Oxygen potential of (U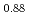 Pu
Pu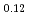 )O
)O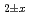 and (U
and (U Pu
Pu )O
)O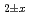 at high temperatures of 1673-1873 K
at high temperatures of 1673-1873 K
(U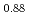 Pu
Pu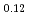 )O
)O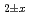 及び(U
及び(U Pu
Pu )O
)O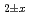 の1673-1873Kでの酸素ポテンシャル
の1673-1873Kでの酸素ポテンシャル
加藤 正人 

 ; 武内 健太郎
; 武内 健太郎  ; 内田 哲平; 砂押 剛雄*; 小無 健司*
; 内田 哲平; 砂押 剛雄*; 小無 健司*
Kato, Masato; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Uchida, Teppei; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Konashi, Kenji*
MOXの酸素ポテンシャルは、多くの報告がされているが、それらのデータは、大きなバラツキを持っている。本研究では、12%と30%Puを含むMOXについて1673-1873Kの温度範囲でガス平衡法により酸素ポテンシャル測定を行った。測定データは、点欠陥モデルにより解析され、定比組成の酸素ポテンシャルを決定し、酸素ポテンシャルに及ぼすPu含有率の影響について評価した。MOXの酸素ポテンシャルは、Pu含有率の増加で上昇した。12%と30%Puを含むMOXの酸素ポテンシャルは、1773Kで-334kJ/mol及び-296kJ/molと得た。
Many studies on oxygen potentials have been reported, but their data were scattered and the data at high temperatures are limited. In this work, the oxygen potential of (U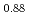 Pu
Pu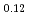 )O
)O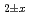 and (U
and (U Pu
Pu )O
)O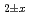 was measured at high temperatures of 1673-1873 K using gas equilibrium method using thermo-gravimetry. The influence of Pu addition on the oxygen potential of MOX was discussed. The oxygen potential and the O/M ratio were decided by in-situ analysis. The oxygen partial pressure was adjusted by controlling the ratio of
was measured at high temperatures of 1673-1873 K using gas equilibrium method using thermo-gravimetry. The influence of Pu addition on the oxygen potential of MOX was discussed. The oxygen potential and the O/M ratio were decided by in-situ analysis. The oxygen partial pressure was adjusted by controlling the ratio of 
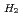 /
/
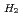 O in the flowing gas atmosphere, and the oxygen potential was determined. The oxygen potentials measured by the point defect model. The deviation x varied with the relation of in the near stoichiometric composition region. The oxygen potential increased with increasing Pu content. The values of stoichiometric MOX containing 12% and 30%Pu were determined to be -334 kJ/mol and -296 kJ/mol, respectively, at 1773 K.
O in the flowing gas atmosphere, and the oxygen potential was determined. The oxygen potentials measured by the point defect model. The deviation x varied with the relation of in the near stoichiometric composition region. The oxygen potential increased with increasing Pu content. The values of stoichiometric MOX containing 12% and 30%Pu were determined to be -334 kJ/mol and -296 kJ/mol, respectively, at 1773 K.