Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kagi, Takumi; Araki, Daisuke; Yanai, Tomohiro; Kuwabara, Ryota; Sugaya, Naoto; Nishimura, Arashi; Ebisawa, Hiroyuki; Watahiki, Shunsuke; Tanimoto, Masataka
JAEA-Testing 2024-005, 24 Pages, 2025/03
On September 9, 2019, the strong winds of Typhoon No. 15 caused the secondary cooling system cooling tower of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) to collapse. The cooling tower collapsed from east to west, and four secondary cooling system pipes connected to it also pulled down, and all four pipes were damaged at their riser sections. Because the exterior wall slate material (asbestos slate) covering the collapsed cooling tower contained asbestos, it was necessary to ensure the safety of the workers and to minimize the impact of asbestos on the surrounding environment during the removal work. This report describes the work plan devised while complying with the relevant laws and the results of its implementation to ensure worker safety and reduce the environmental impact of asbestos during the removal work, storage management, and transportation of the asbestos slate material from the cooling tower of the secondary cooling system.
Nakagawa, Akinori; Oyokawa, Atsushi; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Sasaki, Toshiki; Okada, Shota; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Sakai, Akihiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2021-006, 186 Pages, 2021/06
Radioactive wastes generated from R&D activities have been stored in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to reduce the risk of taking long time to process legacy wastes, countermeasures for acceleration of waste processing and disposal were studied. Work analysis of waste processing showed bottleneck processes, such as evaluation of radioactivity concentration, segregation of hazardous and combustibles materials. Concerning evaluation of radioactivity concentration, a radiological characterization method using a scaling factor and a nondestructive gamma-ray measurement should be developed. The number of radionuclides that are to be selected for the safety assessment of the trench type disposal facility can decrease using artificial barriers. Hazardous materials, will be identified using records and nondestructive inspection. The waste identified as hazardous will be unpacked and segregated. Preliminary calculations of waste acceptance criteria of hazardous material concentrations were conducted based on environmental standards in groundwater. The total volume of the combustibles will be evaluated using nondestructive inspection. The waste that does not comply with the waste acceptance criteria should be mixed with low combustible material waste such as dismantling concrete waste in order to satisfy the waste acceptance criteria on a disposal facility average. It was estimated that segregation throughput of compressed waste should be increased about 5 times more than conventional method by applying the countermeasures. Further study and technology development will be conducted to realize the plan.
Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Nakajima, Junya; Yoshida, Keisuke; Kato, Saori; Nishino, Sho; Nozaki, Teo; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Tsunoda, Junichi; Sugaya, Yuki; Hasegawa, Rie; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-004, 57 Pages, 2017/03
In emergency situation of nuclear facilities, we need to estimate the radiation dose due to radiation and radioactivity to grasp the influence range of the accident in the early stage. Therefore, we prepare the case studies of dose assessment for public exposure dose and personal exposure dose and contribute them to emergency procedures. This document covers about accidents of nuclear facilities in Nuclear Science Research Institute and past accident of nuclear power plant, and it can be used for inheritance of techniques of emergency dose assessment.
Sugaya, Yuki; Sakazume, Yoshinori; Akutsu, Hideyuki; Inoue, Toshihiko; Yoshimochi, Hiroshi; Sato, Soichi; Koyama, Tomozo; Nakayama, Shinichi
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2017/00
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing the research and development facilities, "Okuma Analysis and Research Center", in order to ascertain the properties of radioactive wastes and fuel debris towards the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. This paper outlines the concept of "Laboratory-1" which will analyze low and medium level samples in the Okuma Analysis and Research Center with a focus on the research plan.
Sakatani, Keiichi; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Funabashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-008, 53 Pages, 2014/06
The safety assessment of the sub-surface disposal system should ensure that calculated dose will be lower than the dose assigned to the scenario in question during the period from now to future. In order to realize the safety disposal, we have developed several assessment tools on the GoldSim platform and calculated doses since 2008, and these assessment tools have been improved reflecting the last view of assessment. This report describes idea of assessment models and structure of assessment tools for land use scenarios.
Sugaya, Yuki; Narita, Ayumi; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 502(1), p.012040_1 - 012040_4, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sakatani, Keiichi; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Funabashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2013-015, 63 Pages, 2013/11
The safety assessment of the sub-surface disposal system should ensure that calculated dose will be lower than the dose assigned to the scenario in question during the period from now to future. In order to realize the safety disposal, we have developed several assessment tools on the GoldSim platform and calculated doses since 2008, and these assessment tools have been improved reflecting the last view of assessment. This report describes safety functions of the disposal system, idea of nuclide migration, formulas for nuclides migration, formulas of exposure dose and structure of assessment tool for groundwater scenario.
Ishibashi, Toshihiro*; Tomota, Yo*; Sugaya, Satoshi*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Horita, Zenji*; Suzuki, Hiroshi
Materials Transactions, 54(9), p.1562 - 1569, 2013/09
Bulky averaged microstructural parameters like vacancy density, texture, intergranular stress, etc. for 99.99% Cu subjected to Equal-Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) were investigated using Accelerator-based gamma-ray-Induced Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy (AIPAS) and neutron diffraction. The Doppler-broadening parameter (S) for positron annihilation peaks of AIPAS increased by the first ECAP cycle and then decreased slightly with further ECAP cycles. Upon annealing, the S recovered at a lower temperature for the eight-cycle ECAP processed sample than for the one-cycle processed sample. The texture and intergranular stresses generated by ECAP are determined by neutron diffraction analyses. Changes in FWHM and intensity of neutron diffractions monitored in situ during annealing indicate the early onset of recrystallization in the eight-cycle ECAP sample. These bulky averaged data show good agreements qualitatively with local SEM/EBSD observations and the results of mechanical tests.
Takemoto, Noriyuki; Sugaya, Naoto; Otsuka, Kaoru; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Onuma, Yuichi; Hosokawa, Jinsaku; Hori, Naohiko; Kaminaga, Masanori; Tamura, Kazuo*; Hotta, Koji*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2013-013, 44 Pages, 2013/06
A real-time simulator for operating both a reactor and irradiation facilities of a materials testing reactor, Simulator of Materials Testing Reactors, was developed for understanding reactor behavior and upskilling in order to utilize for a nuclear human resource development and to promote partnership with developing countries which have a plan to introduce nuclear power plant. The simulator is designed based on the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) and it simulates operation, irradiation tests and various kinds of anticipated operational transients and accident conditions caused by the reactor and irradiation facilities. The development of the simulator was sponsored by the Japanese government as one of the specialized projects of advanced research infrastructure in order to promote basic as well as applied researches. This report summarizes the simulation model, hardware specification and operation procedure of the simulator.
Shiina, Takuya; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Shiraishi, Iyo; Suzuki, Masao*; Sugaya, Yuki; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 52(1), p.99 - 112, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:63.72(Biology)Ishitoya, Kimihide; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Funabashi, Hideyuki
JAEA-Research 2011-046, 32 Pages, 2012/02
Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan (NSC) issued "Policy of the Safety Assessment of Sub-surface Disposal after the Period for Active Control" (April 1, 2010). Then, we investigated the parameters for dose assessment in tunnel excavation scenario and large-scale land use scenario which were described in the "Policy of the Safety Assessment", in order to perform the assessment based on actual conditions. To be concrete, we investigated the tunnel excavating speeds in Japan for the former scenario, and investigated technical standards of the filling for the latter scenario. We studied the realistic parameters for the dose assessment with the results of those investigations.
Nakatani, Takayoshi; Ishitoya, Kimihide; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Sone, Tomoyuki; Shimada, Hidemitsu*; Nakai, Kunihiro*
JAEA-Research 2009-064, 104 Pages, 2010/03
The purpose of this study was to assess exposure dose of "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios" on sub-surface disposal. It was one of "Classification of three types scenarios" in "Basic Policy for Safety Regulation Concerning Land Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (Interim Report)" formulated by the Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan. Selection of the assessed scenarios, development of the assessment tool and preliminary exposure dose assessment were conducted. Exposure dose of "Well water drinking scenario" was the highest in the assessed scenarios. This scenario assumed that the groundwater in Excavation Disturbed Zone (EDZ) was directly used as drinking water without any dilution. Although this was very conservative condition and the result exceeded 10 mSv/y, it was under the upper limit of standard dose value (10 100 mSv/y) in the Interim Report for "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios".
100 mSv/y) in the Interim Report for "Inadvertent Human Intrusion or Rare Natural Event Scenarios".
Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Sone, Tomoyuki; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Ishitoya, Kimihide; Funabashi, Hideyuki; Sasaki, Ryoichi*; Shimoda, Satoko*; Kurosawa, Mitsuru*
JAEA-Research 2009-063, 80 Pages, 2010/03
The purpose of this study was to assess exposure dose of "Likely Scenarios" and "Less-likely Scenarios" on sub-surface disposal. They were two of "Classification of three types scenarios" in "Basic Policy for Safety Regulation Concerning Land Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (Interim Report)" formulated by the Nuclear Safety Commission of Japan. Selection of the assessed scenarios, development of the assessment tool and preliminary exposure dose assessment were conducted. Maximum exposure doses for "Likely Scenarios" and "Less-likely Scenarios" were less than each standard dose value in the Interim Report (Likely Scenarios: 10 Sv/y, Less-likely Scenarios: 300
Sv/y, Less-likely Scenarios: 300 Sv/y).
Sv/y).
Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Takano, Yugo*; Kimura, Yukihiko*; Sugaya, Atsushi; Onizawa, Toshikazu
JAEA-Technology 2008-063, 135 Pages, 2008/10
This paper is reported that result of leaching tests for bituminized waste and Waste solidified by epoxy resin, done from 2003 to 2006. We've get precious knowledge and data, as follows. (1) In leaching tests for bituminized waste, it has detected iodine-129 peak, considered difficult too low energy  to detect. We've get data and knowledge of iodine-129 behavior first. Leached radioactivity for 50 days calculated by peak area was equal for about 40% and 100% of including radioactivity in bituminized waste sample. And we've get data of behavior of nitric acid ion and so on, important to study for disposal, in various condition of sample shape or leaching liquid temperature. (2) In leaching test for waste solidified by epoxy resin, we've get data of behavior of TBP, radionuclides and so on.
to detect. We've get data and knowledge of iodine-129 behavior first. Leached radioactivity for 50 days calculated by peak area was equal for about 40% and 100% of including radioactivity in bituminized waste sample. And we've get data of behavior of nitric acid ion and so on, important to study for disposal, in various condition of sample shape or leaching liquid temperature. (2) In leaching test for waste solidified by epoxy resin, we've get data of behavior of TBP, radionuclides and so on.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kamiyama, Kenji; Kondo, Satoru; Morita, Koji*; Fischer, E. A.; Brear, D. J.; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Cao, X.; et al.
JNC TN9400 2003-071, 340 Pages, 2003/08
An advanced safety analysis computer code, SIMMER-III, has been developed to investigate postulated core disruptive accidents in liquid-metal fast reactors (LMFRs). SIMMER-III is a two-dimensional, three-velocity-field, multiphase, multicomponent, Eulerian, fluid-dynamics code coupled with a space-dependent neutron kinetics model. By completing and integrating all the physical models originally intended at the beginning of this code development project, SIMMER-III is now applicable to integral reactor calculations and other complex multiphase flow problems. A systematic code assessment program, conducted in collaboration with European research organizations, has shown that the advanced features of the code have resolved many of the limitations and problem areas in the previous SIMMER-II code. In this report, the models, numerical algorithms and code features of SIMMER-III Version 3.A are described along with detailed program description. Areas which require future model refinement are also discussed. SIMMER-III Version 3.A, a coupled fluid-dynamics and neutronics code system, is expected to significantly improve the flexibility and reliability of LMFR safety analyses.
 (
(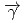 ,
,
 )
) and
and  (
(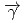 ,
,
 )
)
 reactions for
reactions for 
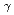 =1.5-2.4 GeV
=1.5-2.4 GeVZegers, R. G. T.*; Sumihama, Mizuki*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Dat , S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(9), p.092001_1 - 092001_4, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 = +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutron
= +1 Baryon resonance in photoproduction from the neutronNakano, Takashi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Ahn, J. K.*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Asano, Yoshihiro; Chang, W. C.*; Date, S.*; Ejiri, Hiroyasu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 91(1), p.012002_1 - 012002_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:1023 Percentile:99.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Sugaya, Toshio; ; Kitagawa, Kazushi*; Matsunaga, Shigeru*; Hayakawa, Toru*
JNC TN1400 2002-009, 400 Pages, 2002/07
no abstracts in English
Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Sugaya, Toshio; Kitagawa, Kazushi*; Matsunaga, Shigeru*; Hayakawa, Toru*
JNC TN1400 2001-004, 360 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Uto, Nariaki; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Negishi, Hitoshi; ; Sugaya, Toshio; Sakai, Takaaki
SNS2000, 16 Pages, 2000/00
None