Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Co gamma irradiation test results with calculated results
Co gamma irradiation test results with calculated resultsTakeda, Ryoma; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Seki, Misaki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Testing 2024-007, 33 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. In this report, we compare and verify these test results with the theoretical output results obtained by the calculation code created in the JAEA report (JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018). The comparison was made with the irradiation test results of SPGD, a cobalt-60 gamma irradiation facility. As a result, it was found that the calculation results reproduced the test results well when the emitter diameter was relatively small compared to the range of Compton scattered electrons by the gamma rays. On the other hand, when the emitter diameter is relatively large, the output current in the test results is only about half of the calculated output current. The self-shielding effect of the emitter may be one of the reasons for the difference in the emitter diameter, and a new formulation, such as incorporating the effect of self-shielding caused by a larger emitter diameter or a non-isotropic  -ray field as a change in the mean electron range or mean minimum energy in the calculation code, is necessary. The new formulation is necessary.
-ray field as a change in the mean electron range or mean minimum energy in the calculation code, is necessary. The new formulation is necessary.
Hirota, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Demura, Masahiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshinao*
The IV International Scientific Forum "Nuclear Science and Technologies"; AIP Conference Proceedings 3020, p.030007_1 - 030007_6, 2024/01
Dynamic strain aging (DSA) and intergranular stress corrosion cracking (intragranular SCC) occur in high temperature pressurized water simulating a boiling water reactor environment due to changes in dissolved oxygen (DO) content, respectively. In order to clearly understand the difference between these phenomena, the mechanism of their occurrence was summarized. As a result, it was found that DSA due to intragranular cracking occurred in SUS304 stainless steel at low DO  1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
1 ppb, while DSA was suppressed at DO 100 to 8500 ppb due to the formation of oxide films on the surface. On the other hand, when DO was increased to 20000 ppb, the film was peeled from the matrix, O element diffused to the grain boundary of the matrix, resulting in intergranular SCC. These results are indicated that the optimum DO concentration must be adjusted to suppress crack initiation due to DSA and intergranular SCC.
 Tc separation/concentration technology from
Tc separation/concentration technology from  Mo by (n,
Mo by (n,  ) method
) methodFujita, Yoshitaka; Hu, X.*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Takeda, Ryoma; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; Hori, Junichi*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*; Ide, Hiroshi
KURNS Progress Report 2022, P. 110, 2023/07
no abstracts in English
Takabe, Yugo; Otsuka, Noriaki; Fuyushima, Takumi; Sayato, Natsuki; Inoue, Shuichi; Morita, Hisashi; Jaroszewicz, J.*; Migdal, M.*; Onuma, Yuichi; Tobita, Masahiro*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-040, 45 Pages, 2023/03
Because of the decommission of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), the domestic neutron irradiation facility, which had played a central role in the development of innovative nuclear reactors and the development of technologies to further improve the safety, reliability, and efficiency of light water reactors, was lost. Therefore, it has become difficult to pass on the operation techniques of the irradiation test reactors and irradiation technologies, and to train human resources. In order to cope with these issues, we conducted a study on the implementation of irradiation tests using overseas reactors as neutron irradiation sites as an alternative method. Based on the "Arrangement between the National Centre for Nuclear Research and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency for Cooperation in Research and Development on Testing Reactor," the feasibility of conducting an irradiation test at the MARIA reactor (30 MW) owned by the National Centre for Nuclear Research (NCBJ) using the temperature control system, which is one of the JMTR irradiation technologies, was examined. As a result, it was found that the irradiation test was possible by modifying the ready-made capsule manufactured in accordance with the design and manufacturing standards of the JMTR. After the modification, a penetration test, an insulation continuity test, and an operation test in the range of room temperature to 300 C, which is the operating temperature of the capsule, were conducted and favorable results were obtained. We have completed the preparations prior to transport to the MARIA reactor.
C, which is the operating temperature of the capsule, were conducted and favorable results were obtained. We have completed the preparations prior to transport to the MARIA reactor.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n,  ) method, 4
) method, 4Fujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Ngo, M. C.*; Do, T. M. D.*; Hu, X.*; Yang, Y.*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 118, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Hiroko; Fuyushima, Takumi; Tsuguchi, Akira*; Nakamura, Mutsumi*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2022-007, 34 Pages, 2022/06
In order to investigate the phenomenon of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) for structural materials at the light water reactor (LWR), it is important to manage a water quality for simulating high-temperature and high-pressure water. Generally, dissolved hydrogen (DH) concentration in water loop has been controlled by the bubbling method of pure hydrogen gas or standard gas with high hydrogen concentration. However, it is necessary to equip the preventing hydrogen explosion in the area installed experimental apparatus. In general, in order to prevent accident by hydrogen, it is required to take measures such as limiting the amount of leakage, eliminating hydrogen, shutting off the power supply, and suppressing combustion before an explosion occurs. Thus, the dissolved hydrogen concentration control apparatus by electrolysis method has been developed which has two electrolysis cells to control DH concentration by electrolyzing water loop. In this study, small basic experimental devices were set up. The preliminary data were acquired regarding the simple performance of two electrolysis cells and the change of DH concentration in circulation. Based on the preliminary data, the dissolved hydrogen concentration control apparatus was designed to be connected to the high-temperature and high-pressure water loop test equipment. This report describes the test results with the small basic experimental devices for the design of the dissolved hydrogen concentration control apparatus.
Seki, Misaki; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Zhang, J.*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Hori, Junichi*; Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; et al.
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 29(1), p.2 - 9, 2022/06
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Seki, Misaki; Shibata, Akira; Nakamura, Jinichi; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018, 42 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. However, most of the results are based on the design study of the detector development and the results of in-core irradiation tests and gamma irradiation tests using Cobalt-60. In this report, a numerical code is developed based on the paper "Neutron and Gamma-Ray Effects on Self-Powered In-Core Radiation Detectors" written by H.D. Warren and N.H. Shah in 1974, in order to theoretically evaluate the self-powered radiation detectors.
Omori, Takazumi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Endo, Yasuichi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2021-015, 57 Pages, 2021/11
The JMTR reactor facility was selected as a decommissioning one in the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities formulated on April 1, 2017. Therefore, the decommissioning plan was submitted to Nuclear Regulation Authority on September 18, 2019, and the approval was obtained on March 17, 2021 after two amendments. Currently, preparations for decommissioning are underway. The JMTR reactor facility has been aged for more than 50 years since the first criticality in March 1968. However, some of the water piping systems has not been updated since its construction, and there is a possibility of pipe wall thinning due to corrosion, etc. Therefore, the integrity of the water piping was investigated for the facilities that circulate cooling water and pump radioactive liquid waste. In this investigation, the main circulation system of the reactor primary cooling system, the pool canal circulation system, the CF pool circulation system, the drainage system of the liquid waste disposal system, and the hydraulic rabbit irradiation system of the main experimental facility were measured for the pipe wall thickness using the Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement (UTM) method. These values satisfied the technical standards for research and test reactor facilities. No loss of integrity is expected to occur during the upcoming decommissioning period. In the future, we will periodically confirm that there is no wall thinning in the piping of the cooling water circulation and the water transmission system during the decommissioning period by using this result as basic data.
Hirota, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1276 - 1286, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The influence of materials of mineral-insulated (MI) cables on their electrical characteristics upon exposure to high-temperature conditions was examined via a transmission test, in the objective of achieving the stability of the potential distribution along the cable length. Occurrence of a voltage drop along the cable was confirmed for aluminum oxide (Al O
O ) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al
) and magnesium oxide (MgO), as insulating materials of the MI cable. A finite-element method (FEM)-based analysis was performed to evaluate the leakage in the potentials, which was found at the terminal end. Voltage drop yields by the transmission test and the analysis were in good agreement for the MI cable of Al O
O and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires (
and MgO materials, which suggests the reproducibility of the magnitude relationship of the experimental results via the FEM analysis. To suppress the voltage drop, the same FEM analysis was conducted, the diameter of the core wires ( ) and the distance between them (
) and the distance between them ( ) were varied. Considering the variation of
) were varied. Considering the variation of  , the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio
, the potential distribution in the MI cable produced a minimum voltage drop corresponding to a ratio 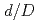 of 0.35, obtained by dividing
of 0.35, obtained by dividing  with that of the insulating material (
with that of the insulating material ( ). In case of varying
). In case of varying  , a minimum voltage drop was l/
, a minimum voltage drop was l/ of 0.5.
of 0.5.
Seki, Misaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Nagata, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Omori, Takazumi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ide, Hiroshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (62), p.9 - 19, 2020/09
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) has been contributing to various research and development activities such as the fundamental research of nuclear materials/fuels, safety research and development of power reactors, and radioisotope production since the beginning of the operation in 1968. JMTR, however, was decided as a one of decommission facilities in April 2017 and it is taken an inspection of a plan concerning decommissioning because the performance of JMTR does not confirm with the stipulated earthquake resistance. As aluminum and beryllium are used for the core structural materials in JMTR, it is necessary to establish treatment methods of these materials for the fabrication of stable wastes. In addition, a treatment method for the accumulated spent ion-exchange resins needs to be examined. This report describes the overview of these examination situations.
Watanabe, Takashi*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ozawa, Osamu*; Komanome, Hirohisa*; Akahori, Tomoyuki*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Proceedings of 2019 International Image Sensor Workshop (IISW 2019) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2019/06
Radiation hard image sensors have been developed past decades among the world. Almost papers discussed properties before and after radiation but images during radiation were not described yet. We have developed a new type of rad-hard pixel and integrated to 1.3M-pixel, 18-bit digital CMOS image sensor. Pixel area consists of several types of variation and the sensor has been analyzed during gamma ray radiation higher than 1 kGy/h up to 200 kGy. As the result, one type of pixel showed almost zero dark current increase at whole period.
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Iida, Tatsuya*; Ozawa, Osamu*; Shibagaki, Taro*; Komanome, Hirohisa*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
QST-M-16; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2017, P. 67, 2019/03
no abstracts in English
Otsuka, Noriaki; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Shibagaki, Taro*; Komanome, Hirohisa*
Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2017) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2018/11
no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Otsuka, Noriaki; Watanabe, Takashi*; Tanaka, Shigeo*; Ozawa, Osamu*; Komanome, Hirohisa*; Ueno, Shunji*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2017) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2018/11
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Takashi*; Ozawa, Osamu*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki
Denki Gakkai-Shi, 138(8), p.529 - 534, 2018/08
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Hiroko; Hirota, Noriaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 5(2), p.17-00594_1 - 17-00594_12, 2018/04
no abstracts in English
Otsuka, Kaoru; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Nagata, Hiroshi; Omori, Takazumi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
UTNL-R-0496, p.13_1 - 13_11, 2018/03
no abstracts in English
Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Uehara, Toshiaki*; Ueno, Shunji*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Kumahara, Hajime*; Shibagaki, Taro*; Komanome, Hirohisa*
JAEA-Technology 2017-026, 26 Pages, 2018/02
Under severe accidents, high-integrity transmission techniques are necessary so as to monitor the situation of the nuclear power plant. In this study, effects of gamma irradiation up to 10 Gy on properties of optical devices were evaluated toward the development of a radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system using visible light. After the irradiation, for the LEDs, the total luminous flux decreased and the browning of resin lenses occurred. Meanwhile, the current-voltage characteristics hardly changed. For the PDs, the light sensitivity decreased and the browning of resin window occurred. The dark currents of PDs did not become large enough to adversely affect transmission. These results indicated that both the decreases of the total luminous flux of the LEDs and the light sensitivity of the PDs were mainly caused by not the degradation of the semiconductor parts but the browning of the resin parts by the irradiation. In addition, basic decrease behaviors of light transmission of several different types of glasses by gamma irradiation were also obtained so as to select the suitable optical windows and filters for the developing radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system.
Gy on properties of optical devices were evaluated toward the development of a radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system using visible light. After the irradiation, for the LEDs, the total luminous flux decreased and the browning of resin lenses occurred. Meanwhile, the current-voltage characteristics hardly changed. For the PDs, the light sensitivity decreased and the browning of resin window occurred. The dark currents of PDs did not become large enough to adversely affect transmission. These results indicated that both the decreases of the total luminous flux of the LEDs and the light sensitivity of the PDs were mainly caused by not the degradation of the semiconductor parts but the browning of the resin parts by the irradiation. In addition, basic decrease behaviors of light transmission of several different types of glasses by gamma irradiation were also obtained so as to select the suitable optical windows and filters for the developing radiation-resistant in-water wireless transmission system.
Shibata, Hiroshi; Nakano, Hiroko; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Otsuka, Noriaki; Nishikata, Kaori; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Hirota, Noriaki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Testing 2017-002, 138 Pages, 2017/12
From the viewpoints of utilization improvement of the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR), the experimental devices have been established for the out-pile tests in the irradiation technology development building. The devices for the irradiation capsule assembly, material tests and inspections were established at first and experimental data were accumulated before the neutron irradiation tests. On the other hand, after the Great East Japan Earthquake, the repairs and earthquake-resistant measures of the existing devices were carried out. New devices and equipments were also established for the R&D program for power plant safety enhancement of the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and  Mo/
Mo/ Tc production development under the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone. This report describes the outline and basic operation manuals of the devices established from 2011 to 2016 and the management points for the safety works in the irradiation technology development building.
Tc production development under the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone. This report describes the outline and basic operation manuals of the devices established from 2011 to 2016 and the management points for the safety works in the irradiation technology development building.