Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CrN
CrN H
HFine, L.*; Lav n, R.*; Wei, Z.*; 津森 竜也*; 陰山 洋*; 梶本 亮一; Jimen
n, R.*; Wei, Z.*; 津森 竜也*; 陰山 洋*; 梶本 亮一; Jimen z-Ruiz, M.*; Koza, M. M.*; Karlsson, M.*
z-Ruiz, M.*; Koza, M. M.*; Karlsson, M.*
Chemistry of Materials, 37(1), p.489 - 496, 2024/12
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)We report results on the configuration and vibrational dynamics of hydride-ions (H ) in the novel nitridehydride catalyst Ca
) in the novel nitridehydride catalyst Ca CrN
CrN H, by means of variable temperature inelastic neutron scattering (INS) experiments, harmonic phonon calculations, and machine-learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) calculations. The combined analyses of experimental and theoretical data show that the vibrational dynamics of H
H, by means of variable temperature inelastic neutron scattering (INS) experiments, harmonic phonon calculations, and machine-learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) calculations. The combined analyses of experimental and theoretical data show that the vibrational dynamics of H are manifested as a broad, asymmetric vibrational band between 80 and 130 meV. Crucially, these modes are polarized along the crystallographic
are manifested as a broad, asymmetric vibrational band between 80 and 130 meV. Crucially, these modes are polarized along the crystallographic  axis, and their dispersive character reveals significant interactions between neighbouring H
axis, and their dispersive character reveals significant interactions between neighbouring H in the material. We find that most H
in the material. We find that most H are surrounded by two other H
are surrounded by two other H and that the H
and that the H sites of the studied sample have an occupancy of at least 95%. We argue that this high H
sites of the studied sample have an occupancy of at least 95%. We argue that this high H occupancy may be related to the material's high efficiency as a catalyst for ammonia synthesis.
occupancy may be related to the material's high efficiency as a catalyst for ammonia synthesis.
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Wei, T.*; 余語 覚文*; et al.
第45回日本核物質管理学会年次大会会議論文集(インターネット), 4 Pages, 2024/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a non-destructive method applicable for measuring nuclear material using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. To realize a high resolution compact NRTA system, use of a short-pulsed neutron source is essential. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) are well-suit for generating such neutron beams due to their short pulse width. The advances in laser technology will further reduce the system's size and improve practicality. In this study, we demonstrate the measurement of a neutron transmission TOF spectrum of a sample containing indium and silver using the LDNS of the Osaka University. The obtained spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, showcasing for the first time the potential of an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 弘中 浩太; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.21916_1 - 21916_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) can generate strong short-pulse neutron beams, which are valuable for scientific studies and engineering applications. Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a nondestructive technique used for determining the areal density of each nuclide in a material sample using pulsed thermal and epithermal neutrons. Herein, we report the first successful NRTA performed using an LDNS driven by the Laser for Fast Ignition Experiment at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. The key challenge was achieving a well-resolved resonance transmission spectrum for material analysis using an LDNS with a limited number of laser shots in the presence of strong background noise. We addressed this by employing a time-gated  Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to
Li-glass scintillation neutron detector to measure the transmission spectra, reducing the impact of electromagnetic noise and neutron and gamma-ray flashes. Output waveforms were recorded for each laser shot and analyzed offline using a counting method. This approach yielded a spectrum with distinct resonances, which were attributed to  In and
In and  Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Ag, as confirmed through neutron transmission simulation. The spectrum was analyzed using the least-square nuclear-resonance fitting program, REFIT, demonstrating the possibility of using an LDNS for nondestructive areal-density material characterization.
Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Morace, A.*; 早川 岳人*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 小泉 光生; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5365_1 - 5365_7, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:79.20(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The temperature measurement of material inside of an object is one of the key technologies for control of dynamical processes. For this purpose, various techniques such as laser-based thermography and phase-contrast imaging thermography have been studied. However, it is, in principle, impossible to measure the temperature of an element inside of an object using these techniques. One of the possible solutions is measurements of Doppler brooding effect in neutron resonance absorption (NRA). Here we present a method to measure the temperature of an element or an isotope inside of an object using NRA with a single neutron pulse of approximately 100 ns width provided from a high-power laser. We demonstrate temperature measurements of a tantalum (Ta) metallic foil heated from the room temperature up to 617 K. Although the neutron energy resolution is fluctuated from shot to shot, we obtain the temperature dependence of resonance Doppler broadening using a reference of a silver (Ag) foil kept to the room temperature. A free gas model well reproduces the results. This method enables element(isotope)-sensitive thermometry to detect the instantaneous temperature rise in dynamical processes.
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 森 隆人*; Golovin, D.*; 早川 岳人*; 岩田 夏弥*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:96.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutrons are powerful tools for investigating the structure and properties of materials used in science and technology. Recently, laser-driven neutron sources (LDNS) have attracted the attention of different communities, from science to industry, in a variety of applications, including radiography, spectroscopy, security, and medicine. However, the laser-driven ion acceleration mechanism for neutron generation and for establishing the scaling law on the neutron yield is essential to improve the feasibility of LDNS. In this paper, we report the mechanism that accelerates ions with spectra suitable for neutron generation. We show that the neutron yield increases with the fourth power of the laser intensity, resulting in the neutron generation of 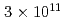 in
in 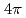 at a maximum, with
at a maximum, with 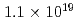 Wcm
Wcm , 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub-
, 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub- s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
He, Z.*; Wei, J.*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of 25th North American Particle Accelerator Conference (NA-PAC '13) (Internet), p.1298 - 1300, 2013/09
The power of the cooling laser currently available in a compact ion cooler ring S-LSR, Kyoto University, is quite limited for generating ultralow-temperature ion beams. Therefore, parameters of laser cooling should be carefully determined in order to approach the lowest possible temperature in the experiment. This paper mainly concerns optimization of laser-cooling parameters and prediction of a possible lower limit of beam temperature in S-LSR, based on systematic molecular dynamics simulations. The adiabatic capture process of the ion beam was introduced to prevent the emittance from blowing up during bunching. The spot size of the laser was optimized with the total laser power limited. An optimum solenoid field strength was obtained for three-dimensional cooling. The lowest beam temperature achievable in S-LSR was predicted by choosing the parameters optimized.
池上 雅紀*; Fang, Z.*; 二ツ川 健太*; 宮尾 智章*; 丸田 朋史; 佐甲 博之; 三浦 昭彦; Wei, G.; 田村 潤
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.3293 - 3295, 2012/05
J-PARCは2011年3月に発生した東北大震災によって甚大な被害を被り、長期間の停止を余儀なくされた。復興作業後、加速器運転を再開したのは2011年12月である。本論文では、ビーム運転再開後のリニアックの運転状況について報告する。12月のビーム運転再開後、1月上旬にかけて実施した計14日間のビーム調整により、1月下旬には震災以前の強度には及ばないものの、利用運転に耐える状況を構築した。また利用運転再開後も、継続的にビームロスの低減に取り組み、原因をひとつひとつ取り除いた。本論文では、特にマクロパルス先頭の顕著なロス、地震の揺れによるビームダクト歪みに起因したロスの詳細について報告している。これらの取り組みにより、最終的に残留放射線レベルをビーム運転再開当初から1桁改善させることに成功した。この結果、3月から震災以前と同じ強度で安定的な運転を達成している。しかしながら、依然としてビームロスは震災以前よりも高く、さらにビームロス低減に取り組む必要がある。また震災後に加速空洞1台が不調となっており、設計値からずれた設定で運転する等、懸念事項も存在する。今後もこれらの事柄について取り組んでいく。
Yu, P.*; He, Z.*; Wei, J.*; Sessler, A. M.*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.1943 - 1945, 2010/05
In the process of beam cooling, the main heating source is intra-beam scattering (IBS), in which Coulomb collisions among particles lead to a growth of the beam's 6D phase-space volume. The results of molecular dynamics simulations have shown an increase of heating rate as the temperature increases from absolute zero, then a peak in the heating rate, and subsequent decrease with increasing temperature. On the other hand, in the traditional IBS theory, heating rate increases monotonically as the temperature becomes lower and lower. In this paper, we attempt to extend the traditional IBS theory valid at high temperatures to relatively low temperature range, by including some many-body effects in the traditional IBS theory. In particular, we take into account the static and dynamic effect of the self-electromagnetic field of the beam. We shall show how these effects modify the traditional theory, and present the evaluation of IBS heating rate of an ion beam in the low temperature range.
Xu, L.*; Yue, Z.*; Wang, M.*; Zhai, M.*; 吉井 文男; 瀬古 典明; Peng, J.*; Wei, G.*; Li, J.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 265(1), p.394 - 398, 2007/12
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:40.30(Instruments & Instrumentation)水に対して不溶性のヒドロキシプロピルメチルセルロースのフタル酸エステルをナトリウム型に転化した後、ペースト状態で 線照射することにより橋かけさせることに成功した。また、メチル
線照射することにより橋かけさせることに成功した。また、メチル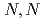 ビスアクリルアミド(MBA)やエチレングリコールジメタクリレート(EGDMA)などの橋かけ助剤を用いることで、MBAについては架橋後のゲルが剛直になり、EGDMAについては、より柔らかく、加工しやすい特性を有するゲルを作製できることがわかった。
ビスアクリルアミド(MBA)やエチレングリコールジメタクリレート(EGDMA)などの橋かけ助剤を用いることで、MBAについては架橋後のゲルが剛直になり、EGDMAについては、より柔らかく、加工しやすい特性を有するゲルを作製できることがわかった。
大島 武; 小野田 忍; 牧野 高紘; 岩本 直也*; Johnson, B. C.*; Lohrmann, A.*; Karle, T.*; McCallum, J. C.*; Castelletto, S.*; 梅田 享英*; et al.
no journal, ,
固体中の単一発光源(SPS)の有するスピンや発光を制御することで、量子コンピューティングやフォトニクスを実現しようという試みが行われている。本研究ではSiCを母材としたSPSの探索を行った。半絶縁性(SI)六方晶(4H)SiC基板に室温にて2MeVのエネルギーの電子線照射後、Ar中、30分間の熱処理を行った。室温又は低温におけるフォトルミネッセンス(PL)測定及び室温における共焦点蛍光顕微鏡(CFM)を用いたアンチバンチング測定によりSPSを探索した。1 10
10 /cm
/cm の電子線照射後に300
の電子線照射後に300 Cで熱処理を行った試料に対して80KでのPL測定を行ったところ、850
Cで熱処理を行った試料に対して80KでのPL測定を行ったところ、850 950nm付近にSi空孔が起因のVラインと呼ばれるPL発光が、650
950nm付近にSi空孔が起因のVラインと呼ばれるPL発光が、650 700nm付近にC
700nm付近にC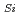 V
V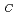 起因のABラインと呼ばれる二種類のPL発光が観測された。ABラインの発光を有する欠陥中心に対して、CFMを用いて室温でアンチバンチグ測定を行った結果、C
起因のABラインと呼ばれる二種類のPL発光が観測された。ABラインの発光を有する欠陥中心に対して、CFMを用いて室温でアンチバンチグ測定を行った結果、C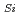 V
V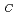 が単一発光源であることが判明した。また、これまでSteedsらによりABラインは中性のC
が単一発光源であることが判明した。また、これまでSteedsらによりABラインは中性のC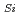 V
V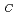 と主張されていたが、ab initio計算から、この波長領域にPL発光を持つためには正に帯電しているC
と主張されていたが、ab initio計算から、この波長領域にPL発光を持つためには正に帯電しているC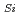 V
V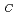 であるという結果を得た。
であるという結果を得た。
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 早川 岳人*; 小泉 光生; Wei, T.*; Shi, B.*; 石本 崇*; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; et al.
no journal, ,
High penetration power of neutrons is potentially useful for realizing opaque object analysis in non-destructive way. Large-scale particle accelerators and nuclear reactors are mostly used for development of neutron analyzing method. A Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) has been proposed as a new approach of neutron generation for non-destructive analysis. Demonstration experiments on neutron resonance measurement ware performed at ILE, Osaka Univ., Japan. The Peta-watt laser LFEX was used to shoot a CD (deuterated plastic) foil target to produce accelerated charged deuterons. Neutrons are generated by nuclear reaction between a cylindrical beryllium and the accelerated deuteron, and then moderated by a high-density polyethylene (HDP). Neutrons of 1 20 eV were observed with a neutron detector at a 1.8 m using neutron resonance diagnosis technology. This report describes the results of the first experimental demonstration.
20 eV were observed with a neutron detector at a 1.8 m using neutron resonance diagnosis technology. This report describes the results of the first experimental demonstration.
余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 岩本 晃史*; 早川 岳人*; 小泉 光生; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Lan, Z.*; et al.
no journal, ,
大阪大学のLFEXレーザー施設において、大強度レーザーを用いたパルス中性子源(LDNS)の開発およびそれを利用した応用研究を進めている。レーザーは、パルス巾が1.5psで、最大出力は、1kJ(1.5 10
10 Wcm
Wcm である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10
である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10 で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance diagnosis technology has been developed on reactors and accelerators for over ten years. By employing neutron beams with high transmittance, it is possible to analyse elementary composition, internal temperature and shock waves of thick objects in a non-destructive way. We developed a new approach to generate short-pulse epithermal neutron beams using relativistic intensity laser for the neutron resonance spectral diagnosis, which is known as Laser-driven Epithermal Neutron Source (LDENS). The neutron resonance measuring experiment was implemented at ILE, Osaka Univ. with peta-watt laser LFEX. The experimental results in 2020 demonstrated that LDENS is applicable for neutron resonance measurement. In 2021 experiments, we developed the system to record neutron spectrum with higher quality. Multiple resonance peaks of various isotopes with different temperature were clearly measured. The presentation will introduce the experimental results and discussions including characteristic evaluation of LDENS and temperature dependency of neutron resonance peaks.
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 早川 岳人*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; 小泉 光生
no journal, ,
高強度レーザーで加速した陽子・重陽子をBe等のコンバータで中性子に変換するレーザー駆動中性子源を開発しており、これまでにレーザー1ショットで発生した単一パルスの中性子で、中性子共鳴スペクトルの計測に成功している。本発表では、サンプルを300-600Kの範囲で昇温し、共鳴吸収ピークのドップラー広がりが温度の平方根に依存する結果を得たので報告する。
Lan, Z.*; 早川 岳人*; Wei, T.*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; 森 隆人*; et al.
no journal, ,
As a new approach of neutron generation with the ultra-short pulse duration and high flux, a Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) has been studied. A demonstration experiment of neutron resonance spectroscopy using a LDNS has been performed using the petawatt laser LFEX at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. A CD foil target was used for an high-density plasma generation. Neutrons were produced by the impact of the high energy ions on a boron converter. A high-density polyethylene surrounding the boron converter slowed down neutron energy to epithermal temperature. A single shot neutron resonance experiment was carried out at a neutron beam line of 1.8m. The neutron resonance peak at 4.28 eV of Ta was measured with different temperature.
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; 藤岡 慎介*; et al.
no journal, ,
レーザー駆動中性子源は、高強度レーザーパルスを薄膜の1次ターゲットに集光して、プラズマの作る瞬間的な電場でMeVエネルギーイオン(陽子・重陽子)を発生し、それを2次ターゲット(ベリリウム等)に照射して、短パルスの高速中性子を発生する。2次ターゲットに小型の減速材を取り付けて、パルス熱外中性子を発生し、1.8mのビームラインで飛行時間法によるエネルギースペクトルを分析した。ビームラインに銀(Ag),タンタル(Ta),インジウム(In)の合板を設置したところ、3.81eV ( In), 4.28eV (
In), 4.28eV ( Ta), 5.19eV (
Ta), 5.19eV ( Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; 早川 岳人*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; Morace, A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
A Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) is a novel neutron that provides neutron beam of ultra-short pulse duration and high flux. This technique would be useful for neutron resonance non-destructive diagnosis application. A demonstration experiment was carried out using an LDNS developed for the LFEX laser of Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. A neutron resonance spectrum was observed with a single laser shot. The technique can be used as a "nuclear thermometer" because the resonance shape is broadened as a function of the sample material temperature.
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; 早川 岳人*; Wei, T.*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance diagnosis technology has been developed worldwide for over ten years. By employing neutron beams with high transmittance, it is possible to measure the resonance spectral of samples in the neutron beam-line. We developed a new approach to generate short pulse epithermal neutron beams using relativistic intensity laser for the neutron resonance spectral diagnosis, which is known as Laser-Driven Epithermal Neutron Source (LDENS). Benefit from highly focused laser, the LDENS can provide high temporal accuracy with a compact volume of the source. Therefore, the minimal change of neutron resonance peaks caused by Doppler broadening effect of atom temperature could be detected via single pulse of LDENS. In experiment, we measured resonance at 4.28eV of a 0,1mm Ta plate with serial temperature points (300K-600K) and another resonance at 5.18eV of an Ag plate was recorded as a reference of the neutron signal. The experimental data shows the feasibility of isotope-discriminating atomic thermometer using a single shot of LDENS. More results will be reported in the presentation.