Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyahara, Shinya; Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Konishi, Kensuke
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
A CONTAIN-LMR code has been developed in JAEA for application to PRA of LMFRs since the original CONTAIN code had been introduced from SNL of U.S. in 1982. The code is a best-estimate, integrated analysis tool for predicting the physical, chemical and radiological conditions inside a containment building of LMFRs following a severe accident with reactor vessel melt-through. The code is also able to predict the source term to the environment in the accident. This code can treat many important phenomena consistently such as sodium fire, radioactive aerosol behavior, hydrogen burn, sodium-concrete reaction and core debris-concrete interaction occurred in the accident with inter-cell heat and mass flow under the multiple cell geometry. This paper describes the chronology of the code development in JAEA briefly as an introduction, and after that, the outline of computational models in the code, the examples of the code validation, and the future plan of the code application are described.
Seino, Hiroshi; Ohno, Shuji; Yamamoto, Ikuo*; Miyahara, Shinya
Proceedings of 8th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2012/12
A hydrogen combustion experiment was conducted to simulate the sodium-concrete reaction under oxygen-existing conditions. As a result, it was found that hydrogen was burnt at the sodium pool surface because as sodium combustion heat played a role of the ignition energy, and the hydrogen combination ratio increased with the increase of the oxygen concentration in the atmosphere.
Ohno, Shuji; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-8) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2010/10
This research has compiled technical basis which is necessary to carry out a probabilistic safety assessment (Level 2 PSA) for a sodium-cooled fast reactor. The accumulated technical information consists of experimental and analytical information which help ones to understand the loading to a containment vessel, as well as the existing information on dominant factors of important ex-vessel phenomena.
Ohno, Shuji; Seino, Hiroshi; Miyahara, Shinya
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), p.9110_1 - 9110_9, 2009/05
Typical ex-vessel accident sequences in the JSFR are discussed in this paper and dominant behaviors or factors in the sequences are investigated through parametric calculations using the CONTAIN/LMR code. Scenarios to be focused on are, (1) sodium vapor leakage from the reactor vessel and (2) sodium-concrete reaction, which are both to be considered in the LOHRS accident category and might be followed by an early containment failure due to the thermal effect of sodium combustion and hydrogen burning respectively. The calculated results clarify that the sodium vapor leak rate and the scale of sodium-concrete reaction are the important factors to dominate the ex-vessel accident progression. In addition, the results also provide the specific information such as pressure loading value to the containment and the timing of pressurization, which is indispensable as technical base in Level 2 PSA for developing event trees and for quantifying the accident consequences.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Futagami, Satoshi; Ohno, Shuji; Miyahara, Shinya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(2), p.149 - 160, 2007/06
no abstracts in English
Ohno, Shuji; Miyahara, Shinya; Kurata, Yuji
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-15) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2007/04
Evaporation tests were conducted to investigate fundamental liquid-to-gas transfer behavior of volatile radionuclides  Po, Cs, and Te in a lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) using the "transpiration" method, which has already contributed in a Na-cooled FBR study. Since both LBE test and Na test focus on the evaporation of the same nuclides, it is possible to compare the nuclides' volatility between in LBE and in Na. This paper describes first the reviewed evaporation characteristics of fission products in Na, next the evaporation test results of fission or activation products in LBE. The importance of investigating
Po, Cs, and Te in a lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) using the "transpiration" method, which has already contributed in a Na-cooled FBR study. Since both LBE test and Na test focus on the evaporation of the same nuclides, it is possible to compare the nuclides' volatility between in LBE and in Na. This paper describes first the reviewed evaporation characteristics of fission products in Na, next the evaporation test results of fission or activation products in LBE. The importance of investigating  Po evaporation is demonstrated through the estimation of vapor amount in a cover gas region of an LBE-cooled system. Furthermore, comparison is made for the volatility of Cs and Te in two kinds of coolant Na and LBE based on the test results. The accumulated data can serve as significant database utilized in liquid-metal-cooled reactor accident analysis tools.
Po evaporation is demonstrated through the estimation of vapor amount in a cover gas region of an LBE-cooled system. Furthermore, comparison is made for the volatility of Cs and Te in two kinds of coolant Na and LBE based on the test results. The accumulated data can serve as significant database utilized in liquid-metal-cooled reactor accident analysis tools.
Ohno, Shuji; Kurata, Yuji; Miyahara, Shinya; Katsura, Ryoei*; Yoshida, Shigeru*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(11), p.1359 - 1369, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:76.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental study using the transpiration method investigated equilibrium evaporation behavior of radionuclide polonium ( Po) generated and accumulated in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) cooled nuclear systems. The experiment consisted of two series of tests: preliminary evaporation tests for homologue element tellurium (Te) in LBE, and evaporation tests for
Po) generated and accumulated in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) cooled nuclear systems. The experiment consisted of two series of tests: preliminary evaporation tests for homologue element tellurium (Te) in LBE, and evaporation tests for  Po-accumulated LBE in which test specimens were prepared by neutron irradiation. The evaporation tests of Te in LBE provided the suggestion that Te would exist in a chemical form of PbTe as well as the information for confirming the validity of technique and conditions of Po test. From the evaporation tests of
Po-accumulated LBE in which test specimens were prepared by neutron irradiation. The evaporation tests of Te in LBE provided the suggestion that Te would exist in a chemical form of PbTe as well as the information for confirming the validity of technique and conditions of Po test. From the evaporation tests of  Po in LBE, we obtained fundamental data and empirical equations such as
Po in LBE, we obtained fundamental data and empirical equations such as  Po vapor concentration in the gas phase,
Po vapor concentration in the gas phase,  Po partial vapor pressure, thermodynamic activity coefficients, and gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficients of
Po partial vapor pressure, thermodynamic activity coefficients, and gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficients of  Po in LBE in the temperature range from 450
Po in LBE in the temperature range from 450 C to 750
C to 750 C. Additionally, radioactivity concentration of
C. Additionally, radioactivity concentration of  Po and
Po and 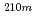 Bi vapor in a cover gas region of a typical LBE-cooled nuclear system was estimated based on the obtained experimental results, and the importance of
Bi vapor in a cover gas region of a typical LBE-cooled nuclear system was estimated based on the obtained experimental results, and the importance of  Po evaporation behavior was demonstrated.
Po evaporation behavior was demonstrated.
Ohno, Shuji; Miyahara, Shinya; Kurata, Yuji; Katsura, Ryoei*; Yoshida, Shigeru*
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-14) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2006/07
Equilibrium evaporation behavior was experimentally investigated for polonium ( Po) in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) and for rare-earth elements gadolinium (Gd) and europium (Eu) in LBE to understand and clarify the transfer behavior of toxic impurities from LBE coolant to a gas phase. The experiments utilized the "transpiration method" in which saturated vapor in an isothermal evaporation pot was transported by inert carrier gas and collected outside of the pot. While the previous paper ICONE12-49111 has already reported the evaporation behavior of LBE and of tellurium in LBE, this paper summarizes the outlines and the results of experiments for important impurity materials
Po) in liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) and for rare-earth elements gadolinium (Gd) and europium (Eu) in LBE to understand and clarify the transfer behavior of toxic impurities from LBE coolant to a gas phase. The experiments utilized the "transpiration method" in which saturated vapor in an isothermal evaporation pot was transported by inert carrier gas and collected outside of the pot. While the previous paper ICONE12-49111 has already reported the evaporation behavior of LBE and of tellurium in LBE, this paper summarizes the outlines and the results of experiments for important impurity materials  Po and rare-earth elements which are accumulated in liquid LBE as activation products and spallation products. In the experiments for rare-earth elements, non-radioactive isotope was used. The LBE pool is about 330-670 g in weight and has a surface area of 4cm
Po and rare-earth elements which are accumulated in liquid LBE as activation products and spallation products. In the experiments for rare-earth elements, non-radioactive isotope was used. The LBE pool is about 330-670 g in weight and has a surface area of 4cm 14cm.
14cm.  Po experiments were carried out with a smaller test apparatus and radioactive
Po experiments were carried out with a smaller test apparatus and radioactive  Po produced through neutron irradiation of LBE in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). We obtained fundamental and instructive evaporation data such as vapor concentration, partial vapor pressure of
Po produced through neutron irradiation of LBE in the Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR). We obtained fundamental and instructive evaporation data such as vapor concentration, partial vapor pressure of  Po in the gas phase, and gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficients of the impurities in LBE under the temperature condition between 450 and 750
Po in the gas phase, and gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficients of the impurities in LBE under the temperature condition between 450 and 750 C. The
C. The  Po test revealed that Po had characteristics to be retained in LBE but was still more volatile than LBE solvent. A part of Eu tests implied high volatility of rare-earth elements comparable to that of Po. This tendency is possibly related to the local enrichment of the solute near the pool surface and needs to be investigated more. These results are useful and indispensable for the evaluation of radioactive materials transfer to the gas phase in LBE-cooled nuclear systems.
Po test revealed that Po had characteristics to be retained in LBE but was still more volatile than LBE solvent. A part of Eu tests implied high volatility of rare-earth elements comparable to that of Po. This tendency is possibly related to the local enrichment of the solute near the pool surface and needs to be investigated more. These results are useful and indispensable for the evaluation of radioactive materials transfer to the gas phase in LBE-cooled nuclear systems.
Miyahara, Shinya; Ohno, Shuji; Yamamoto, Nobuhiro; Saito, Junichi; Hirabayashi, Masaru
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-14) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2006/07
The experimental study has been carried out to investigate reaction, transport and settling behavior of lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) in flowing liquid sodium. In the test, 168 g of LBE were poured into flowing sodium from the top of a vertical-type sodium loop which contained 23.2 kg of sodium. The initial temperature of LBE and sodium was 673 K. The flow rate and the maximum velocity of sodium in the loop were controlled and measured at 20 dm /min and 1 m/sec, respectively, using an electro-magnetic pump and an electro-magnetic flow meter. The sodium loop has a settling chamber at the lower part to investigate the concentration decrease behavior of solid particle reaction products in the sodium due to the settling effect. The concentration was measured by sodium sampling from the 11 positions of the loop during the experiment and its post-test chemical analysis. The temperature changes at the various parts of the loop were also measured during the experiment by thermo-couples attached on the outer surface of the loop. Ultrasonic detectors were attached on the outer surface of the loop below the position of a LBE pour nozzle to demonstrate the utility as a leak detector.
/min and 1 m/sec, respectively, using an electro-magnetic pump and an electro-magnetic flow meter. The sodium loop has a settling chamber at the lower part to investigate the concentration decrease behavior of solid particle reaction products in the sodium due to the settling effect. The concentration was measured by sodium sampling from the 11 positions of the loop during the experiment and its post-test chemical analysis. The temperature changes at the various parts of the loop were also measured during the experiment by thermo-couples attached on the outer surface of the loop. Ultrasonic detectors were attached on the outer surface of the loop below the position of a LBE pour nozzle to demonstrate the utility as a leak detector.
Ohno, Shuji; Miyahara, Shinya; Kurata, Yuji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(7), p.593 - 599, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:76.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)We carried out reflection seismic and multi-offset VSP surveys at JNC Shobasama-site to develop the investigation technique in the granite area, and evaluated the applicability of these geophysical methods. As the result of this study, we consider that a) It is possible to infer the existence of the lower angle fracture zone in the granite by eflection seismic survey and b) Multi-offset VSP supplements the result of reflection seismic survey and it is possible to infer the distribution of the fracture zone in deeper area in the granite.
Ohno, Shuji*; Miyahara, Shinya*; Kurata, Yuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(7), p.593 - 599, 2005/07
no abstracts in English
Doda, Norihiro; Ishikawa, Hiroyasu; Ohno, Shuji; Miyahara, Shinya
JNC TN9400 2005-048, 52 Pages, 2005/04
The burning behavior of a single sodium droplet has been studied for understanding of spray combustion which is one of the combustion forms in sodium leakage. This study serves as the basis of the mechanistic sodium fire analysis method. A burning experiment with initial droplet size of 3.34mm and 5.85mm different from FD-2 experiment condition (4.75mm), an inert gas condition experiment and a polypropylene sphere experiment were performed to investigate the relation between initial droplet size and burnt mass, and the effect of burning phenomena on the droplet motion. (1)Drag coefficient of a burning sodiuum droplet is 1.4 2.2 times greater than that of a solid sphere of the same size. (2)The increase in drag force of a burning sodium droplet is mainly due to the increase in gaseous viscosity around the droplet with heat of combustion. Sodium droplet has the ellipsoidal shape with aspect ratio 0.89 when falling by about 8 meters, but the effect of droplet deformation is negligible small. In addition, evaporation and buoyancy have also little effect on the increase in drag force. (3)The burning of sodium droplet follows the D
2.2 times greater than that of a solid sphere of the same size. (2)The increase in drag force of a burning sodium droplet is mainly due to the increase in gaseous viscosity around the droplet with heat of combustion. Sodium droplet has the ellipsoidal shape with aspect ratio 0.89 when falling by about 8 meters, but the effect of droplet deformation is negligible small. In addition, evaporation and buoyancy have also little effect on the increase in drag force. (3)The burning of sodium droplet follows the D -law when the initial droplet diameter changes. In the calculation which assumes that the sodium combustion quantity agrees with the measurement and that combustion of sodium droplet obeys that law, the Na
-law when the initial droplet diameter changes. In the calculation which assumes that the sodium combustion quantity agrees with the measurement and that combustion of sodium droplet obeys that law, the Na O ratio of reaction products becomes 0.51-0.75.
O ratio of reaction products becomes 0.51-0.75.
Toyohara, Daisuke*; Ohno, Shuji; Matsuki, Takuo*; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Miyahara, Shinya
JNC TN9520 2004-004, 151 Pages, 2005/01
A computer code TRACER (Transport Phenomena of Radionuclides for Accident Consequence Evaluation of Reactor) version 2.3 has been developed to evaluate the species and the quantities of fission products (FPs) released into cover gas during fuel pin failure accident in an LMFBR. TRACER version 2.3 includes new and modified models shown below. a) Booth model, a new model for FPs release from fuel. b) Modified model for FPs transfer from fuel to bubble or sodium coolant. c) Modified model for bubbles dynamics in coolant. Computer models, input data and output data of TRACER Version 2.3 are described in this user's manual.
Ohno, Shuji; Nishimura, Masahiro; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Miyahara, Shinya; Sasa, Toshinobu*; Kurata, Yuji*
JNC TN9400 2004-072, 52 Pages, 2005/01
A series of equilibrium evaporation experiment was performed to acquire the essential and the fundamental knowledge about the transfer behavior of lead-bismuth eutectic(LBE) and impurity tellurium in LBE from liquid to gas phase. The experiments were conducted using the transpiration method in which saturated vapor in an isothermal evaporation pot was transported by inert carrier gas and collected outside of the pot. The size of the used evaporation pot is 8cm inner diameter and 15cm length. The weight of the LBE pool in the pot is about 500g. The investigated temperature range was 450deg-C to 750deg-C. From this experiment and discussion using the data in literature, we have obtained several instructive and useful data on the LBE evaporation behavior such as saturated vapor pressure of LBE, vapor concentration of Pb, Bi and Bi2 in LBE saturated gas phase, and activity coefficient of Pb in the LBE. The LBE vapor pressure equation is represented as the sum of Pb, Bi and Bi2 vapor in the temperature range between 550deg-C and 750deg-C as logP[Pa]=10.2-10100/T[K]. The gas-liquid equilibrium partition coefficient of tellurium in LBE is in the range of 10 to 100, with no remarkable temperature dependency between 450deg-C and 750deg-C.
Ohno, Shuji; Sato, Isamu; Nakagiri, Toshio; Hirosawa, Takashi; Miyahara, Shinya; Namekawa, Takashi
JAERI-Review-2004-021, p.199 - 208, 2004/10
Out-of-pile experiments on the release of fission products (FPs) under transient heating conditions were carried out for mixed oxide fuels. The fuels used in the experiments, the plutonium content of which was 30wt%, were irradiated up to 65 GWd/t in the experimental fast reactor JOYO. The experiments consisted of two runs, FP-1 and FP-2. In FP-1, the fuel sample was first heated to 2,000 C and then up to 3,000
C and then up to 3,000 C. The holding time was 30 min at each temperature. In FP-2, the terminal temperatures were 1,500
C. The holding time was 30 min at each temperature. In FP-2, the terminal temperatures were 1,500 C and 2,500
C and 2,500 C, and the holding time was 30 min in the same manner. The release of Cs, a volatile FP, was detected as soon as the fuel sample was heated up. The release rate, after peaking in several minutes, decreased gradually via a diffusion process in the fuel matrix. The "gross" diffusion coefficient agreed well with the data reported in other experiments using LWR fuels. The release fractions were identical in both experiments, namely Cs 100%, Sb~100%, Ru 10%, Ce 0% and Eu 0%.
C, and the holding time was 30 min in the same manner. The release of Cs, a volatile FP, was detected as soon as the fuel sample was heated up. The release rate, after peaking in several minutes, decreased gradually via a diffusion process in the fuel matrix. The "gross" diffusion coefficient agreed well with the data reported in other experiments using LWR fuels. The release fractions were identical in both experiments, namely Cs 100%, Sb~100%, Ru 10%, Ce 0% and Eu 0%.
Saito, Junichi; Sagawa, Norihiko; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Miyahara, Shinya
JNC TN9400 2004-059, 133 Pages, 2004/09
The simplified secondary sodium cooling system, in which utilized lead-bismuth eutectic is utilized as an intermediate coolant has been selected as one of candidate system for the "Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Reactor System (Phase I)". The purpose of this study for the "FS (PhaseII)" is to understand transfer behavior of lead-bismuth in liquid sodium by experiment. The experiments which trickles liquid lead-bismuth into liquid sodium are carried out of under various test temperature and amount of lead-bismuth. The effects of test temperature and amount of lead-bismuth on reaction behavior of sodium and lead-bismuth are clarified from the experimental results. The obtained results from experiments are as follows. (1) The experiment under lower test temperature takes longer time for reaction between sodium and lead-bismuth than that under higher test temperature. It means that test temperature affects the reaction behavior between sodium and lead-bismuth. (2) The amount of dropping lead-bismuth affects an amount and kind of reaction products which are formed by reaction between sodium and lead-bismuth. (3) Reaction heat obtained from the experiments is similar to estimated reaction heat using formation enthalpy of BiNa3 which is one of dominant reaction products.
Ishikawa, Hiroyasu; Ohno, Shuji; Miyahara, Shinya
JNC TN9400 2004-038, 84 Pages, 2004/04
Nitrogen gas can be an extinguisher or a mitigating material in the case of sodium leak and fire accident in an air atmosphere, which may occur at a liquid metal cooled nuclear power plant. However, sodium combustion residuum sometimes reignites in the air atmosphere even at room temperature when it was produced by nitrogen gas injection to the burning sodium. Then, in this study we executed conclusive experiments of prevention measures against sodium combustion residuum reignition by a mixture of carbon-dioxide (C0 sub2) gas, humidity and nitrogen gas. The experiments were carried out with the FRAT-1 test equipment; the humidity conditions were changed in air which were used to sodium combustion atmosphere and exposure air for confirmation of prevented combustion residue reignition. First of all, the sodium of about 2.5kg was leaked in air atmosphere, and next, the sodium combustion was stopped by nitrogen gas injection. Next, the combustion residuum was cooled in the nitrogen atmosphere, and then the combustion residuum was exposed to atmosphere of carbon-dioxide (4%); humidity (6000vppm); oxygen (3%)-nitrogen (based gas) mixture. It was confirmed that the combustion residuum was not reignition even if exposed to the air atmosphere again at the end of experiment. We had confirmed that the prevention measures against sodium combustion residuum reignition to establish by this research were effective.
Ishikawa, H.; Ohno, Shuji; Miyahara, Shinya
Kasai, 54(6), 43-49 Pages, 2004/00
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Ohno, Shuji*; Miyahara, Shinya*; Kurata, Yuji
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-12) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; Takai, Toshihide; Sagawa, Norihiko; Ohno, Shuji; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Miyahara, Shinya
JNC TN9400 2003-057, 87 Pages, 2003/06
The simplified secondary sodium cooling system utilized lead-bismuth eutectic as an intermediate coolant has been selected one of candidate system for the "Feasibility Studies on Commercialized Fast Reactor System (Phase I)". The purpose of this study for the "FS (Phase II)" is to understand transfer behavior of lead-bismuth in liquid sodium by experiment. From the experimental results the fundamental data are obtained for the feasibility evaluation of the simplified secondary sodium cooling system. Twice experiments which trickles liquid lead-bismuth into liquid sodium are carried out at 400 degress centigrade are obtained. (1) From the ICP analyses of L1-1 and L1-2 test, the lead concentration of sodium is higher than the bismuth concentration. This shows that the amount of dissolution of lead into liquid sodium was larger than that of bismuth. This result agrees with data of the previous solubility data in Pb-Na and Bi-Na binary system in sodium. The solid black particles observed in sodium contain a large amount of bismuth. (2) Temperature of liquid sodium rises when the drops of liquid lead-bismuth are added into liquid sodium. The total heating value calculated using temperature rises observed at several parts in equipment is 137 kJ/mol-LBE on L1-2 test. This heat of reaction is promising for leak detection of lead-bismuth into sodium. (3) Many black solid products are observed in sodium taken from L1-1 and L1-2 test apparatus. The reaction products taken from upper location in a sampling finger are very fine and the size was 5 ~ 10 10
10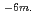 Those from lower location increase in size and the size was 50 ~100
Those from lower location increase in size and the size was 50 ~100 10-6m.
10-6m.