Evidence for hindrance in fusion between sulfur and lead nuclei
硫黄と鉛原子核の核融合反応の阻害
Khuyagbaatar, J.*; 西尾 勝久 

 ; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Block, M.*; Heinz, S.*; He
; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Block, M.*; Heinz, S.*; He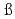 berger, F. P.*; 廣瀬 健太郎
berger, F. P.*; 廣瀬 健太郎 
 ; 池添 博; Kindler, B.*; Lommel, B.*; 牧井 宏之
; 池添 博; Kindler, B.*; Lommel, B.*; 牧井 宏之 

 ; 光岡 真一; 西中 一朗; 大槻 勤*; 若林 泰生*; Yan, S.*
; 光岡 真一; 西中 一朗; 大槻 勤*; 若林 泰生*; Yan, S.*
Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Block, M.*; Heinz, S.*; He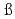 berger, F. P.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Kindler, B.*; Lommel, B.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yan, S.*
berger, F. P.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Kindler, B.*; Lommel, B.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Otsuki, Tsutomu*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yan, S.*
The influence of the structure of projectile and target nuclei on the capture cross-sections was investigated for the reactions 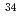 S+
S+ Pb and
Pb and  S+
S+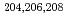 Pb. Capture cross-sections were deduced by measuring the fission fragments using multi-wire proportional counters. An enhancement of the capture cross-sections relative to an one-dimensional barrier penetration model was observed for all reactions at energies below the interaction barriers. The enhancement is larger in the case of reactions with
Pb. Capture cross-sections were deduced by measuring the fission fragments using multi-wire proportional counters. An enhancement of the capture cross-sections relative to an one-dimensional barrier penetration model was observed for all reactions at energies below the interaction barriers. The enhancement is larger in the case of reactions with 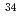 S than with
S than with  S. This observation is explained by a stronger coupling to the vibrational states in the reactions with
S. This observation is explained by a stronger coupling to the vibrational states in the reactions with 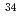 S. Comparing the capture cross-sections and the evaporation-residue cross-sections for the reactions
S. Comparing the capture cross-sections and the evaporation-residue cross-sections for the reactions  S+
S+ Pb and
Pb and 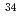 S+
S+ Pb, both yielding the same compound nucleus
Pb, both yielding the same compound nucleus  Cf, it is shown that the latter reaction has a lower fusion probability.
Cf, it is shown that the latter reaction has a lower fusion probability.