Magnetic correlations and the influence of atomic disorder in frustrated isosceles triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuMnO
フラストレーション三角格子CuMnO の原子配列の乱れと磁気相関
の原子配列の乱れと磁気相関
寺田 典樹*; 土屋 佳則*; 北澤 英明*; 長壁 豊隆 
 ; 目時 直人
; 目時 直人 

 ; 井川 直樹
; 井川 直樹 

 ; 大山 研司*
; 大山 研司*
Terada, Noriki*; Tsuchiya, Yoshinori*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Metoki, Naoto; Igawa, Naoki; Oyama, Kenji*
三角格子反強磁性体CuMnO の磁気相関を研究した。
の磁気相関を研究した。
 以上で磁気励起は2次元(2D)短距離相関によって特徴づけられる。
以上で磁気励起は2次元(2D)短距離相関によって特徴づけられる。
 以下で
以下で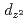 軌道にほぼ平行なコリニアー構造に磁気秩序することを確認した。
軌道にほぼ平行なコリニアー構造に磁気秩序することを確認した。 軸方向の積層構造は原子の乱れを導入することで反強磁性から強磁性体に変化する。われわれは第二最近接の層間相互作用が積層構造に重要な役割をすることを発見した。
軸方向の積層構造は原子の乱れを導入することで反強磁性から強磁性体に変化する。われわれは第二最近接の層間相互作用が積層構造に重要な役割をすることを発見した。
 以下の磁気励起は三次元長距離磁気秩序に伴う集団励起によって特徴付けられる6meVのエネルギーギャップを持つスピン波励起と、比熱で示されるスピン液体のような二次元励起が観察された。
以下の磁気励起は三次元長距離磁気秩序に伴う集団励起によって特徴付けられる6meVのエネルギーギャップを持つスピン波励起と、比熱で示されるスピン液体のような二次元励起が観察された。
We have studied the magnetic correlations of the isosceles triangular lattice antiferromagnet CuMnO . Above
. Above 
 , the magnetic correlations are characterized by a two-dimensional (2D) short-range correlation. Below
, the magnetic correlations are characterized by a two-dimensional (2D) short-range correlation. Below 
 , the magnetic structures have been identified to be collinear with the magnetic moments almost parallel to the
, the magnetic structures have been identified to be collinear with the magnetic moments almost parallel to the 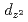 orbitals. The stacking sequence along the
orbitals. The stacking sequence along the  direction is changed from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic by atomic disorder. We find that the second-nearest-neighbor interlayer interaction plays an important role for the magnetic stacking along the
direction is changed from antiferromagnetic to ferromagnetic by atomic disorder. We find that the second-nearest-neighbor interlayer interaction plays an important role for the magnetic stacking along the  axis. The magnetic excitation below
axis. The magnetic excitation below 
 is characterized by collective spin-wave excitation with an energy gap of 6 meV from the three-dimensional long-range magnetic order and by spin-liquid-like 2D excitation, indicated by specific heat.
is characterized by collective spin-wave excitation with an energy gap of 6 meV from the three-dimensional long-range magnetic order and by spin-liquid-like 2D excitation, indicated by specific heat.