Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Nishida, Naoki; Kobayashi, Daisuke; Nemoto, Ryo*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Kitao, Takahiko; Kuno, Takehiko
JAEA-Technology 2023-004, 30 Pages, 2023/06
Glove-box gloves, that are used for handling nuclear fuel materials at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, have an expiration date by internal rules. All gloves are replaced at a maximum of every 4-year. However, degrees of glove deterioration varies depending on its usage environment such as frequency, chemicals, and radiation dose. Therefore, physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation, hardness of gloves are measured and technical evaluation method for the glove life-time is established. It was found that gloves without any defects in its appearance have enough physical properties and satisfies the acceptance criteria values of new gloves. Thus, it was considered that the expired gloves could be used for total of 8-year, by adding 4-year of new glove life-time. In addition, the results of extrapolation by plotting the glove's physical properties versus the used years showed that the physical properties at 8-year is on the safer side than the reported physical properties of broken glove. Also, the data are not significantly different from the physical properties of the long-term storage glove (8 and 23 years). Based on these results, life-time of gloves at TRP is set to be 8-year. The frequency of glove inspections are not changed, and if any defects is found, the glove is promptly replaced. Thus, the risk related to glove usage is not increased. The cost of purchasing gloves, labor for glove replacement, and the amount of generated waste can be reduced by approximately 40%, respectively, resulting in more efficient and rationalized glove management.
Kobayashi, Daisuke; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Nishida, Naoki; Miyoshi, Ryuta; Nemoto, Ryo*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Kato, Keisuke; Nishino, Saki; Kuno, Takehiko; Kitao, Takahiko; et al.
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-18-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.237 - 240, 2022/07
All gloves attached to glove-box in Tokai Reprocessing Plant have a fixed expiration date and have to be replaced every 4-year. However, degrees of glove deterioration are different depending on its usage environment (frequency, chemicals, radiation, etc.), because of rubber products. Therefore, physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation, hardness of gloves are measured, and the life-time of gloves are estimated. As a result, gloves without any defects in its appearance have enough physical property for acceptance criteria of new glove. The extrapolated physical property of glove is sufficiently larger than the reported values of damaged glove. No deterioration in physical properties of gloves, that are periodically replaced without any defects in its appearance, is observed and the usable life-time of the glove is estimated to be 8 years.
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Hisano, Naoki*; Abe, Jun*; Suzuki, Akio*
American Mineralogist, 107(3), p.325 - 335, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:20.65(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The basaltic glass structure were investigated to 18 GPa using in situ X-ray and neutron diffraction. The O-O coordination number (CN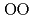 ) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r
) starts to rise with maintaining the mean O-O distance (r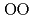 ) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN
) above 2-4 GPa, and then CN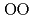 stops increasing and r
stops increasing and r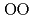 begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN
begins to shrink along with the increase in the Al-O coordination number (CN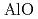 ) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN
) above 9 GPa. This is interpreted by the change in the contraction mechanism from tetrahedral network bending to oxygen packing ratio increase via the CN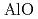 increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN
increase. The oxygen packing fraction exceeds the value for dense random packing, suggesting that the oxygen-packing hypothesis cannot account for the pressure-induced structural transformations of silica and silicate glasses. The CN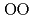 increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at
increase at 2-4 GPa reflects the elastic softening of silicate glass, which may causes anomalous elastic moduli of basaltic glass at  2 GPa.
2 GPa.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Do, V. K.; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 152, p.37 - 44, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:65.94(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)An online measurement system using an alpha liquid scintillation counter ( -LSC) coupled to microchip solvent extraction has been developed. A flow-through cell of
-LSC) coupled to microchip solvent extraction has been developed. A flow-through cell of  -LSC has been prepared by packing PTFE tube into glass tube to combine microchip. Two-phase flow in microchannel has been stabilized by using coiled tube. The Pu in organic phase has been mixed with scintillation cocktail by T-junction connectors. The system separates and detects Pu by online with detection limit of 6.5 Bq/mL, generating only
-LSC has been prepared by packing PTFE tube into glass tube to combine microchip. Two-phase flow in microchannel has been stabilized by using coiled tube. The Pu in organic phase has been mixed with scintillation cocktail by T-junction connectors. The system separates and detects Pu by online with detection limit of 6.5 Bq/mL, generating only  L-level wastes.
L-level wastes.
Do, V. K.; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Takamura, Yuzuru*; Surugaya, Naoki; Kuno, Takehiko
Talanta, 183, p.283 - 289, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:39.09(Chemistry, Analytical)We develop a novel analytical method employing liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry for measurement of total cesium in highly active liquid wastes. Limit of detection and limit of quantification are 0.005 mg/L and 0.02 mg/L, respectively. The method is validated and applied to the real samples.
Do, V. K.; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Current Analytical Chemistry, 14(2), p.111 - 119, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.98(Chemistry, Analytical)A direct coupling of two-phase flow solvent extraction microfluidics with ICP-MS for element-selective analysis is successfully established. Two-phase flow in microchannels of two combined glass chips for continuous extraction and back-extraction is stabilized through balancing the pressure by using an external coiled tube that functions as a flow resistor. The difference of fluid flow rate between microchannels and ICP-MS is adjusted by a proposed interface system including T-junction mixer and a switching valve. An online measurement of rhenium is successfully demonstrated. The calibration curve for Re is carried out in the range of 1  g/L to 20
g/L to 20  g/L. The limit of detection is 0.2
g/L. The limit of detection is 0.2  g/L with a needed sample volume of one milliliter. Total time including extraction, back-extraction, and measurement is less than one hour. The development of the online coupling is a first step towards future applications to the selective measurement of highly radioactive elements.
g/L with a needed sample volume of one milliliter. Total time including extraction, back-extraction, and measurement is less than one hour. The development of the online coupling is a first step towards future applications to the selective measurement of highly radioactive elements.
Horigome, Kazushi; Taguchi, Shigeo; Nishida, Naoki; Goto, Yuichi; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-14-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.381 - 384, 2017/08
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Tanaka, Naoki; Goto, Yuichi; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-14-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.385 - 389, 2017/08
Greenhouse is used in order to prevent diffusion of radioactive materials on the maintenance of machineries and decomposition of the analytical equipment such as glove box in Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP). The specifications of the greenhouse change depending on a risk of the radiation exposure, operation and environment. Design and application of original greenhouses in the analytical laboratory of TRP is summarized.
Horigome, Kazushi; Taguchi, Shigeo; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2017-016, 20 Pages, 2017/07
Mixed spikes of uranium and plutonium have been prepared for the determination of uranium and plutonium in dissolved MOX solution by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Enriched uranium metal NBL CRM116 and plutonium metal NBL CRM126 were accurately weighed and then dissolved in nitric acid, respectively. Their dissolved solutions were mixed in a mass ratio of 1 to 2. The preparation values of uranium and plutonium were 1.0530  0.0008 mg/g (k=2) of uranium with a
0.0008 mg/g (k=2) of uranium with a  U relative mass fraction of 93.114 wt% and 2.0046
U relative mass fraction of 93.114 wt% and 2.0046  0.0019 mg/g (k=2) of plutonium with a
0.0019 mg/g (k=2) of plutonium with a  Pu relative mass fraction of 97.934 wt%, respectively. The concentrations of uranium and plutonium in spike were confirmed by reverse isotope dilution mass spectrometry using tracer of
Pu relative mass fraction of 97.934 wt%, respectively. The concentrations of uranium and plutonium in spike were confirmed by reverse isotope dilution mass spectrometry using tracer of  U and
U and  Pu. Finally, the prepared spike was validated by parallel analysis of simulated sample of dissolved MOX solution. This spike was applied to measure the uranium and plutonium amount content of dissolved MOX solutions using isotope dilution mass spectrometry.
Pu. Finally, the prepared spike was validated by parallel analysis of simulated sample of dissolved MOX solution. This spike was applied to measure the uranium and plutonium amount content of dissolved MOX solutions using isotope dilution mass spectrometry.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Holland, M. K.*; Cordaro, J. V.*; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2017-014, 63 Pages, 2017/06
In this study, the controlled-potential coulometry has been applied as a primary method for characterizing the Pu master solutions being used as alternative source material for IDMS spikes. The coulometry system compliance with ISO12183 has been used for measurement. It has been calibrated using equipment traceable to the SI units. Plutonium standard samples have been measured to confirm the accuracy. The relative standard deviation is below 0.05%. The results agree with the reference value within  0.05%. It is found that the Pu can be precisely analyzed by the coulometry system. Then, the Pu nitrate solution, which has been purified from mixed oxide powder containing relatively high
0.05%. It is found that the Pu can be precisely analyzed by the coulometry system. Then, the Pu nitrate solution, which has been purified from mixed oxide powder containing relatively high  Pu, has been measured. The relative standard deviation is below 0.05%. The relative expanded uncertainty is less than 0.074% at the 95% confidence interval (k=2). It is indicated that coulometric assay of Pu is fit for the purpose of characterizing reference materials.
Pu, has been measured. The relative standard deviation is below 0.05%. The relative expanded uncertainty is less than 0.074% at the 95% confidence interval (k=2). It is indicated that coulometric assay of Pu is fit for the purpose of characterizing reference materials.
 2016.10
2016.10Horigome, Kazushi; Taguchi, Shigeo; Ishibashi, Atsushi; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2017-008, 14 Pages, 2017/05
The plutonium solution had been converted into MOX powder to mitigate the potential hazards of storage plutonium solution such as hydrogen generation at the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. The plutonium conversion operations had been started in April, 2014, and had been finished in July, 2016. With respect to the samples taken from the conversion process, about 2,200 items of plutonium/uranium solutions and MOX powders had been analyzed for the operation control in the related analytical laboratories at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. This paper describes the reports on analytical activities and related maintenance works in the analytical laboratories conducted from December, 2015 to October, 2016.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Holland, M. K.*; Cordaro, J. V.*; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/02
Precise and accurate determination of plutonium is necessary. The high reliability is required for standard materials used in the plutonium determination. In this study, JAEA and SRNL have collaborated on a mission to apply controlled-potential coulometry as a primary method for characterizing the plutonium master solution being used for reference materials of isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The measurement cell and electrodes were upgraded and optimized compliance with ISO12183. The instruments were calibrated traceable to the SI. The samples of plutonium standard solution were measured to confirm the accuracy of the method. The results have been in good agreement with the reference values. Therefore, the plutonium solution which were purified from MOX powder have been characterized. The total measurement uncertainty was less than 0.07%. The results indicated that coulometry assay of plutonium are fit for the purpose of characterizing reference material.
Furuse, Takahiro*; Taguchi, Shigeo; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2016-028, 19 Pages, 2016/12
Metal impurities in MOX powder obtained from uranium and plutonium recovered from reprocessing process of spent nuclear fuel are needed to be determined for its characterization. Direct current arc atomic emission spectroscopy (DCA-AES) is one of the useful methods for direct analysis of powder sample without dissolving the analyte into aqueous solution. However, the selection of standard material, which can overcome concerns such as matrix matching, is quite important to create adequate calibration curves for DCA-AES. In this study, we apply standard addition method using the certified U O
O containing known amounts of metal impurities to avoid the matrix problems. The proposed method provides good results for determination of Fe, Cr and Ni at a significant quantity level contained in MOX samples.
containing known amounts of metal impurities to avoid the matrix problems. The proposed method provides good results for determination of Fe, Cr and Ni at a significant quantity level contained in MOX samples.
 2015.12
2015.12Horigome, Kazushi; Suzuki, Hisanori; Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Ishibashi, Atsushi; Taguchi, Shigeo; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2016-026, 21 Pages, 2016/12
In order to mitigate potential hazards of storage plutonium in solution such as hydrogen generation, conversion of plutonium solution into MOX powder has been carried out since 2014 in the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. With respect to the samples taken from the conversion process, about 3500 items of plutonium/uranium solutions and MOX powders have been analyzed for the operation control in the related analytical laboratories at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. This paper describes the reports on analytical activities and related maintenance works in the analytical laboratories conducted from April 2014 to December 2015.
Masui, Kenji; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-13-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.25 - 30, 2016/07
no abstracts in English
Goto, Yuichi; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-13-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.31 - 34, 2016/07
Chloroprene rubber gaskets are often used to seal the glove box body and its panels. Such gaskets are deformed with compressive pressure and its elastic restoring force keeps sealing property. Therefore, gaskets play an important role in glove box sealing. However, physical properties of those used in glove box have not reported so far. In this study, hardness, elongation, tensile strength and compression set are investigated and its sealing performances are evaluated. The gaskets samples are taken from the glove box, which is used for 37 years. It is found that hardness, elongation and tensile strength of gaskets are changed due to the aging but its values are within the specification of chloroprene rubber. Also, the compression-set is less than the value that sealing performance is decreased. The results show that even the gaskets are used for long time, it has the property to keep sealing performances of glove box.
Holland, M. K.*; Cordaro, J. V.*; Morales-Arteaga, M. E.*; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Since 2007, the laboratory at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) have collaborated on a new mission to apply controlled-potential coulometry as a primary method for characterizating plutonium master solutions. Measurement results are being used to prepare traceable and certifiable large-size dry (LSD) spike standards for safeguards measurements by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The collaboration activities performed by JAEA and SRNL were authorized and funded under the JAEA & United States NNSA/DOE Permanent Coordinating Group. This report will chronicle the collaboration activities of JAEA and SRNL, and provide the detail on the periodic coulometer component calibration, the coulometric plutonium measures and measure practices, including the uncertainty propagation for the most recent plutonium master solution used for LSD Spike preparation.
Nishida, Naoki; Suwa, Toshio; Tanaka, Naoki; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-11-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.121 - 126, 2014/07
Corroded pore was found at stainless pipe for liquid waste solution from the analytical laboratory. Part of the pipe was cut for preparing samples to investigate the cause of the corrosion. The same size of stainless pipe was welded to recover it, under the strict radiation control. The restoration work was done inside of the vinyl house, as it is called "greenhouse", which was the small room completely separated by vinyl sheet. All the works, cutting, decontamination, digging groove and welding with back seal gas, were done inside of the greenhouse. We report the work method for recovery of corroded pipe containing radioactive materials
Tanaka, Naoki; Suwa, Toshio; Nishida, Naoki; Kuno, Takehiko; Inami, Shinichi
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-11-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.127 - 131, 2014/07
Corroded pore was found at stainless pipe for liquid waste solution from the analytical laboratory. In order to find out the cause of corrosion, analytical samples were prepared cutting from the pipe. Reagents contained chloride, which had been used analytical laboratory more than ten years before the date, were found to be the trigger of the localized corrosion. We checked up all the pipes, which have been wasted including chloride solutions, by phased array instrument. We report the investigation of cause of corrosion and results of non-destructive testing.
Sumi, Mika; Surugaya, Naoki; Kurosawa, Akira; Suzuki, Toru; Kuno, Yusuke
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-31-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/12
For the long-term stable operation of nuclear fuel cycle facilities, it is essential to satisfy the requirements of IAEA safeguards agreement. The requirements to maintain and improve the precision of DA are supposed to grow along with nuclear fuel cycle fully in progress and Pu handling amount increases. In order to maintain long-term stability of quality level of accountancy analysis for safeguards, a special committee on "Quality Assurance (QA) for Accountancy / Safeguards analysis" was established at Atomic Energy Society Japan supported by INNN-Japan. Experts for safeguards analysis, reference materials, statistics and QA were gathered and drafted the committee standard document for isotope dilution mass spectrometry, the major accountancy analysis technique for Pu and U, supported Pu standard preparation at JAEA and summarized the items needed for QA of DA.