Measurement of neutron production double-differential cross-sections on carbon bombarded with 430 MeV/nucleon carbon ions
核子当たり430MeV炭素イオンの入射した炭素標的からの中性子生成二重微分断面積の測定
板敷 祐太朗*; 今林 洋一*; 執行 信寛*; 魚住 祐介*; 佐藤 大樹 

 ; 梶本 剛*; 佐波 俊哉*; 古場 裕介*; 松藤 成弘*
; 梶本 剛*; 佐波 俊哉*; 古場 裕介*; 松藤 成弘*
Itashiki, Yutaro*; Imabayashi, Yoichi*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Satoh, Daiki; Kajimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*
重粒子線治療は、根治性の高さや患者への身体的負担の小さなガン治療法として成果を上げているが、患者には術後の2次発ガンのリスクが伴う。このリスク評価では、体内の放射線挙動や核反応の理解が不可欠となり、放射線輸送計算コードが有用なツールとなる。計算コードの重イオン核反応に対する検証は十分でないため、放射線生成過程の実験データが必要となる。そこで、本研究では、新しいガン治療用のビームとして使用されている核子あたり430MeVの炭素ビームと人体構成物質との核反応から放出される中性子の二重微分断面積の実験データを整備した。実験は、放射線医学総合研究所のHIMAC加速器において実施した。核子当たり430MeVの炭素ビームを45 に傾けた5cm
に傾けた5cm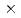 5cm
5cm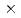 1cmの固体炭素標的に入射し、生成される中性子を15
1cmの固体炭素標的に入射し、生成される中性子を15 , 30
, 30 , 45
, 45 , 60
, 60 , 75
, 75 および90
および90 方向に設置した中性子検出器で測定した。また、中性子の運動エネルギーは飛行時間法により決定した。取得した実験データとPHITSの計算値を比較したところ、PHITSはこのエネルギー領域における炭素からの中性子生成を適切に模擬できることが分かった。
方向に設置した中性子検出器で測定した。また、中性子の運動エネルギーは飛行時間法により決定した。取得した実験データとPHITSの計算値を比較したところ、PHITSはこのエネルギー領域における炭素からの中性子生成を適切に模擬できることが分かった。
Carbon ion therapy has achieved satisfactory results because of high curability and minimally invasiveness. However, patients have a risk to get a secondary cancer. In order to estimate the risk, it is essential to understand particle transportation and nuclear reactions in the patient's body. The particle transport Monte Carlo simulation code is a useful tool to understand them. Since the code validation for heavy ion incident reactions is not enough, the experimental data of the elementary reaction processes is needed. We measured neutron production double-differential cross-sections (DDXs) on a carbon bombarded with 430 MeV/nucleon carbon beam which is a possible candidate of future therapy beam. The experiment was performed at PH2 beam line of the HIMAC of National Institute of Radiological Sciences. The 430 MeV/nucleon carbon beam was irradiated on a 5 cm 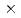 5 cm
5 cm 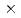 1 cm graphite target rotated 45
1 cm graphite target rotated 45 to the beam axis. The beam intensity was set to 10
to the beam axis. The beam intensity was set to 10 particles / spill. A 0.5 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillator was placed to monitor the beam intensity. Neutrons produced in the target were measured with two sizes of NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at six angles of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90
particles / spill. A 0.5 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillator was placed to monitor the beam intensity. Neutrons produced in the target were measured with two sizes of NE213 liquid organic scintillators located at six angles of 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 . The 5.08 cm long one was used to obtain the neutron spectra from 1 MeV to 10 MeV and the 12.7 cm long one was used above 5 MeV. The 2 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillators to discriminate charged particles were set in front of the neutron detectors. The kinetic energies of neutrons were determined by the time-of-flight (TOF) method. Background neutrons were estimated by a measurement with iron shadow bars between the target and each neutron detector. An electronic circuit for data acquisition consisted of NIM and CAMAC modules. The experimental data was compared with calculated results obtained by Monte Carlo simulation codes as PHITS. The PHITS code reproduced the experimental data well.
. The 5.08 cm long one was used to obtain the neutron spectra from 1 MeV to 10 MeV and the 12.7 cm long one was used above 5 MeV. The 2 mm thick NE102A plastic scintillators to discriminate charged particles were set in front of the neutron detectors. The kinetic energies of neutrons were determined by the time-of-flight (TOF) method. Background neutrons were estimated by a measurement with iron shadow bars between the target and each neutron detector. An electronic circuit for data acquisition consisted of NIM and CAMAC modules. The experimental data was compared with calculated results obtained by Monte Carlo simulation codes as PHITS. The PHITS code reproduced the experimental data well.