanism in a wider range of temperature and atmosphere. Synthesis results of Cesium silicates, which was expected to form under a severe accident, was described in this presentation.
Takai, Toshihide; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
To develop reliable thermodynamic database of fission products is necessary for more accurate evaluation of fission product release and transport behavior using progression process analysis code under severe accident. This presentation introduces maintenance situation of high temperature mass spectrometer and reliability evaluation result.
 by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometry
by Knudsen effusion mass spectrometryNakajima, Kunihisa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Gaseous cesium metaborate, CsBO (g), is predicted to be the main cesium vapor species, depending on temperature, in severe light water reactor accidents according to thermodynamic analysis, which treats chemical reactions between boron and cesium. But quality of the thermodynamic data of CsBO
(g), is predicted to be the main cesium vapor species, depending on temperature, in severe light water reactor accidents according to thermodynamic analysis, which treats chemical reactions between boron and cesium. But quality of the thermodynamic data of CsBO (g) used in this thermodynamic analysis is considered to be poor. Thus, Knudsen-effusion mass-spectrometric measurement of CsBO
(g) used in this thermodynamic analysis is considered to be poor. Thus, Knudsen-effusion mass-spectrometric measurement of CsBO was performed to obtain reliable thermodynamic quantities of CsBO
was performed to obtain reliable thermodynamic quantities of CsBO (g). The standard enthalpy values of formation of CsBO
(g). The standard enthalpy values of formation of CsBO (g),
(g), 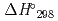 (CsBO
(CsBO ,g), were obtained by the 2nd law and the 3rd law treatments from measured vapor pressures and found to be -700.6
,g), were obtained by the 2nd law and the 3rd law treatments from measured vapor pressures and found to be -700.6  9.8kJ/mol and -698.0
9.8kJ/mol and -698.0  10.6kJ/mol, respectively. These two values agree within the error limits and the evaluated thermodynamic data of CsBO
10.6kJ/mol, respectively. These two values agree within the error limits and the evaluated thermodynamic data of CsBO (g) are considered to be reliable.
(g) are considered to be reliable.
Osaka, Masahiko; Miwa, Shuhei; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Takai, Toshihide; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Nagase, Fumihisa
no journal, ,
Fission product (FP) chemistry under the LWR severe accident (SA) conditions should be deeply understood for more accurate evaluation of FP release and transport behavior, which can lead to reduction of uncertainty in the evaluation of source term. This paper describes the contents of research program that is focused on the FP chemistry. Results of the FP chemical form just after release from fuel by a chemical equilibrium calculation considering dependences of release kinetics for related elements showed that dominant vapor species have changed according to the atmospheres and Cs-B-O species became dominant in the presence of B C. As for the Cs-chemisorption behavior, it was found by a literature review that resultant compounds formed by the Cs-chemisorption onto the SS could be divided into two categories, Cs-Cr-O and Cs-Si-O compounds.
C. As for the Cs-chemisorption behavior, it was found by a literature review that resultant compounds formed by the Cs-chemisorption onto the SS could be divided into two categories, Cs-Cr-O and Cs-Si-O compounds.
 O-B
O-B O
O system
systemNakajima, Kunihisa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
There are limited thermodynamic data available for compounds in the Cs-B-O system. We have a plan to evaluate the thermodynamic properties of the cesium borates from their equilibrium vapor pressures determined by a Knudsen effusion mass spectrometry. Cesium borates such as triborate, CsB O
O , were prepared and phase relations in the Cs-B-O system were investigated using a powder X-ray diffractometer. As one of the results, it was found that CsB
, were prepared and phase relations in the Cs-B-O system were investigated using a powder X-ray diffractometer. As one of the results, it was found that CsB O
O has an orthorhombic crystal structure.
has an orthorhombic crystal structure.