Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ga K-edge XANES study of Ga-exchanged zeolites at high temperatures under different atmospheres including vacuum, CO, and pressurized H
Ga K-edge XANES study of Ga-exchanged zeolites at high temperatures under different atmospheres including vacuum, CO, and pressurized H
Huang, M.*; Kinjo, Tetsuya*; Yasumura, Shunsaku*; Toyao, Takashi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Shimizu, Kenichi*; Namiki, Norikazu*; Maeno, Zen*
Catalysis Science & Technology, 13(23), p.6832 - 6838, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical) Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:83.53(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 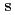 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 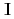 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 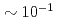 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (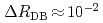 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-011, 67 Pages, 2020/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 5th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Koji; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-010, 46 Pages, 2020/07
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2020. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2020 are described in detail based on the JAEA 3rd Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-006, 66 Pages, 2019/11
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 4th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 83(11), p.434 - 440, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.1(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2019-010, 46 Pages, 2019/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2019. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2019 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-015, 89 Pages, 2019/03
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Shimizu, Mayuko; Sano, Naomi; Ueki, Tadamasa; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yasue, Kenichi*; Niwa, Masakazu
Island Arc, 28(2), p.e12295_1 - e12295_13, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.2(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-020, 46 Pages, 2019/01
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2018. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2018 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
 Ni
NiShimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Futamura, Yasunori*; Sakurai, Tetsuya*; Mizusaki, Takahiro*; Otsuka, Takaharu*
Physics Letters B, 753, p.13 - 17, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.96(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nuclear level density plays an important role in applications to nuclear energy and nuclear astrophysics, dominating neutron-capture cross sections. In this paper, we propose a new, practical and accurate method of estimating nuclear level density within the framework of the nuclear shell model, and show its feasibility and usefulness. This method is based on the idea that the level density is obtained by the number of eigenstates that is represented as a contour integral in the complex plane. We first confirm the feasibility of this method using a small system in which the exact eigenstates are available, and then calculate parity-dependent level density in  Ni, which cannot be calculated with direct eigenstate counting. We succeed in reproducing the experimental result that the
Ni, which cannot be calculated with direct eigenstate counting. We succeed in reproducing the experimental result that the 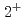 and
and 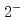 level densities are almost identical in low-energy regions, which cannot be obtained with conventional methods of estimating level densities.
level densities are almost identical in low-energy regions, which cannot be obtained with conventional methods of estimating level densities.
 imaging device of high spatial resolution ZnO scintillator
imaging device of high spatial resolution ZnO scintillatorNakazato, Tomoharu*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Yamanoi, Kohei*; Sakai, Kohei*; Takeda, Kohei*; Nishi, Ryosuke*; Minami, Yuki*; Cadatal-Raduban, M.*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(12), p.122202_1 - 122202_4, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:37.91(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate the potential of a hydrothermal method-grown ZnO as a high-spatial resolution imaging device for in-situ soft X-ray laser diagnostics by characterizing the exciton emission patterns. By plotting the emission pattern radii at each position, we estimated the evolution of the beam radius around the focal point. The beam profile of the Ni-like Ag ion plasma laser was estimated from the waist radii as 29 and 21 m, the divergence angle as 7.2 and 11 mrad and the M2 factor as 47 and 50 in the horizontal- and vertical-axis, respectively. Spatial resolution of the magnifier was estimated to be 6
m, the divergence angle as 7.2 and 11 mrad and the M2 factor as 47 and 50 in the horizontal- and vertical-axis, respectively. Spatial resolution of the magnifier was estimated to be 6 m and is expected to improve by optimizing the optics of the magnifier and using a telescope. Our results would enhance the use of ZnO as an imaging device that would play a crucial role in the development and application of soft X-ray light sources.
m and is expected to improve by optimizing the optics of the magnifier and using a telescope. Our results would enhance the use of ZnO as an imaging device that would play a crucial role in the development and application of soft X-ray light sources.
Tanaka, Momoko; Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Yamanoi, Kohei*; Sakai, Kohei*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Ochi, Yoshihiro; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2011-001, p.126 - 128, 2011/03
The spatial resolution of hydrothermal method grown zinc oxide (ZnO) scintillator was evaluated using X-ray laser focused with Fresnel zone plate. The fluorescence image of the ZnO scintillator was measured to be less than 10um using CCD camera coupled with a Schbartzchild expander mirror. The availability of large size ZnO crystal up to 3-inch is quite attractive for future lithography and imaging applications.
Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Yamanoi, Kohei*; Sakai, Kohei*; Ehrentraut, D.*; Fukuda, Tsuguo*; Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kawachi, Tetsuya
Reza Kenkyu, 39(3), p.193 - 196, 2011/03
Development of light sources in the soft X-ray/X-ray region, such as laser induced plasma emission and XFEL, is in demand for applications in various fields of science, medicine, and industry, among others. To promote this endeavor, development of imaging devices as diagnostic tools in this wavelength region is required. ZnO is a prominent candidate material for high spatial and temporal resolution imaging devices because of its emission at 380 nm, lifetime of less than 1 ns, and availability of large and cheap but high quality crystals. We obtained a single shot image of ZnO emission pattern excited by an X-ray laser at the Advanced Photon Research Center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The spatial resolution was estimated to be around 10  m. This result shows that ZnO can be used as a powerful imaging device for applications such as EUV lithography.
m. This result shows that ZnO can be used as a powerful imaging device for applications such as EUV lithography.
 states in
states in 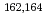 Gd populated by the
Gd populated by the  decay of
decay of 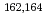 Eu
EuNagae, Daisuke*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Asai, Masato; Makii, Hiroyuki; Osa, Akihiko; Sato, Tetsuya; Ichikawa, Shinichi; Shimizu, Yoshifumi*; Shoji, Takuya*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1224, p.156 - 160, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.1(Physics, Nuclear)Oya, Kaoru*; Inai, Kensuke*; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Toma, Mitsunori*; Tomita, Yukihiro*; Kawamura, Gakushi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(10), p.695 - 703, 2009/10
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Momoko; Furukawa, Yusuke*; Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Tatsumi, Toshihiro*; Murakami, Hidetoshi*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Kagamitani, Yuji*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2008; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.130, p.501 - 505, 2009/00
We measured the time-resolved fluorescence spectra of ZnO and GaN single crystals excited by an X-ray laser operating at 13.9 nm and evaluated their scintillation properties for EUV excitation as compared with UV excitation case. For ZnO, a clear fluorescence peak of excitonic origin was observed at around 380 nm and the decay lifetime of less than 3 ns is found to be almost similar to the UV excitation case. The fluorescence at 380 nm is ideal for scintillator device design in the EUV and further applications. For GaN, the lifetimes are much longer than ZnO and the temporal profile of the EUV-excited fluorescence differs with the UV excitation case. As such, the EUV scintillation properties of ZnO is said to be more favorable than GaN. Finally, it is also demonstrated that an X-ray laser is an excellent tool for spectroscopic characterization of materials intended for next-generation lithography applications.
Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya; Shimizu, Katsusuke*; Inoue, Masahiko*; Watanabe, Mitsunori*; Iguchi, Masashi*; Sugimoto, Tomoko*; Inohara, Takashi*; Nakamura, Junichi*
JAEA-Technology 2008-076, 99 Pages, 2008/12
The primary vacuum pumping system of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) exhausts a helium (He) ash resulting from the DT-burn with excess DT fueling gas, as well as performing a variety of functions such as pump-down, leak testing and wall conditioning. A mechanical based vacuum pumping system has some merits of a continuous pumping, a much lower tritium inventory, a lower operational cost and easy maintenance, comparing with a cryopump system, although demerits of an indispensable magnetic shield and insufficient performance for hydrogen (H ) pumping are well recognized. To overcome the demerits, we newly fabricated and tested a helical grooved pump (HGP) unit suitable for H
) pumping are well recognized. To overcome the demerits, we newly fabricated and tested a helical grooved pump (HGP) unit suitable for H pumping at the ITER divertor pressure of 0.1-10 Pa. Through this R&D, we successfully established many design and manufacturing databases of large HGP units for the lightweight gas pumping. Based on the databases, we conceptually designed the ITER vacuum pumping system mainly comprising the HGP with an optimal pump unit layout and a magnetic shield. We also designed conceptually the reduced cost (RC)-ITER pumping system, where a compound molecular pump combining turbine bladed rotors and helical grooved ones was mainly used. The ITER mechanical based primary pumping system proposed has eventually been a back-up solution, whereas a cryopump based one was formally selected to the ITER for construction.
pumping at the ITER divertor pressure of 0.1-10 Pa. Through this R&D, we successfully established many design and manufacturing databases of large HGP units for the lightweight gas pumping. Based on the databases, we conceptually designed the ITER vacuum pumping system mainly comprising the HGP with an optimal pump unit layout and a magnetic shield. We also designed conceptually the reduced cost (RC)-ITER pumping system, where a compound molecular pump combining turbine bladed rotors and helical grooved ones was mainly used. The ITER mechanical based primary pumping system proposed has eventually been a back-up solution, whereas a cryopump based one was formally selected to the ITER for construction.
 Al
Al
Honda, Fuminori*; M asson, M.-A.*; Nakano, Yasunori*; Yoshitani, Naohisa*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Yamagami, Hiroshi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; et al.
asson, M.-A.*; Nakano, Yasunori*; Yoshitani, Naohisa*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Yamagami, Hiroshi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Settai, Rikio*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(4), p.043701_1 - 043701_4, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:81.62(Physics, Multidisciplinary)