Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 173, p.105236_1 - 105236_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The theme of this paper is how to efficiently analyse extreme realizations of neutron effective multiplication factor (keff) over random media replicas modelled by incomplete randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF). To this end, a new bounded amplification (BA) technique is applied to IRWF. Numerical results indicate that the BA-applied IRWF reduces a required number of random media replicas at least by an order of magnitude. To validate this efficiency gain, generalized extreme value (GEV) analysis is applied to a data set of keff values obtained without applying BA. It turns out that the extreme values of these keff values follow the Weibull distribution. Therefore, the theory of GEV guarantees the existence of the upper limit of these keff values, and the actually computed upper limit is indeed smaller than the top two keff values obtained from an order-of magnitude reduced number of BA-applied IRWF random media replicas. This means that the efficiency gain via BA has been confirmed by GEV analysis.
Suyama, Kenya; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Shimada, Kazuya; Fujita, Tatsuya; Ueki, Taro; Nguyen, H.
JAEA-Conf 2024-001, 40 Pages, 2024/07
The 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) was held from October 1 to October 6, 2023, at the Sendai International Center (Aobayama, Aoba-ku, Sendai, Miyagi-prefecture 980-0856, Japan), organized by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and co-organized by the Reactor Physics Division of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan (AESJ) and the Nuclear Energy Agency of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA). 224 presentations passed peer review and 273 technical session registrations, bringing the total number of registered participants to 289, including accompanying persons. Technical tours were also conducted to i) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of TEPCO holdings and Interim Storage Facility Information Center, ii) Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA (STACY Renewable Reactor and FCA), iii) NanoTerasu of Tohoku University (synchrotron radiation facility) and Onagawa Nuclear Power Station of Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc. This report summarizes the conference and compiles the papers that were presented and agreed to be published in the Proceedings.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Ueki, Taro; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Reactors (PHYSOR 2024) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/04
Solomon, a Monte Carlo solver being developed by JAEA, can calculate criticality in multi-material randomized systems for criticality evaluation of fuel debris. This study investigates the applicability of Solomon to critical mass calculations of fuel debris. We performed critical mass calculations of fuel randomization systems using Solomon. The fuel randomization systems, where burned fuels with different burnups and water are randomly distributed, were modeled by the incomplete randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF) model or voxel geometry in Solomon. Critical mass calculations of simple homogeneous and heterogeneous systems were also performed, and the critical sizes were compared to fuel randomization systems. The results showed that the fuel randomization causes significant variations in the critical mass. The obtained critical sizes were distributed close to a normal distribution, which made it reasonable to estimate the uncertainty of critical mass as the standard deviation. The critical sizes with uncertainty obtained by Solomon were smaller than those of a simple heterogeneous system. This indicates Solomon would be useful for estimating or evaluating a reasonable safety margin in criticality safety evaluations of fuel debris.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai; Yamane, Yuichi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Kikuchi, Takeo; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
To remove and store safely the fuel debris generated by the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in 2011 is one of the most important and challenging topics for decommissioning of the damaged reactors in Fukushima. To validate the adopted method for the evaluation of criticality safety control of the fuel debris through comparison with the experimental data obtained by the criticality experiments, the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) of Japan funds a research and development project which was entrusted to the Nuclear Safety Research Center (NSRC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) from 2014. In this project, JAEA has been conducting such activities as i) comprehensive computation of the criticality characteristics of the fuel debris and making database (criticality map of the fuel debris), ii) development of new continuous energy Monte Carlo code, iii) evaluation of criticality accident and iv) modification of the critical assembly STACY for the experiments for validation of criticality safety control methodology. After the last ICNC2019, the project has the substantial progress in the modification of STACY which will start officially operation from May 2024 and the development of the Monte Carlo Code "Solomon" suitable for the criticality calculation for materials having spatially random distribution complies with the power spectrum. We present the whole picture of this research and development project and status of each technical topics in the session.
Ueki, Taro
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/10
A Monte Carlo Solver Solomon has been under development as an object-oriented code written in the C++14 standards. It consists of regular capabilities of criticality safety analysis and a special capability of random media criticality. In the latter capability, Solomon is equipped with a class for the random media modeled by the incomplete randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF). By this modeling, the uncertainty of random media criticality can be evaluated by executing criticality calculations over many IRWF-replicas. However, it is impossible to know beforehand how many IRWF-replicas should be computed. To deal with this issue, a bounded amplification (BA) technique has been newly equipped in Solomon. Applying BA to IRWF, it is possible to reduce the number of IRWF-replicas by more than 95% in terms of the upper limit estimation of neutron effective multiplication factor. Solomon is also equipped with a voxel-overlay (VO). This functionality is shown to be valuable for evaluating the resonance self-shielding effect.
Suyama, Kenya; Ueki, Taro; Gunji, Satoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; Araki, Shohei; Fukuda, Kodai
Proceedings of 20th International Symposium on the Packaging and Transportation of Radioactive Materials (PATRAM22) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/06
Since the 1990s, the importance of the handbook has changed significantly, as the computational power has improved and continuous energy Monte Carlo codes have become widely used, which enables highly accurate criticality calculations, when necessary, irrespective of the complexity of the system. Because the value of performing a large number of calculations in advance and summarizing the data has decreased, since the second edition was published publicly in 1999, there has been no revision of criticality safety handbooks in Japan for nearly a quarter of a century. In Japan, where the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident occurred in 2011, it became necessary to deal with criticality safety issues in the transport and storage of the fuel debris which contains complex constituent elements, and the summary the criticality safety management for such material is an urgent issue. In the area of burnup credit, the transport and storage of fuel assemblies with low achieved burnups due to the consequences of accidents might be the problem. In addition, nuclear data, which is the input for the continuous energy Monte Carlo code, has been improved several times, now JENDL-5 is available from the end of 2021, and its incorporation becomes a need in the field. This report provides an overview of the latest criticality safety research in Japan and the planned revision of the Criticality Safety Handbook, which could be applied to the transport and storage sectors.
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 159, p.104630_1 - 104630_9, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this work, the methodology of Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) is applied to criticality tallies in Monte Carlo fission source cycles in order to evaluate the utility value of the distribution tail ends. Numerical results obtained under a sufficiently large number of particles per cycle show that the extreme value index (EVI) in GEV falls within the range of Weibull distribution including the EVI of Gumbel distribution as the role of a boundary value layer. GEV is also applied to a historically-challenging loosely-coupled system for demonstrating population diagnosis under an insufficient number of particles per cycle. It turns out that the transition from one equilibrium to other equilibrium makes the EVIs of upper and lower distribution tail ends depart from each other so that one of them falls in the range of Weibull distribution and the other in that of Frechet distribution.
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 144, p.104099_1 - 104099_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Randomized Weierstrass function (RWF) has been under development for evaluating the uncertainty of random media criticality due to the material mixture under disorder. In this work, the modelling capability of RWF is refined so that the spectrum range can be controlled by specifying its lower and upper ends of the frequency domain variable. As a result, it becomes possible to make fair criticality comparison among replicas of random media under inverse power law power spectra. Technically, the infinite sum of trigonometric terms in RWF is extended to cover the arbitrarily low frequency domain and then truncated to finite terms for the sole purpose of spectrum range control. This means that the refinement is free of the convergence issue towards a fractal characteristic of Weierstrass function and thus termed Incomplete Randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF). As a demonstration, a three-dimensional version of IRWF is applied to the mixture of three fuels with different burnups in a water-moderated environment. Monte Carlo criticality calculations are carried out to evaluate the uncertainty of neutron effective multiplication factor due to the indeterminacy of the fuel mixture formation.
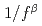 random media
random mediaAraki, Shohei; Yamane, Yuichi; Ueki, Taro; Tonoike, Kotaro
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 195(10), p.1107 - 1117, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)Criticality control of random media such as fuel debris is one of the most important safety issues in post-accident management. 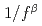 spectrum randomizing model is expected to simulate such random media because it is well known that the
spectrum randomizing model is expected to simulate such random media because it is well known that the 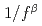 noise can describe a diverse range of random and disordered natural phenomena. In this paper, we focused on the relationship between the multiplication factor and moderation condition in the
noise can describe a diverse range of random and disordered natural phenomena. In this paper, we focused on the relationship between the multiplication factor and moderation condition in the 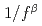 random media. A number of random media were realized with the
random media. A number of random media were realized with the 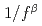 spectrum randomizing model that is based on the Randomized Weierstrass function (RWF). The volume ratio of concrete to fuel was adopted as an index for the moderation condition. The multiplication factors were calculated with a two-energy group Monte Carlo calculation. The calculation results were analyzed by using variance, skewness, and kurtosis. Those statistical parameters had an extreme value around the optimum moderation condition. This result suggested that it is possible to predict the rough trend of variation range, distortion, and outlier of multiplication factors in the
spectrum randomizing model that is based on the Randomized Weierstrass function (RWF). The volume ratio of concrete to fuel was adopted as an index for the moderation condition. The multiplication factors were calculated with a two-energy group Monte Carlo calculation. The calculation results were analyzed by using variance, skewness, and kurtosis. Those statistical parameters had an extreme value around the optimum moderation condition. This result suggested that it is possible to predict the rough trend of variation range, distortion, and outlier of multiplication factors in the 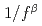 random media.
random media.
Ueki, Taro
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 195(2), p.214 - 226, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:65.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)A dynamical system under extreme physical disorder has the tendency of evolving toward the equilibrium state characterized by an inverse power law power spectrum. In this paper, a practically implementable three-dimensional model is proposed for the random media formed by multi-materials mixture under such a power spectrum using a randomized form of Weierstrass function, its extension covering the white noise, and partial volumes pairings of constituent materials. The proposed model is implemented in the SOLOMON Monte Carlo solver with delta tracking. Two sets of numerical results are shown using the JENDL-4 nuclear data libraries.
Ueki, Taro
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 194(6), p.422 - 432, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In Monte Carlo criticality calculation, the convergence-in-distribution check of the sample mean of tallies can be approached in terms of the influence range of autocorrelation. In this context, it is necessary to evaluate the attenuation of autocorrelation coefficients over lags. However, in just one replica of calculation, it is difficult to accurately estimate small ACCs at large lags because of the comparability with statistical uncertainty. This paper proposes a method to overcome such an issue. Its essential component is the transformation of a standardized time series of tallies so that the resulting series asymptotically converges in distribution to Brownian motion. The convergence-in-distribution check is constructed based on the independent increment property of Brownian motion. The judgment criterion is set by way of the spectral analysis of fractional Brownian motion. Numerical results are demonstrated for extreme and standard types of criticality calculation.
 on effective multiplication factor in 1/f
on effective multiplication factor in 1/f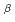 spectrum random system
spectrum random systemAraki, Shohei; Yamane, Yuichi; Ueki, Taro; Tonoike, Kotaro
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; Transition To A Scalable Nuclear Future (PHYSOR 2020) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2020/03
We investigated the  dependence of the effective multiplication factor (k
dependence of the effective multiplication factor (k ) in the 1/f
) in the 1/f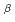 noise model. We conducted the two-group Monte Carlo calculations. We found that the standard deviation of the k
noise model. We conducted the two-group Monte Carlo calculations. We found that the standard deviation of the k distribution showed the positive correlation with the
distribution showed the positive correlation with the  value because the spatial distribution of the fuel became less uniform as the
value because the spatial distribution of the fuel became less uniform as the  value increased.
value increased.
Nagaya, Yasunobu; Ueki, Taro; Tonoike, Kotaro
Proceedings of 11th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2019) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2019/09
A new Monte Carlo solver Solomon has been developed for the application to fuel-debris systems. It is designed not only for usual criticality safety analysis but also for criticality calculations of damaged reactor core including fuel debris. This paper describes the current status of Solomon and demonstrates the applications of the randomized Weierstrass function (RWF) model and the RWF model superimposed voxel geometry.
Ueki, Taro
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 193(7), p.776 - 789, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is known that the convergence of standardized time series (STS) to Brownian bridge yields standard deviation estimators of the sample mean of correlated Monte Carlo tallies. In this work, a difference scheme based on a stochastic differential equation is applied to STS in order to obtain a new functional statistic (NFS) that converges to Brownian motion (BM). As a result, statistical error estimation improves twofold. First, the application of orthonormal weighting to NFS yields a new set of asymptotically unbiased standard deviation estimators of sample mean. It is not necessary to store tallies once the updating of estimator computation is finished at each generation. Second, it becomes possible to assess the convergence of sample mean in an assumption-free manner by way of the comparison of power spectra of NFS and BM. The methodology is demonstrated for three different types of problems encountered in Monte Carlo criticality calculation.
Ueki, Taro
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics and Computational Methods applied to Nuclear Science and Engineering (M&C 2019) (CD-ROM), p.151 - 160, 2019/00
A dynamical system under extreme physical disorder has the tendency of evolving toward the equilibrium state characterized by an inverse power law spectrum. In this paper, the author proposes a practically implementable modeling of random media under such a spectrum using a randomized form of the Weierstrass function. The proposed modeling is demonstrated by the continuous energy Monte Carlo particle transport with delta tracking for the criticality calculation of a randomized version of the Topsy spherical core in International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project.
Ueki, Taro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(10), p.1180 - 1192, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.30(Nuclear Science & Technology)In Monte Carlo criticality analysis under material distribution uncertainty, it is necessary to evaluate the response of neutron effective multiplication factor (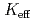 ) to the space-dependent random fluctuation of volume fractions within a prescribed bounded range. Normal random variables, however, cannot be used in a straightforward manner since the normal distribution has infinite tails. To overcome this issue, a methodology has been developed via forward-backward-superposed reflection Brownian motion (FBSRBM). Here, the forward-backward superposition makes the variance of fluctuation spatially constant and the reflection Brownian motion confines the fluctuation driven by normal noise in a bounded range. FBSRBM was implemented using Karhunen-Loeve expansion and applied to the fluctuation of volume fractions in a model of UO
) to the space-dependent random fluctuation of volume fractions within a prescribed bounded range. Normal random variables, however, cannot be used in a straightforward manner since the normal distribution has infinite tails. To overcome this issue, a methodology has been developed via forward-backward-superposed reflection Brownian motion (FBSRBM). Here, the forward-backward superposition makes the variance of fluctuation spatially constant and the reflection Brownian motion confines the fluctuation driven by normal noise in a bounded range. FBSRBM was implemented using Karhunen-Loeve expansion and applied to the fluctuation of volume fractions in a model of UO -concrete media with stainless steel.
-concrete media with stainless steel.
Ueki, Taro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(12), p.1310 - 1320, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:46.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)In Monte Carlo criticality calculation, confidence interval estimation is based on the central limit theorem (CLT) for a series of tallies. A fundamental assertion resulting from CLT is the convergence in distribution (CID) of the interpolated standardized time series (ISTS) of tallies. In this work, the spectral analysis of ISTS has been conducted in order to assess the convergence of tallies in terms of CID. Numerical results indicate that the power spectrum of ISTS is equal to the theoretically predicted power spectrum of Brownian motion for effective neutron multiplication factor; on the other hand, the power spectrum of ISTS for local power fluctuates wildly while maintaining the spectral form of fractional Brownian motion. The latter result is the evidence of a case where a series of tallies is away from CID, while the spectral form supports normality assumption on the sample mean.
Ueki, Taro
Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematics & Computational Methods Applied to Nuclear Science & Engineering (M&C 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2017/04
In Monte Carlo criticality calculation, the formation of a confidence interval is based on the central limit theorem for a series of tallies from generations in equilibrium. A fundamental assertion of the theorem is the convergence in distribution (CID) of an interpolated standardized time series (ISTS) of tallies. This article reports a spectral analysis approach to ISTS in order to assess the convergence of tallies in terms of CID. Numerical results are demonstrated for a preliminary model of uranium-concrete debris.
Ueki, Taro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(3), p.267 - 279, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)Analysis framework under material distribution uncertainty is investigated for the Monte Carlo (MC) criticality calculation of continuously mixed media formed via molten core concrete interaction. Deterministic trigonometric functions and randomized Weierstrass functions are utilized to represent the spatially continuous variation. Numerical results indicate that the effective multiplication factor (k ) under random spatial variation can depart significantly from the k
) under random spatial variation can depart significantly from the k of a reference uniform medium. It is also shown that the deterministic modeling provides an upper-bound measure for extreme results from random realizations.
of a reference uniform medium. It is also shown that the deterministic modeling provides an upper-bound measure for extreme results from random realizations.
Ueki, Taro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.312 - 322, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)In Monte Carlo criticality calculation (MCCC), each output quantity of interest is a series of tallies under autocorrelation. As a consequence from the functional central limit theorem, the stepwise interpolation of standardized tallies (SIST) converges in distribution to Brownian bridge (BB). Here, the standardization of tallies is a functional version of the statistic in the central limit theorem with the sample mean at each generation and the true mean replaced by the sample mean at the final generation. Fractional Brownian motion (FBM) is a family of stochastic processes and assumes a unique value of the box counting dimension (BCD) in fractal geometry. This work shows that the BCD of SIST is an effective diagnostic measure for the run length of MCCC. The sufficiency of the number of generations run can be judged by relating the BCD of FBM to that of BB. Numerical results are presented for power distribution tallies of a pressurized water reactor and the effective multiplication factor (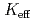 ) tallies of the criticality problem by D. Mennerdahl.
) tallies of the criticality problem by D. Mennerdahl.