断層の活動性と断層ガウジの化学組成の関係; 線形判別分析による試み
Relationship between fault activity and chemical composition of fault gouge; An Attempt by linear discriminant analysis
立石 良*; 島田 耕史 

 ; 丹羽 正和
; 丹羽 正和 

 ; 末岡 茂
; 末岡 茂 

 ; 清水 麻由子
; 清水 麻由子 

 ; 菅野 瑞穂; 石井 千佳子; 石丸 恒存
; 菅野 瑞穂; 石井 千佳子; 石丸 恒存 
Tateishi, Ryo*; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Sueoka, Shigeru; Shimizu, Mayuko; Kanno, Mizuho; Ishii, Chikako; Ishimaru, Tsuneari
活断層と非活断層の大きな違いは最新活動後の経過時間であり、活断層が概ね百年から万年オーダーと考えられるのに対して、非活断層は十万年以上である。したがって、断層活動により生じる現象は両者とも同じであったとしても、その後の断層活動休止期間に生じる化学的な変化は大きく異なる可能性があることから、こうした現象が確認されれば活断層の認定に応用できる可能性がある。そこで活断層か非活断層かが既知である断層粘土の化学組成を、文献値と実際の分析により収集し、両者の化学組成による識別の可否を線形判別分析により検討した。今回の検討では、統計学的に妥当性の高い方法である対数比変換を元素の濃度に対して施した。赤池情報量基準に基づき選択された11元素によって、活断層45試料,非活断層51試料は96%の判別率で識別された。活断層の最新活動時期を新しいものからIからIV、非活断層をVと分けた時、判別得点はこの順に変化する。元素のなかでもTiO とP
とP O
O は、最新活動時期が新しいものほど濃集する傾向が見られた。これらの濃集メカニズムと、長期にわたる減少メカニズムについては今後の課題である。
は、最新活動時期が新しいものほど濃集する傾向が見られた。これらの濃集メカニズムと、長期にわたる減少メカニズムについては今後の課題である。
The major difference between active faults and inactive faults is the elapsed time after the latest activity, and while active faults are considered to be on the order of 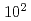 to
to 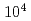 years, inactive faults are over
years, inactive faults are over 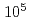 years. Therefore, even if the phenomena caused by fault activity are the same in both cases, the chemical changes that occur during the subsequent rest period of fault activity may differ significantly. In this study, the chemical composition of fault clay was collected by literature values and actual analysis, and the feasibility of discrimination by the chemical composition examined by linear discriminant analysis. According to the 11 elements selected based on the AIC, 45 active fault samples and 51 inactive fault samples were identified with a discrimination rate of 96%. Among the elements, TiO
years. Therefore, even if the phenomena caused by fault activity are the same in both cases, the chemical changes that occur during the subsequent rest period of fault activity may differ significantly. In this study, the chemical composition of fault clay was collected by literature values and actual analysis, and the feasibility of discrimination by the chemical composition examined by linear discriminant analysis. According to the 11 elements selected based on the AIC, 45 active fault samples and 51 inactive fault samples were identified with a discrimination rate of 96%. Among the elements, TiO and P
and P O
O tended to be concentrated as the latest activity period was newer. These concentration mechanisms are for future work.
tended to be concentrated as the latest activity period was newer. These concentration mechanisms are for future work.