Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takasho, Hideki*; Kasahara, Naoto; Kazuteru Garatani/CRC Solution*
JNC TN9400 2003-096, 76 Pages, 2003/12
Commercialized fast reactors, intend to adopt large scale heat exchangers, since they aim at capacity enlargement and reduction of the cooling loops from a demand of the economical efficiency. And, they have planned the adoption of the double-wall heat transfer tubes for reliable design against sodium coolant, which become straight type without tube welding. As the result, steam generators change to large double straight pipe types and the large-scale dished tubesheets are required from a balance with the pressure proof design. The establishment of method of structural analysis for the complicated and three-dimensional shape is required in order to realize the large-scale dished tubesheets. Conventional analysis models for tubesheets are equivalent solid plates with stress multipliers, which are difficult to be applied to dished tubesheets since their un-homogeneity. A large-scale three-dimensional analysis model is desirable to consider precious configurations around holes.. The iterative solver for efficiently calculating, when the large-scale analysis is carried out, was developed, and it was mounted to FINAS code. A dished tubesheet model for commercialized fast reactors was made in three-dimensional element which exceeded 1 million degrees of freedom. FINAS code with the iterative solver analyzed thermal transient stress under the manual trip condition. 20 step calculation was carried out within 72 hours on PC. As the result, it was confirmed that applicability of three dimensional analysis methods to dished tubesheets.
*; *; *; *; *; *
PNC TJ9270 98-003, 161 Pages, 1996/03
A general purpose finite element nonlinear structural analysis system FINAS has been developed since 1976 for fast breeder reactor components. Improvement, extension and maintenance of this system has been continued hitherto. This report describes the results of the work which was carried out during october 1995 to March 1996. The items of improvement, extension and maintenance are as follows. (1)Treatment of anisotropic materials (2)Application of advanced constitutive equations (3)Improvement of calculation efficiency of the matrix reduction procedure and FASTENING function (4)Revision of a finite element (5)Arrangement of FINAS (V.13.0) and preparation for release
;
PNC TN9410 94-030, 85 Pages, 1994/04
To evaluate the applicability of a precise constitutive model to the prediction of inelastic behavior of structural materials, a creep ratchetting test using a 3-bar structure model subjected to cyclic thermal loads was conducted and alalysis of the creep ratchetting test was performed by using the nonlinear cyclic hardening constitutive model (Ohno model) installed in FINAS. The followig results were obtained. (1)It is confirmed that the compressive creep ratchetting deformation occurrs under cyclic thermal loads only. Ratchetting strain per cycle measured in the test decreased cyclically and became constant after about 15-th cyclc. (2)The analysis of the 3-bar model in which the time constant 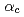 equals to 1/3 predects the creep ratchetting deformation observed in the test very well. Consequently, the nonlinear cyclic hardening constitutive model is applicable to the creep ratchetting analysis of structures. (3)It is confirmed by the analysis that the ratchetting strain increases as increasing of the hold time at high temperature and the compressive ratchetting strain is enhanced by the creep deformation.
equals to 1/3 predects the creep ratchetting deformation observed in the test very well. Consequently, the nonlinear cyclic hardening constitutive model is applicable to the creep ratchetting analysis of structures. (3)It is confirmed by the analysis that the ratchetting strain increases as increasing of the hold time at high temperature and the compressive ratchetting strain is enhanced by the creep deformation.
Kasahara, Naoto; Garatani, Kazuteru
PNC TN9410 93-184, 113 Pages, 1993/08
Temperature dependency of material properties for structural analysis and strain concentration evaluation methods have influences on thermal transient strength evaluation result, and those effects were investigated. It appeared that temperature dependency of material properties has small influences. On the strain concentration evaluation method, effects of (1) thermal peak stress, (2) Poisson's ratio, and (3) Nonlinearity of materials on strain concentration, a degee of which is described by elastic follow-up parameters, were evaluated as follws, (1) Relations between thermal peak stresses and elastic follow-up parameters [peak stress index  =0.499
=0.499  =0.3] [Tn=1.5, 1.48, 1.04] [Tn=2.0, 1.54, 1.08] [Tn=2.5, 1.57, 1.11] [Tn=3.0, 1.58, 1,12] [Tn=5,0, 1.58, 1,12] (2)An elastic follow-up parameter for Poison's ratio [
=0.3] [Tn=1.5, 1.48, 1.04] [Tn=2.0, 1.54, 1.08] [Tn=2.5, 1.57, 1.11] [Tn=3.0, 1.58, 1,12] [Tn=5,0, 1.58, 1,12] (2)An elastic follow-up parameter for Poison's ratio [ =1.4] (3)Relations between nonlinearity of materials and elastic follow-up parameters [stress-strain index, elastic follow-up parameter] [N=3, 1.539] [N=5, 1.578] [N=7, 1.603] (4)If peak stress and Poison's ratio effect are overlapped, elastic follow-up parameters are multiplied. The following strain concentration factor is proposed, though this study. [
=1.4] (3)Relations between nonlinearity of materials and elastic follow-up parameters [stress-strain index, elastic follow-up parameter] [N=3, 1.539] [N=5, 1.578] [N=7, 1.603] (4)If peak stress and Poison's ratio effect are overlapped, elastic follow-up parameters are multiplied. The following strain concentration factor is proposed, though this study. [ t=K
t=K (
( n+
n+ F)] [K
F)] [K =1+(q-1)
=1+(q-1) 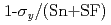 , q=5/3] where
, q=5/3] where  n+
n+ F: elastic analysis result,
F: elastic analysis result,  t: slastic-plastic strain, K
t: slastic-plastic strain, K :strain concentration factor.
:strain concentration factor.
; *; ; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki;
PNC TN9410 92-191, 93 Pages, 1992/04
The development of advanced constitutive models which can represent material behaviors precisely are key ingredients for occurate inelastic analyses. The aim of this research is to prove the performance of the two surface cyclic plasticity model which has been developed to represent detailed material behaviors of austenite stainless steel. Cyclic loading tests for slitted plate (CPVT:Cyclic Plasticity Verification Test) were conducted and cyclic hardening behaviors at the strain concentrated port was observed. The detailed elastoplastic analyses by the two surface cyclic plosticity model were performed using general purpose structural analysis program FINAS. The following conclusions were obtained. (1)The magnification of stress range and the reduction of strain range at strain concentrated region of specimen was predicted from detailed elastopllastic analysis by the two surface cyclic plasticity model. (2)Strain concentration behaviors were analyzed by CPVT in plastic region. But the strain behaviors greater than 2% by range at which the typical cyclic hardening would reveal could not be measured, because most of the strain gauge come to peel off. (3)The experimental results coincided well with the analytical results small strain range region where the experimental data were available but the cyclic plasticity effect would not dominant.
; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki;
PNC TN9410 92-197, 189 Pages, 1992/03
This report describes the functional extension of general purpose finite element nonlinear structural analysis system FINAS (Finite Element Nonlinear Structural Analysis System) which has been developed to solve various kind of structural analysis problem for fast reactor components. Extension, improvement and maintenance of this system has been continued since 1990. The following functions were added or extended. (1)The material data library for Mod.9Cr-1Mo stecl was added. (2)The plane element was extended to 3-D space. (3)Static condensation procedure for dynamic analysis was implemented. (4)User's subroutines to introduce arbitrary constitutive models were developed. (5)User's subroutines to introduce arbitrary finite clements were developed. (6)The automatic load incrementation function was improved. (7)The function of fluid-structure interaction analysis with large displacements of fluid was studied. (8)Printing and plotting formats were improved. (9)The post processor for calculation of fracture mechanics parameters (FNSFRCT) was improved. (10)The examples of surface contact problem were analyzed. After verification of these function with example analyses, the new version of FINAS (FINAS V12.0) is to be published. This report describes with these functional extensions and verification examples.
; ; ;
PNC TN9410 92-069, 75 Pages, 1992/01
Strain gauge calibration test was performed to confirm the characteristics of foil type strain gauges which were used for CPVT (Cyclic Plasticity Verification Test) by sticking 6 type of commercial strain gauges on a material test piece subjected to cyclic strain range (
 = 2000
= 2000
 14000
14000 ) of 50 cycles at room temperature. The following results were obtained. (1)The origin of strain gauge output was shiflted to tension direction when strain range grater than 7000
) of 50 cycles at room temperature. The following results were obtained. (1)The origin of strain gauge output was shiflted to tension direction when strain range grater than 7000 in this experiment. The values of shift becomes bigger when strain range increase. (2)KFE seriese represented higher performance than KFG seriese for valiation of factor or non-linearity, and same performance for shift character. The stress consentration gauge was worst for all of characters, and valiation of each gauge was large. (3)Shift and factor characters were chenged between increasing and decreasing applied strain range. Those values assumed to depend on strain history. (4)The constant shift occurs at each cycle when 50 cycle strain (
in this experiment. The values of shift becomes bigger when strain range increase. (2)KFE seriese represented higher performance than KFG seriese for valiation of factor or non-linearity, and same performance for shift character. The stress consentration gauge was worst for all of characters, and valiation of each gauge was large. (3)Shift and factor characters were chenged between increasing and decreasing applied strain range. Those values assumed to depend on strain history. (4)The constant shift occurs at each cycle when 50 cycle strain (
 = 13500
= 13500 ) given for vargain KFG and KFE seriese strain gauge. (5)The correction equation was shown such a case (4) under consideration of CPVT.
) given for vargain KFG and KFE seriese strain gauge. (5)The correction equation was shown such a case (4) under consideration of CPVT.
Garatani, Kazuteru; Yamashita, Takuya; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Nakamura, Mitsugu*; Iwata, Koji
PNC TN9410 91-350, 62 Pages, 1991/11
The thermal stress ratchetting is one of the important failure modes to be prevented in the design of FBR components. To avoid this kind of deformation, the Bree diagram expressed by the combination of primary and secondary stresses has been used in the design of FBR. However, even without primary stress, there is a possibility of ratchetting due to temperature dependence of yield stress when large variations of temperature exist locally. The purpose of this study is to confirm those phenomena by experiment and FEM analysis, and to prove this mechanism by a theoretical model. The following results were obtained. (1) The occurrence of compressive ratchetting deformation was demonstrated by a three bar thermal ratchetting test where the temperature of the central bar was varied cyclically from 20 C to 500
C to 500 C. (2) The analysis of the three bar ratchetting test was performed by using the nonlinear cyclic hardening model (Ohno model) installed in FINAS. It is confirmed that the result of analysis represents the experimental ratchetting behavior well. (3) The ratchetting strain per one cycle :
C. (2) The analysis of the three bar ratchetting test was performed by using the nonlinear cyclic hardening model (Ohno model) installed in FINAS. It is confirmed that the result of analysis represents the experimental ratchetting behavior well. (3) The ratchetting strain per one cycle : 
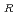 of a three bar thermal ratchetting model was derived by using the elastic-perfect plastic model in consideration of temperature dependence of yield stress. [
of a three bar thermal ratchetting model was derived by using the elastic-perfect plastic model in consideration of temperature dependence of yield stress. [
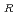 =-
=-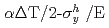 : the first cycle a)] [
: the first cycle a)] [
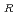 =-
=-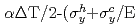 : following cycle b)]
: following cycle b)]  : thermal expansion ratio,
: thermal expansion ratio,  T : variation of temperature, E : Young's modulas,
T : variation of temperature, E : Young's modulas, 
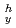 ,
, 
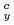 ; :yield stress at higher and lower temperature respectively. The ratchetting occurs when the first term of right side is greater than the second term of b) equation. (4) The analytical solution by (3) represents well the initial ratchetting behavior of the test. This type of ratchetting occurs due to the temperature dependence of the yield stress of the material.
; :yield stress at higher and lower temperature respectively. The ratchetting occurs when the first term of right side is greater than the second term of b) equation. (4) The analytical solution by (3) represents well the initial ratchetting behavior of the test. This type of ratchetting occurs due to the temperature dependence of the yield stress of the material.
;
PNC TN9410 91-103, 154 Pages, 1991/01
Advanced constitutive models which can represent material behavior realistically and sophisticated solutlon algorithms are key ingredients for accurate and efficient inelastic analyses. The first chapter of this report reviews various kind of elastoplastic and unified constitutuve models, and investigate the characteristics of the models, using the multiaxial inelastic behavior simulation program ADMODEL. The procedures of determining model constants are given for representative models. The second chapter deals with the inelastic analysis algorithms, or lntegration procedures for elastoplastic and unified constitutive equations, and time increment determination procedure for the unified models. The follwing conclusions were obtained. (1)The nonlinear, cyclic, non-hardening region model and the CRIEPI model are most suitable for representing the material behavior of the 304 stainless steel. (2)All the unified models treated in this report can represent nonlinear hardening, strain rate dependency and creep behavior. (3)The most precise and effective integration procedure for the elasto-plastic model is use of the exact solutions, but which are not developed for the isotropic hardening. The sub-step integration method is the most adaptative one. (4)The Walker's integrating method for the unified model is effective, but its applicability is still limitted. The Miller's method (NONSS) may not always be effective for small to large scale problems. (5)The Kumar's and the Arya's time increment determination procedure are both effective. But the Arya's method may have a possivility of divergence.
*
PNC TN9410 90-108, 80 Pages, 1990/06
A constitutive model which can express material behavior accurately is needed to perform inelastic analysis with high precision. The nonlinear cyclic hardening model using nonhardening strain region developed by Ohno and his co-workers, is worthy of notice becase it can express fundamental aspects of cyclic plasticity behavior of 304 type stainless steel. The prupose of this report is to evaluate their model through the determination of model constants and inelastic structural analyses for plactical problems. The following results were obtained. (1)The determination procedure of model constants was proposed,and its computer program was developed. Then the model constants for 304 type stainless steel was decided from experimental data obtained at PNC, (2)For uniaxial and constant strain rangc cyclic problem, this model agrce well with the experimental result under isothermal condition. (3)Analysis for the notched bar under cyclic loading and the straight pipe under cyclic thermal transients were performed by using the present constitutive model implemented in FINAS. It can be said that this model is applicable to the pracrical structural analysis under cyclic loadings. (4)It was shown that further investigation should be required for this model to improve the precision, under temperature changing condition and multiaxial problem.
*; *; *; *; *
PNC TJ9270 89-001, 314 Pages, 1988/02
A general purpose finite element nonlinear structural analysis system FINAS has been developed since 1976 for the development of fast breeder reactors (FBRs). Extension, improvement and maintenance of this system has been continued hitherto. This report describes the results of the work which was carried out during September 1987 to February 1988. FINAS is equipped with basic capabilities of a general purpose program as the results of the past ten years development. However improvement and enhancement of this system are needed to cover more wide range of problems. In this year, inelastic analysis. large deformation analysis, fracture mechanics analysis, heat transfer analysis and dynamic analysis were mainly extended, improved and developed. The first part of this report is the result of maintenance and extension obtained in this year. In second part, the theory of structural analysis and numerical method employed in FINAS are described. Finally, numerical examples intended for verification and demonstration of applicability to practical problems are illustrated.
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles (FR '91), ,
None