Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C
CPham, V. H.; Kurata, Masaki; Nagae, Yuji; Ishibashi, Ryo*; Sasaki, Masana*
Corrosion Science, 255, p.113098_1 - 113098_9, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0Wada, Yuki; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hibiki, Takashi*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 249, p.127219_1 - 127219_16, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0Luu, V. N.; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Udagawa, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114222_1 - 114222_15, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe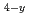 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyYamashita, Takayuki*; Koga, Norimitsu*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Fujii, Hidetoshi*; Umezawa, Osamu*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Ichiba, Yuta*
Radiation Measurements, 187, p.107486_1 - 107486_8, 2025/09
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Fukushima University*
JAEA-Review 2025-002, 108 Pages, 2025/07
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of methodology combining chemical analysis technology with informatics technology to understand perspectives property of debris and tie-up style human resource development" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. The present study aims to Goal of this study is to implement a research plan relate to a development of combinational technology of new chemical analysis with informatics, and the aim is to develop new system for whole image estimation system using small quantities of information. Conducting the collaboration study with JAEA researchers (tie-up style) make connect to the development of human resource from master's course student to post-doctoral researchers who are progress in the local-based and/or many academics fields research. We are in progress to grow international-minded human resources.
Araki, Shohei; Aizawa, Eiju; Murakami, Takahiko; Arakaki, Yu; Tada, Yuta; Kamikawa, Yutaka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 217, p.111323_1 - 111323_8, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has modified the STACY from a homogeneous system using solution fuel to a heterogeneous system using fuel rods in order to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris. The modification of the STACY was completed in December 2023. A series of performance inspections were conducted for the start of experimental operations. A new thermal power calibration is required for the performance inspections in order to operate at less than 200 W, which is the permitted thermal power. However, the thermal power measurement method and calibration data used in the former STACY is no longer available due to the modification of the modified STACY. We measured the thermal power of the STACY using the activation method that was improved to adapt to the measurement condition and calibrated the power meter system. Since the positions where activation foils could be installed were very limited, the thermal power was evaluated using numerical calculations supplemented by experimental data. Neutron flux data at the positions of the activation foil was measured by the activation method. Neutron distribution in the core was calculated by the Monte Carlo code MVP. A response function of the activation foil was calculated using the PHITS. The uncertainty of the thermal power measurement was conservatively estimated to be about 15%. Four operations were conducted for the thermal power measurement. The power meter was calibrated by using three operational data and tested with the one operational data. It was found that the indicated value of the meter adjusted by the STACY before the modification work would tend to overestimate the actual output by about 40%. In addition, the current calibration was able to calibrate the meter to within 3% accuracy.
Mochizuki, Akihito; Matsui, Hiroya; Nakayama, Masashi; Sakamoto, Ryo*; Shibata, Masahito*; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Jo, Mayumi*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 22, p.e04648_1 - e04648_20, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)The properties of low-pH cement used in the geological disposal of radioactive waste may change through atmospheric carbonation and degradation caused by groundwater during the long-term operation of a repository. In this study, we investigated the effects of atmospheric carbonation and groundwater contact on the chemical, microstructural, and transport properties of shotcrete made from low-pH, high-fly-ash silica-fume cement (HFSC) over a period of 16 years in an underground research laboratory. In both carbonated and degraded zones of the HFSC shotcrete, capillary porosity increased for pores of  300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
Johansen, M. P.*; Gwynn, J. P.*; Carpenter, J. G.*; Charmasson, S.*; Mori, Airi; Orr, B.*; Simon-Cornu, M.*; Osvath, I.*; McGinnity, P.*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 287, p.107706_1 - 107706_8, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 4 of others*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hamdani, A.; Soma, Shu; Abe, Satoshi; Shibamoto, Yasuteru
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 185, p.105771_1 - 105771_13, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kinase, Masami
Radioisotopes, 74(2), p.233 - 238, 2025/07
no abstracts in English
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gao, S.*; Ito, Tatsuya; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development
JAEA-Review 2025-017, 43 Pages, 2025/06
Naraha Center for Remote Control Technology Development (NARREC) was established in Japan Atomic Energy Agency to promote a decommissioning work of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (Fukushima Daiichi NPS). NARREC consists of a Full-scale Mock-up Test Building and Research Management Building. Various test facilities are installed in these buildings for the decommissioning work of Fukushima Daiichi NPS. These test facilities are intended to be used for various users, such as companies engaged in the decommissioning work, research and development institutions, educational institutions and so on. The number of NARREC facility uses was 88 in FY2023. We participated booth exhibitions and presentations on the decommissioning related events. Moreover, we also contributed to the development of human resources by supporting the 8th Creative Robot Contest for Decommissioning. As a new project, "Narahakko Children's Classroom" was implemented for elementary school students in Naraha Town. And, Subsidy program work of "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water and Treated Management", entitled "Development of Technologies for Work Environmental Improvement in R/B" was carried out as scheduled. This report summarizes the activities of NARREC in FY2023, such as the utilization of facilities and equipment of NARREC, arrangement of the remote-control machines for emergency response, and training for operators by using the machines.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-001, 94 Pages, 2025/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2023, along with the verification of each system, a three-dimensional reconstruction model was generated using images acquired from a moving camera on the monitoring platform in a simulated environment, and an integrated experiment was conducted to demonstrate that it is possible to present images from the optimal viewpoint for the visualization target, with the cooperation of each research theme.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2024-064, 118 Pages, 2025/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of extremely small amount analysis technology for fuel debris analysis" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. Understanding the properties of fuel debris is necessary for handling, criticality control, storage control, etc. A key technique is the chemical analysis of actinide nuclides. We developed sample pretreatment technology and separation / analysis process required for chemical analysis. The purpose of this study is to streamline future planned fuel debris analysis. To promote 1F decommissioning, we will train human resources through on-the-job training. In particular, we applied the extremely small amount analysis (ICP-MS/MS), which has recently been successful in the fields of analytical chemistry and radiochemistry, to the nuclear field. This method allows high-accuracy analysis without pretreatment to isolate the nuclide to be measured. The separation pretreatment can be skipped and a rapid analysis process can be established.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2025-003, 24 Pages, 2025/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (RuO ) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. RuO
) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. RuO is expected to be absorbed chemically into water dissolving nitrous acid. Condensation of mixed vapor plays an important role for Ru transporting behavior in the facility building. The thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code. The latent heat, which is a governing factor for vapor condensing behavior, has almost same value for nitric acid and water at the temperature range under 120 centigrade. Considering this thermal characteristic, it is assumed that the amount of nitric acid is substituted with mole-equivalent water in MELCOR simulation. Compensating modeling induced deviation by this assumption have been assembled with control function features of MELCOR. The comparison results have been described conducted between original simulation and modified simulation with compensating model in this report. It has been revealed that the total amount of pool water in the facility was as same as both simulations.
is expected to be absorbed chemically into water dissolving nitrous acid. Condensation of mixed vapor plays an important role for Ru transporting behavior in the facility building. The thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code. The latent heat, which is a governing factor for vapor condensing behavior, has almost same value for nitric acid and water at the temperature range under 120 centigrade. Considering this thermal characteristic, it is assumed that the amount of nitric acid is substituted with mole-equivalent water in MELCOR simulation. Compensating modeling induced deviation by this assumption have been assembled with control function features of MELCOR. The comparison results have been described conducted between original simulation and modified simulation with compensating model in this report. It has been revealed that the total amount of pool water in the facility was as same as both simulations.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Motome, Yuiko
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
The detailed computational models for nuclear criticality analyses on the first startup cores of NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), which is categorized as a TRIGA-ACPR (Annular Core Pulse Reactor), were created for the purposes of deeper understandings of safety inspection data on the neutron absorber rod worths of reactivity and improvement of determination technique of the reactivity worths. The uncertainties in effective neutron multiplication factor (k ) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k
) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029
for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029  k
k . It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k
. It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2025-005, 106 Pages, 2025/06
JAEA has been creating input data for pressurized water reactor (PWR) analysis with RELAP5/MOD3.3 code, mainly based on design information for the four-loop PWR's Tsuruga Power Station Unit-2 as the reference reactor of the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF). The cold leg large-break loss-of-coolant accident (LBLOCA) calculation in the flamework of the BEMUSE program is cited as a representative OECD/NEA activity related to the PWR analysis. The new regulatory requirements for PWRs in Japan include the event of loss of recirculation functions from emergency core cooling system (ECCS) in the cold leg LBLOCA. This event should be evaluated the effectiveness of measures against severe core damage. The input data for this study were made preparations to analyze the PWR LBLOCA, which is one of the design basis accidents that should be postulated in the safety design. This report describes the main features of the input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis. The PWR model comprised a reactor vessel, pressurizer (PZR), hot legs, steam generators (SGs), SG secondary-side system, crossover legs, cold legs, and ECCS. A four-loop PWR was simulated by two loops in the LBLOCA calculation. Specifically, loop-A attached with the PZR corresponded to three loops, and loop-B mounted with the break was equal to one loop. The nodalization schemes of the PWR components were referred to those of the LSTF components. Moreover, interpretations were added to the main input data for the PWR LBLOCA analysis, and further information such as the basis for determining the input data was provided. In addition, transient analysis was performed employing the prepared input data for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event. The present transient analysis was confirmed to be appropriate generally by comparing with the calculation in the previous study using the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code. Furthermore, sensitivity analyses were executed exploiting the RELAP5/MOD3.3 code to clarify the effects of a discharge coefficient through the break and water injection flow rate of the alternative recirculation on the fuel rod cladding surface temperature. This report explains the results of the sensitivity analyses within the defined ranges, which complement some of the content of the previous study's calculation for the loss of ECCS recirculation functions event.