Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hu, F.-F.*; Qin, T.-Y.*; Ao, N.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; 菖蒲 敬久; Kang, G.-Z.*; Ren, M.-M.; et al.
Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 25(2), p.75 - 93, 2025/04
To accurately predict the remaining lifetime of surface-strengthened railway axles, a damage tolerance method considering three-dimensional (3D) residual stresses was proposed. By taking the induction-hardened carbon steel S38C axle as an example, two-dimensional (2D) distribution characterization of residual strain and 3D residual stress measurement were performed through comprehensive application of the neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging and angle-dispersive neutron diffraction experiments. A numerical method was employed to implant the 3D residual stress into the axle model, and the remaining lifetime of the full-scale axle was studied by coupling the measured load spectrum, press-fit loads, and residual stresses. Experimental results shows that, both axial and hoop directions present a compressive residual strain gradient layer of about 3 mm, with a maximum compressive residual strain of up to -4500 
 in the surface layer, yet a maximum tensile strain of up to 1000
in the surface layer, yet a maximum tensile strain of up to 1000 
 in the core. The maximum axial and hoop compressive stresses of the axle are about -500 MPa and -303 MPa respectively, while radial stresses overall fluctuate in the zero mean stress range. At depths beyond 4.5 mm from the surface layer, all three components are tensile stresses. The axle surface layer is subjected to compressive residual stresses, and crack propagation does not occur if the crack depth is less than 4.5 mm. Nevertheless, cracks propagate accelerates when the crack depth is greater than 4.5 mm. Different crack propagation depth thresholds lead to a larger calculated remaining lifetime for the residual stress-free condition than for the case where 3D residual stresses are taken into account. However, the axle remaining service mileage of the axle of 227000 Km under the most conservative conditions exceeds 3.5 non-destructive inspection (NDI) cycles, with a large safety margin. The experimental results can provide a scientific reference for the development and optimization of NDI cycles for surface-strengthened railway axles.
in the core. The maximum axial and hoop compressive stresses of the axle are about -500 MPa and -303 MPa respectively, while radial stresses overall fluctuate in the zero mean stress range. At depths beyond 4.5 mm from the surface layer, all three components are tensile stresses. The axle surface layer is subjected to compressive residual stresses, and crack propagation does not occur if the crack depth is less than 4.5 mm. Nevertheless, cracks propagate accelerates when the crack depth is greater than 4.5 mm. Different crack propagation depth thresholds lead to a larger calculated remaining lifetime for the residual stress-free condition than for the case where 3D residual stresses are taken into account. However, the axle remaining service mileage of the axle of 227000 Km under the most conservative conditions exceeds 3.5 non-destructive inspection (NDI) cycles, with a large safety margin. The experimental results can provide a scientific reference for the development and optimization of NDI cycles for surface-strengthened railway axles.
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; 服部 高典; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)二次元ファンデルワールス強磁性体Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
(FGT)は、その高いキュリー温度、容易な調整性、空気中での優れた構造安定性から、スピントロニクスデバイスへの応用に大きな可能性を秘めている。理論的研究により、外部パラメータとしての圧力が強磁性特性に大きく影響することが示されている。本研究では、5GPaまでの高圧中性子粉末回折(NPD)実験を行い、FGTの静水圧による構造及び磁気特性の変化を調べた。NPDデータは、静水圧による見かけ上の抑制にもかかわらず、FGTにおける強磁性の頑健性を明らかにした。圧力が0から5GPaまで増加すると、キュリー温度は225(5)Kから175(5)Kまで単調減少し、Feの秩序モーメントが劇的に抑制されることがわかった。圧力による構造相転移は5GPaまで観測されなかったが、結合長と結合角の変化を定量的に解析した結果、交換相互作用が大きく変化していることがわかった。
Sans-Planell, O.*; 篠原 武尚; Grazzi, F.*; Cantini, F.*; Su, Y. H.; 松本 吉弘*; Parker, J. D.*; Manke, I.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 95(11), p.113702_1 - 113702_5, 2024/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)This study presents a significant development in the Energy-Resolved Neutron Imaging System RADEN, in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, Japan. Through a systematic study, the collimation power of the facility was reevaluated. To perform the calculation of the L/D factor of the beam, a state-of-the-art method has been used, along with a standard reference sample to measure the resolution of neutron images. To add robustness to the results, the study compares five different scintillators of different composition and thickness.
渡辺 賢一*; 須貝 優介*; 長谷川 創大*; 田中 清志朗*; 人見 啓太朗*; 野上 光博*; 篠原 武尚; Su, Y. H.; Parker, J. D.*; Kockelmann, W.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.25224_1 - 25224_13, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Thallium bromide (TlBr) semiconductor detectors are being developed as promising candidates for high-detection-efficiency, high-energy-resolution, and room-temperature gamma-ray spectrometers. This study presents methods for evaluating TlBr crystal quality and carrier transport characteristics using neutron Bragg-dip imaging and the time-of-flight method for pulsed-laser-induced carriers, respectively. In this study, two samples obtained from both the upstream and downstream region in the crystal ingot were evaluated.
 RhSi
RhSi社本 真一; 山内 宏樹; 飯田 一樹*; 池内 和彦*; 金子 耕士; Chen, Y.-S.*; 矢野 真一郎*; Hsu, P.-T.*; Lee, M. K.*; Hall, A. E.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.033303_1 - 033303_7, 2024/09
Mn RhSiの磁気励起は少なくとも0.3から140meVに広がる。200Kでの非弾性散乱強度を積分することで、Mnサイト当たり約5
RhSiの磁気励起は少なくとも0.3から140meVに広がる。200Kでの非弾性散乱強度を積分することで、Mnサイト当たり約5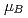 の磁気モーメントは、約5
の磁気モーメントは、約5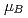 であることがわかった。一方で、長距離磁気秩序の磁気モーメントは4Kでわずか2.61
であることがわかった。一方で、長距離磁気秩序の磁気モーメントは4Kでわずか2.61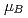 であり、多くの部分が低温まで揺らいでいることがわかった。
であり、多くの部分が低温まで揺らいでいることがわかった。
Wang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Su, Y. H.; Li, B.*
Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 60(8), p.1001 - 1016, 2024/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:41.92(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The correlation between the atomic structure, microstructure, and macroscopic properties of structural materials remains a core issue in materials research. In recent years, substantial progress has been achieved in constructing accelerator-based neutron sources and related experimental techniques, offering a robust platform for an in-depth understanding of the aforementioned correlation under real-time and in situ conditions. This article reviews the latest advancements in the application of major neutron characterization techniques, including neutron diffraction, Bragg-edge imaging, small-angle neutron scattering, pair distribution function analysis, and quasi-elastic/inelastic neutron scattering, in structural materials. Furthermore, it particularly highlights the origins and evolution of internal stresses during the phase transformations of steels, deformation mechanisms in light metals such as magnesium alloys, and microstructure and residual stress analyses using Bragg-edge imaging. Finally, a brief outlook on future development trends is provided.
Hu, F. F.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Parker, J. D.*; 篠原 武尚; Chen, J.*; Wu, S. C.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 306, p.110267_1 - 110267_18, 2024/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:60.53(Mechanics)Non-destructive and quantitative mapping of gradient residual strain distribution in surface-hardened railway S38C axles could provide a positive reference for determining service lifetime and maintenance strategy. To tackle this concern, time-of-flight neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging was employed by real axle samples with and without impacted crater. A novel and simple procedure to formulate the residual strain field was also developed in this work, with the transmission batch code in Appendix A. By mapping the global two- dimensional residual strains, it can be verified that the residual strains into the axle are uniformly distributed in the hoop direction. Subsequently, it was revealed that the axial and hoop residual strains, respectively in the cylinder and the long strip samples prepared from a real S38C hollow axle, indicated a gradient evolution distribution with a depth of  8 mm, covering a range of -5500
8 mm, covering a range of -5500  1000
1000 
 for axial strains and -6500
for axial strains and -6500  1000
1000 
 for hoop strains. More importantly, the maximum compressive lattice strain of the cylinder sample was increased by 15.61%, and 22.35% at the impacting speeds of 100, and 125 m/s, respectively; and that of the long strip sample increased by 29.17%, and 43.70%, respectively. It can thus be concluded that lattice strains have redistributed around the impact crater, demonstrating the local alteration of the residual strain field. These new findings suggest the localized variation in residual strains should be taken into account while evaluating the service damage evolution of railway axles, especially those affected by high-speed impacts during operation.
for hoop strains. More importantly, the maximum compressive lattice strain of the cylinder sample was increased by 15.61%, and 22.35% at the impacting speeds of 100, and 125 m/s, respectively; and that of the long strip sample increased by 29.17%, and 43.70%, respectively. It can thus be concluded that lattice strains have redistributed around the impact crater, demonstrating the local alteration of the residual strain field. These new findings suggest the localized variation in residual strains should be taken into account while evaluating the service damage evolution of railway axles, especially those affected by high-speed impacts during operation.
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; 菖蒲 敬久; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 185, p.108336_1 - 108336_13, 2024/08
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:94.71(Engineering, Mechanical)Gradient distribution of triaxial residual stresses to a depth of several millimeters is retained in middle carbon steel S38C axles after high-frequency induction hardening, which has become a critical concern for fatigue structural integrity. To address this, the axial, hoop, and radial gradient residual strains inside the axles were measured for the first time by advanced neutron diffraction. The SIGINI Fortran subroutine was then adopted to reconstruct the global initial residual stress field from the measured data. Experimental and simulation results show that residual stresses of about -520 MPa (axial), -710 MPa (hoop), and -40 MPa (radial) residual stress were retained below the axle surface. Subsequently, the fatigue crack propagation behavior of S38C axles was numerically investigated in the framework of fracture mechanics. The calculated results clearly show that the compressive residual stresses at a depth of 0?3 mm from the axle surface lead to a low crack growth driving force, and that fatigue cracks do not propagate as long as the crack depth is less than 3.7 mm for hollow S38C axles. These results further indicate that the maximum defect size allowed in routine inspections is acceptable from a safety and economic point of view. Accurate measurement and characterization of the global gradient residual stress field through experiments and simulations can provide an important reference for optimizing the mileage intervals of nondestructive testing (NDT) of surface defects in these surface-strengthened railway axles.
Wang, Y. W.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; Ma, Y. L.*; Wang, H. H.*
Physics Examination and Testing, 42(4), p.32 - 41, 2024/08
With the rapid technological development of large spallation neutron source facilities, the neutron beam flux obtained has been greatly improved and neutron imaging techniques have been further developed. Due to the limitation of neutron beam flux, conventional neutron imaging techniques require neutron beams with a wide wavelength range to obtain relatively high neutron beam flux conditions. Recently, spallation neutron sources using large proton accelerators have made it possible to obtain high-flux pulsed neutron beams. Energy (wavelength) resolved neutron imaging technique based on the Bragg edge effect (neutron Bragg edge transmission imaging technique) is expected to have a wide range of applications because of its high energy resolution, high spatial resolution, and ability to detect crystallographic information. The basic principle of this technique is briefly introduced. Several applications in the evaluation of residual strain, phase composition, dislocation density, and oriented structure are also reviewed to play an active role in promoting the wider applications of related technique.
Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; 徐 平光; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(7), p.2175 - 2185, 2024/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:75.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-speed railway S38C axles undergo surface induction hardening for durability, but are susceptible to fatigue cracks from foreign object impact. The neutron diffraction method was employed to measure the residual strain in S38C axles, obtaining microscopic lattice distortion data, for the gradient layer at a depth of 8 mm under the surface. The results showed that after induction-hardening, the microscopic lattice distortion had a gradient distribution, decreasing with the distance from the surface. However, in the case of impacting speed of 600 km/m, the average microscopic lattice distortion increased with the distance from the surface, reaching a maximum augmentation of 55 pct. These findings indicate a strong experimental basis, and improve our understanding of the relationship between macroscopic residual stress and decision-making, in regard to operation and maintenance.
 complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transition
complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transitionJi, T.*; Su, S.*; Wu, S.*; 堀 優太*; 重田 育照*; Huang, Y.*; Zheng, W.*; Xu, W.*; Zhang, X.*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 63(25), p.e202404843_1 - e202404843_6, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we investigated reversible intermolecular proton shifting (IPS) coupled with spin transition (ST) in a novel Fe complex. The host Fe
complex. The host Fe complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
 CoSi
CoSi山内 宏樹; Sari, D. P.*; 安井 幸夫*; 坂倉 輝俊*; 木村 宏之*; 中尾 朗子*; 大原 高志; 本田 孝志*; 樹神 克明; 井川 直樹; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(1), p.013144_1 - 013144_9, 2024/02
 -Mn-type family alloys Mn
-Mn-type family alloys Mn
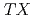 have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn
have three-dimensional antiferromagnetic (AFM) corner-shared triangular network. The antiferromagnet Mn RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N
RhSi shows magnetic short-range order (SRO) over a wide temperature range of approximately 500 K above the N el temperature
el temperature  = 190 K. Mn
= 190 K. Mn CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest
CoSi has the smallest lattice parameter and the lowest  in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15
in the family compounds. The quantum critical point (QCP) from AFM to the quantum paramagnetic state is expected near a cubic lattice parameter of 6.15 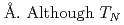 of Mn
of Mn CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn
CoSi is only 140 K, quantum critical behavior is observed in Mn CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient
CoSi as the enhancement of the electronic specific heat coefficient  . We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn
. We study how the magnetic SRO appears in Mn CoSi by using neutron scattering,
CoSi by using neutron scattering,  SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn
SR, and physical property measurements. The experimental results show that the neutron scattering intensity of the magnetic SRO does not change much regardless of the suppressed magnetic moment in the long-range magnetic ordered state compared to those of Mn RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of
RhSi. The initial asymmetry drop ratio of  SR above
SR above  becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature
becomes small, and the magnetic SRO temperature 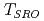 is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn
is suppressed to 240 K. The results suggest that the Mn CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
CoSi is close to the QCP in the Mn
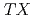 system.
system.
渡辺 賢一*; 須貝 優介*; 長谷川 創大*; 人見 啓太朗*; 野上 光博*; 篠原 武尚; Su, Y. H.; Parker, J. D.*; Kockelmann, W.*
Sensors and Materials, 36(1), p.149 - 154, 2024/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:67.31(Instruments & Instrumentation)Thallium bromide (TlBr) semiconductor detectors are promising candidates for high-detection-efficiency, high-energy-resolution, and room-temperature gamma-ray spectrometers. In this study, we conducted neutron Bragg dip and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) imaging of TlBr crystals to measure the crystal orientation distribution. We confirmed that crystal grains were continuous over a certain distance along the solidification direction for samples fabricated with the current growth procedure.
Wang, Y. W.*; Wang, H. H.*; Su, Y. H.; 徐 平光; 篠原 武尚
Materials Science & Engineering A, 887, p.145768_1 - 145768_13, 2023/11
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:67.79(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)A unique impact fracture behavior is found in a high-Mn austenitic steel (24Mn-4Cr-0.4C-0.3Cu) in this work. The steel exhibits concurrent twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) effect and the transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. By analyzing the load-deflection curves recorded during Charpy impact testing, the resistance to crack initiation and propagation is quantified from the absorbed energy. The high-Mn steel demonstrates good resistance to crack initiation at 273 K and 77 K. However, as the temperature decreases from 273 K to 77 K, there is an accelerated transition from stable crack growth to unstable crack growth during impact, resulting in the deterioration of resistance to crack propagation. The plastic deformation of the impact-tested samples, especially in the region close to the crack-path profile was quantitatively analyzed using neutron Bragg-edge transmission (BET) imaging. The deformation zones, divided by using the width of the 200 Bragg edge, exhibit good agreement with the impact absorbed energy characteristics obtained from dynamic load-deflection curves. Moreover, the unstable growth transition point was roughly determined on the impact-tested sample. Then, the electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique is employed to examine the deformation microstructure along the crack-path in the impact-tested samples. The results revealed the dual roles of TRIP effect in impact toughness of the high-Mn steel. On one hand, the TRIP effect plays a positive role in improving resistance to crack initiation and propagation. On the other hand, the excessive accumulation of brittle  /
/ '-martensite caused by the enhanced TRIP effect at 77 K leads to quasi-cleavage fracture, thereby playing a negative role. Finally, we discussed the prominent toughening mechanisms associated with the TWIP and TRIP effects, which greatly impact the impact fracture behavior.
'-martensite caused by the enhanced TRIP effect at 77 K leads to quasi-cleavage fracture, thereby playing a negative role. Finally, we discussed the prominent toughening mechanisms associated with the TWIP and TRIP effects, which greatly impact the impact fracture behavior.
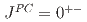 and
and 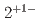
Xi, H.-Z.*; Jiang, Y.-W.*; Chen, H.-X.*; 保坂 淳; Su, N.*
Physical Review D, 108(9), p.094019_1 - 094019_13, 2023/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:51.67(Astronomy & Astrophysics)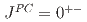 と
と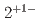 の量子数をもつ、ストレンジクォークのみからなるテトラクォークを理論的に調べた結果を報告する。前者および後者の質量はそれぞれ2.47GeV、3.07GeVであるなど、いくつかの予言値を得た。
の量子数をもつ、ストレンジクォークのみからなるテトラクォークを理論的に調べた結果を報告する。前者および後者の質量はそれぞれ2.47GeV、3.07GeVであるなど、いくつかの予言値を得た。
及川 健一; 佐藤 博隆*; 渡辺 賢一*; Su, Y. H.; 篠原 武尚; 甲斐 哲也; 鬼柳 善明*; 長谷美 宏幸
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012013_1 - 012013_6, 2023/10
Spectral data of Bragg-edge imaging, which is one of the energy-resolved neutron imaging methods, can be analyzed by single-edge analysis and full-pattern analysis with the Bragg-edge analysis code RITS developed by Sato et al. This program has a function to generate neutron transmission data considering wavelength-dependent pulse-shape function, atomic number density, crystalline structure, etc., and to extract these parameters from the measured data by the nonlinear least-squares fitting. Last year, we worked on updating the operating environment of the platform Scientific Linux 6 and the language Python 2, which have been discontinued, to Windows 10 and Python 3, and added some functions to improve usability. GUI-RITS for the windows platform has been released to users. In this presentation, we will show concrete examples of the results of the analysis of the same data by the old and new programs, and compare the efficiency of data analysis.
Su, Y. H.; 及川 健一; 篠原 武尚; 甲斐 哲也; 堀野 孝*; 井戸原 修*; 三阪 佳孝*; 友田 陽*
International Journal of Fatigue, 174, p.107729_1 - 107729_12, 2023/09
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:86.54(Engineering, Mechanical)A novel procedure, double induction quenching (DIQ), effective for improving the fatigue strength of gear products, has been used for producing gears with steep gradients of compressive residual stress generated in the tooth surface. We performed a Bragg edge imaging experiment at a pulsed neutron source to determine the spatial distribution of the {110} lattice spacing (d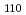 ) and the broadening of the {110} Bragg edge (w
) and the broadening of the {110} Bragg edge (w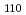 ) on the DIQ gear product after tooth-bending fatigue tests to which different loading cycles were applied. No significant difference occurred in the d
) on the DIQ gear product after tooth-bending fatigue tests to which different loading cycles were applied. No significant difference occurred in the d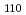 and the w
and the w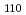 at Hofer 's critical section of the teeth with different loading conditions within the accuracy of data analysis. However, we detected a decrease in the w
at Hofer 's critical section of the teeth with different loading conditions within the accuracy of data analysis. However, we detected a decrease in the w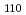 and changes in the residual lattice strain distribution in the axial direction along the tooth root directions at the opposite side of Hofer 's critical section for both teeth after 3
and changes in the residual lattice strain distribution in the axial direction along the tooth root directions at the opposite side of Hofer 's critical section for both teeth after 3 10
10  and 8
and 8 10
10  cycles, relieving the compressive residual stresses during the fatigue process. The residual stress close to the gear tooth surface determined by X-ray diffraction using sequential polishing showed a slight relaxation and redistribution from the tensile side in the hoop direction, complementary to the neutron Bragg edge imaging.
cycles, relieving the compressive residual stresses during the fatigue process. The residual stress close to the gear tooth surface determined by X-ray diffraction using sequential polishing showed a slight relaxation and redistribution from the tensile side in the hoop direction, complementary to the neutron Bragg edge imaging.
Ao, N.*; Zhang, H.*; Xu, H. H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Liu, D.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.; Kang, Q. H.*; Kang, G. Z.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 281, p.109166_1 - 109166_14, 2023/03
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:83.88(Mechanics)Considering the complex service environments that high-speed railway axles are subjected to, the fatigue crack growth (FCG) behavior of a structurally gradient axle steel with different pre-crack depths both in air and corrosive medium was investigated at a frequency of 5 Hz. The results indicated that in the high 
 region, FCG rate was dramatically accelerated by corrosion, but the gap narrows as
region, FCG rate was dramatically accelerated by corrosion, but the gap narrows as 
 decreased. The accelerated corrosion FCG rate was a comprehensive result of the acceleration effect of the anodic dissolution, hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity and the retardation effect of corrosion-induced crack-tip blunting. Despite the fact that the corrosion resistance gradually decreased as the pre-crack depth increased, the FCG rate in the corrosive medium gradually decreased. This was because fatigue loading played a more important role than corrosion in accelerating the corrosion FCG rate.
decreased. The accelerated corrosion FCG rate was a comprehensive result of the acceleration effect of the anodic dissolution, hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity and the retardation effect of corrosion-induced crack-tip blunting. Despite the fact that the corrosion resistance gradually decreased as the pre-crack depth increased, the FCG rate in the corrosive medium gradually decreased. This was because fatigue loading played a more important role than corrosion in accelerating the corrosion FCG rate.
Zhang, H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Ao, N.*; Zhang, J. W.*; Li, H.*; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.
International Journal of Fatigue, 166, p.107296_1 - 107296_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:83.58(Engineering, Mechanical)Abnormal damages in railway axles can lead to a significant hazard to running safety and reliability. To this end, a surface treatment was selected to effectively inhibit fatigue crack initiation and growth. In this study, a single edge notch bending fatigue test campaign with artificial notches was conducted to elucidate the fatigue crack non-propagation behavior in railway S38C axles subjected to an induction hardening process. The fatigue cracking behavior in the gradient structure was revealed by optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction, and fractography. The microhardness distribution was measured using a Vickers tester. The obtained results show that the microhardness of the strengthening layer is nearly triple that of the matrix. Owing to the gradient microstructures and hardness, as well as compressive residual stress, the fatigue long crack propagates faster once it passes through the hardened zone (approximately 2.0 mm in the radial depth). Thereafter, local retarding (including deflection, branching, and blunting) of the long crack occurs because of the relatively coarse ferrite and pearlite in the transition region and matrix. Totally, this fatigue cracking resistance is reasonably believed to be due to the gradient microstructure and residual stress. These findings help to tailor a suitable detection strategy for maximum defects or cracks in railway axles.
笹田 星児*; Takahashi, Yoshihito*; Takeuchi, Keisuke*; 廣井 孝介; Su, Y. H.; 篠原 武尚; 渡辺 賢一*; 瓜谷 章*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 61(4), p.046004_1 - 046004_8, 2022/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Applied)Residual strains in a punched electrical steel sheet increase the iron loss in the steel sheet. To accurately estimate the effect of residual strain on iron loss, the residual strain distribution in a punched electrical steel sheet should be evaluated. In this study, we demonstrated the two- dimensional imaging of the residual strain distribution in a punched electrical steel sheet using the neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging method. To improve the accuracy of strain measurement with minimal deterioration of spatial resolution, we applied a process of superposing many specimen images. The tensile strain near the punched edge and the compressive strain inside the core were experimentally confirmed using this method. Finally, the neutron Bragg-edge imaging results and those obtained from kernel average misorientation map using electron backscattered diffraction were compared to verify the validity of the proposed method.