Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2024-019, 102 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a new corrosion mitigation technology using nanobubbles toward corrosion mitigation in PCV system under the influence of  /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to corrosion, which is considered to be an important factor in the aging degradation of confinement functions (PCV, negative pressure maintenance system, etc.) during the fuel debris removal process. If the chemical species (especially H
-rays radiolysis" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to corrosion, which is considered to be an important factor in the aging degradation of confinement functions (PCV, negative pressure maintenance system, etc.) during the fuel debris removal process. If the chemical species (especially H O
O ) generated by radiolysis become locally concentrated in the areas where short-range
) generated by radiolysis become locally concentrated in the areas where short-range  - and
- and  -radiation emitting nuclides come into contact, the corrosion of steels may be greatly accelerated in those areas.
-radiation emitting nuclides come into contact, the corrosion of steels may be greatly accelerated in those areas.
Shikaze, Yoshiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.894 - 910, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Among the radioactive nuclides inside the nuclear reactor buildings emitted by the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactor accident, high-energy beta-ray sources, such as strontium-90 and yttrium-90, generate bremsstrahlung photons in the building materials, comprising the wall, floor, and interior structure. Therefore, evaluating the radiation dose of the bremsstrahlung to the workers in the nuclear reactor building is crucial for radiation protection. The precision of the evaluation calculation of the bremsstrahlung dose was investigated by comparing the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) and the GEometry ANd Tracking (GEANT4) simulation code results. In the calculation, behind various shielding plates (lead, copper, aluminum, glass, and polyethylene, with thicknesses ranging from 1.0 to 40 mm), the water cylinder was set as the evaluated material, the absorbed dose and the deposited energy spectrum by the bremsstrahlung photons were obtained, and the characteristics and differences for both simulation codes were investigated. In the comparison results of the deposited energy spectrum, the spectral shapes have consistent trends. In the energy range below several tens of keV, a peak is seen in the PHITS spectrum for the lead shielding material. In comparing the absorbed dose under various conditions of the shielding plate for generating bremsstrahlung photons, most results for both codes correlate within an  10% difference for 2.280 MeV beta-ray sources and an
10% difference for 2.280 MeV beta-ray sources and an  20% difference for 0.5459 MeV beta-ray sources, except for
20% difference for 0.5459 MeV beta-ray sources, except for  30% for 20 mm thick lead. Although there were differences in some cases, the evaluation results of the two simulation codes were concluded to correlate well with the above precision.
30% for 20 mm thick lead. Although there were differences in some cases, the evaluation results of the two simulation codes were concluded to correlate well with the above precision.
 -delayed neutron emitters
-delayed neutron emitters 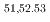 K
KXu, Z. Y.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 49 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 133(4), p.042501_1 - 042501_7, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillation
Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillationOuchi, Kazuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Hirose, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Yuika*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Shingo*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1298, p.342399_1 - 342399_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Given that conventional methods of high-dose sample analysis pose substantial exposure risks and generate large amounts of secondary radioactive waste, faster procedures allowing for decreased radiation emission are highly desirable. To address this need, we developed a  Sr
Sr quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed
quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed  Sr
Sr in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify
in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify  Sr
Sr in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
 ,
,  , and X-rays (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
, and X-rays (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Japan Chemical Analysis Center*
JAEA-Review 2023-022, 93 Pages, 2023/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of rapid and sensitive radionuclide analysis method by simultaneous analysis of  ,
,  , and X-rays" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple
, and X-rays" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple  -ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereinafter referred to as "SDM") was developed. In the research in 2022, we developed a code that handles measurement data of LSC, singles Ge, and 2D spectra (multiple
-ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereinafter referred to as "SDM") was developed. In the research in 2022, we developed a code that handles measurement data of LSC, singles Ge, and 2D spectra (multiple  ). In addition, to develop an integrated database, spectral data of 40 nuclides were obtained by actual measurements and simulation calculations.
). In addition, to develop an integrated database, spectral data of 40 nuclides were obtained by actual measurements and simulation calculations.
 /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-069, 114 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a new corrosion mitigation technology using nanobubbles toward corrosion mitigation in PCV system under the influence of  /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2021. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where
-rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2021. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where  - and
- and  -ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
-ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
 ,
,  , and X-rays (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
, and X-rays (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Japan Chemical Analysis Center*
JAEA-Review 2022-037, 118 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of rapid and sensitive radionuclide analysis method by simultaneous analysis of  ,
,  , and X-rays" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple
, and X-rays" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple  -ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereafter referred to "SDM") was developed. In the study, the
-ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereafter referred to "SDM") was developed. In the study, the  -ray measuring device was installed, and the measurement system consisting of the Ge detector, CeBr
-ray measuring device was installed, and the measurement system consisting of the Ge detector, CeBr detector, and NaI detector was completed in FY2021. In the SDM development, standard spectra of
detector, and NaI detector was completed in FY2021. In the SDM development, standard spectra of  -ray singles, multiple
-ray singles, multiple  -ray measurements, …
-ray measurements, …
 -rays of fuel debris
-rays of fuel debrisMatsumura, Taichi; Okumura, Keisuke; Fujita, Manabu*; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 199, p.110298_1 - 110298_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.88(Chemistry, Physical) /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
-rays radiolysis (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-002, 85 Pages, 2022/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a new corrosion mitigation technology using nanobubbles toward corrosion mitigation in PCV system under the influence of  /
/ /
/ -rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2020. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where
-rays radiolysis" conducted in FY2020. In this work, in order to ensure the long-term reliability of steel structures that ensure important confinement functions in the debris removal process, such as existing PCVs and newly constructed negative pressure maintenance systems and piping, corrosion phenomena in wet environments where  - and
- and  -ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
-ray emitting nuclides come into contact with steel are clarified for the first time.
 Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steel
Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.110 - 115, 2022/04
no abstracts in English
 ,
,  , and X-rays (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
, and X-rays (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Japan Chemical Analysis Center*
JAEA-Review 2021-060, 105 Pages, 2022/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of rapid and sensitive radionuclide analysis method by simultaneous analysis of  ,
,  , and X-rays" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, and develops the measurement system such as multiple
, and X-rays" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, and develops the measurement system such as multiple  -ray detection method. We develop a spectral determination method (SDM method) for integrated analysis by constructing a spectral database for nuclides including
-ray detection method. We develop a spectral determination method (SDM method) for integrated analysis by constructing a spectral database for nuclides including  -rays and X-rays by measurement using this system and radiation simulation calculation. This method enables simultaneous quantification of multiple nuclides and reduces the chemical separation process.
-rays and X-rays by measurement using this system and radiation simulation calculation. This method enables simultaneous quantification of multiple nuclides and reduces the chemical separation process.
Kato, Takuma*; Nagaoka, Mika; Guo, H.*; Fujita, Hiroki; Aida, Taku*; Smith, R. L. Jr.*
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(39), p.55725 - 55735, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)In this work, hydrothermal leaching was applied to simulated soils (clay minerals vermiculite, montmorillonite, kaolinite) and actual soils (Terunuma, Japan) to generate organic acids with the objective to develop an additive-free screening method for determination of Sr in soil. Stable strontium (SrCl ) was adsorbed onto soils for study and ten organic acids were evaluated for leaching Sr from simulated soils under hydrothermal conditions (120 to 200
) was adsorbed onto soils for study and ten organic acids were evaluated for leaching Sr from simulated soils under hydrothermal conditions (120 to 200 C) at concentrations up to 0.3 M. For strontium-adsorbed vermiculite (Sr-V), 0.1 M citric acid was found to be effective for leaching Sr at 150
C) at concentrations up to 0.3 M. For strontium-adsorbed vermiculite (Sr-V), 0.1 M citric acid was found to be effective for leaching Sr at 150 C and 1 h treatment time. Based on these results, the formation of organic acids from organic matter in Terunuma soil was studied. Hydrothermal treatment of Terunuma soil produced a maximum amount of organic acids at 200
C and 1 h treatment time. Based on these results, the formation of organic acids from organic matter in Terunuma soil was studied. Hydrothermal treatment of Terunuma soil produced a maximum amount of organic acids at 200 C and 0.5 h reaction time. To confirm the possibility for leaching of Sr from Terunuma soil, strontium-adsorbed Terunuma soil (Sr-S) was studied. For Sr-S, hydrothermal treatment at 200
C and 0.5 h reaction time. To confirm the possibility for leaching of Sr from Terunuma soil, strontium-adsorbed Terunuma soil (Sr-S) was studied. For Sr-S, hydrothermal treatment at 200 C for 0.5 h reaction time allowed 40% of the Sr to be leached at room temperature, thus demonstrating an additive-free method for screening of Sr in soil. The additive-free hydrothermal leaching method avoids calcination of solids in the first step of chemical analysis and has application to both routine monitoring of metals in soils and to emergency situations.
C for 0.5 h reaction time allowed 40% of the Sr to be leached at room temperature, thus demonstrating an additive-free method for screening of Sr in soil. The additive-free hydrothermal leaching method avoids calcination of solids in the first step of chemical analysis and has application to both routine monitoring of metals in soils and to emergency situations.
Sato, Yuki; Minemoto, Kojiro*; Nemoto, Makoto*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 16(10), p.C10008_1 - C10008_8, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:25.07(Instruments & Instrumentation) = 82, 81 nuclei by shell-model calculations
= 82, 81 nuclei by shell-model calculationsShimizu, Noritaka*; Togashi, Tomoaki*; Utsuno, Yutaka
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2021(3), p.033D01_1 - 033D01_15, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:44.93(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Sr+
Sr+ Y beta field; Full-face mask respirator shielding and dosemeter positioning
Y beta field; Full-face mask respirator shielding and dosemeter positioningTsujimura, Norio; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yamazaki, Takumi; Momose, Takumaro; Aoki, Katsunori; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yokoyama, Sumi*
KEK Proceedings 2020-5, p.21 - 28, 2020/11
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Tachiki, Shuichi*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Aoki, Katsunori; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tsujimura, Norio
Radiation Measurements, 138, p.106399_1 - 106399_5, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:35.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tsujimura, Norio
Radioisotopes, 69(8), p.253 - 261, 2020/08
The Japan Coast Guard observation vessel Takuyo encountered nuclear fallout originating from a U.S. nuclear weapon test detonated at Bikini Atoll on July 12, 1958. The exposure occurred two days after the detonation when the vessel was sailing southbound, about 300 km west of the danger area set up around the test site. From a small amount of rain sampled at the beginning of a rainsquall, a gross beta radioactivity of 16 kBq/L was observed, but no total precipitation measurement was made at that time. Therefore, the total amount of gross beta activity surface deposition density was alternatively derived based on an indication of a NaI(Tl) scintillation detector placed 0.3-m above the after deck of the Takuyo. By combining the maximum measured dose rate of 3.1  Sv/h aboard with the results of Monte Carlo simulations, the surface deposition density on the Takuyo was estimated to be 2 PBq/km
Sv/h aboard with the results of Monte Carlo simulations, the surface deposition density on the Takuyo was estimated to be 2 PBq/km , about 10 times higher than the past maximum observed in Japan in 1966. The resultant effective dose to crew members was also estimated to be below 100
, about 10 times higher than the past maximum observed in Japan in 1966. The resultant effective dose to crew members was also estimated to be below 100  Sv over the entire period of the voyage.
Sv over the entire period of the voyage.
Tsujimura, Norio
Isotope News, (768), p.38 - 39, 2020/04
no abstracts in English
Matsumura, Taichi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Katakura, Junichi*; Suzuki, Masahide*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 166, p.108493_1 - 108493_9, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.88(Chemistry, Physical)In this work, when radiation sources of  Cs,
Cs,  Sr and
Sr and  Y were assumed to be put in the front of a plain SUS304 plate as a typical material submerged in water, energy spectra of secondary photons and electrons at the front and back sides of plate were simulated with changing the thickness of plate, and spacing between the source and plate by using a Monte Carlo calculation code of PHITS. In the case of
Y were assumed to be put in the front of a plain SUS304 plate as a typical material submerged in water, energy spectra of secondary photons and electrons at the front and back sides of plate were simulated with changing the thickness of plate, and spacing between the source and plate by using a Monte Carlo calculation code of PHITS. In the case of  Cs gamma-ray (monochromatic 662 keV), the energy spectra at the front side was smaller than those at the back side due to the existence of plate. Then the dependence of spectra on the plate thickness was observed more clearly at the back side than at the front side. It was clearly shown how the energy spectra of photons and electrons varied with the incident radiation type, the spacing, and the thickness.
Cs gamma-ray (monochromatic 662 keV), the energy spectra at the front side was smaller than those at the back side due to the existence of plate. Then the dependence of spectra on the plate thickness was observed more clearly at the back side than at the front side. It was clearly shown how the energy spectra of photons and electrons varied with the incident radiation type, the spacing, and the thickness.
 -lactoglobulin
-lactoglobulinYoshida, Koji*; Zenin, Tomohiro*; Fujiyoshi, Ayako*; Sanada, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Murata, Kunihiko*; Takata, Shinichi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahiro, Takekiyo*; Yoshimura, Yukihiro*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 293, p.111477_1 - 111477_9, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.71(Chemistry, Physical)