Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Bi
Bi
Park, P.*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Spargue, M.*; Sakuya, A. P.*; Chen, S. A.*; Frontzek, M. D.*; Tian, W.*; Sibille, R.*; Mazzone, D. G.*; 田端 千紘; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.4384_1 - 4384_9, 2025/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kagome metals with van Hove singularities (VHSs) near the Fermi level can host intriguing quantum phenomena, including chiral loop currents, electronic nematicity, and unconventional superconductivity. However, unconventional magnetic states driven by VHSs, such as spin-density waves (SDWs), have yet to be observed experimentally in kagome metals. Here, we present a comprehensive investigation of the magnetic and electronic structure of the layered kagome metal CeTi Bi
Bi , where the Ti kagome electronic structure interacts with a magnetic sublattice of Ce
, where the Ti kagome electronic structure interacts with a magnetic sublattice of Ce
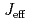 = 1/2 moments. Our findings establish the rare-earth Kagome metals LnTi3Bi4 as a model platform where characteristic electronic structure of the kagome lattice plays a pivotal role in magnetic order.
= 1/2 moments. Our findings establish the rare-earth Kagome metals LnTi3Bi4 as a model platform where characteristic electronic structure of the kagome lattice plays a pivotal role in magnetic order.
Thennakoon, A.*; 横倉 涼雅*; Yang, Y.*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; 林 真弘*; 道岡 千城*; Chern, G.-W.*; Broholm, C.*; 植田 浩明*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.3939_1 - 3939_13, 2025/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The pursuit of quantum spin liquid (QSL) states in condensed matter physics has drawn attention to kagome antiferromagnets (AFM) where a two-dimensional corner-sharing network of triangles frustrates conventional magnetic orders. While quantum kagome AFMs based on Cu (
(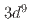 ,
, 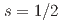 ) ions have been extensively studied, there is so far little work beyond copper-based systems. Here we present our bulk magnetization, specific heat and neutron scattering studies on single crystals of a new titanium fluorides Cs
) ions have been extensively studied, there is so far little work beyond copper-based systems. Here we present our bulk magnetization, specific heat and neutron scattering studies on single crystals of a new titanium fluorides Cs RbK
RbK Ti
Ti F
F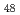 where Ti
where Ti (
(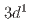 ,
, 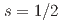 ) ions form a modulated quantum kagome antiferromagnet that does not order magnetically down to 1.5 K. Our comprehensive map of the dynamic response function
) ions form a modulated quantum kagome antiferromagnet that does not order magnetically down to 1.5 K. Our comprehensive map of the dynamic response function 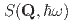 acquired at 1.5 K where the heat capacity is
acquired at 1.5 K where the heat capacity is  -linear reveals a dispersive continuum emanating from soft lines that extend along (100). The data indicate fractionalized spinon-like excitations with quasi-one-dimensional dispersion within a quasi two-dimensional spin system.
-linear reveals a dispersive continuum emanating from soft lines that extend along (100). The data indicate fractionalized spinon-like excitations with quasi-one-dimensional dispersion within a quasi two-dimensional spin system.
Sanfilippo, A.*; 安邊 啓明; 他27名*
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.2016_1 - 2016_11, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mantle processes control plate tectonics and exert an influence on biogeochemical cycles. However, the proportion of the mantle accessible to sampling is minimal, and a significant portion of our knowledge is derived from xenoliths, orogenic peridotite massifs exposed on land, and abyssal peridotites. Sampling of in-situ sections of the mantle is extremely challenging because they are buried beneath a magmatic crust with its sedimentary cover. In this study, we report the lithological characteristics of two mantle sections from an embryonic, very young, (~3 Ma) oceanic basin drilled by the International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP) in the central Tyrrhenian Sea. In contrast to observations made in drilled mantle sections from Mid Ocean Ridges (MORs) and hyperextended passive margins such as those in Iberia and Newfoundland, our findings revealed an exceptionally heterogeneous and generally fertile mantle. This represents a snapshot of young oceanic basement in a continental rifting environment characterised by general igneous starvation. The lithological heterogeneity ranges from fertile lherzolites to depleted harzburgites and dunites, variably interlayered with pyroxenites. Plagioclase- and clinopyroxene-rich layers, hydrous potassic magmatic veins, and gabbroic intrusions in these peridotites indicate substantial mantle re-fertilization and delayed inception of magmatic crust. The diverse lithological recovery indicates that magma-poor rifts do not necessarily require a chemically depleted mantle, too refractory to melt. Instead, we propose that deep lithospheric processes such as mantle refertilisation and prolonged lithospheric thinning hinder melt focusing and the formation of a steady-state spreading centre.
Yoon, J.-Y.*; 竹内 祐太朗*; 武智 涼太*; Han, J.*; 内山 友宏*; 山根 結太*; 金井 駿*; 家田 淳一; 大野 英男*; 深見 俊輔*
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.1171_1 - 1171_8, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Spin-orbit torque (SOT) provides a promising mechanism for electrically encoding information in magnetic states. Unlike existing schemes, where the SOT is passively determined by the material and device structures, an active manipulation of the intrinsic SOT polarity would allow for flexibly programmable SOT devices. Achieving this requires electrical control of the current-induced spin polarization of the spin source. Here we demonstrate a proof-of-concept current-programmed SOT device. Using a noncollinear-anti-ferromagnetic/nonmagnetic/ferromagnetic Mn Sn/Mo/CoFeB hetero-structure at zero magnetic eld, we show current-induced switching in the CoFeB layer due to the spin current polarized by the magnetic structure of the Mn
Sn/Mo/CoFeB hetero-structure at zero magnetic eld, we show current-induced switching in the CoFeB layer due to the spin current polarized by the magnetic structure of the Mn Sn; by properly tuning the driving current, the spin current from the CoFeB further reverses the magnetic orientation of the Mn
Sn; by properly tuning the driving current, the spin current from the CoFeB further reverses the magnetic orientation of the Mn Sn, which determines the polarity of the subsequent switching of the CoFeB. This scheme of mutual switching can be achieved in a spin-valve-like simple protocol because each magnetic layer serves as a reversible spin source and target magnetic electrode. It yields intriguing proof-of-concept functionalities for unconventional logic and neuromorphic computing.
Sn, which determines the polarity of the subsequent switching of the CoFeB. This scheme of mutual switching can be achieved in a spin-valve-like simple protocol because each magnetic layer serves as a reversible spin source and target magnetic electrode. It yields intriguing proof-of-concept functionalities for unconventional logic and neuromorphic computing.
Zheng, X.-G.*; 山内 一宏*; 萩原 雅人; 西堀 英治*; 河江 達也*; 渡邊 功雄*; 内山 智貴*; Chen, Y.*; Xu, C.-N.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.9989_1 - 9989_12, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Like the crystallization of water to ice, magnetic transition occurs at a critical temperature after the slowing down of dynamically fluctuating short-range correlated spins. Here, we report a unique type of magnetic transition characterized by a linear increase in the volume fraction of unconventional static short-range-ordered spin clusters, which triggered a transition into a long-range order at a threshold fraction perfectly matching the bond percolation theory in a new quantum antiferromagnet of pseudo-trigonal Cu (OH)
(OH) Cl
Cl . Static short-range order appeared in its Kagome lattice plane below Ca. 20 K from a pool of coexisting spin liquid, linearly increasing its fraction to 0.492(8), then all Kagome spins transitioned into a stable two-dimensional spin order at
. Static short-range order appeared in its Kagome lattice plane below Ca. 20 K from a pool of coexisting spin liquid, linearly increasing its fraction to 0.492(8), then all Kagome spins transitioned into a stable two-dimensional spin order at  _
_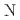
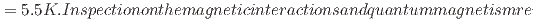 _
_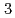
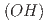 _
_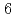
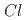 _
_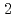 $. The unconventional static nature of the short-range order was inferred to be due to a pinning effect by the strongly correlated coexisting spin liquids. This work presents a unique magnetic system to demonstrate a complete bond percolation process toward the critical transition. Meanwhile, the unconventionally developed magnetic order in this chemically clean system should shed new light on spin-liquid physics.
$. The unconventional static nature of the short-range order was inferred to be due to a pinning effect by the strongly correlated coexisting spin liquids. This work presents a unique magnetic system to demonstrate a complete bond percolation process toward the critical transition. Meanwhile, the unconventionally developed magnetic order in this chemically clean system should shed new light on spin-liquid physics.
小澤 孝拓*; 福谷 克之; 他7名*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.9558_1 - 9558_8, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hydrogen, the smallest and lightest element, readily permeates a variety of materials and modulates their physical properties. Identification of the hydrogen lattice location and its amount in crystals is key to understanding and controlling the hydrogen-induced properties. Combining nuclear reaction analysis (NRA) with the ion channeling technique, we experimentally determined the locations of H and D in epitaxial nanofilms of titanium hydrides from the analysis of the two-dimensional angular mappings of NRA yields. Here we show that 11 at% of H are located at the octahedral site with the remaining H atoms in the tetrahedral site. Density functional theory calculations revealed that the structures with the partial octahedral site occupation are stabilized by the Fermi level shift and Jahn-Teller effect induced by hydrogen. In contrast, D was found to solely occupy the tetrahedral site owing to the mass effect on the zero-point vibrational energy. These findings suggest that site occupation of hydrogen can be controlled by changing the isotope mixture ratio, which leads to promising manifestation of novel hydrogen-related phenomena.
町田 晃彦*; 齋藤 寛之*; 杉本 秀彦*; 服部 高典; 佐野 亜沙美; 遠藤 成輝*; 片山 芳則*; 飯塚 理子*; 佐藤 豊人*; 松尾 元彰*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.8861_1 - 8861_2, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)前回の論文(Nature Commun. 5, 5063 (2014))では、988Kと6.3GPaで収集した中性子粉末回折パターンのリートベルト精密化によって、fcc Fe金属格子に溶解したD原子のサイト占有率を調べた。fcc金属格子には、八面体サイトと四面体サイトの2つのD原子収容可能な格子間サイトがある。リートベルト精密化により、D原子は主に八面体サイトを0.532占有し、わずかに四面体サイトを0.056占有することがわかった。その後、Antonov (Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019))による密度汎関数理論(DFT)計算の結果、四面体サイトの占有エネルギーは八面体サイトの占有エネルギーよりも著しく高く、988Kの高温でも四面体サイトの占有は起こりにくいことがわかった。消衰補正は粉末回折パターンに適用されることはまれであり、前回の精密化には含まれていなかった。その結果、八面体の占有率は0.60に増加し、四面体の占有率はゼロに減少した。D原子の八面体サイトのみの占有は、以前の結果とは対照的ではあるが、DFT計算と一致している。
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; 服部 高典; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:88.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)明るい一重項励起子と三重項励起子を同時に発現する発光材料は、オプトエレクトロニクス、サイネージ、情報暗号化において大きな可能性を秘めている。しかしながら、高性能の白色発光を実現するためには、蛍光と燐光の寄与が不均衡であることが大きな障害となっている。ここでは、水素結合の協同効果による圧力処理エンジニアリングによって、n- -
- 遷移の混合を実現し、イソフタル酸(IPA)中で三重項状態の発光を7%から40%に高めることで、この課題に対処した。加圧処理したIPAでは、蛍光と燐光のハイブリッドに基づく優れた白色発光が得られ、フォトルミネッセンス量子収率は当初の19%(青色発光)から75%に増加した。その場での高圧IRスペクトル、X線回折、中性子回折から、圧力の上昇に伴い水素結合が連続的に強化されることが明らかになった。さらに、この強化された水素結合は、圧力処理後も常圧条件下まで保持され、バランスの取れた一重項/三重項励起子集団のための効率的な系間交差を目的としたIPAに与え、効率的な白色発光をもたらした。この研究は、有機低分子の三重項状態を明るくするルートを提案するだけでなく、一重項励起子と三重項励起子の比率を調節して、高性能の白色発光を構築するものである。
遷移の混合を実現し、イソフタル酸(IPA)中で三重項状態の発光を7%から40%に高めることで、この課題に対処した。加圧処理したIPAでは、蛍光と燐光のハイブリッドに基づく優れた白色発光が得られ、フォトルミネッセンス量子収率は当初の19%(青色発光)から75%に増加した。その場での高圧IRスペクトル、X線回折、中性子回折から、圧力の上昇に伴い水素結合が連続的に強化されることが明らかになった。さらに、この強化された水素結合は、圧力処理後も常圧条件下まで保持され、バランスの取れた一重項/三重項励起子集団のための効率的な系間交差を目的としたIPAに与え、効率的な白色発光をもたらした。この研究は、有機低分子の三重項状態を明るくするルートを提案するだけでなく、一重項励起子と三重項励起子の比率を調節して、高性能の白色発光を構築するものである。
Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Morace, A.*; 早川 岳人*; 佐藤 博隆*; 加美山 隆*; Wei, T.*; 巽 湧太*; 小泉 光生; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5365_1 - 5365_7, 2024/07
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:75.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The temperature measurement of material inside of an object is one of the key technologies for control of dynamical processes. For this purpose, various techniques such as laser-based thermography and phase-contrast imaging thermography have been studied. However, it is, in principle, impossible to measure the temperature of an element inside of an object using these techniques. One of the possible solutions is measurements of Doppler brooding effect in neutron resonance absorption (NRA). Here we present a method to measure the temperature of an element or an isotope inside of an object using NRA with a single neutron pulse of approximately 100 ns width provided from a high-power laser. We demonstrate temperature measurements of a tantalum (Ta) metallic foil heated from the room temperature up to 617 K. Although the neutron energy resolution is fluctuated from shot to shot, we obtain the temperature dependence of resonance Doppler broadening using a reference of a silver (Ag) foil kept to the room temperature. A free gas model well reproduces the results. This method enables element(isotope)-sensitive thermometry to detect the instantaneous temperature rise in dynamical processes.
 O ice observed by neutron diffraction
O ice observed by neutron diffraction小松 一生*; 服部 高典; Klotz, S.*; 町田 真一*; 山下 恵史朗*; 伊藤 颯*; 小林 大輝*; 入舩 徹男*; 新名 亨*; 佐野 亜沙美; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5100_1 - 5100_7, 2024/06
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:67.98(Multidisciplinary Sciences)水素結合の対称化とは、水素原子が水素結合の中心に位置する現象である。理論的研究により、氷VIIの水素結合は、圧力が増加するにつれて、水素の分布を変化させながら、いくつかの中間状態を経て、最終的に対称化すると予測されている。これまで、多くの実験的研究が行われてきたにもかかわらず、その水素の位置や転移圧力は一貫していない。われわれは、100GPa以上の圧力で中性子回折実験を行い、氷中の水素分布を決定し、隣接酸素間での分布が80GPa付近で2つから1つになり水素結合が対称化することを世界で初めて観測した。
Lei, Y.-J.*; 松村 大樹; 他15名*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.3325_1 - 3325_12, 2024/04
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:98.58(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The effective flow of electrons through bulk electrodes is crucial for achieving high-performance batteries, although the poor conductivity of homocyclic sulfur molecules results in high barriers against the passage of electrons through electrode structures. This phenomenon causes incomplete reactions and the formation of metastable products. To enhance the performance of the electrode, it is important to place substitutable electrification units to accelerate the cleavage of sulfur molecules and increase the selectivity of stable products during charging and discharging. Herein, we develop a single-atom-charging strategy to address the electron transport issues in bulk sulfur electrodes. The establishment of the synergistic interaction between the adsorption model and electronic transfer helps us achieve a high level of selectivity towards the desirable short-chain sodium polysulfides during the practical battery test. These finding indicates that the atomic manganese sites have an enhanced ability to capture and donate electrons. Additionally, the charge transfer process facilitates the rearrangement of sodium ions, thereby accelerating the kinetics of the sodium ions through the electrostatic force. These combined effects improve pathway selectivity and conversion to stable products during the redox process, leading to superior electrochemical performance for room temperature sodium-sulfur batteries.
都留 智仁; Han, S.*; 松浦 周太郎*; Chen, Z.*; 岸田 恭輔*; Lobzenko, I.; Rao, S.*; Woodward, C.*; George, E.*; 乾 晴行*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1706_1 - 1706_10, 2024/02
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:98.70(Multidisciplinary Sciences)耐火ハイエントロピー合金(RHEA)は、超高温用途への応用の可能性から注目されている。しかし、体心立方結晶をもつため面心立方HEAよりも脆く、さらに、主要なNi基超合金やFCC合金系の材料よりも著しく低いクリープ強度を示す。これらの欠点を克服し、RHEAを実用的な構造材料に発展させるためには、強度と延性を制御する要因の基礎的な理解を深める必要がある。本研究では、TiZrHfNbTaとVNbMoTaWという2つのモデルRHEAを調査し、前者は77Kまで塑性圧縮可能であるのに対し、後者は298K以下では圧縮不可能であることを示した。TiZrHfNbTaの六方最密充填(HCP)元素は、すべての構成元素がBCCであるVNbMoTaWと比較して、転位芯エネルギーを下げ、格子歪みを大きくし、せん断弾性率を下げることで、高い延性と相対的に高い降伏強度につながることがわかった。転位芯構造はVNbTaMoWではコンパクトで、TiZrHfNbTaでは拡張しており、2つのRHEAで異なる滑り面が活性化していることがわかった。これらは、いずれもHCP元素の濃度に起因していることが第一原理計算により明らかになった。この結果は、HCP元素とBCC元素の比率に関連した電子構造の変化を利用して、強度、延性、すべり挙動を制御し、より効率的な発電所や輸送のための次世代高温材料を開発できることを実証している。
雨倉 宏*; Chettah, A.*; 鳴海 一雅*; 千葉 敦也*; 平野 貴美*; 山田 圭介*; 山本 春也*; Leino, A. A.*; Djurabekova, F.*; Nordlund, K.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.1786_1 - 1786_10, 2024/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:57.35(Multidisciplinary Sciences)高い電子的阻止能領域の照射条件で高エネルギー重イオンを固体に照射すると、イオンの飛跡に沿って潜在イオントラックと呼ばれる柱状の損傷領域が形成される。イオントラックは、多くの物質中で形成されていることが知られているが、ダイヤモンドにおいて観察された例は皆無であった。高エネルギー(GeV)のウランイオンにおいてさえ、観察された例はない。本研究では、2-9MeV C フラーレンイオンを照射したダイヤモンドにおいて、初めてイオントラックが観察された。高分解能電子顕微鏡による観察により、イオントラックの内部がアモルファス化していることが示唆され、さらに、電子エネルギー損失分光法による分析によって、グラファイト由来の
フラーレンイオンを照射したダイヤモンドにおいて、初めてイオントラックが観察された。高分解能電子顕微鏡による観察により、イオントラックの内部がアモルファス化していることが示唆され、さらに、電子エネルギー損失分光法による分析によって、グラファイト由来の -結合の信号が検知された。分子動力学法に基づく計算シミュレーションで、上記の実験結果を再現することに成功した。
-結合の信号が検知された。分子動力学法に基づく計算シミュレーションで、上記の実験結果を再現することに成功した。
 TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Kang, Y.-G.*; Avdeev, M.*; Sibille, R.*; 飯田 一樹*; 梶本 亮一; Lee, K. H.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.8346_1 - 8346_9, 2023/12
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:86.45(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The triangular lattice antiferromagnet (TLAF) has been the standard paradigm of frustrated magnetism for several decades. The most common magnetic ordering in insulating TLAFs is the 120 structure. However, a new triple-
structure. However, a new triple-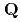 chiral ordering can emerge in metallic TLAFs, representing the short wavelength limit of magnetic skyrmion crystals. We report the metallic TLAF Co
chiral ordering can emerge in metallic TLAFs, representing the short wavelength limit of magnetic skyrmion crystals. We report the metallic TLAF Co TaS
TaS as the first example of tetrahedral triple-
as the first example of tetrahedral triple-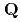 magnetic ordering with the associated topological Hall effect (non-zero
magnetic ordering with the associated topological Hall effect (non-zero 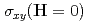 ). We also present a theoretical framework that describes the emergence of this magnetic ground state, which is further supported by the electronic structure measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Additionally, our measurements of the inelastic neutron scattering cross section are consistent with the calculated dynamical structure factor of the tetrahedral triple-
). We also present a theoretical framework that describes the emergence of this magnetic ground state, which is further supported by the electronic structure measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Additionally, our measurements of the inelastic neutron scattering cross section are consistent with the calculated dynamical structure factor of the tetrahedral triple-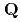 state.
state.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:92.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnon polarons are novel elementary excitations possessing hybrid magnonic and phononic signatures, and are responsible for many exotic spintronic and magnonic phenomena. Despite long-term sustained experimental efforts in chasing for magnon polarons, direct spectroscopic evidence of their existence is hardly observed. Here, we report the direct observation of magnon polarons using neutron spectroscopy on a multiferroic Fe Mo
Mo O
O possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
 probed by anisotropic low-energy excitations
probed by anisotropic low-energy excitations石原 滉大*; 六本木 雅生*; 小林 雅之*; 今村 薫平*; 水上 雄太*; 酒井 宏典; Opletal, P.; 常盤 欣文; 芳賀 芳範; 橋本 顕一郎*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.2966_1 - 2966_7, 2023/05
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:97.57(Multidisciplinary Sciences)重い電子系超伝導UTe の超伝導対称性を極低温磁場侵入長測定により研究した。異方的な低エネルギー準粒子励起が観測され、多成分カイラル超伝導を強く示唆する。このうち最も実験をよく説明するのは、カイラル非ユニタリー状態である。
の超伝導対称性を極低温磁場侵入長測定により研究した。異方的な低エネルギー準粒子励起が観測され、多成分カイラル超伝導を強く示唆する。このうち最も実験をよく説明するのは、カイラル非ユニタリー状態である。
Chong, Y.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; 都留 智仁; Zhang, R.*; 井上 耕治*; Gao, W.*; Godfrey, A.*; 光原 昌寿*; Morris, J. W. Jr.*; Minor, A. M.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.404_1 - 404_11, 2023/02
被引用回数:49 パーセンタイル:96.50(Multidisciplinary Sciences)チタンは格子間酸素によって脆化する。特に極低温では顕著な脆化挙動を示すため、チタンやその合金の製造において酸素含有量を厳しく管理する必要がある。この問題を解決するために、我々は結晶粒の微細化という構造戦略を提案した。77Kで非常に脆い粗粒の組織と比較して、Ti-0.3wt.%Oの超微細粒(UFG)組織(粒径 2.0
2.0 m)は、UFG組織特有の超高降伏強度を維持したまま均一延びを1桁上昇させることに成功した。UFG Ti-0.3wt.%Oにおけるこの特異な強度-延性相乗効果は、粒界凝集エネルギー向上に寄与する希薄な酸素の粒界偏析と優れたひずみ硬化能に寄与する
m)は、UFG組織特有の超高降伏強度を維持したまま均一延びを1桁上昇させることに成功した。UFG Ti-0.3wt.%Oにおけるこの特異な強度-延性相乗効果は、粒界凝集エネルギー向上に寄与する希薄な酸素の粒界偏析と優れたひずみ硬化能に寄与する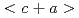 転位の活性化の複合効果によって達成された。この方法は、低温での高強度Ti-O合金の応用の可能性を高めるだけでなく、格子間固溶硬化による延性の低下を生じる他の合金系にも適用できる可能性がある。
転位の活性化の複合効果によって達成された。この方法は、低温での高強度Ti-O合金の応用の可能性を高めるだけでなく、格子間固溶硬化による延性の低下を生じる他の合金系にも適用できる可能性がある。
 archaea
archaeaSchoelmerich, M. C.*; Oubouter, H. T.*; Sachdeva, R.*; Penev, P. I.*; 天野 由記; West-Roberts, J.*; Welte, C. U.*; Banfield, J. F.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.7085_1 - 7085_11, 2022/11
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:72.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Anaerobic methanotrophic archaea (ANME) make energy from the breakdown of methane, an important driver of global warming, yet the extrachromosomal genetic elements that impact the activities of ANME are little understood. Here we describe large plasmids associated with ANME of the Methanoperedens Genus. These have been maintained in two enrichment bioreactors that are highly dominated by different  species and associate with
species and associate with  species in other anaerobic environments. By manual curation we show that two of the plasmids are large (155,607 bp and 191,912 bp), circular, and replicate bidirectionally. The group of
species in other anaerobic environments. By manual curation we show that two of the plasmids are large (155,607 bp and 191,912 bp), circular, and replicate bidirectionally. The group of  species that carry these plasmids is related to
species that carry these plasmids is related to  ,
,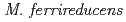 and
and 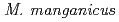 and the plasmids occur in the same copy number as the main chromosome. The larger plasmid encodes transporters that potentially enhance
and the plasmids occur in the same copy number as the main chromosome. The larger plasmid encodes transporters that potentially enhance  access to Ni, which is required for the MCR complex, Co required for the cobalamin cofactor needed for methyltransferases tied to central processes and amino acid uptake. We show that many plasmid genes are actively transcribed, including genes involved in plasmid chromosome maintenance and segregation, a Co
access to Ni, which is required for the MCR complex, Co required for the cobalamin cofactor needed for methyltransferases tied to central processes and amino acid uptake. We show that many plasmid genes are actively transcribed, including genes involved in plasmid chromosome maintenance and segregation, a Co /Ni
/Ni transporter and cell protective proteins. Notably, plasmid-borne genes for a ribosomal protein uL16 and adjacent elongation factor eEF2 are highly expressed. These are not encoded in the host
transporter and cell protective proteins. Notably, plasmid-borne genes for a ribosomal protein uL16 and adjacent elongation factor eEF2 are highly expressed. These are not encoded in the host  genome, indicating an obligate interdependence between this plasmid and its host. The finding of plasmids of
genome, indicating an obligate interdependence between this plasmid and its host. The finding of plasmids of  opens the way for the development of genetic vectors that could be used to probe little understood aspects of
opens the way for the development of genetic vectors that could be used to probe little understood aspects of  physiology. Ultimately, this may provide a route to introduce or alter genes that may enhance growth and overall metabolism to accelerate methane oxidation rates.
physiology. Ultimately, this may provide a route to introduce or alter genes that may enhance growth and overall metabolism to accelerate methane oxidation rates.
Xu, S.*; 大平 拓実*; 佐藤 駿介*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Seiner, H.*; Zoubkov , K.*; 村上 恭和*; et al.
, K.*; 村上 恭和*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.5307_1 - 5307_8, 2022/09
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:82.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Crystalline metals can have large theoretical elastic strain limits. However, a macroscopic block of conventional crystalline metals practically suffers a very limited elastic deformation of  0.5% with a linear stress-strain relationship obeying Hooke's law. Here, we report on the experimental observation of a large tensile elastic deformation with an elastic strain of
0.5% with a linear stress-strain relationship obeying Hooke's law. Here, we report on the experimental observation of a large tensile elastic deformation with an elastic strain of  4.3% in a Cu-based single crystalline alloy at its bulk scale at room temperature. The large macroscopic elastic strain that originates from the reversible lattice strain of a single phase is demonstrated by in situ microstructure and neutron diffraction observations. Furthermore, the elastic reversible deformation, which is nonhysteretic and quasilinear, is associated with a pronounced elastic softening phenomenon. The increase in the stress gives rise to a reduced Young's modulus, unlike the traditional Hooke's law behaviour. The experimental discovery of a non-Hookean large elastic deformation offers the potential for the development of bulk crystalline metals as high-performance mechanical springs or for new applications via "elastic strain engineering."
4.3% in a Cu-based single crystalline alloy at its bulk scale at room temperature. The large macroscopic elastic strain that originates from the reversible lattice strain of a single phase is demonstrated by in situ microstructure and neutron diffraction observations. Furthermore, the elastic reversible deformation, which is nonhysteretic and quasilinear, is associated with a pronounced elastic softening phenomenon. The increase in the stress gives rise to a reduced Young's modulus, unlike the traditional Hooke's law behaviour. The experimental discovery of a non-Hookean large elastic deformation offers the potential for the development of bulk crystalline metals as high-performance mechanical springs or for new applications via "elastic strain engineering."

Chen, L.*; Mao, C.*; Chung, J.-H.*; Stone, M. B.*; Kolesnikov, A. I.*; Wang, X.*; 村井 直樹; Gao, B.*; Delaire, O.*; Dai, P.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.4037_1 - 4037_7, 2022/07
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:81.53(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Spin and lattice are two fundamental degrees of freedom in a solid, and their fluctuations about the equilibrium values in a magnetic ordered crystalline lattice form quasiparticles termed magnons (spin waves) and phonons (lattice waves), respectively. In most materials with strong spin-lattice coupling (SLC), the interaction of spin and lattice induces energy gaps in the spin wave dispersion at the nominal intersections of magnon and phonon modes. Here we use neutron scattering to show that in the two-dimensional (2D) van der Waals honeycomb lattice ferromagnetic CrGeTe , spin waves propagating within the 2D plane exhibit an anomalous dispersion, damping, and breakdown of quasiparticle conservation, while magnons along the c axis behave as expected for a local moment ferromagnet. These results indicate the presence of dynamical SLC arising from the zero-temperature quantum fluctuations in CrGeTe
, spin waves propagating within the 2D plane exhibit an anomalous dispersion, damping, and breakdown of quasiparticle conservation, while magnons along the c axis behave as expected for a local moment ferromagnet. These results indicate the presence of dynamical SLC arising from the zero-temperature quantum fluctuations in CrGeTe , suggesting that the observed in-plane spin waves are mixed spin and lattice quasiparticles fundamentally different from pure magnons and phonons.
, suggesting that the observed in-plane spin waves are mixed spin and lattice quasiparticles fundamentally different from pure magnons and phonons.