Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Birkholzer, J. T.*; Graupner, B. J.*; Harrington, J.*; Jayne, R.*; Kolditz, O.*; Kuhlman, K. L.*; LaForce, T.*; Leone, R. C.*; Mariner, P. E.*; McDermott, C.*; et al.
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100685_1 - 100685_17, 2025/06
Rochman, D.*; Minato, Futoshi; Watanabe, Tomoaki; 52 of others*
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.9_1 - 9_83, 2024/10
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; Bertolotti, D.*; Bonaldi, C.*; Fontana, C.*; Fujimoto, Masami*; Geerts, W.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Macias, M.*; Nonneman, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/05
Togawa, Orihiko; Okura, Takehisa; Kimura, Masanori
JAEA-Review 2022-049, 76 Pages, 2023/01
Before construction and after operation of nuclear facilities, environmental consequence assessments are conducted for normal operation and an emergency. These assessments mainly aim at confirming safety for the public around the facilities and producing relief for them. Environmental consequence assessments are carried out using observations/ measurements by environmental monitoring and/or model predictions by calculation models, sometimes using either of which and at other times using both them, according to the situations and necessities. First, this report investigates methods, roles, merits/demerits and relationship between observations/measurements and model predictions which are used for environmental consequence assessments of nuclear facilities, especially holding up a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant at Rokkasho, Aomori as an example. Next, it explains representative examples of utilization of data on observations/measurements and results on model predictions, and considers points of attention at using them. Finally, the report describes future direction, for example, improvements of observations/measurements and model predictions, and fusion of both them.
Rodriguez, D.; Abbas, K.*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Nonneman, S.*; Oberstedt, S.*; Pedersen, B.*; Rossi, F.; Schillebeeckx, P.*; Takahashi, Tone
Proceedings of INMM 63rd Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/09
Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Katsuyama, Kozo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.383 - 398, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:69.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kitamura, Akira; Akahori, Kuniaki; Nagata, Masanobu*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.83 - 93, 2020/12
Direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) in deep underground repositories (hereafter "direct disposal") is a concept that disposal canisters stored fuel assemblies dispose without reprocessing. Behavior of radionuclide release from SNF must be different from that from vitrified glass. The present study established a methodology on determination of instant release fraction (IRF) of radionuclides from SNF, which is the one of the parameters on radionuclide release based on the latest safety assessment reports in other countries, especially for IRF values proportional to a fission gas release ratio (FGR). Recommended and maximum values of FGR have been estimated using the fuel performance code FEMAXI-7 after collecting FGR values on Japanese SNFs. Furthermore, recommended and maximum values of IRF for Japanese SNFs used in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) have been estimated using the presently obtained FGR values and experimentally obtained IRF values on foreign SNFs. The recommended and maximum IRF values obtained in the present study have been compared with those of the latest safety assessment reports in other countries.
 Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MS
Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MSAsai, Shiho; Ohata, Masaki*; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(5), p.973 - 983, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:58.89(Biochemical Research Methods)Determination of radiopalladium  Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of
Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of  Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study,
Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study, 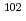 Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of
Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of  Pd/
Pd/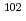 Pd. The amount of
Pd. The amount of  Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
 -radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 1 Review of research into the effects of
-radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 1 Review of research into the effects of  -radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canisters
-radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canistersKitamura, Akira; Takase, Hiroyasu*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(1), p.1 - 18, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.67(Nuclear Science & Technology)Not only geological disposal of vitrified waste generated by spent fuel (SF) reprocessing, but also the possibility of disposing of SF itself in deep geological strata (hereinafter "direct disposal of SF") may be considered in the Japanese geological disposal program. In the case of direct disposal of SF, the radioactivity of the waste is higher and the potential effects of the radiation are greater. Specific examples of the possible effects of radiation include: increased amounts of canister corrosion; generation of oxidizing chemical species in conjunction with radiation degradation of groundwater and accompanying oxidation of reducing groundwater; and increase in the dissolution rate and the solubility of SF. Focusing especially on the effects of  -radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed research into the effects of
-radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed research into the effects of  -radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canisters.
-radiation on the spent nuclear fuel, canisters and outside canisters.
 -radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 2; Review of research into safety assessments of direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel in Europe and North America
-radiation on a direct disposal system for spent nuclear fuel, 2; Review of research into safety assessments of direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel in Europe and North AmericaKitamura, Akira; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Metcalfe, R.*; Penfold, J.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(1), p.19 - 33, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)Not only geological disposal of vitrified waste generated by spent fuel (SF) reprocessing, but also the possibility of disposing of SF itself in deep geological strata (hereinafter "direct disposal of SF") may be considered in the Japanese geological disposal program. In the case of direct disposal of SF, the radioactivity of the waste is higher and the potential effects of the radiation are greater. Specific examples of the possible effects of radiation include: increased amounts of canister corrosion; generation of oxidizing chemical species in conjunction with radiation degradation of groundwater and accompanying oxidation of reducing groundwater; and increase in the dissolution rate and the solubility of SF. Therefore, the influences of radiation, which are not expected to be significant in the case of geological disposal of vitrified waste, must be considered in safety assessments for direct disposal of SF. Focusing especially on the effects of  -radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed safety assessments in countries other than Japan that are planning direct disposal of SF. The review has identified issues relevant to safety assessment for the direct disposal of SF in Japan.
-radiation in safety assessment, this study has reviewed safety assessments in countries other than Japan that are planning direct disposal of SF. The review has identified issues relevant to safety assessment for the direct disposal of SF in Japan.
Iijima, Shizuka; Uchida, Naoki; Taguchi, Katsuya; Washiya, Tadahiro
JAEA-Review 2015-018, 39 Pages, 2015/11
There is a possibility that the fuel assemblies stored in the spent fuel pool (SFP) at Fukushima Daiichi NPS (or Nuclear Power Station) are not only exposed to seawater and concrete fragments, but also damaged by fallen rubbles. We checked the reprocessing experiences of leak fuels at Tokai Reprocessing Plant and overseas reprocessing facilities, and the storage conditions and the checked and inspected results of the fuel stored in the SFP at Fukushima Daiichi NPS, after that, we listed up the technological problems with reprocessing damaged nuclear fuels and selected elements of the research for the purpose of drawing indicators to make a judgmental decision of the possibility of damaged nuclear fuels reprocessing. And we drew the indicators to make a judgmental decision on the possibility of reprocessing based on the results of the examination and the study about elements of the research.
Aihara, Haruka; Kitawaki, Shinichi; Nomura, Kazunori; Taguchi, Katsuya
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.1076 - 1083, 2015/09
Otaki, Kiyoshi*; Tanaka, Yoji*; Katsurai, Kiyomichi*; Aoki, Kazuo*
JAERI-Review 2005-035, 79 Pages, 2005/09
In order to collect technical information for the assessment on future nuclear power reactors and fuel cycle systems in Japan, investigation has been made on the characteristics and performance of future reactor options including reduced moderation water reactors (RMWRs) and their fuel cycle systems since the fiscal year 1998. The subjects of investigation are divided into three categories; breeder reactors and their fuel cycle, alternative to sodium-cooled FBR systems,plutonium recycling, spent fuel reprocessing and waste disposal. This report is a summary of the investigation carried out so far.
Review Group on the Structure of the Spent Nuclear Fuel Transportation Casks for
JAERI-Review 2005-023, 133 Pages, 2005/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) constructed two stainless steel transportation casks, JRC-80Y-20T, for spent nuclear fuels of research reactors and had utilized them for transportation since 1981. A modification of the design was applied to the USA for transportation of silicide fuels. Additional analyses employing the impact analysis code LS-DYNA that was often used for safety analysis were submitted by the JAERI to the USA to show integrity of the packages; the casks were still not approved, because inelastic deformation was occurred on the surface of the lid touching to the body. To resolve this problem on design approval of transportation casks, a review group was formed at the end of this June. The group examined the impact analyses by reviewing the input data and performing the sensitivity analyses. As the drop impact analyses were found to be practically reasonable, it was concluded that the approval of the USA for the transportation casks could not be obtained just by revising the analyses; therefore, remodelling the casks is required.
Shimizu, Kenichi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Senta Nyusu, 33(7), p.8 - 10, 2004/07
USA established Foreign research Reactor Nuclear Spent Fuel Acceptance Program (FRR SNF Acceptance Program) in May 1996, and research and test reactors have been sent back to USA with a contract under this program. The report explans a current progress of FRR NSF Acceptance Program.
Tachimori, Shoichi
JAERI-Research 2001-048, 23 Pages, 2001/10
A new chemical process, ARTIST process, is proposed for the treatment of spent nuclear fuel. The main concept of the ARTIST process is to recover and stock all actinides (Ans) in two groups, uranium (U) and a mixture of transuranics (TRU), to preserve their resource value and to dispose solely fission products (FPs). The process composed of two main steps, an U exclusive isolation and a total recovery of TRU; which copes with the nuclear non-proliferation measures, and additionally Pu separation process and soft N-donor process if requested, and optionally processes for separation of long-lived FPs. These An products: U-product and TRU-product, are to be solidified by calcination and allowed to the interim stockpile for future utilization. These separations are achieved by use of amidic extractants in accord with the CHON principle. The technical feasibility of the ARTIST process was explained by the performance of both the branched-alkyl monoamides the diglycolic amide (TODGA) in thorough extraction of all TRU by tridentate fashon.
Togawa, Orihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 33(10), p.792 - 803, 1996/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 in the presence of adsorbed phthalic acid
in the presence of adsorbed phthalic acidKumagai, Yuta; Jonsson, M.*
no journal, ,
Contact of water with spent nuclear fuel is anticipated in scenarios of failure of the repository system for the direct disposal of spent fuel. Upon the direct contact of water, the UO matrix of the fuel is expected to gradually dissolve due to oxidation of uranium by the action of ionizing radiation. In this study, we examined effects of organic acid on the UO
matrix of the fuel is expected to gradually dissolve due to oxidation of uranium by the action of ionizing radiation. In this study, we examined effects of organic acid on the UO dissolution by using phthalic acid as a model compound. We investigated oxidation of UO
dissolution by using phthalic acid as a model compound. We investigated oxidation of UO by exposure to H
by exposure to H O
O in aqueous solution containing phthalic acid. Significant adsorption of phthalic acid on UO
in aqueous solution containing phthalic acid. Significant adsorption of phthalic acid on UO was observed. The coverage of the surface was estimated to reach 80 %. The H
was observed. The coverage of the surface was estimated to reach 80 %. The H O
O -exposure experiments revealed that adsorbed phthalic acid has no significant effect on the redox reaction by H
-exposure experiments revealed that adsorbed phthalic acid has no significant effect on the redox reaction by H O
O on the UO
on the UO surface, despite the high surface density. H
surface, despite the high surface density. H O
O oxidation of UO
oxidation of UO with adsorbed phthalic acid resulted in U dissolution to similar extents with the U dissolution measured in aqueous bicarbonate solutions.
with adsorbed phthalic acid resulted in U dissolution to similar extents with the U dissolution measured in aqueous bicarbonate solutions.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Oba, Hironori*; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Karino, Takahiro; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Sakamoto, Kan*; Ikeda, Yuji*; Taira, Takunori*
no journal, ,
Ioka, Ikuo; Kato, Hitoshi; Ogawa, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
When the function of cooling system for a spent fuel pool is lost, the spent fuel pin is exposed to steam and air environment. In addition, oxidation behavior of the cladding may be changed due to axial temperature gradient and induced stress gradient during the process of dry out of the spent fuel pool. The oxidation behavior of the Zircaloy-2 cladding under axial temperature gradient was investigated in this study. The axial temperature gradients was about 100  C/cm. The oxidation test was carried out at 600
C/cm. The oxidation test was carried out at 600  C in the saturated steam flow with Ar of 0.5 l/min as a career gas. Little difference was seen in the configuration of the surface cracks and the oxide thickness of specimens oxidized with different temperature gradients. Consequently, the high-temperature oxidation of Zircaloy-2 cladding was hardly changed by the steep axial temperature gradient of about 100
C in the saturated steam flow with Ar of 0.5 l/min as a career gas. Little difference was seen in the configuration of the surface cracks and the oxide thickness of specimens oxidized with different temperature gradients. Consequently, the high-temperature oxidation of Zircaloy-2 cladding was hardly changed by the steep axial temperature gradient of about 100  C/cm in this study.
C/cm in this study.