Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 path-integral simulations of hydrogen-isotope diffusion in face-centred cubic metals
path-integral simulations of hydrogen-isotope diffusion in face-centred cubic metals君塚 肇*; 尾方 成信*; Thomsen, B.; 志賀 基之
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 37(19), p.193001_1 - 193001_16, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)第一原理経路積分法を用いて、面心立方格子金属の水素同位体拡散係数を計算したところ、拡散係数の温度依存性が特異な形状をとることがわかった。これは温度依存性の異なる核量子効果の競合に起因しており、通常の同位体効果と逆同位体効果の間の異常なクロスオーバーのメカニズムを説明するものである。また、密度汎関数理論計算とほぼ同じ精度で、機械学習ベースの原子間ポテンシャルを用いて、近似的な量子ダイナミクスを記述する経路積分シミュレーションの結果も紹介する。この計算法は、様々な固体物質における水素同位体の量子的振る舞いを解明する道を開くものである。
関 剛斎*; 内田 健一*; 高梨 弘毅
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 36(33), p.333001_1 - 333001_11, 2024/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:12.05(Physics, Condensed Matter)Spin caloritronics, a research field studying on the interconversion between a charge current (J ) and a heat current (J
) and a heat current (J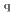 ) mediated by a spin current (J
) mediated by a spin current (J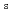 ) and/or magnetization (M), has attracted much attention not only for academic interest but also for practical applications. Newly discovered spin-caloritronic phenomena such as the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) have stimulated the renewed interest in the thermoelectric phenomena of a magnet, which have been known for a long time, e.g. the anomalous Nernst effect (ANE). These spin-caloritronic phenomena involving the SSE and the ANE have provided with a new direction for thermoelectric conversion exploiting J
) and/or magnetization (M), has attracted much attention not only for academic interest but also for practical applications. Newly discovered spin-caloritronic phenomena such as the spin Seebeck effect (SSE) have stimulated the renewed interest in the thermoelectric phenomena of a magnet, which have been known for a long time, e.g. the anomalous Nernst effect (ANE). These spin-caloritronic phenomena involving the SSE and the ANE have provided with a new direction for thermoelectric conversion exploiting J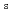 and/or M. Importantly, the symmetry of ANE allows the thermoelectric conversion in the transverse configuration between J
and/or M. Importantly, the symmetry of ANE allows the thermoelectric conversion in the transverse configuration between J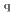 and J
and J . Although the transverse configuration is totally different from the conventional longitudinal configuration based on the Seebeck effect and has many advantages, we are still facing several issues that need to be solved before developing practical applications. The primal issue is the improvement of conversion efficiency. In the case of ANE-based applications, a material with a large anomalous Nernst coefficient (S
. Although the transverse configuration is totally different from the conventional longitudinal configuration based on the Seebeck effect and has many advantages, we are still facing several issues that need to be solved before developing practical applications. The primal issue is the improvement of conversion efficiency. In the case of ANE-based applications, a material with a large anomalous Nernst coefficient (S ) is the key for solving the issue. This review article introduces the increase of S
) is the key for solving the issue. This review article introduces the increase of S can be achieved by forming superlattice structures, which has been demonstrated for several kinds of materials combinations. The overall picture of studies on spin caloritronics is first surveyed. Then, we mention the pioneering work on the transverse thermoelectric conversion in superlattice structures, which was performed using Fe-based metallic superlattices, and show the recent studies for the Ni-based metallic superlattices and the ordered alloy-based metallic superlattices.
can be achieved by forming superlattice structures, which has been demonstrated for several kinds of materials combinations. The overall picture of studies on spin caloritronics is first surveyed. Then, we mention the pioneering work on the transverse thermoelectric conversion in superlattice structures, which was performed using Fe-based metallic superlattices, and show the recent studies for the Ni-based metallic superlattices and the ordered alloy-based metallic superlattices.
坂口 佳史*; 高田 慎一; 川北 至信; 藤村 由希; 近藤 啓悦
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(41), p.415403_1 - 415403_11, 2023/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)It is well-known that eutectic gold-silicon (Au-Si) alloys exhibit anomalous melting point depression, which is more than 1000  C from the melting point of elemental Si (1414
C from the melting point of elemental Si (1414  C). The melting point depression in eutectic alloys is generally explained in terms of a decrease of the free energy by mixing. However, it is difficult to understand the anomalous melting point depression only from the stability of the homogeneous mixing. Some researchers suggest that there are concentration fluctuations in the liquids, where the atoms are inhomogeneously mixed. In this paper, we measure the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) of Au
C). The melting point depression in eutectic alloys is generally explained in terms of a decrease of the free energy by mixing. However, it is difficult to understand the anomalous melting point depression only from the stability of the homogeneous mixing. Some researchers suggest that there are concentration fluctuations in the liquids, where the atoms are inhomogeneously mixed. In this paper, we measure the small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) of Au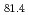 Si
Si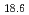 (eutectic composition) and Au
(eutectic composition) and Au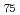 Si
Si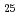 (off-eutectic composition) at temperatures from room temperature to 900
(off-eutectic composition) at temperatures from room temperature to 900  C in both solid and liquid states to observe such concentration fluctuations directly.
C in both solid and liquid states to observe such concentration fluctuations directly.
 inferred from muon study
inferred from muon study門野 良典*; 平石 雅俊*; 岡部 博孝*; 幸田 章宏*; 伊藤 孝
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285503_1 - 285503_13, 2023/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.32(Physics, Condensed Matter)Magnesium hydride has great potential as a solid hydrogen (H) storage material because of its high H storage capacity of 7.6 wt%. However, its slow hydrogenation and dehydrogenation kinetics and the high temperature of 300  C required for decomposition are major obstacles to small-scale applications such as automobiles. The local electronic structure of interstitial H in MgH
C required for decomposition are major obstacles to small-scale applications such as automobiles. The local electronic structure of interstitial H in MgH is an important fundamental knowledge in solving this problem, which has been studied mainly based on density functional theory (DFT). However, few experimental studies have been performed to assess the results of DFT calculations. We have therefore introduced muon (Mu) as pseudo-H into MgH
is an important fundamental knowledge in solving this problem, which has been studied mainly based on density functional theory (DFT). However, few experimental studies have been performed to assess the results of DFT calculations. We have therefore introduced muon (Mu) as pseudo-H into MgH and investigated the corresponding interstitial H states by analyzing their electronic and dynamical properties in detail. As a result, we observed multiple Mu states similar to those observed in wide-gap oxides, and found that their electronic states can be attributed to relaxed-excited states associated with donor/acceptor levels predicted by the recently proposed ambipolarity model. This provides an indirect support for the DFT calculations on which the model is based via the donor/acceptor levels. An important implication of the muon results for improved hydrogen kinetics is that dehydrogenation, serving as a reduction for hydrides, stabilises the interstitial H
and investigated the corresponding interstitial H states by analyzing their electronic and dynamical properties in detail. As a result, we observed multiple Mu states similar to those observed in wide-gap oxides, and found that their electronic states can be attributed to relaxed-excited states associated with donor/acceptor levels predicted by the recently proposed ambipolarity model. This provides an indirect support for the DFT calculations on which the model is based via the donor/acceptor levels. An important implication of the muon results for improved hydrogen kinetics is that dehydrogenation, serving as a reduction for hydrides, stabilises the interstitial H state.
state.
巽 一厳; 奥平 琢也*; 古府 麻衣子; Rozyczko, P.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 36(37), p.375901_1 - 375901_13, 2023/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)This study re-evaluates the theoretical approach to analyzing inelastic neutron spectra of hydrogen-containing metals and intermetallic compounds. Previously, these analyses utilized hydrogen quantum nuclear states, modeled as solutions to the Schr dinger equation. The potential surfaces in these models were approximated from the total energies derived from first-principles electronic structure calculations. The current study improves upon this method by employing more efficient and accurate treatments for sampling the potential surface. It utilizes symmetrically irreducible sampling points arranged on densely populated mesh grids for the first-principles calculations. A comparative analysis of the theoretical predictions with experimental spectra for hydrides of Ti
dinger equation. The potential surfaces in these models were approximated from the total energies derived from first-principles electronic structure calculations. The current study improves upon this method by employing more efficient and accurate treatments for sampling the potential surface. It utilizes symmetrically irreducible sampling points arranged on densely populated mesh grids for the first-principles calculations. A comparative analysis of the theoretical predictions with experimental spectra for hydrides of Ti Sb and Ti
Sb and Ti Sb, as well as a LaNi
Sb, as well as a LaNi hydrogen primary solid solution, demonstrates that this approach is promising for elucidating the unknown local environments of hydrogen atoms in systems where the approximate potential well describes the hydrogen quantum states.
hydrogen primary solid solution, demonstrates that this approach is promising for elucidating the unknown local environments of hydrogen atoms in systems where the approximate potential well describes the hydrogen quantum states.
Constantini, J.-M.*; 小川 達彦; Gourier, D.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285701_1 - 285701_12, 2023/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)従来、物質への放射線照射で発生するルミネッセンスはエネルギー付与に基づいて推定されるが、入射粒子がもたらす仮想光子のスペクトルに基づいて計算する方法を本研究で新たに開発し、その妥当性を実験に基づいて検証した。入射荷電粒子(電子,陽子, 粒子)が仮想光子を周囲に放出し、標的物質である
粒子)が仮想光子を周囲に放出し、標的物質である -アルミナの欠陥や不純物準位にある電子を励起すると仮定して、仮想光子スペクトルと準位の光子吸収スペクトルを理論計算し、その畳み込み積分によって励起遷移強度を算出した。この計算にPHITSの飛跡構造解析計算コードITSARTを利用することによって、荷電入射粒子が二次電子を散乱し、その二次電子が試料中の電子を励起する二次的な効果も考慮した。この励起遷移強度を荷電粒子飛跡上で積分し、実験的に得られたルミネッセンス強度と比較したところ、実験値の傾向を再現することができた。
-アルミナの欠陥や不純物準位にある電子を励起すると仮定して、仮想光子スペクトルと準位の光子吸収スペクトルを理論計算し、その畳み込み積分によって励起遷移強度を算出した。この計算にPHITSの飛跡構造解析計算コードITSARTを利用することによって、荷電入射粒子が二次電子を散乱し、その二次電子が試料中の電子を励起する二次的な効果も考慮した。この励起遷移強度を荷電粒子飛跡上で積分し、実験的に得られたルミネッセンス強度と比較したところ、実験値の傾向を再現することができた。
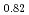 La
La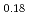 Fe
Fe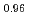 Ni
Ni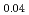 As
As
Xie, T.*; Liu, C.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; Li, S.*; Luo, H.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(47), p.474001_1 - 474001_8, 2022/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering (INS) investigations on the spin fluctuation spectrum in the 112-type iron-based superconductor (FeSC) Ca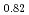 La
La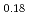 Fe
Fe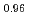 Ni
Ni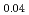 As
As (CaLa-112). In comparison to the 122-type FeSCs with a centrosymmetric tetragonal lattice structure (space group
(CaLa-112). In comparison to the 122-type FeSCs with a centrosymmetric tetragonal lattice structure (space group 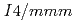 ) at room temperature and an in-plane stripe-type antiferromagnetic (AF) order at low temperature, the 112 system has a noncentrosymmetric structure (space group
) at room temperature and an in-plane stripe-type antiferromagnetic (AF) order at low temperature, the 112 system has a noncentrosymmetric structure (space group 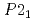 ) with additional zigzag arsenic chains between Ca/La layers and a magnetic ground state with similar wavevector
) with additional zigzag arsenic chains between Ca/La layers and a magnetic ground state with similar wavevector 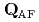 but different orientations of ordered moments in the parent compounds. Our INS study clearly reveals that the in-plane dispersions and the bandwidth of spin excitations in the superconducting CaLa-112 closely resemble to those in 122 systems. While the total fluctuating moments
but different orientations of ordered moments in the parent compounds. Our INS study clearly reveals that the in-plane dispersions and the bandwidth of spin excitations in the superconducting CaLa-112 closely resemble to those in 122 systems. While the total fluctuating moments 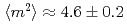
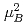 /Fe are larger than 122 system, the dynamic correlation lengths are similar (
/Fe are larger than 122 system, the dynamic correlation lengths are similar (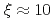
 ). These results suggest that superconductivity in iron arsenides may have a common magnetic origin under similar magnetic exchange couplings with a dual nature from local moments and itinerant electrons, despite their different magnetic patterns and lattice symmetries.
). These results suggest that superconductivity in iron arsenides may have a common magnetic origin under similar magnetic exchange couplings with a dual nature from local moments and itinerant electrons, despite their different magnetic patterns and lattice symmetries.

青木 大*; Brison, J.-P.*; Flouquet, J.*; 石田 憲二*; Knebel, G.*; 徳永 陽; 柳瀬 陽一*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(24), p.243002_1 - 243002_41, 2022/06
被引用回数:132 パーセンタイル:90.46(Physics, Condensed Matter)The novel spin-triplet superconductor candidate UTe attracted enormous attention. We review key experimental and theoretical progress which has been achieved in different laboratories. UTe
attracted enormous attention. We review key experimental and theoretical progress which has been achieved in different laboratories. UTe has been expected to be close to a ferromagnetic instability, showing many similarities to the U-based ferromagnetic superconductors, URhGe and UCoGe. The competition between different types of magnetic interactions and the duality between the local and itinerant character of the 5 f Uranium electrons, as well as the shift of the U valence appear as key parameters in the rich phase diagrams discovered recently under extreme conditions like low temperature, high magnetic field, and pressure. We discuss macroscopic and microscopic experiments at low temperature to clarify the normal phase properties at ambient pressure for field applied along the three axis of this orthorhombic structure.
has been expected to be close to a ferromagnetic instability, showing many similarities to the U-based ferromagnetic superconductors, URhGe and UCoGe. The competition between different types of magnetic interactions and the duality between the local and itinerant character of the 5 f Uranium electrons, as well as the shift of the U valence appear as key parameters in the rich phase diagrams discovered recently under extreme conditions like low temperature, high magnetic field, and pressure. We discuss macroscopic and microscopic experiments at low temperature to clarify the normal phase properties at ambient pressure for field applied along the three axis of this orthorhombic structure.

芳賀 芳範; Opletal, P.; 常盤 欣文; 山本 悦嗣; 徳永 陽; 神戸 振作; 酒井 宏典
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(17), p.175601_1 - 175601_7, 2022/04
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:86.06(Physics, Condensed Matter)Single crystals of the unconventional superconductor UTe have been grown in various conditions. Superconducting samples are nearly stoichiometric within an experimental error of about 1%, while non-superconducting sample significantly deviates from the ideal composition. The superconducting UTe
have been grown in various conditions. Superconducting samples are nearly stoichiometric within an experimental error of about 1%, while non-superconducting sample significantly deviates from the ideal composition. The superconducting UTe showed that the large density of states was partially gapped in the normal state, while the non-superconducting sample is characterized by the relatively large electronic specific heat as reported previously.
showed that the large density of states was partially gapped in the normal state, while the non-superconducting sample is characterized by the relatively large electronic specific heat as reported previously.
 Nb
Nb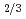 )O
)O
米田 安宏; 谷口 博基*; 野口 祐二*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 33(3), p.035401_1 - 035401_8, 2021/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:22.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)放射光高エネルギーX線回折実験を用いて、リラクサーPb(Mg Nb
Nb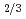 )O
)O (PMN)のナノスケール構造解析を行った。PMNはよく知られたリラクサー強誘電体であるが、平均構造が立方晶構造であることから、強誘電性のミクロ構造を説明するために種々のモデルが提案されてきた。我々は2体相関分布関数法(pair distribution function, PDF)を使って20nmまでの広いレンジの局所構造解析を行った。
(PMN)のナノスケール構造解析を行った。PMNはよく知られたリラクサー強誘電体であるが、平均構造が立方晶構造であることから、強誘電性のミクロ構造を説明するために種々のモデルが提案されてきた。我々は2体相関分布関数法(pair distribution function, PDF)を使って20nmまでの広いレンジの局所構造解析を行った。
Kataoka, Noriyuki*; Tanaka, Masashi*; Hosoda, Wataru*; Taniguchi, Takumi*; 藤森 伸一; Wakita, Takanori*; Muraoka, Yuji*; Yokoya, Takashi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 33(3), p.035501_1 - 035501_6, 2021/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:22.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have performed soft X-ray spectroscopy in order to study thephotoirradiation time dependence of the valence band structure and chemicalstates of layered transition metal nitride chloride TiNCl. Under the soft X-ray irradiation, the intensities of the states near the Fermi level (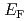 )and the Ti
)and the Ti component increased, while the Cl 2
component increased, while the Cl 2 intensity decreased. Ti2
intensity decreased. Ti2 -3
-3 resonance photoemission spectroscopy confirmed a distinctive Fermiedge with Ti 3
resonance photoemission spectroscopy confirmed a distinctive Fermiedge with Ti 3 character. These results indicate the photo-inducedmetallization originates from deintercalation due to Cl desorption, and thusprovide a new carrier doping method that controls the conducting propertiesof TiNCl.
character. These results indicate the photo-inducedmetallization originates from deintercalation due to Cl desorption, and thusprovide a new carrier doping method that controls the conducting propertiesof TiNCl.
 single unit-cell FeSe superconductor
single unit-cell FeSe superconductor深谷 有喜; Zhou, G.*; Zheng, F.*; Zhang, P.*; Wang, L.*; Xue, Q.-K.*; 社本 真一
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 31(5), p.055701_1 - 055701_6, 2019/02
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:26.76(Physics, Condensed Matter)本研究では、SrTiO 基板上の単層FeSeの構造が上下方向に非対称化していることを報告する。SrTiO
基板上の単層FeSeの構造が上下方向に非対称化していることを報告する。SrTiO 基板上の単層FeSeは、鉄系超伝導体において最も高い転移温度(50K以上)を示す。全反射高速陽電子回折(TRHEPD)を用いた構造解析の結果、真空側と界面側のSe-Fe層間隔は異なり、上下方向に非対称な構造であることがわかった。これらの層間隔および結合角の平均値は、圧力下のバルクFeSeにおいて高い転移温度を示す最適値と一致している。したがって、SrTiO
基板上の単層FeSeは、鉄系超伝導体において最も高い転移温度(50K以上)を示す。全反射高速陽電子回折(TRHEPD)を用いた構造解析の結果、真空側と界面側のSe-Fe層間隔は異なり、上下方向に非対称な構造であることがわかった。これらの層間隔および結合角の平均値は、圧力下のバルクFeSeにおいて高い転移温度を示す最適値と一致している。したがって、SrTiO 基板上の単層FeSeは非対称化することにより高い転移温度を発現するための最適構造を形成したと考えられる。
基板上の単層FeSeは非対称化することにより高い転移温度を発現するための最適構造を形成したと考えられる。
 and 5
and 5 materials studied by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy
materials studied by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy藤森 伸一
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 28(15), p.153002_1 - 153002_31, 2016/04
被引用回数:39 パーセンタイル:38.92(Physics, Condensed Matter)Recent remarkable progresses in angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES) made it possible to directly observe the band structures of 4 and 5
and 5 materials. In particular, ARPES with various light sources such as laser or high-energy synchrotron radiations shed light on the bulk band structures of strongly-correlated materials with the energy scales from few meV to several eV. The main purpose of the present article is to summarize the behaviors of 4
materials. In particular, ARPES with various light sources such as laser or high-energy synchrotron radiations shed light on the bulk band structures of strongly-correlated materials with the energy scales from few meV to several eV. The main purpose of the present article is to summarize the behaviors of 4 and 5
and 5 band structures of various rare earth and actinide materials observed by modern ARPES techniques, and understand how they can be described by various theoretical frameworks. For 4
band structures of various rare earth and actinide materials observed by modern ARPES techniques, and understand how they can be described by various theoretical frameworks. For 4 -electron materials, ARPES studies of CeMIn
-electron materials, ARPES studies of CeMIn and YbRh
and YbRh Si
Si with various incident photon energies are summarized. For U 5
with various incident photon energies are summarized. For U 5 compounds, ARPES studies of UFeGa
compounds, ARPES studies of UFeGa , UPd
, UPd , and URu
, and URu Si
Si are summarized based on various ARPES studies. The present status of the field as well as possible future directions are discussed.
are summarized based on various ARPES studies. The present status of the field as well as possible future directions are discussed.
Chen, Y.-T.*; 高橋 三郎*; 中山 裕康*; Althammer, M.*; Goennenwein, S. T. B.*; 齊藤 英治; Bauer, G. E. W.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 28(10), p.103004_1 - 103004_15, 2016/03
被引用回数:93 パーセンタイル:61.66(Physics, Condensed Matter)スピンホール効果によってスピン流が発生する金属と磁性絶縁体との二重層におけるいわゆるスピンホール磁気抵抗(SMR)を概観する。関連する角運動量が強磁性層に伝達され、それにより電気抵抗が印加電流と磁化方向との間の角度によって変調される。SMRは、絶縁体の磁化方向とスピン伝達トルクを非侵入的に測定するための便利なツールを提供する。SMR、すなわちスピン拡散理論および量子力学的境界条件を計算するための最小の理論的手段を紹介する。これは、実験に適合させることができる少数のパラメータを導出する。理論の限界と、強磁性近接効果やRashbaスピン軌道トルクなどの代替メカニズムについて議論し、新しい展開を指摘する。
 Pt
Pt As
As (Fe
(Fe Pt
Pt As)
As)
池内 和彦*; 小林 義明*; 鈴木 一範*; 伊藤 正行*; 梶本 亮一; Bourges, P.*; Christianson, A. D.*; 中村 博樹; 町田 昌彦; 佐藤 正俊*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 27(46), p.465701_1 - 465701_7, 2015/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:13.75(Physics, Condensed Matter)中性子非弾性散乱実験による超伝導体Ca Pt
Pt As
As (Fe
(Fe Pt
Pt As)
As) のフォノンの測定結果を報告する。特に転移温度33K付近でのクーパー対に対する軌道揺らぎの影響を調査し、弾性定数
のフォノンの測定結果を報告する。特に転移温度33K付近でのクーパー対に対する軌道揺らぎの影響を調査し、弾性定数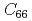 に対応する面内横音響フォノンに少しソフト化が起きていることを観測した。また、転移温度以上の温度で面内光学フォノンが異常に強く変化するのを観測した。このモードは鉄と砒素の面内振動に対応しており、鉄のd軌道の軌道揺らぎと格子系の結合に関する情報を与えている。この結果は超伝導発現機構やいわゆるネマティック相の研究に有益な情報をもたらすものである。
に対応する面内横音響フォノンに少しソフト化が起きていることを観測した。また、転移温度以上の温度で面内光学フォノンが異常に強く変化するのを観測した。このモードは鉄と砒素の面内振動に対応しており、鉄のd軌道の軌道揺らぎと格子系の結合に関する情報を与えている。この結果は超伝導発現機構やいわゆるネマティック相の研究に有益な情報をもたらすものである。
Li, H.; 前川 雅樹; 河裾 厚男; 谷村 直樹*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 27(24), p.246001_1 - 246001_5, 2015/06
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:29.96(Physics, Condensed Matter)Positron lifetime spectra of Fe, Co and Ni were measured under magnetic field using a  Na source. Very small but distinguishable difference of positron lifetime upon magnetic field reversal was observed suggesting the existence of two bulk lifetimes associated with majority and minority spin electrons. Using two spin-dependent Fe bulk lifetimes, the difference Doppler broadening of annihilation radiation spectra between majority and minority spin electrons were also examined. Agreement between experiment and theory indicates that spin-polarized positron annihilation spectroscopy may have potential in investigation of spin-aligned electron momentum distribution.
Na source. Very small but distinguishable difference of positron lifetime upon magnetic field reversal was observed suggesting the existence of two bulk lifetimes associated with majority and minority spin electrons. Using two spin-dependent Fe bulk lifetimes, the difference Doppler broadening of annihilation radiation spectra between majority and minority spin electrons were also examined. Agreement between experiment and theory indicates that spin-polarized positron annihilation spectroscopy may have potential in investigation of spin-aligned electron momentum distribution.
内田 健一*; 石田 真彦*; 吉川 貴史*; 桐原 明宏*; 村上 朝夫*; 齊藤 英治
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(34), p.343202_1 - 343202_15, 2014/08
被引用回数:232 パーセンタイル:84.79(Physics, Condensed Matter)The spin Seebeck effect refers to the generation of spin voltage as a result of a temperature gradient in ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic materials. When a conductor is attached to a magnet under a temperature gradient, the thermally generated spin voltage in the magnet injects a spin current into the conductor, which in turn produces electric voltage owing to the spin-orbit interaction. The spin Seebeck effect is of increasing importance in spintronics, since it enables direct generation of a spin current from heat and appears in a variety of magnets ranging from metals and semiconductors to insulators. Recent studies on the spin Seebeck effect have been conducted mainly in paramagnetic metal/ferrimagnetic insulator junction systems in the longitudinal configuration in which a spin current flowing parallel to the temperature gradient is measured. This "longitudinal spin Seebeck effect" (LSSE) has been observed in various sample systems and exclusively established by separating the spin-current contribution from extrinsic artefacts, such as conventional thermoelectric and magnetic proximity effects. The LSSE in insulators also provides a novel and versatile pathway to thermoelectric generation in combination of the inverse spin-Hall effects. In this paper, we review basic experiments on the LSSE and discuss its potential thermoelectric applications with several demonstrations.
森 道康; 小椎八重 航*; 挽野 真一*; 前川 禎通
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(25), p.255702_1 - 255702_5, 2014/06
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:13.77(Physics, Condensed Matter)A magnetic domain wall (DW) behaves as a massive particle with elasticity. Sliding and oscillation of the DW have been observed experimentally, whereas vibration of a width in the DW, "breathing mode", has not been measured so far. We theoretically propose how to observe the breathing mode by the Josephson junction having a ferromagnetic layer between superconducting electrodes. The current-voltage ( -
- ) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the
) curve is calculated by an equivalent circuit of the resistively shunted junction model. The breathing mode is identified by stepwise structures in the  -
- curve, which appear at the voltages
curve, which appear at the voltages  =
=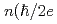 )
) with the fundamental constant
with the fundamental constant 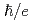 , integer number
, integer number  , and the frequency of the breathing mode
, and the frequency of the breathing mode  .
.
 explored using
explored using  In nuclear quadrupole resonance
In nuclear quadrupole resonance中堂 博之; Koutroulakis, G.*; 安岡 弘志; Bauer, E. D.*; Tobash, P. H.*; Mitchell, J. N.*; Thompson, J. D.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(3), p.036001_1 - 036001_5, 2014/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:22.43(Physics, Condensed Matter)PuIn における
における In NQR測定の結果について報告する。
In NQR測定の結果について報告する。 Inの核スピン
Inの核スピン =9/2に期待される4本のNQR共鳴線のうちの3本の共鳴線を観測した。20Kにおいて、それらの共鳴線は等間隔であり、そこからNQR周波数
=9/2に期待される4本のNQR共鳴線のうちの3本の共鳴線を観測した。20Kにおいて、それらの共鳴線は等間隔であり、そこからNQR周波数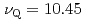 MHzと電場勾配の非対称パラメータの
MHzと電場勾配の非対称パラメータの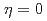 が導かれた。14Kにおいて、NQR共鳴線の形状と核スピン緩和率1/
が導かれた。14Kにおいて、NQR共鳴線の形状と核スピン緩和率1/ は反強磁性転移により変化を生じる。14K以下において、NQRスペクトルより見積もられた内部交番磁化
は反強磁性転移により変化を生じる。14K以下において、NQRスペクトルより見積もられた内部交番磁化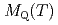 と1/
と1/ の温度依存性はスピン揺らぎのSCR理論によりよく説明される。さらに、
の温度依存性はスピン揺らぎのSCR理論によりよく説明される。さらに、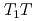 と
と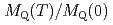 はSCR理論から予言される通りに比例している。これらの結果はPuIn
はSCR理論から予言される通りに比例している。これらの結果はPuIn が弱い反強磁性体、すなわち有限温度において反強磁性波数近傍のスピン揺らぎが物性を支配している証拠である。
が弱い反強磁性体、すなわち有限温度において反強磁性波数近傍のスピン揺らぎが物性を支配している証拠である。
 Si
Si and DyCu
and DyCu Si
Si
三本 啓輔*; 後藤 沙織*; 根本 祐一*; 赤津 光洋*; 後藤 輝孝*; Dung, N. D.*; 松田 達磨; 芳賀 芳範; 竹内 徹也*; 杉山 清寛*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 25(29), p.296002_1 - 296002_8, 2013/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:9.37(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have investigated quadrupole effects in tetragonal crystals of PrCu Si
Si and DyCu
and DyCu Si
Si by means of low-temperature ultrasonic measurements. The elastic constant C
by means of low-temperature ultrasonic measurements. The elastic constant C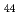 of PrCu
of PrCu Si
Si exhibits pronounced softening below 70 K, which is described in terms of a quadrupole susceptibility for a doublet ground state.
exhibits pronounced softening below 70 K, which is described in terms of a quadrupole susceptibility for a doublet ground state.