Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Seno, Yasuhiro*; Nakayama, Masashi; Sugita, Yutaka; Tanai, Kenji; Fujita, Tomoo
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-011, 164 Pages, 2016/11
The cementitious materials are used as candidate materials for the tunnel support of the deep geological repository of high-level radioactive wastes (HLW).Generally the pH of leachate from concrete mixed Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) shows a range of 12 to 13. The barrier function of bentonite used as a buffer material and that of host rock might be damaged by the high alkaline leachate from cementitious materials. Therefore, low alkalinity that does not damage each barrier function is necessary for cementitious materials used for the tunnel support system of the HLW geological repository. JAEA has developed a low alkaline cement named as HFSC (Highly Fly-ash contained Silicafume Cement) which the pH of the cement leachate could lower approximately 11. We have confirmed the applicability of HFSC for the tunnel support materials, by using experimentally as the shotcreting materials to the part of gallery wall at 140m, 250m and 350m depth in Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. And moreover, HFSC has been used as the cast-in-place concrete for the shaft lining concrete at the depth of 374m-380m. This Data/Code summarized the past HFSC mix proportion test results about the fresh concrete properties and hardened concrete properties, in order to offer the information as a reference for selecting the mix proportion of HFSC concrete adopted to the disposal galleries et al. in the future.
Seno, Yasuhiro*; Noguchi, Akira*; Nakayama, Masashi; Sugita, Yutaka; Suto, Shunkichi; Tanai, Kenji; Fujita, Tomoo; Sato, Haruo*
JAEA-Technology 2016-011, 20 Pages, 2016/07
Cementitious materials are expected to be used for the construction of an underground repository for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes. Ordinary Portland Cement(OPC) would conventionally be used in the fields of civil engineering and architecture, however, OPC has the potential to generate a highly alkaline plume (pH 12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
12.5), which will likely degrade the performance of other barriers in the repository such as the bentonite buffer and/or host rock. Low alkaline cementitious materials are therefore being developed that will mitigate the generation of a highly alkaline plume. JAEA has developed a High-volume Fly ash Silica fume Cement (HFSC) as a candidate low alkaline cementitious material. The workability of the HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by conducting In-situ full scale construction tests in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. This report summarizes the results of immersion tests to assess the long-term pH behavior of hardened HFSC cement pastes made with mix designs that are expected to be able to be used in the construction of an underground repository in Japan.
Hirano, Toru*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Hikima, Ryoichi; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2011-019, 51 Pages, 2011/09
In order to establish the scientific and technical basis for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is proceeding with the geoscientific research in the research galleries excavated at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). One of the scientific and technical objective of this project is to understand the change of geological environment due to excavation of research galleries. The investigation described herein is the measurement of the rock strain / displacement while pre-excavation grouting or excavating of the shaft around the GL.-200m level research gallery.
Hirano, Toru; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2010-013, 51 Pages, 2010/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is proceeding with the geoscientific research at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In this project, developing a conceptual model of the geological environment is one of the scientific and technical objectives. Once excavation of research galleries began, the model could be improved using more detailed information from underground-based investigations. The investigation described here in is the measurement of the rock mechanical properties and initial stress of the rock mass around the GL.-200m level research gallery. The average physical and mechanical properties determined using core from the Toki Granite on this level is consistent with the properties from MIZ-1 testing. In situ stress measurements indicate that the  1 is 10.6 MPa and horizontal in the NW-SE direction matched to the observations in MIZ-1 at the same depth. This indicates that the surface based investigations in MIZ-1 are valid at this level.
1 is 10.6 MPa and horizontal in the NW-SE direction matched to the observations in MIZ-1 at the same depth. This indicates that the surface based investigations in MIZ-1 are valid at this level.
Hirano, Toru; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2010-005, 41 Pages, 2010/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is carrying out a geoscientific research project at the Mizunami, to establish the scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. The project is currently in Phase II. The Phase II goals are to construct models of the geological environment from all investigation results obtained during the construction. These models describe the geological environment at the construction points that were affected by excavation of the shafts and the galleries. To achieve these goals, we are examing the relationship between scope of investigation and accuracy of data, an assessment of investigation methods, validation of the Phase I geological environment models and construction of block scale geological environment models. As part of these studies, rock mechanical investigations involving both laboratory testing and in situ stress measurements every 100m along the shaft. This report presents the FY2008 activities undertaken to achieve the above goals.
Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Yamada, Atsuo*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2010-002, 48 Pages, 2010/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is advancing the geo-scientific research at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory. In Phase II of the research, improvement on the previous conceptual model of the geological environment is one of the objectives. So the additional rock mechanical investigations on the GL.-100m level research gallery was conducted. As a result, the average rock physical and mechanical properties are consistent with the results from MIZ-1 testing. This means that the surface based investigations in MIZ-1 are valid at this level. Almost all in situ stress measurements indicate that the maximum principal stress is oriented in the NW-SE direction and match the observations in MIZ-1 at GL.-200m depth. But the observed stress level is not the expected value extrapolated from the MIZ-1 results. This suggests that the in situ stress has likely been decoupled at the rock boundary located about GL.-150m level between the Toki Lignite-bearing formation and the Toki granite.
Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Yamada, Atsuo*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2009-031, 58 Pages, 2009/11
JAEA is advancing the geo-scientific research at the Mizunami Underground Laboratory. In this project, the purpose of rock mechanics investigations is to understand the rock mechanical conditions deep underground and to construct a rock mechanical model of this site. This report describes the rock mechanics results from MIZ-1 borehole investigations. A brief summary is shown as follows. The rock mechanical properties are consistent with the results of similar investigations in the nearby Shobasama site. The AE/DRA and ASR stress measurement give very low confidence results due to very small deformation during drilling. The DSCA and hydraulic fracturing stress measurement show that the horizontal, maximum principal stress is oriented to NW-SE. About 600(m) depth, the in situ stress state is reverse fault type. But below it, the stress state changed to a wrench or normal fault type. In consideration of the investigations and geological model, we proposed a rock mechanical model.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-001, 110 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2006 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Mikake, Shinichiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Amano, Kenji; Oyama, Takuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Hama, Katsuhiro; Yoshida, Haruo*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-073, 99 Pages, 2009/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at MIU is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following results of the research and development performed in 2005 fiscal year, as a part of the Construction Phase based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation at the MIU Construction Site, (2) Construction at the MIU Construction Site, (3) Research Collaboration.
Nishio, Kazuhisa; Oyama, Takuya; Mikake, Shinichiro; Mizuno, Takashi; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Amano, Kenji; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Hama, Katsuhiro; Seno, Yasuhiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-072, 28 Pages, 2009/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is developing a geoscientific research project named the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) project in crystalline rock environment in order to establish scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of HLW. Geoscientific research at the MIU project is planned to be carried out in three phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase 1), Construction Phase (Phase 2) and Operation Phase (Phase 3). Currently, the project is under the Construction Phase. This document presents the following 2008 fiscal year plan based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2002, (1) Investigation Plan, (2) Construction Plan, (3) Research Collaboration Plan, etc.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-090, 52 Pages, 2008/11
This report describes the results of the works in the fiscal year 2007. In Chapter 1, we described the overview and background of this study. In Chapter 2 a reaction theory of pressure dissolution of quartz was proposed and by using a homogenization analysis the dissolution of quartz in bentonite was simulated by a modified diffusion model. In Chapter 3 CLSM was used to acquire clearly focused three-dimensional images of granite specimens of Mizunami underground lab for stress relaxation tests, and observed the change of micro-scale structure including the mineral configuration under applying compression stress. The local strain distributions suggest that a shearing mode is dominant in the granite samples. In Chapter 4 a strong discontinuity concept is introduced in the micro-scale problem of the multi-scale homogenization analysis, and Toki granite sample problems were solved.
Seno, Yasuhiro*; Nakama, Shigeo; Yamada, Atsuo*; Hirano, Toru; Sato, Toshinori*
JAEA-Research 2008-084, 35 Pages, 2008/11
To establish a scientific and technical basis of geological disposal of high level radioactive waste, Japanese Atomic Energy Agency is advancing the geo-scientific research project of Mizunami Underground laboratory (MIU) in crystalline rock environment at Tono Geo-science Center. At MIU, the geo-scientific research is planned to be carried out in three Phases over a period of 20 years; Surface-based Investigation Phase, Construction Phase and Operation Phase. Currently, the Project is under the Construction Phase. This report presents the following results about rock mechanics studies conducted in the 2006 fiscal year, (1) The boring investigation for rock mechanics, from the connection gallery opened on G.L.-100m, (2) The advanced study for determination of three dimensional distributions of the initial rock stress, (3) The advanced study to evaluation of rock-stress using boring cores, (4) The basic study on crystalline rock for evaluation of long-term behavior.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Seno, Yasuhiro*; Hirano, Toru; Nakama, Shigeo; Matsui, Hiroya
JAEA-Research 2008-065, 51 Pages, 2008/08
This report describes the results of the works in the fiscal year 2007. In Chapter 1, we described the overview and background of this study. In Chapter 2, the result of continuing creep test of Tage tuff which was started from the fiscal year 1997 was described. Although there was some annual variability, the precious data were obtained. In Chapter 3, the control program for the generalized relaxation test was developed. The generalized relaxation test of Toki granite was conducted in order to get basically data. In Chapter 4, the extended constitutive equation of variable compliance was analytically discussed. Using the data obtained in Chapter 3, the parameters of Toki granite of the constitutive equation were obtained and numerical simulation was conducted.
Toida, Masaru*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Seno, Shoji*; Atsumi, Hiroyuki*; Ogata, Nobuhisa
JAEA-Research 2008-035, 89 Pages, 2008/03
"Geoscientific research" performed at the Tono Geoscience Center is developing site investigation, characterization and assessment techniques for understanding of geological environment. Their important themes are to establish a methodology for analyzing uncertainties in heterogeneous geological environment, and to develop investigation techniques for reducing the uncertainties efficiently. This study proposes a new approach where all the possible options in the models and data-sets that cannot be excluded in the light of the evidence available, are identified. This approach enables uncertainties associated with the understanding at a given stage of the site characterization to be made explicitly using an uncertainty analysis technique based on Fuzzy geostatistics. This, in turn, supports the design of the following investigation stage to reduce the uncertainties efficiently. In the study, current knowledge had been compiled, and the technique had been advanced through geological modeling and groundwater analyses in the Tono area. This report systematized the uncertainty analysis methodology associated with the characterization of the geological environment, and organized the procedure of the methodology with the application examples in the study. This report also dealt with investigation techniques for reducing the uncertainties efficiently, and underground facility design options for handling geological uncertainties based on the characterization of the geological environment.
Ichikawa, Yasuaki*; Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Research 2008-005, 60 Pages, 2008/03
In this research we aim to clarify a long term behavior of crystalline rocks, and performed the following subjects: (1) Uniaxial and stress relaxation tests under observation of a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) by using granite specimens of Mizunami underground lab. (2) Pressure dissolution experiment using specimens of quartz single crystal and glass beads. (3) Theory establishment of pressure dissolution of quartz and a homogenization analysis for quartz dissolution. In Chapter 2 CLSM was used to acquire clearly focused three-dimensional images of granite specimens of Mizunami underground lab for uniaxial and stress relaxation tests, and observed the change of microscale structure including the mineral configuration under applying compression stress. The local strain distributions were calculated by using quadrilateral meshes of finite elements arranged on the surface of each specimen. In Chapter 3 we performed pressure dissolution experiments using specimens of quartz single crystal and glass beads, since the dissolution reaction is engaged with a deformation and failure process of polycrystalline rock. After applying stress the surface of contacted area of quartz was observed by CLSM and found traces of dissolution and reprecipitation. In Chapter 4 a reaction theory of pressure dissolution of quartz was proposed and by using a homogenization analysis the dissolution of quartz in bentonite was simulated.
Okubo, Seisuke*; Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Sato, Toshinori*; Hirano, Toru
JAEA-Research 2007-088, 118 Pages, 2008/03
This report describes the results of the works in the FY2005 and 2006. In Chapter 2, as the fundamental study on time-dependent behavior, followings were described; (1) The result of continuing creep test of Tage tuff which was started from the FY1997. (2) The results of multi-stage creep test of Inada granite at mid-range temperature. (3) The consideration of the generalized relaxation test. (4) The consideration of new testing method to determine the parameter in the constitutive equation supposed by Okubo. In Chapter 3, followings were described; (1) The results of rock mechanical tests of Toki granite. (2) The results of obtained parameters for the constitutive equation considering time-dependent behavior by mechanical tests and numerical simulations. Furthermore, in this report, following two related studies were attached in appendix; (1) Study on evaluating the effects of scatter in in-situ rock properties. (2) Study on new rock classification method considering long-term behavior of rock mass.
Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Sato, Toshinori*; Goke, Mitsuo*; Tada, Hiroyuki*; Sakurai, Hideyuki*
JAEA-Research 2007-081, 120 Pages, 2008/01
A 3D Crack Tensor Model analysis was carried out to predict the rock mass behavior of the complex (articulated) section at -500 m. Properties were chosen based on the Rock Mechanics Model constructed in the Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I). The Virtual Fracture Model was applied to analyze the change the hydraulic conductivity.
Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Sato, Toshinori*; Mori, Takayuki*; Morikawa, Seiji*; Tabei, Kazuto*; Suyama, Yasuhiro*; Murakami, Koji*
JAEA-Research 2007-080, 112 Pages, 2008/01
A 3D MBC(Micro-mechanics Based Continuum model) numerical analysis was carried out to predict the rock mass behavior of the complex (articulated) section at -500 m. Properties were chosen based on the Rock Mechanics Model constructed in the Surface-based Investigation Phase (Phase I).
Hirano, Toru; Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Okubo, Seisuke*
Dai-37-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.397 - 402, 2008/01
Toki granite was tested to obtain parameters for the constitutive equation and numerical simulations were carried out. The testing method was uniaxial compressive loading at the moderate a constant strain rate that is decreased after yielding to obtain the complete stress-strain curve. In addition, two kinds of the strain rate were alternately switched to obtain the parameter  from one specimen. The
from one specimen. The  represents the strength time-dependence in the constitutive equation. Based on
represents the strength time-dependence in the constitutive equation. Based on  and the complete stress-strain curve, second parameter
and the complete stress-strain curve, second parameter 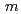 can be calculated by numerical simulations. The
can be calculated by numerical simulations. The 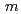 accounts for the behavior after yielding. According to the results, Toki granite has
accounts for the behavior after yielding. According to the results, Toki granite has  =52 and
=52 and 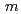 =60. Thus shows relatively low time-dependence.
=60. Thus shows relatively low time-dependence.
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Seno, Yasuhiro; Nakama, Shigeo; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Amano, Kenji; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Onoe, Hironori; Mizuno, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2007-043, 337 Pages, 2007/03
The Mizunami Underground Laboratory (MIU) Project is a comprehensive research project investigating the deep underground environment within crystalline rock being conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency at Mizunami City in Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. This report summarizes the results of the Surface-based Investigation Phase, identifies future issues and provides direction for research to be conducted during Construction Phase and Operation Phase. The results compiled in this report will be utilized for the technical knowledge base on geological disposal of HLW, and can be used to enhance the technical basis for waste disposal in general and for development of government regulations.