Discovery of ion-adsorption type deposits of rare earth elements (REE) in Southwest Japan with speciation of REE by extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy
日本西南地方におけるイオン吸着型希土類元素鉱床の発見及びEXAFS法を用いた化学種解析
山口 瑛子* 
 ; 本多 翼*; 田中 雅人*; 田中 万也
; 本多 翼*; 田中 雅人*; 田中 万也 
 ; 高橋 嘉夫*
; 高橋 嘉夫*
Yamaguchi, Akiko*; Honda, Tasuku*; Tanaka, Masato*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshio*
風化花崗岩中にみられるイオン吸着型鉱床は重要な希土類元素資源として知られている。しかし、日本においてはこうしたイオン吸着型鉱床の存在の有無はほとんど調査されてこなかった。そこで本研究では広島県と島根県において風化花崗岩試料を採取し、希土類元素の分析を行った。その結果、中国でみられるイオン吸着型鉱床と同程度の希土類元素を含むことが分かった。EXAFSスペクトルを測定した結果、塩化アンモニウム水溶液により抽出される交換性の希土類元素は外圏型錯体として吸着していることが明らかとなった。一方、抽出されなかった画分は内圏型錯体を形成していた。
Ion-adsorption type REE deposits in weathered granite are main sources of REE essential for high-technology industries. However, these type deposits have not been searched in Japan. In this study, Bulk REE abundances (= REE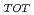 ), ion-exchangeable REE (= REE
), ion-exchangeable REE (= REE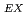 ) by ammonium chloride solution, and percentage of REE
) by ammonium chloride solution, and percentage of REE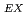 relative to REE
relative to REE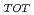 (= REE
(= REE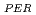 ) in fresh and weathered granite samples in Southwest Japan (i.e., Hiroshima and Shimane Prefectures) were determined. The REE
) in fresh and weathered granite samples in Southwest Japan (i.e., Hiroshima and Shimane Prefectures) were determined. The REE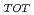 and REE
and REE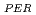 were comparable to those of ion-adsorption type REE deposits in China. Extended X-ray adsorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectra of REE in original samples and samples after the extraction of ion-exchangeable REE showed that (i) REE in samples with high REE
were comparable to those of ion-adsorption type REE deposits in China. Extended X-ray adsorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectra of REE in original samples and samples after the extraction of ion-exchangeable REE showed that (i) REE in samples with high REE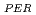 mainly forms outer-sphere complexes and (ii) the remaining REE in the rocks after the extraction forms inter-sphere complexes.
mainly forms outer-sphere complexes and (ii) the remaining REE in the rocks after the extraction forms inter-sphere complexes.