Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 )
) (SrAl
(SrAl Ta
Ta O
O )
) with
with 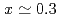
Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
Interactions (Internet), 245(1), p.25_1 - 25_7, 2024/12
Tian, Q.*; Feng, L.*; Wu, C.*; Wen, J.*; Qiu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Yu, Q.*
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 669, p.1006 - 1014, 2024/09
Abe, Satoshi; Shibamoto, Yasuteru
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 202, p.110461_1 - 110461_16, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05Li, C.-Y.; Watanabe, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.935 - 957, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2024-006, 48 Pages, 2024/06
In the future, radioactive waste which generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. It is necessary to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of the radioactive wastes. In this work, we studied the evaluation methodology of the radioactivity concentrations in concrete waste generated from JPDR. In order to construct the evaluation methodology of the radioactivity concentration, the validity of the evaluation methods was confirmed by mainly theoretical calculation and using the result of radiochemical analysis. Correcting the theoretical calculations using results of nuclide analysis, it is possible to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of nuclides preliminary selected.
Shimazaki, Yosuke; Jidaisho, Tatsuya; Ishii, Toshiaki; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Iigaki, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2024-005, 23 Pages, 2024/06
HTTR has newly assumed Beyond Design Basis Accident (BDBA) as part of conformity assessment with the new regulatory standards and has established measures to prevent the spread of BDBA. Among these measures, to prevent the spread of BDBA caused by cooling water leaks from spent fuel storage pool, the Oarai Research Institute's fire engine was selected as an equipment to prevent the spread of BDBA, and required performances such as pumping water performance were determined. After all required performances were confirmed by inspections, the fire engine passed the operator's pre-use inspection and contributed to the restart of the HTTR operations.
Nuclear System Technology Review Committee
JAEA-Review 2024-018, 38 Pages, 2024/06
In the R&D activities related to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology's Innovative Nuclear R&D Program, "Development of Integrated Energy System Simulation Method Utilizing Small Modular Reactors for Enhanced System Decarbonization and Resilience," Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) established the "Nuclear System Technology Review Committee," consisting of experts in the subject areas, to obtain advice on the feasibility of deploying Design-standardized, Factory-built, Site-independent Small Modular Reactors (DFS-SMRs) in Japan and other countries. The Committee met three times during the 2021-2024 project period to discuss proposals for a regulatory framework for the potential commercial deployment of DFS-SMRs in Japan. The starting point for the Committee's discussions was the view that Japan's nuclear regulatory framework, like most other countries with existing commercial nuclear power plants in operation, focuses on large Light Water Reactors. Another consideration was the Committee's view on the basic structure of the regulatory framework, consistent with other regulatory initiatives around the world. Specifically, that the most effective regulatory frameworks need to be less prescriptive, less technology-dependent, and more performance-based. This report focuses on the United States, which has played a leading role in the deployment of SMRs and other advanced reactors, and summarizes the discussions regarding the proposal for a licensing framework for SMRs in Japan, an analysis of the gaps between Japan's current licensing framework and the proposed framework, and specific recommendations for closing the gaps. The Committee is hopeful that the changes to the regulatory framework proposed in this report will become a reality.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Kogakuin University*
JAEA-Review 2024-005, 79 Pages, 2024/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishment of characterization method for small fuel debris using the world's first isotope micro imaging apparatus" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to obtain, for the first time in the world, the important data necessary for clarifying the retrieval of small amounts of fuel debris, and to evaluate and examine them. SEM-EDS and TEM-EDS cannot be used for isotopic identification and analysis of Pu and B. On the other hand, bulk analysis such as ICP-MS lacks the information in a micro region.
Amaya, Masaki
High Temperature Corrosion of Materials, 101(3), p.455 - 469, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2023-048, 151 Pages, 2024/05
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a hybrid method for evaluating the long-term structural soundness of nuclear reactor buildings using response monitoring and damage imaging technologies" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to develop an evaluation method necessary to obtain a perspective on the long term structural soundness of accident-damaged reactor buildings, where accessibility to work sites is extremely limited due to high radiation dose rate and high contamination. In FY2022, the second year of the three-year plan, some tests and other activities on the following research items were conducted following FY2021, based on the specific research methods and research directions clarified in FY2021.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; i-Lab*
JAEA-Review 2023-029, 77 Pages, 2024/05
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge to advancement of debris composition and direct isotope measurement by microwave-enhanced LIBS" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to increase the emission intensity of LIBS (laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy) by superimposing MW (microwave) and apply it to uranium isotope measurement. In FY2022, we improved the cooling method and reduce unnecessary functions in of the semiconductor microwave oscillator, and apply the optimized conditions obtained from simulations to the LIBS experiment for the microwave antenna gave better results.
Endo, Akira
JAEA-Research 2024-002, 90 Pages, 2024/05
This report presents a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between three quantities used for area monitoring - ambient dose equivalent  , maximum dose equivalent
, maximum dose equivalent 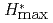 , and ambient dose
, and ambient dose  - and effective dose for external irradiation by photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions, and helium ions. For the analysis, calculations were performed using PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System) and the ICRU sphere. The analysis result shows that
- and effective dose for external irradiation by photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions, and helium ions. For the analysis, calculations were performed using PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System) and the ICRU sphere. The analysis result shows that  and
and 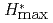 can induce large differences in the estimation of effective dose over a wide energy range for various particle types covered by ICRP Publication 116 while
can induce large differences in the estimation of effective dose over a wide energy range for various particle types covered by ICRP Publication 116 while  can conservatively estimate effective dose within the acceptable range for area monitoring. In other words,
can conservatively estimate effective dose within the acceptable range for area monitoring. In other words,  and
and 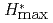 have limitations in estimating effective dose, and using
have limitations in estimating effective dose, and using  is recommended as a more appropriate quantity for the purpose. This conclusion supports the proposal of ICRU Report 95 to use
is recommended as a more appropriate quantity for the purpose. This conclusion supports the proposal of ICRU Report 95 to use  for estimating effective dose in various external exposure situations. The use of ambient dose
for estimating effective dose in various external exposure situations. The use of ambient dose  is particularly important in situations where various types of radiation are encountered, such as the use of radiation in the medical and academic fields and exposure in aviation and can meet the evolving requirements of radiation monitoring for the expansion of the field of radiological protection.
is particularly important in situations where various types of radiation are encountered, such as the use of radiation in the medical and academic fields and exposure in aviation and can meet the evolving requirements of radiation monitoring for the expansion of the field of radiological protection.
Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ishimaru, Sora*; Yamauchi, Sara*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Watanabe, Masao; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011010_1 - 011010_7, 2024/05
Batsaikhan, M.; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Saeki, Morihisa*; Karino, Takahiro; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(5), p.658 - 670, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Seki, Takeshi*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 36(33), p.333001_1 - 333001_11, 2024/05
Kato, Masato; Oki, Takumi; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Ozawa, Takayuki; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 107(5), p.2998 - 3011, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Ceramics)Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Uritani, Akira*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1062, p.169227_1 - 169227_6, 2024/05
Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Imai, Yasutomo*; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nuclear Technology, 210(5), p.814 - 835, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the study of safety enhancement on advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor, it is essential to clarify the thermal-hydraulics under various operation conditions in a fuel assembly (FA) with the wire-wrapped fuel pins to assess the structural integrity of the fuel pin. A finite element thermal-hydraulics analysis code named SPIRAL has been developed to analyze the detailed thermal-hydraulics phenomena in a FA. In this study, the numerical simulations of the 37-pin bundle sodium experiments at different Re number conditions, including a transitional condition between laminar and turbulent flows and turbulent flow conditions, were performed to validate the hybrid turbulence model equipped in SPIRAL. The temperature distributions predicted by SPIRAL was consistent with those measured in the experiments. Through the validation study, the applicability of the hybrid turbulence model in SPIRAL to thermal-hydraulic evaluation of sodium-cooled FA in the wide range of Re number was confirmed.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Okajima, Shigeaki*; Mukaiyama, Takehiko*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.478 - 497, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A series of integral experiments was conducted to evaluate the fission and the capture cross- sections of transuranic (TRU) nuclides at the fast critical facility FCA of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The experiments were carried out using seven uranium-fueled assemblies of the FCA. The neutron energy spectra of the core regions were adjusted so as to change from an intermediate neutron spectrum to a fast neutron spectrum on an assembly-by-assembly basis. The integral data measured with these experimental configurations provide some neutron energy characteristics: 1) fission rate ratios (FRRs) of  Np,
Np,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am, and
Am, and  Cm relative to
Cm relative to  Pu by using absolutely calibrated fission chambers, 2) small sample reactivity worths (SRWs) of
Pu by using absolutely calibrated fission chambers, 2) small sample reactivity worths (SRWs) of  Np,
Np,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am, and
Am, and  Am where oxide powders of around 15 to 20 grams were used, 3) criticalities, and 4) spectral indices such as fission rate ratios of
Am where oxide powders of around 15 to 20 grams were used, 3) criticalities, and 4) spectral indices such as fission rate ratios of  U relative to
U relative to  U. In this paper, details of the SRW measurements are reported, and the latest Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 is tested by using the integral data obtained in systematically varied neutron energy spectra.
U. In this paper, details of the SRW measurements are reported, and the latest Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library JENDL-5 is tested by using the integral data obtained in systematically varied neutron energy spectra.
Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00461_1 - 23-00461_10, 2024/04