Change of the Fermi surface across the critical pressure in CeIn ; The de Haas-van Alphen study under pressure
; The de Haas-van Alphen study under pressure
CeIn の臨界圧力におけるフェルミ面の変化; 加圧下におけるドハース・ファンアルフェン効果測定
の臨界圧力におけるフェルミ面の変化; 加圧下におけるドハース・ファンアルフェン効果測定
摂待 力生*; 久保 徹雄*; 城本 智行*; 本田 大輔*; 宍戸 寛明*; 杉山 清寛*; 芳賀 芳範 

 ; 松田 達磨; 別役 潔*; 播磨 尚朝*; 小林 達生*; 大貫 惇睦
; 松田 達磨; 別役 潔*; 播磨 尚朝*; 小林 達生*; 大貫 惇睦
Settai, Rikio*; Kubo, Tetsuo*; Shiromoto, Tomoyuki*; Honda, Daisuke*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Betsuyaku, Kiyoshi*; Harima, Hisatomo*; Kobayashi, Tatsuo*; Onuki, Yoshichika
反強磁性体CeIn のドハース・ファンアルフェン効果測定を圧力3GPaまで行い、フェルミ面の変化を調べた。加圧とともに10Kのネール点は下がり、約2.6GPaでゼロになる。この臨界圧以上では、大きな主要フェルミ面aが観測されるようになり、このことは4f電子が局在から遍歴へと変化したことを示唆していると考えられる。2.7GPaでのサイクロトロン有効質量は、異常に増強されており
のドハース・ファンアルフェン効果測定を圧力3GPaまで行い、フェルミ面の変化を調べた。加圧とともに10Kのネール点は下がり、約2.6GPaでゼロになる。この臨界圧以上では、大きな主要フェルミ面aが観測されるようになり、このことは4f電子が局在から遍歴へと変化したことを示唆していると考えられる。2.7GPaでのサイクロトロン有効質量は、異常に増強されており 100
100 において60
において60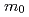 にも達する。
にも達する。
We have studied a change of the Fermi surface in an antiferromagnet CeIn via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment under pressure up to 3 GPa. With increasing pressure P, the Neel temperature
via the de Haas-van Alphen experiment under pressure up to 3 GPa. With increasing pressure P, the Neel temperature 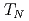 =10 K decreases and becomes zero at a critical pressure Pc
=10 K decreases and becomes zero at a critical pressure Pc  2.6 GPa. In the pressure region
2.6 GPa. In the pressure region  , we have observed a large main Fermi surface named a, which indicates that the electronic state of 4 f electron in CeIn
, we have observed a large main Fermi surface named a, which indicates that the electronic state of 4 f electron in CeIn changes from localized to itinerant at Pc, as observed in the similar antiferromagnets CeRh
changes from localized to itinerant at Pc, as observed in the similar antiferromagnets CeRh Si
Si and CeRhIn
and CeRhIn . The cyclotron effective mass
. The cyclotron effective mass 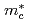 of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced around Pc:
of this main Fermi surface is extremely enhanced around Pc: 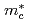
 60
60 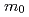 at 2.7 GPa for the magnetic field along the
at 2.7 GPa for the magnetic field along the  100
100 direction.
direction.