Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
津田 修一; 佐藤 達彦; 小川 達彦
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 141, 2016/09
イオンビームに対する生物学的効果を評価する上で、生体中でのイオンビームの飛跡およびその近傍における詳細なエネルギー付与分布は重要なデータである。本研究では、PHITSに組み込まれている最新の生物学的線量評価モデルのエネルギー付与分布計算の精度検証を行うため、高崎量子応用研究所TIARAで 壁なし型組織等価比例計数管にペンシル状のビームを照射し、径方向の線エネルギー( )分布データおよび
)分布データおよび の線量平均値(
の線量平均値(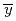
 )を取得した。その結果、PHITSによる計算結果は測定した
)を取得した。その結果、PHITSによる計算結果は測定した 分布をよく再現することがわかった。また30MeV陽子は、陽子より重いイオンの場合と異なり、ビーム軸上で
分布をよく再現することがわかった。また30MeV陽子は、陽子より重いイオンの場合と異なり、ビーム軸上で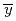
 値は最小となり、ビーム軸に対する垂直面の径方向の距離とともに緩やかに増加した。これは陽子ビームと二次的に生成されるデルタ線の阻止能がほぼ等しいことに起因するためであり、約30MeV以上の陽子ビームでは飛跡構造がほぼ一様であることを実験的に示した。
値は最小となり、ビーム軸に対する垂直面の径方向の距離とともに緩やかに増加した。これは陽子ビームと二次的に生成されるデルタ線の阻止能がほぼ等しいことに起因するためであり、約30MeV以上の陽子ビームでは飛跡構造がほぼ一様であることを実験的に示した。
横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 池田 裕子; 坂下 哲哉; 鈴木 芳代; 小林 泰彦
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 67, 2016/02
本研究ではバイスタンダー効果における一酸化窒素(NO)の役割を調べた。ヒト正常線維芽細胞に 線(LETは0.2keV/
線(LETは0.2keV/ m)あるいは炭素イオンビーム(108keV/
m)あるいは炭素イオンビーム(108keV/ m)を照射した後、非照射細胞と共培養した。24時間の共培養後に非照射細胞の生存率と培養液に含まれるNOの酸化物である亜硝酸イオンの濃度を測定した。非照射細胞の生存率低下は照射細胞に曝露する線量に依存したが線質には依存しなかった。非照射細胞の生存率と亜硝酸イオン濃度には負の相関関係が認められた。一方で、NO発生剤であるNOC12を培養液に加えるだけでは、細胞の生存率は低下しなかった。以上の結果から、細胞内で生成されるNOの量がバイスタンダー効果の決定因子の一つであるが、細胞間情報伝達因子ではない可能性が示された。
m)を照射した後、非照射細胞と共培養した。24時間の共培養後に非照射細胞の生存率と培養液に含まれるNOの酸化物である亜硝酸イオンの濃度を測定した。非照射細胞の生存率低下は照射細胞に曝露する線量に依存したが線質には依存しなかった。非照射細胞の生存率と亜硝酸イオン濃度には負の相関関係が認められた。一方で、NO発生剤であるNOC12を培養液に加えるだけでは、細胞の生存率は低下しなかった。以上の結果から、細胞内で生成されるNOの量がバイスタンダー効果の決定因子の一つであるが、細胞間情報伝達因子ではない可能性が示された。
 -ray irradiation facilities
-ray irradiation facilities上松 敬; 宇野 定則; 花屋 博秋; 山縣 諒平; 清藤 一; 長尾 悠人; 山崎 翔太; 川島 郁男*; 八木 紀彦*; 高木 雅英*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 173, 2016/02
高崎量子応用研究所の電子加速器及び 線照射施設を2014年度年間計画に基づいて照射利用に供した。利用件数は、2013年度に比べ、電子加速器では故障のため減少し、
線照射施設を2014年度年間計画に基づいて照射利用に供した。利用件数は、2013年度に比べ、電子加速器では故障のため減少し、 線ではわずかに増加し、それぞれ205件及び857件だった。東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故に対する復興対応関連の課題については、電子加速器では35件、
線ではわずかに増加し、それぞれ205件及び857件だった。東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故に対する復興対応関連の課題については、電子加速器では35件、 線照射施設においては172件の利用があった。
線照射施設においては172件の利用があった。
 irradiation
irradiation武内 伴照; 柴田 裕司; 大塚 紀彰; 上原 聡明; 熊原 肇*; 土谷 邦彦
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 29, 2016/02
水中でも伝送可能かつ耐放射線性をもつ可視光無線伝送システムの構築を目指して、発光波長がほぼ同じで比較的光量の大きい異なった2種類のLEDを選定し、その 線照射効果を調べた。照射劣化を評価するため、照射前後におけるLEDの電流電圧特性や全光束を測定した結果、照射後に全光束が減少するとともに樹脂レンズ部が着色したが、電流電圧特性はほとんど変化は無かった。このことから、両素子の特性劣化の主因は半導体部分の劣化ではなく、樹脂の着色によるものであることが示唆された。一方、試験した内の1種類のLEDについて、照射量に対する全光束の減少速度が小さかったことから、開発中の無線伝送システムの発光素子に適すると考えられることが分かった。
線照射効果を調べた。照射劣化を評価するため、照射前後におけるLEDの電流電圧特性や全光束を測定した結果、照射後に全光束が減少するとともに樹脂レンズ部が着色したが、電流電圧特性はほとんど変化は無かった。このことから、両素子の特性劣化の主因は半導体部分の劣化ではなく、樹脂の着色によるものであることが示唆された。一方、試験した内の1種類のLEDについて、照射量に対する全光束の減少速度が小さかったことから、開発中の無線伝送システムの発光素子に適すると考えられることが分かった。
 -ray irradiation induced radicals in binder materials of alanine dosimeter components
-ray irradiation induced radicals in binder materials of alanine dosimeter components清藤 一; 佐伯 誠一; 小日向 基史夫*; 小嶋 拓治*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 147, 2016/02
In order to develop the alanine dosimeter for practical applications, we tried to apply certain polymers as the binders. The three different binder materials and alanine dosimeter (Aminogray) were irradiated with  Co
Co  -ray pencil source in the Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The concentration of free radicals trapped in the binder materials was measured with electron spin resonance (ESR). These spectra were observed with amplification of the ESR signal, since the spectral intensity of sucrose fatty acid ester at a given dose was considerably lower than that of Aminogray. Normalizing the sample weight and dose, the ratio of peak height of ESR spectra from maltitol radicals and crystalline cellulose radicals to that from alanine radicals was negligibly small. These results suggest maltitol, crystalline cellulose and sucrose fatty acid ester can be applicable as binder of alanine dosimeter components.
-ray pencil source in the Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The concentration of free radicals trapped in the binder materials was measured with electron spin resonance (ESR). These spectra were observed with amplification of the ESR signal, since the spectral intensity of sucrose fatty acid ester at a given dose was considerably lower than that of Aminogray. Normalizing the sample weight and dose, the ratio of peak height of ESR spectra from maltitol radicals and crystalline cellulose radicals to that from alanine radicals was negligibly small. These results suggest maltitol, crystalline cellulose and sucrose fatty acid ester can be applicable as binder of alanine dosimeter components.
 by ion beam breeding technology
by ion beam breeding technology佐藤 勝也; 上田 涼史郎*; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 100, 2016/02
Bioremediation uses biological organisms to solve an environmental problem. However, microorganisms are sometimes not enough effective to achieve efficient recovery. Therefore, enhancing the functionality of microorganisms is needed to promote the active use of bioremediation. This study began with the purpose of development of Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Previously, we suggested that  is the most suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Candidates of Cs-accumulating mutant were screened from the mutagenized cells by ion beam breeding technology on the basis of the luminescent intensity and the cell area as indicators of intracellular Cs level and cell growth, respectively. As a result, we obtained 33 candidates, whose Cs-accumulating abilities were over 2-fold higher than that of the wild-type, from the population of mutagenized cells.
is the most suitable species for the development of high Cs-accumulating bacteria by ion beam breeding technology. Candidates of Cs-accumulating mutant were screened from the mutagenized cells by ion beam breeding technology on the basis of the luminescent intensity and the cell area as indicators of intracellular Cs level and cell growth, respectively. As a result, we obtained 33 candidates, whose Cs-accumulating abilities were over 2-fold higher than that of the wild-type, from the population of mutagenized cells.
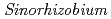 with
with 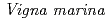 under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding
under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding丸山 雄大*; 武田 喜代子*; 友岡 憲彦*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 99, 2016/02
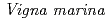 is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants.
is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants. 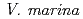 can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on
can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on 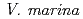 have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus
have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus 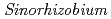 having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45
having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45  C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however,
C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however, 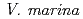 cannot develop root nodules with
cannot develop root nodules with 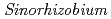 at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of
at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of 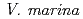 with
with 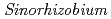 under high salt conditions,
under high salt conditions, 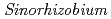 bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
荻野 千秋*; Kahar, P.*; Lee, J. M.*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 近藤 昭彦*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 105, 2016/02
Ethanol fermentation from hydrolyzed lignocellulosic biomass with yeast is very important. However, in common sense, there are several chemical inhibitors for yeast from hydrolyzed biomass. Therefore, screening of yeast strain, possessing the tolerance properties against these chemical inhibitors, should be found from nature resources or mutant libraries. To overcome the problem, we have screened yeast strains tolerant to many chemical inhibitors contained in bagasse sugar lysate (BSL) at high temperature (35  C) from 1500 strains out of national bio-resource center yeast collection. We found that F118 strain could grow and ferment BSL and produce ethanol. For increasing of the yield and ethanol fermentation efficiency of F118 strain, the adaptation of F118 strain to high temperature was conducted, followed by carbon ion beam irradiation. Consequently, we have successfully obtained F118S88 strain as a good candidate for ethanol production from BSL at high temperature.
C) from 1500 strains out of national bio-resource center yeast collection. We found that F118 strain could grow and ferment BSL and produce ethanol. For increasing of the yield and ethanol fermentation efficiency of F118 strain, the adaptation of F118 strain to high temperature was conducted, followed by carbon ion beam irradiation. Consequently, we have successfully obtained F118S88 strain as a good candidate for ethanol production from BSL at high temperature.

上田 涼史郎*; 佐藤 勝也; 林 秀謙*; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 101, 2016/02
It is suggesting a possibility that the polyphosphate granules in cells could accumulate harmful metal ions such as radiocesium to protect the cells from cytotoxicity. In this study, we investigated the accumulation of cesium and its association with intracellular polyphosphate in  using the gene disruptant and overexpressing strains. The cesium accumulation level in the disruptant and overexpressing strains was compared with that of the wild-type strain. The cesium accumulations in the
using the gene disruptant and overexpressing strains. The cesium accumulation level in the disruptant and overexpressing strains was compared with that of the wild-type strain. The cesium accumulations in the 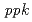 disruptant and overexpressing strains were slightly decreased and almost same, respectively. Like the intracellular polyphosphate level, the cesium accumulation level was significantly increased in the
disruptant and overexpressing strains were slightly decreased and almost same, respectively. Like the intracellular polyphosphate level, the cesium accumulation level was significantly increased in the 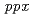 disruptant strain. These results suggested that the intracellular polyphosphate level was positively correlated with the cesium accumulation level in
disruptant strain. These results suggested that the intracellular polyphosphate level was positively correlated with the cesium accumulation level in  .
.
増渕 隆*; 渡口 和樹*; 林 秀謙*; 池永 裕*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 106, 2016/02
We conducted the gene function analysis of the high ethyl caproate producing sake yeast mutant (No.227) generated by ion beam breeding in order to develop a new method for sake yeast screening and find factors contributing the reduced ability to alcohol fermentation. The genome sequences of the No.227 and Kyokai 901 (its parental strain) were determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy using pyrosequencing method. And the determined sequences were compared with that of the sake yeast strain Kyokai 7, which is characterized by the fermentation properties. Consequently, the No.227 carried mutations in the 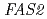 and
and 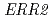 genes as heterozygous state. It was suggested that these mutations in the
genes as heterozygous state. It was suggested that these mutations in the 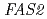 and
and 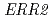 genes in the No.227 might be attributed to the high ethyl caproate production and the low alcohol fermentation ability, respectively.
genes in the No.227 might be attributed to the high ethyl caproate production and the low alcohol fermentation ability, respectively.
 in a greenhouse for tomato cultivation
in a greenhouse for tomato cultivation石井 里美; 山崎 治明*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 河地 有木; 島田 浩章*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 93, 2016/02
Tomato is popularly grown in environmentally controlled system such as a greenhouse for improvement of bioproduction. It is important to control the condition in the greenhouse for increasing the translocation of fixed carbon from the leaves to the growing fruits. Elevation of CO concentration is widely employed for that purpose; however, it is difficult to estimate its effect quantitatively because tomato plants have too large inter-individual variations with developing fruits. In this study, we employed a PETIS which is a live-imaging system of nutrients in plant body using short-lived radioisotopes including
concentration is widely employed for that purpose; however, it is difficult to estimate its effect quantitatively because tomato plants have too large inter-individual variations with developing fruits. In this study, we employed a PETIS which is a live-imaging system of nutrients in plant body using short-lived radioisotopes including  C. We also established a closed cultivation system to feed a test plant with CO
C. We also established a closed cultivation system to feed a test plant with CO at set concentrations of 400, 1,500 and 3,000 ppm and a pulse of
at set concentrations of 400, 1,500 and 3,000 ppm and a pulse of  CO
CO .
.
田中 淳; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊; 石川 秀高*; 小池 亜紀*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 96, 2016/02
アジア原子力協力フォーラム(FNCA)は、内閣府/文部科学省が主導する原子力平和利用協力の枠組みであり、その1つの活動として放射線育種プロジェクトがある。イネの突然変異育種の第二期プロジェクト(2013 2017)として、バングラデシュ, 中国, インドネシア, 韓国, マレーシア, モンゴル, フィリピン, タイ, ベトナム及び日本の10ヶ国が参加して、「持続的農業のためのイネの品種改良(環境耐性、少肥料多収等)」が実施されている。バングラデシュでは、イオンビームを用いて高収量の新品種が数系統確立され、その内の1品種BINAdhan-14は2013年に品種登録され、実用栽培が開始されている。マレーシアでは、品種MR219への照射に由来する、渇水耐性や病害抵抗性の強い変異系統の選抜に成功し、実用化を予定している。ベトナムでは品種Khang danへの照射により、高収量で耐倒伏性の高い系統を獲得した。
2017)として、バングラデシュ, 中国, インドネシア, 韓国, マレーシア, モンゴル, フィリピン, タイ, ベトナム及び日本の10ヶ国が参加して、「持続的農業のためのイネの品種改良(環境耐性、少肥料多収等)」が実施されている。バングラデシュでは、イオンビームを用いて高収量の新品種が数系統確立され、その内の1品種BINAdhan-14は2013年に品種登録され、実用栽培が開始されている。マレーシアでは、品種MR219への照射に由来する、渇水耐性や病害抵抗性の強い変異系統の選抜に成功し、実用化を予定している。ベトナムでは品種Khang danへの照射により、高収量で耐倒伏性の高い系統を獲得した。
田之頭 優樹*; 永吉 実孝*; 渡辺 剛史*; 長谷 純宏
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 98, 2016/02
これまでの夏秋スプレーギク品種「サザンチェルシー(桃色)」へのイオンビーム照射による花色変異体作出では、白色、赤樺色の変異体は出現するものの、黄色変異体は出現しなかった。そこで、得られた花色変異体の出現率や色素分析結果を踏まえ、目的とする花色変異体の出現率を想定した。原品種(桃色)への照射による赤樺色変異体の出現率、すなわちカロテノイド含量の増加が生じる頻度は1.4%と想定された。一方、白色変異体の出現率、すなわちアントシアニンの消失が生じる頻度は0.6%と想定された。カロテノイド及びアントシアニン含量の変化は、それぞれの生合成経路が異なることから独立の変異によって生じると考えられる。したがって、1回の変異誘発でアントシアニン消失とカロテノイド含量増加の2つの変化を併せ持つ黄色変異体が作出される頻度は極めて低く、0.0084%と推定される。この結果から、黄色変異体を得るためには、白色変異体への再照射によってカロテノイド含量の増加を引き起こすことが最も効率的であると考えられた。このことは、複数の形質を対象とした突然変異育種においては段階的に変異を誘発する方法が効率的であることを示唆する。
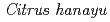

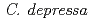 )の植物体再生率に対する炭素イオンの照射効果
)の植物体再生率に対する炭素イオンの照射効果納富 麻子*; 長谷 純宏; 田中 義樹*; 竹下 大樹*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 102, 2016/02
佐賀県で選抜されたノビレチン高含有香酸カンキツ「佐系69」を材料として、さらにノビレチンを高含有する系統などの作出を目的としてイオンビームの適性照射線量を検討した。実生胚軸上のカルスにイオンビームを照射し、植物体の再分化率に及ぼす影響を調査した。非照射区の再分化率は97.7%であった。2, 4及び8Gy照射区では非照射区に比べて再分化率が低下したが、線量反応は明確ではなかった。4Gy照射区においても約8割の個体が再分化したことから、「佐系69」の放射線感受性は、これまで試験したカンキツ類のなかでは最も放射線感受性が低かった川野ナツダイダイと同等と考えられた。
松尾 陽一郎*; 泉 佳伸*; 長谷 純宏; 坂本 綾子; 清水 喜久雄*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 104, 2016/02
本研究では出芽酵母S288cを材料として定量的ポリメラーゼ連鎖反応(qPCR)を用いてDNA損傷量の評価を試みた。0.1から10Gyの炭素イオンを照射したゲノムDNAを用い、PCRよってURA3遺伝子領域を増幅した。線量の増加に伴ってPCRによるDNA増幅は抑制された。以前の研究からURA3遺伝子領域内で変異が起こりやすいことが示唆された領域とそれ以外の領域の損傷量において、今回の試験では有意な差はなかったことから、抽出したDNAに対する照射では、損傷量は異ならないことが確認された。
渡邊 武志*; 関塚 史明*; 中村 悟之*; 長谷 純宏
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 110, 2016/02
イオンビームによる突然変異を利用して、亜熱帯地域, 沖縄地域に適する花き類の新規素材を作出するため、対象品目別の最適照射条件を検討した。ハイビスカスは、非照射区においても萌芽後の個体の発根が悪く、ほとんどが枯死したため照射の影響を確認できなかった。セイロンベンケイソウでは、変異誘発に適した照射線量は、50MeV  He
He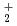 では40
では40 80Gy、107MeV
80Gy、107MeV  He
He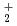 では80Gy以上、炭素イオン(220MeV及び320MeV)では16Gy以上であると考えられた。非照射株を基準として、開花日が早い、節間長が長い、花数が多い、がくの色が濃い等の形質の違いが認められ、これらの発生率は変異誘発に適した照射量において高くなっていた。この形質が遺伝的な変異であるのかを確認するために今後も栽培を継続して再確認を行う。なお、本研究は日本原子力研究開発機構の先端研究施設共用促進事業および施設供用制度を利用して実施した。
では80Gy以上、炭素イオン(220MeV及び320MeV)では16Gy以上であると考えられた。非照射株を基準として、開花日が早い、節間長が長い、花数が多い、がくの色が濃い等の形質の違いが認められ、これらの発生率は変異誘発に適した照射量において高くなっていた。この形質が遺伝的な変異であるのかを確認するために今後も栽培を継続して再確認を行う。なお、本研究は日本原子力研究開発機構の先端研究施設共用促進事業および施設供用制度を利用して実施した。
山口 絵梨香*; 宮谷 真徳*; 河合 隆行*; 渥美 浩久*; 長谷 純宏
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 111, 2016/02
横浜植木が育成したサルビア品種は、生育が旺盛で開花期が長いという特長があるが、種間交雑により作出されたことから不稔であり、交配による育種は困難である。そのため、同品種を材料として、イオンビーム照射による新品種開発を試みた。2系統(SAC33及びSAC7-2)の挿し穂に対して炭素イオンビームを照射し、発根後鉢上げして開花させた。花色の変異やがくの発色が薄くなる変異が確認された。変異の発生率は0.48から1.80%であり、照射線量が高くなるほど変異率が高い傾向が認められた。有望株は商品化に向けた増殖と特性調査を行い、一部の変異系統については再照射による更なる変異拡大について検討する予定である。
 Co
Co  -ray irradiation facilities
-ray irradiation facilities宇野 定則; 花屋 博秋; 山縣 諒平; 清藤 一; 長尾 悠人; 山崎 翔太; 上松 敬; 川島 郁男*; 八木 紀彦*; 高木 雅英*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 172, 2016/02
平成26年度の高崎量子応用研究所の 線照射施設及び電子加速器の運転状況を報告する。
線照射施設及び電子加速器の運転状況を報告する。 線照射施設はおおむね順調に稼働したが、電子加速器は34年間にわたる稼働による経年劣化のために、主に放電による故障が頻発し、約5ヶ月間停止した。
線照射施設はおおむね順調に稼働したが、電子加速器は34年間にわたる稼働による経年劣化のために、主に放電による故障が頻発し、約5ヶ月間停止した。 線照射施設第1棟,第2棟及び食品照射棟の年間運転時間は、各19,907時間、13,831時間及び7,293時間で、電子加速器では746時間であった。
線照射施設第1棟,第2棟及び食品照射棟の年間運転時間は、各19,907時間、13,831時間及び7,293時間で、電子加速器では746時間であった。 線照射施設では2.22PBqの新線源を5本補充し、20本の古い線源を処分した。電子加速器では、前述の故障に対してその都度適切に対処をしたが、完全な修復には至っていない。
線照射施設では2.22PBqの新線源を5本補充し、20本の古い線源を処分した。電子加速器では、前述の故障に対してその都度適切に対処をしたが、完全な修復には至っていない。
 線照射されたアミノ酸中の照射誘導ラジカルの緩和時間
線照射されたアミノ酸中の照射誘導ラジカルの緩和時間永田 夏樹*; 菰田 聖一*; 菊地 正博; 中村 秀夫*; 小林 泰彦; 鵜飼 光子*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 103, 2016/02
照射食品に誘導されたフリーラジカル中の不対電子の緩和時間は、ラジカル間の相互作用の程度を示す指標のひとつとなる。緩和時間は、パルスESR装置で直接測定可能であるが装置が高価で普及していない。そのため、連続波ESR装置の測定結果を用いたシミュレーション解析により算出する手法も用いられ、Lund法は1本線信号の緩和時間の算出に適用される。照射アミノ酸の複数ピークをそのままシミュレーション解析した時、緩和時間はパルスESRの直接測定値とは大きく異なった。そこで3種類の照射アミノ酸で得られる複数ピークについてガウスピーク近似により分離して、それぞれのピークパラメータを用いてLund法のシミュレーション解析に適用した。その結果、算出されたT 値はパルスESRの値とよく一致した。このことは、ピーク分離法が、複数ピークをもつESRスペクトルに対してLund法を適用する際に、緩和時間の計算精度を高める手法として有効であることを示している。
値はパルスESRの値とよく一致した。このことは、ピーク分離法が、複数ピークをもつESRスペクトルに対してLund法を適用する際に、緩和時間の計算精度を高める手法として有効であることを示している。
鈴井 伸郎; 丸山 哲平*; 河地 有木; 三輪 睿太郎*; 樋口 恭子*; 藤巻 秀
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 95, 2016/02
Common reed, which is classified to the same family as rice, is a salt-tolerant plant. In this study, we conducted non-invasive imaging of Na dynamics in intact common reed plants by using
dynamics in intact common reed plants by using  Na tracer and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) in order to understand the salt-tolerant mechanism in common reed. Common reeds and rice plants were cultivated in a nutrient solution containing 50 mM NaCl. After
Na tracer and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) in order to understand the salt-tolerant mechanism in common reed. Common reeds and rice plants were cultivated in a nutrient solution containing 50 mM NaCl. After  Na was fed into the solution, we observed the
Na was fed into the solution, we observed the  Na movement from the solution to the shoot for 24 h using PETIS. As a result,
Na movement from the solution to the shoot for 24 h using PETIS. As a result,  Na was strongly accumulated in the shoot base but not transported to the upper shoot in common reed, whereas
Na was strongly accumulated in the shoot base but not transported to the upper shoot in common reed, whereas  Na was continuously transported to the upper shoot in rice plant. Furthermore, we replaced the original solution with a fresh nutrient solution without
Na was continuously transported to the upper shoot in rice plant. Furthermore, we replaced the original solution with a fresh nutrient solution without  Na and traced the
Na and traced the  Na movement inside the plants for 18 h. Detailed quantitative analysis of the image data revealed that
Na movement inside the plants for 18 h. Detailed quantitative analysis of the image data revealed that  Na migrated downward from the shoot base to the root tip in common reed. These results indicate that common reed has constitutive ability of Na
Na migrated downward from the shoot base to the root tip in common reed. These results indicate that common reed has constitutive ability of Na exclusion only in the direction of root tips, and consequently keeps low Na
exclusion only in the direction of root tips, and consequently keeps low Na concentration in the upper shoot.
concentration in the upper shoot.