Magnetism induced by interlayer electrons in the quasi-two-dimensional electride Y C; Inelastic neutron scattering study
C; Inelastic neutron scattering study
擬2次元エレクトライドY Cにおける層間電子由来磁性
Cにおける層間電子由来磁性
玉造 博夢 

 ; 村上 洋一*; 倉本 義夫*; 佐賀山 基*; 松浦 直人*; 川北 至信
; 村上 洋一*; 倉本 義夫*; 佐賀山 基*; 松浦 直人*; 川北 至信 
 ; 松石 聡*; 鷲尾 康仁*; 井下 猛*; 浜田 典昭*; 細野 秀雄*
; 松石 聡*; 鷲尾 康仁*; 井下 猛*; 浜田 典昭*; 細野 秀雄*
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Murakami, Yoichi*; Kuramoto, Yoshio*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Matsuura, Masato*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuishi, Satoru*; Washio, Yasuhito*; Inoshita, Takeshi*; Hamada, Noriaki*; Hosono, Hideo*
Magnetic excitations in layered electride Y C have been found by inelastic neutron scattering. We have observed weak but clear magnetic scattering around the wave number
C have been found by inelastic neutron scattering. We have observed weak but clear magnetic scattering around the wave number 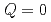 , but no magnetic order down to the lowest temperature measured (7 K). The imaginary part of the dynamical susceptibility deduced is well described by the Lorentz function of energy
, but no magnetic order down to the lowest temperature measured (7 K). The imaginary part of the dynamical susceptibility deduced is well described by the Lorentz function of energy  for each momentum
for each momentum  . The width
. The width 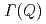 of the Lorentzian is proportional to
of the Lorentzian is proportional to 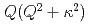 with
with 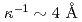 at
at 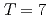 K. We have also found that with increasing
K. We have also found that with increasing  the magnetic form factor decays faster than that of a
the magnetic form factor decays faster than that of a 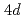 electron in a single Y atom, which indicates a more extended magnetic moment in Y
electron in a single Y atom, which indicates a more extended magnetic moment in Y C. These results provide experimental evidence that the itinerant magnetism in Y
C. These results provide experimental evidence that the itinerant magnetism in Y C originates from the anionic electrons that reside in the interlayers. The Curie-Weiss-like behavior of the magnetic susceptibility reported in Y
C originates from the anionic electrons that reside in the interlayers. The Curie-Weiss-like behavior of the magnetic susceptibility reported in Y C is ascribed to the mode coupling effects of spin fluctuations.
C is ascribed to the mode coupling effects of spin fluctuations.