Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; Ono, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 47(1), p.1 - 7, 2022/03
Background: In Japan, new regulations that revise the dose limit for the lens of the eye (the lens), operational quantities, and measurement positions for the lens dose were enforced in April 2021. Based on the international safety standards, national guidelines, the results of the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund of the Nuclear Regulatory Authority, and other studies, the Working Group of Radiation Protection Standardization Committee, the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS) developed a guideline for radiation dose monitoring for the lens. Materials and Methods: The Working Group of the JHPS discussed the criteria of non-uniform exposure and the management criteria set to not exceed the dose limit for the lens. Results and Discussion: In July 2020, the JHPS guideline was published. The guideline consists of three parts: main text, explanations, and 26 questions. In the questions, the corresponding answers were prepared, and specific examples were provided to enable similar cases to be addressed. Conclusion: With the development of guideline on radiation dose monitoring of the lens, radiation managers and workers will be able to smoothly comply with revised regulations and optimise radiation protection.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Iwai, Satoshi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-15) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
 O
O -Ti
-Ti O
O system
systemTakahama, Ryusei*; Ishii, Toi*; Indo, Daigo*; Arizono, Mitsutoshi*; Terakura, Chieko*; Tokura, Yoshinori*; Takeshita, Nao*; Noda, Masaaki*; Kuwahara, Hideki*; Saiki, Takuo*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 4(7), p.074401_1 - 074401_11, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.3(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) D
D measured with inelastic neutron spectroscopy
measured with inelastic neutron spectroscopyYamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Iimura, Soshi*; Muraba, Yoshinori*; Bang, J.*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Honda, Takashi*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(22), p.220505_1 - 220505_6, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Inelastic neutron scattering was performed for an iron-based superconductor, where most of D (deuterium) replaces oxygen, while a tiny amount goes into interstitial sites. By first-principle calculation, we characterize the interstitial sites for D (and for H slightly mixed) with four equivalent potential minima. Below the superconducting transition temperature Tc = 26 K, new excitations emerge in the range 5-15 meV, while they are absent in the reference system LaFeAsO F
F . The strong excitations at 14.5 meV and 11.1 meV broaden rapidly around 15 K and 20 K, respectively, where each energy becomes comparable to twice of the superconducting gap. The strong excitations are ascribed to a quantum rattling, or a band motion of hydrogen, which arises only if the number of potential minima is larger than two.
. The strong excitations at 14.5 meV and 11.1 meV broaden rapidly around 15 K and 20 K, respectively, where each energy becomes comparable to twice of the superconducting gap. The strong excitations are ascribed to a quantum rattling, or a band motion of hydrogen, which arises only if the number of potential minima is larger than two.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:98.93(Quantum Science & Technology) D
D
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Iimura, Soshi*; Muraba, Yoshinori*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Sagayama, Hajime*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Kuramoto, Yoshio*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(17), p.174415_1 - 174415_6, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Magnetic excitations in a heavily electron-doped antiferromagnet, LaFeAsO D
D , have been investigated using powder inelastic neutron scattering. Unlike other parent compounds of the iron-based superconductors, the magnetic excitation gap in LaFeAsO
, have been investigated using powder inelastic neutron scattering. Unlike other parent compounds of the iron-based superconductors, the magnetic excitation gap in LaFeAsO D
D was not detected down to the lowest measured temperature of 4 K. This result can be understood as a result of quasi-isotropy within the ab plane, which is consistent with the band calculation result that the
was not detected down to the lowest measured temperature of 4 K. This result can be understood as a result of quasi-isotropy within the ab plane, which is consistent with the band calculation result that the 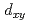 orbital plays the dominant role in the magnetism of LaFeAsO
orbital plays the dominant role in the magnetism of LaFeAsO H
H . In addition, the intensities of the magnetic excitations in this phase are much stronger than those in nondoped LaFeAsO. Even in the paramagnetic phase, the magnetic excitation in LaFeAsO
. In addition, the intensities of the magnetic excitations in this phase are much stronger than those in nondoped LaFeAsO. Even in the paramagnetic phase, the magnetic excitation in LaFeAsO D
D persists. These results corroborate recent studies showing that the electron doping enhances the localized nature in this system.
persists. These results corroborate recent studies showing that the electron doping enhances the localized nature in this system.
Nakamura, Shota*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Shimizu, Yusei*; Kittaka, Shunichiro*; Kono, Yohei*; Haga, Yoshinori; Pospisil, J.; Yamamoto, Etsuji
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.123 - 127, 2018/11
Ueno, Yasuhiro*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 238(1), p.14_1 - 14_6, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:86.37(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Nagaoka, Mika; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-001, 115 Pages, 2017/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2015. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Strasser, P.*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Ito, Takashi; Iwasaki, Masahiko*; et al.
Hyperfine Interactions, 237(1), p.124_1 - 124_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:90.97(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Sakauchi, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-030, 115 Pages, 2015/12
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2014. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Soda, Minoru*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Ibuka, Soshi*; Kawana, Daichi*; Sato, Taku*; Nambu, Yusuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034001_1 - 034001_6, 2015/09
Izawa, Kazuhiko; Tonoike, Kotaro; Sono, Hiroki; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
JAEA-Conf 2014-003, Appendix (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2015/03
Critical assemblies of thermal neutron system are decreasing in number in spite of their important roles in the reactor physics research. On the other hand, the extension of the utilization term of the LWRs brings new research themes requiring critical experiments of thermal neutron system. JAEA is modifying the Static Critical Experiment Facility (STACY) to revive the critical experiments. The modified STACY will be an infrastructure for the experimental research of reactor physics on thermal neutron system. The primary mission of the modified STACY at present is the critical experiments for fuel debris to contribute to the criticality safety control of the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. This report introduces the plan of criticality safety research in Japan Atomic Energy Agency following the accident, and describes the role of the modified STACY in the retrieval work of fuel debris from the damaged reactor.
Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; Goto, Ichiro*; Kibe, Satoshi*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-040, 115 Pages, 2015/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), the effluent control of liquid waste discharged from the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been performed. This report describes the effluent control results of the liquid waste in the fiscal year 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other nuclear fuel material usage facilities were much lower than the limits authorized by the above regulations.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Miyagawa, Naoto; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Inoue, Kazumi; Yoshii, Hideki; Otani, Kazunori*; Hiyama, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-041, 115 Pages, 2014/01
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and bylaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2012, from 1st April 2012 to 31st March 2013. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Miyagawa, Naoto; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Hiyama, Yoshinori; Yoshii, Hideki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Goto, Ichiro*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-005, 116 Pages, 2013/05
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and byelaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2011, from 1st April 2011 to 31st March 2012. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
Hatae, Takaki; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Hayashi, Toshimitsu; Yoshida, Hidetsugu*; Ono, Takehiro; Kusama, Yoshinori
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(10), p.10E344_1 - 10E344_3, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:56.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)A prototype YAG laser system for the edge Thomson scattering system in ITER has been newly developed. Performance of the laser amplifier was improved by using flow tubes made of samarium-doped glass; the small signal gain reached 20 at its maximum. As a result, an output energy of 7.66 J at 100 Hz was successfully achieved, and the performance exceeded the target performance (5 J, 100 Hz).
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Fujita, Hiroki; Kono, Takahiko; Hiyama, Yoshinori; Yoshii, Hideki*; Kikuchi, Masaaki*; Otani, Kazunori*; Goto, Ichiro*
JAEA-Review 2012-006, 114 Pages, 2012/03
Based on the regulations (the safety regulation of Tokai reprocessing plant, the safety regulation of nuclear fuel material usage facilities, the radiation safety rule, the regulation about prevention from radiation hazards due to radioisotopes, which are related with the nuclear regulatory acts, and the local agreement concerning with safety and environment conservation around nuclear facilities, the water pollution control law, and byelaw of Ibaraki prefecture), this report describes the effluent control results of liquid waste discharged from the JAEA's Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories in the fiscal year 2010, from 1st April 2010 to 31st March 2011. In this period, the concentrations and the quantities of the radioactivity in liquid waste discharged from the reprocessing plant, the plutonium fuel fabrication facilities, and the other facilities were much lower than the authorized limits of the above regulations.
Izawa, Kazuhiko; Aoyama, Yasuo; Sono, Hiroki; Ogawa, Kazuhiko; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality (ICNC 2011) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2012/02
For reactor physics and criticality safety researches, the Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) will be modified. In the modification, the present STACY, solution-fuel-type homogeneous cores, will be converted to fuel-pin-type heterogeneous cores moderated by light water. For nuclear safety design of the modified STACY, computational analyses have been carried out by using a Monte Carlo code MVP and a transport code system DANTSYS with cross-section data based on the JENDL-3.3. In the analyses, basic nuclear characteristics have been evaluated, such as criticality, water-level worth and reactor shutdown margin. By the results of these analyses, the feasibility of reactivity control mechanism and the sufficiency of reactor shutdown margin of the modified STACY were confirmed. In addition, temperature and void coefficients of reactivity and kinetic parameters were obtained to comprehend nuclear characteristics of the modified STACY.
 H
H
Matsuishi, Satoru*; Hanna, Taku*; Muraba, Yoshinori*; Kim, S. W.*; Kim, J. E.*; Takata, Masaki*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Smith, R. I.*; Hosono, Hideo*
Physical Review B, 85(1), p.014514_1 - 014514_6, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:84.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed the neutron powder diffraction and synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurements on CeFeAsO (D,H)
(D,H) (
( = 0.0-0.48) as a representative of 1111-type family of iron-based superconductors LnFeAsO
= 0.0-0.48) as a representative of 1111-type family of iron-based superconductors LnFeAsO H
H (
(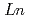 = lanthanoid). These results strongly suggest that H
= lanthanoid). These results strongly suggest that H ions exclusively occupy the oxygen sites in both samples, regardless of the hydrogen species in the starting material.
ions exclusively occupy the oxygen sites in both samples, regardless of the hydrogen species in the starting material.