Temperature dependence on the structure of Zundel cation and its isotopomers
Zundelイオンとその同位体の構造における温度効果
鈴木 机倫*; 立川 仁典*; 志賀 基之 


Suzuki, Kimichi*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; Shiga, Motoyuki
ZundelイオンH O
O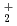 は、酸性水溶液における基本的かつ重要な分子単位の一つである。本研究では、H
は、酸性水溶液における基本的かつ重要な分子単位の一つである。本研究では、H O
O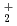 とその重水素置換同位体D
とその重水素置換同位体D O
O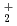 及びT
及びT O
O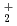 の分子構造ゆらぎの量子効果と温度効果について、経路積分分子動力学シミュレーションを用いて詳しく解析した。温度100Kから900Kの範囲で調べたところ、温度上昇につれ水素結合に関係する酸素間距離,酸素水素間距離のゆらぎが急激に大きくなることを見いだした。また、結合していない水素の位置のゆらぎも温度上昇に伴い大きくなる。この温度変化はH
の分子構造ゆらぎの量子効果と温度効果について、経路積分分子動力学シミュレーションを用いて詳しく解析した。温度100Kから900Kの範囲で調べたところ、温度上昇につれ水素結合に関係する酸素間距離,酸素水素間距離のゆらぎが急激に大きくなることを見いだした。また、結合していない水素の位置のゆらぎも温度上昇に伴い大きくなる。この温度変化はH O
O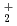 よりもD
よりもD O
O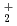 やT
やT O
O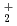 で大きくなるが、これは零点振動の大きさの違いに由来するものであると考えられる。
で大きくなるが、これは零点振動の大きさの違いに由来するものであると考えられる。
Temperature dependence on the structural fluctuations of Zundel cation, H O
O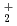 , and its isotopomers, D
, and its isotopomers, D O
O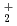 and T
and T O
O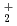 , have been studied using path integral molecular dynamics simulations in which nuclear quantum effect is fully taken into account. It has been found that the fluctuations of hydrogen-oxygen and oxygen-oxygen distances, which are relevant to the hydrogen bonded structure, grow drastically as the temperature increases within the range of investigation between 100 K and 900 K. The fluctuation with respect to the position of non-bonded hydrogen also increases substantially as the temperature increases. The temperature dependence on the fluctuation is greater for D
, have been studied using path integral molecular dynamics simulations in which nuclear quantum effect is fully taken into account. It has been found that the fluctuations of hydrogen-oxygen and oxygen-oxygen distances, which are relevant to the hydrogen bonded structure, grow drastically as the temperature increases within the range of investigation between 100 K and 900 K. The fluctuation with respect to the position of non-bonded hydrogen also increases substantially as the temperature increases. The temperature dependence on the fluctuation is greater for D O
O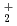 or T
or T O
O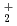 than that of H
than that of H O
O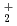 , since the zero-point effect of the former is less than the latter.
, since the zero-point effect of the former is less than the latter.