A Concerted mechanism between proton transfer of Zundel anion and displacement of counter cation
水二量体アニオンのプロトン移動とカウンター陽イオンとの協奏的運動メカニズム
小泉 亮人*; 鈴木 机倫*; 志賀 基之 

 ; 立川 仁典*
; 立川 仁典*
Koizumi, Akihito*; Suzuki, Kimichi*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
本論文では、開発した原子核の量子効果を考慮する第一原理計算手法を、水素結合を有する複数の化合物に応用した場合に得られた成果について発表する。なお、開発当該手法の特徴は、第一原理計算に、経路積分により原子核の量子効果を付加することで、より正確に化合物のダイナミクスが再現可能になった点にあり、その手法の適用例として恰好の対象となる同位体異性化合物のM H
H O
O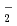 とM
とM D
D O
O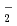 に対して、各々、M
に対して、各々、M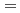 Li, Na, Kとし、そのダイナミクスを比較することで、正イオンの並進運動とプロトン移動の連成が実現していることがわかった。また、小さな正イオンほど、M
Li, Na, Kとし、そのダイナミクスを比較することで、正イオンの並進運動とプロトン移動の連成が実現していることがわかった。また、小さな正イオンほど、M H
H O
O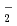 の構造をより大きく歪ませるため、プロトン移動の障壁が高くなり、振動励起エネルギーが低くなることも判明した。これらの成果から、当該手法を用いると、従来、困難とされた水素同位体を含む化合物の詳細な構造解析が可能であることがわかる。以上、本研究成果によりさまざまな同位体を有する化合物の化学反応における同位体効果の理解が進展する。
の構造をより大きく歪ませるため、プロトン移動の障壁が高くなり、振動励起エネルギーが低くなることも判明した。これらの成果から、当該手法を用いると、従来、困難とされた水素同位体を含む化合物の詳細な構造解析が可能であることがわかる。以上、本研究成果によりさまざまな同位体を有する化合物の化学反応における同位体効果の理解が進展する。
 path integral molecular dynamics simulation of M
path integral molecular dynamics simulation of M H
H O
O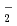 (M = Li, Na, and K) has been carried out to study how the structure and dynamics of low-barrier hydrogen-bonded Zundel anion, H
(M = Li, Na, and K) has been carried out to study how the structure and dynamics of low-barrier hydrogen-bonded Zundel anion, H O
O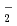 , can be affected by the counter alkali metal cation, M
, can be affected by the counter alkali metal cation, M . Our simulation predicts that the quantum proton transfer in Zundel anion can be strongly coupled to the motion of counter cation located nearby. A smaller cation can induce larger structural distortion of the Zundel anion fragment making the proton transfer barrier higher, and hence lowers the vibration excitation energy. It is also argued that a large H/D isotope effect is present.
. Our simulation predicts that the quantum proton transfer in Zundel anion can be strongly coupled to the motion of counter cation located nearby. A smaller cation can induce larger structural distortion of the Zundel anion fragment making the proton transfer barrier higher, and hence lowers the vibration excitation energy. It is also argued that a large H/D isotope effect is present.