New  -emitting isotope
-emitting isotope  U and abnormal enhancement of
U and abnormal enhancement of  -particle clustering in lightest uranium isotopes
-particle clustering in lightest uranium isotopes
Zhang, Z. Y.*; Yang, H. B.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, M. L.*; Ma, L.*; 他37名*
Zhang, Z. Y.*; Yang, H. B.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, M. L.*; Ma, L.*; 37 of others*
A new  -emitting isotope
-emitting isotope  U, produced by the fusion-evaporation reaction
U, produced by the fusion-evaporation reaction 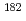 W(
W( Ar,4n)
Ar,4n) U, was identified by employing the gas-filled recoil separator SHANS and the recoil-
U, was identified by employing the gas-filled recoil separator SHANS and the recoil- correlation technique. More precise
correlation technique. More precise  -decay properties of even-even nuclei
-decay properties of even-even nuclei 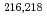 U were also measured in the reactions of
U were also measured in the reactions of  Ar,
Ar,  Ca beams with
Ca beams with 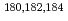 W targets. By combining the experimental data, improved
W targets. By combining the experimental data, improved  -decay reduced widths
-decay reduced widths 
 for the even-even Po-Pu nuclei in the vicinity of the magic neutron number
for the even-even Po-Pu nuclei in the vicinity of the magic neutron number  = 126 are deduced. Their systematic trends are discussed in terms of the
= 126 are deduced. Their systematic trends are discussed in terms of the 
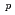

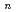 scheme in order to study the influence of proton-neutron interaction on
scheme in order to study the influence of proton-neutron interaction on  decay in this region of nuclei. It is strikingly found that the reduced widths of
decay in this region of nuclei. It is strikingly found that the reduced widths of 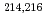 U are significantly enhanced by a factor of two as compared with the
U are significantly enhanced by a factor of two as compared with the 
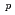

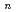 systematics for the 84
systematics for the 84 
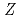
 90 and
90 and 
 126 even-even nuclei. The abnormal enhancement is interpreted by the strong monopole interaction between the valence protons and neutrons occupying the
126 even-even nuclei. The abnormal enhancement is interpreted by the strong monopole interaction between the valence protons and neutrons occupying the  1
1
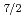 and
and  1
1
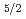 spin-orbit partner orbits, which is supported by the large-scale shell model calculation.
spin-orbit partner orbits, which is supported by the large-scale shell model calculation.