線虫の化学走性学習に対する放射線の修飾的影響とGタンパク質 サブユニットGPC-1の役割
サブユニットGPC-1の役割
Modulatory effect of ionizing radiation on food-NaCl associative learning; The Role of  subunit of G protein in
subunit of G protein in 
坂下 哲哉; 浜田 信行*; 池田 大祐*; 簗瀬 澄乃*; 鈴木 芳代; 石井 直明*; 小林 泰彦
Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ikeda, Daisuke*; Yanase, Sumino*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Ishii, Naoaki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
神経系のモデル生物として知られる線虫( )を用いて、化学走性学習に対する
)を用いて、化学走性学習に対する 線照射の影響を調べた。その結果、化学走性学習の能力は、比較的高線量(約550Gy)の放射線を照射しても有意な影響を受けないが、条件付けの最中に放射線を照射した場合には、照射直後の化学走性が有意に付加的に低下することを発見した。また、条件付け時(4hr.)に低線量率(0.4Gy/min)にて線虫を曝露し続けると、化学走性が負の値、すなわちNaClを忌避する応答を示した。さらに、これらの放射線照射に対する応答が、
線照射の影響を調べた。その結果、化学走性学習の能力は、比較的高線量(約550Gy)の放射線を照射しても有意な影響を受けないが、条件付けの最中に放射線を照射した場合には、照射直後の化学走性が有意に付加的に低下することを発見した。また、条件付け時(4hr.)に低線量率(0.4Gy/min)にて線虫を曝露し続けると、化学走性が負の値、すなわちNaClを忌避する応答を示した。さらに、これらの放射線照射に対する応答が、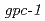 変異体において有意に抑制されることを見いだした。これらの結果は、線虫の化学走性学習に対する放射線照射の影響が、特定の感覚神経に局在するGPC-1を介して修飾的に働く可能性を示唆する。放射線照射により神経系を介した忌避応答が誘導されることから、宇宙飛行士の惑星間飛行時における異常行動の潜在的なリスクの可能性が示唆される。
変異体において有意に抑制されることを見いだした。これらの結果は、線虫の化学走性学習に対する放射線照射の影響が、特定の感覚神経に局在するGPC-1を介して修飾的に働く可能性を示唆する。放射線照射により神経系を介した忌避応答が誘導されることから、宇宙飛行士の惑星間飛行時における異常行動の潜在的なリスクの可能性が示唆される。
Exposure to IR induced an additional decrease in chemotaxis immediately after an acute dose in the transition stage of the salt chemotaxis learning. Chronic irradiation induced negative chemotaxis in the exposed animals, i.e., the primary avoidance response. IR-induced additional decreases in chemotaxis following acute and chronic irradiations were significantly suppressed in the 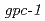 mutant, which was defective in GPC-1 (one of the two
mutant, which was defective in GPC-1 (one of the two  subunits of the heterotrimeric G-protein). Chemotaxis to cAMP, but not to lysine and benzaldehyde, was influenced by IR during the food-NaCl associative learning. Our novel findings suggest that IR behaves as a modulator in the salt chemotaxis learning via
subunits of the heterotrimeric G-protein). Chemotaxis to cAMP, but not to lysine and benzaldehyde, was influenced by IR during the food-NaCl associative learning. Our novel findings suggest that IR behaves as a modulator in the salt chemotaxis learning via  GPC-1 and a specific neuronal network, and may shed light on the modulatory effect of IR on learning.
GPC-1 and a specific neuronal network, and may shed light on the modulatory effect of IR on learning.