Sorption and Diffusion Behavior of Palladium in Bentonite, Granodiorite and Tuff
ベントナイト, 花崗閃緑岩, 凝灰岩中におけるパラジウムの収着及び拡散挙動
舘 幸男 
 ; 澁谷 朝紀; 佐藤 治夫; 柴田 雅博
; 澁谷 朝紀; 佐藤 治夫; 柴田 雅博 
not registered; not registered; Sato, Haruo; Shibata, Masahiro
性能評価に用いるデータセットの信頼性を向上させることを目的として、性能評価上の重要核種の一つであり、かつ、実測データがほとんど存在しないパラジウムのベントナイト、花崗閃緑岩、凝灰岩中における収着・拡散挙動に関するデータを取得した。収着試験については、ベントナイト、花崗閃緑岩、凝灰岩を対象に、pH、イオン強度、液固比をパラメータとしてバッチ法により行った。Pdの分配係数として、10-1 102m3/kgの範囲の値が得られた。ベントナイトに対する分配係数は花崗閃緑岩、凝灰岩に比べ若干高く、花崗閃緑岩と凝灰岩では同程度であった。分配係数のパラメータ依存性はいずれの固相でも同様の傾向を示した。pH依存性については、pH5で最大の分配係数となり、pHの増加に伴い減少する傾向であった。イオン強度の影響は顕著ではなく、液固比については、液固比が高いほど分配係数は高くなる傾向であった。Pdの収着挙動はNi,Co等の2価の金属イオンのそれとは異なり、これらのデータをアナログとしてPdを評価することは不適切であることが示唆された。本試験条件下におけるPdの支配化学種は、熱力学計算から中性のPd(OH)2(aq)と予想された。Pdの分配係数は10-1
102m3/kgの範囲の値が得られた。ベントナイトに対する分配係数は花崗閃緑岩、凝灰岩に比べ若干高く、花崗閃緑岩と凝灰岩では同程度であった。分配係数のパラメータ依存性はいずれの固相でも同様の傾向を示した。pH依存性については、pH5で最大の分配係数となり、pHの増加に伴い減少する傾向であった。イオン強度の影響は顕著ではなく、液固比については、液固比が高いほど分配係数は高くなる傾向であった。Pdの収着挙動はNi,Co等の2価の金属イオンのそれとは異なり、これらのデータをアナログとしてPdを評価することは不適切であることが示唆された。本試験条件下におけるPdの支配化学種は、熱力学計算から中性のPd(OH)2(aq)と予想された。Pdの分配係数は10-1 102m3/kgと比較的高い値であり、中性化学種の収着性は高いことが示された。また、分配係数がpHの増加と共に減少する傾向にあることから、Pdの収着は固相表面のS-OH2+サイトとの反応により支配されている可能性が示唆された。拡散試験については、ベントナイトを対象に密度をパラメータとしてin-diffusion法により行った。薄膜拡散源モデルにより解析された見かけの拡散係数は10-13
102m3/kgと比較的高い値であり、中性化学種の収着性は高いことが示された。また、分配係数がpHの増加と共に減少する傾向にあることから、Pdの収着は固相表面のS-OH2+サイトとの反応により支配されている可能性が示唆された。拡散試験については、ベントナイトを対象に密度をパラメータとしてin-diffusion法により行った。薄膜拡散源モデルにより解析された見かけの拡散係数は10-13 10-12m2/sのオーダーであり、ベントナイト密度の増加と共に減少する傾向であった。見かけの拡散係数から得られた圧縮ベントナイト中での分配係数は10-2
10-12m2/sのオーダーであり、ベントナイト密度の増加と共に減少する傾向であった。見かけの拡散係数から得られた圧縮ベントナイト中での分配係数は10-2 10-1m3/kgとなり、バッチ収着試験により得られた値よりも1
10-1m3/kgとなり、バッチ収着試験により得られた値よりも1 2オーダー低い値であった。しかしながら、分配係数と液固比との関係には相関が見られ、液固比が低いほど分配係数は低くなる傾向であった。
2オーダー低い値であった。しかしながら、分配係数と液固比との関係には相関が見られ、液固比が低いほど分配係数は低くなる傾向であった。
Sorption and diffusion behavior of palladium, which has been identified as one of the hazardous radionuclides in performance assessment of HLW disposal, in bentonite, granodiorite and tuff was studied in order to make reliable data set for the performance assessment. Sorption experiments of Pd on bentonite, granodiorite and tuff were conducted as functions of pH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio by batch method under aerobic conditions at room temperature. The distribution coefficients (K ) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10
) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /kg and were in the order of bentonite
/kg and were in the order of bentonite  granodiorite
granodiorite  tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K
tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K
values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K was not found in a range of 10
was not found in a range of 10 to 10
to 10 , but K
, but K values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K
values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m
was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m /kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH)
/kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH) (aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K
(aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K
values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH
values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO
type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO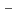 sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D
sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...
values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...