Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs) have emerged as promising materials for light-emitting diode applications. In this study, by using time-of-flight neutron spectroscopy we identified and quantitatively separated the lattice vibrational and molecular rotational dynamics of two perovskites, butylammonium lead iodide (BA) PbI
PbI and phenethyl-ammonium lead iodide (PEA)
and phenethyl-ammonium lead iodide (PEA) PbI
PbI . By examining the corresponding temperature dependence, we found that the lattice vibrations, as evidenced by neutron spectra, are consistent with the lattice dynamics obtained from Raman scattering. We revealed that the rotational dynamics of organic molecules in these materials tend to suppress their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) while the vibrational dynamics did not show predominant correlations with the same. Additionally, we observed photoluminescence emission peak splitting for both systems, which becomes prominent above certain critical temperatures where the suppression of PLQY begins. This study suggests that the rotational motions of polarized molecules may lead to a reduction in exciton binding energy or the breaking of degeneracy in exciton binding energy levels, enhancing non-radiative recombination rates, and consequently reducing photoluminescence yield. These findings offer a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions in 2D HOIPs and could guide the design of more efficient light-emitting materials for advanced technological applications.
. By examining the corresponding temperature dependence, we found that the lattice vibrations, as evidenced by neutron spectra, are consistent with the lattice dynamics obtained from Raman scattering. We revealed that the rotational dynamics of organic molecules in these materials tend to suppress their photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) while the vibrational dynamics did not show predominant correlations with the same. Additionally, we observed photoluminescence emission peak splitting for both systems, which becomes prominent above certain critical temperatures where the suppression of PLQY begins. This study suggests that the rotational motions of polarized molecules may lead to a reduction in exciton binding energy or the breaking of degeneracy in exciton binding energy levels, enhancing non-radiative recombination rates, and consequently reducing photoluminescence yield. These findings offer a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions in 2D HOIPs and could guide the design of more efficient light-emitting materials for advanced technological applications.
Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez Espinoza, V.*; Stakhanova, A.*; Groudev, P.*; Petrova, P.*; Vryashkova, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 211, p.110962_1 - 110962_16, 2025/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:94.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The completed Horizon-2020 project on "Management and Uncertainties of Severe Accidents (MUSA)" has reviewed uncertainty sources and Uncertainty Quantification methodology for the purpose of assessing Severe Accidents (SA). The key motivation of the project has been to bring the advantages of the Best Estimate Plus Uncertainty approach to the field of Severe Accident. The applications brought together a large group of participants that set out to apply uncertainty analysis (UA) within their field of SA modelling expertise, in particular reactor types, but also SA code used (ASTEC, MELCOR, etc.), uncertainty quantification tools used (DAKOTA, RAVEN, etc.), detailed accident scenarios, and in some cases SAM actions. This paper synthesizes the reactor-application work at the end of the project. Analyses of 23 partners are sorted into different categories, depending on whether their main goal is/are (i) uncertainty bands of simulation results; (ii) the understanding of dominating uncertainties in specific sub-models of the SA code; (iii) improving the understanding of specific accident scenarios, with or without the application of SAM actions; or, (iv) a demonstration of the tools used and developed, and of the capability to carry out an uncertainty analysis in the presence of the challenges faced. The partners' experiences made during the project have been evaluated and are presented as good practice recommendations. The paper ends with conclusions on the level of readiness of UA in SA modelling, on the determination of governing uncertainties, and on the analysis of SAM actions.
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; 古府 麻衣子*; 楡井 真実; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Crystalline solids exhibiting inherently low lattice thermal conductivity ( ) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,
) are of great importance in applications such as thermoelectrics and thermal barrier coatings. However,  cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg
cannot be arbitrarily low and is limited by the minimum thermal conductivity related to phonon dispersions. In this work, we report the liquid-like thermal transport in a well-ordered crystalline CsAg Te
Te , which exhibits an extremely low
, which exhibits an extremely low  value of
value of  0.18 Wm
0.18 Wm K
K . On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at
. On the basis of first-principles calculations and inelastic neutron scattering measurements, we find that there are lots of low-lying optical phonon modes at  3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low
3.1 meV hosting the avoided-crossing behavior with acoustic phonons. These strongly localized modes are accompanied by weakly bound rattling Ag atoms with thermally induced large amplitudes of vibrations. Using the two-channel model, we demonstrate that coupling of the particle-like phonon modes and the heat-carrying wave-like phonons is essential for understanding the low  , which is heavily deviated from the
, which is heavily deviated from the 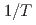 temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg
temperature dependence of the standard Peierls theory. In addition, our analysis indicates that the soft structural framework with liquid-like motions of the fluctuating Ag atoms is the underlying cause that leads to the suppression of the heat conduction in CsAg Te
Te . These factors synergistically account for the ultralow
. These factors synergistically account for the ultralow  value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
value. Our results demonstrate that the liquid-like heat transfer could indeed exist in a well-ordered crystal.
Zeng, Z.*; Zhou, C.*; Zhou, H.*; Han, L.*; Chi, R.*; Li, K.*; 古府 麻衣子; 中島 健次; Wei, Y.*; Zhang, W.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1097 - 1102, 2024/07
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:94.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Emergent quasiparticles with a Dirac dispersion in condensed matter systems can be described by the Dirac equation for relativistic electrons, in analogy with Dirac particles in high-energy physics. For example, electrons with a Dirac dispersion have been intensively studied in electronic systems such as graphene and topological insulators. However, charge is not a prerequisite for Dirac fermions, and the emergence of Dirac fermions without a charge degree of freedom has been theoretically predicted to be realized in Dirac quantum spin liquids. These quasiparticles carry a spin of 1/2 but are charge-neutral and so are called spinons. Here we show that the spin excitations of a kagome antiferromagnet, YCu (OD)
(OD) Br
Br [Br
[Br (OD)
(OD)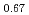 ], are conical with a spin continuum inside, which is consistent with the convolution of two Dirac spinons. The predictions of a Dirac spin liquid model with a spinon velocity obtained from spectral measurements are in agreement with the low-temperature specific heat of the sample. Our results, thus, provide spectral evidence for a Dirac quantum spin liquid state emerging in this kagome lattice antiferromagnet. However, the locations of the conical spin excitations differ from those calculated by the nearest-neighbor Heisenberg model, suggesting the Dirac spinons have an unexpected origin.
], are conical with a spin continuum inside, which is consistent with the convolution of two Dirac spinons. The predictions of a Dirac spin liquid model with a spinon velocity obtained from spectral measurements are in agreement with the low-temperature specific heat of the sample. Our results, thus, provide spectral evidence for a Dirac quantum spin liquid state emerging in this kagome lattice antiferromagnet. However, the locations of the conical spin excitations differ from those calculated by the nearest-neighbor Heisenberg model, suggesting the Dirac spinons have an unexpected origin.
Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:98.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanoprecipitates and nanoscale retained austenite (RA) with suitable stability play crucial roles in determining the yield strength (YS) and ductility of ultrahigh strength steels (UHSSs). However, owing to the kinetics incompatibility between nanoprecipitation and austenite reversion, it is highly challenging to simultaneously introduce high-density nanoprecipitates and optimized RA in UHSSs. In this work, through the combination of austenite reversion treatment (ART) and subsequent flash austenitizing (FA), nanoscale chemical heterogeneity was successfully introduced into a low-cost UHSS prior to the aging process. This chemical heterogeneity involved the enrichment of Mn and Ni in the austenite phase. The resulting UHSS exhibited dual-nanoprecipitation of Ni(Al,Mn) and (Mo,Cr) C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; 辻 伸泰*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:94.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)This paper focused on the characterization and mechanism of the dynamic transformation from the alpha to beta phase during the hot deformation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium. The investigation employed in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations for a comprehensive understanding of the process. Dynamic transformations were observed during deformation of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy and pure titanium below the beta transus temperatures. During isothermal holding after unloading, the in-situ neutron diffraction results for Ti-6Al-4V and pure titanium indicated a sluggish reverse transformation from the beta to alpha phase. The mechanism of dynamic transformation was explored through in-situ neutron diffraction and atomistic simulations, which revealed twofold effects of deformation on dynamic transformation. Firstly, deformation led to a significant rise in the Gibbs energy of the alpha phase relative to the beta phase, expanding the beta phase region and diminishing the alpha phase region. Secondly, deformation lowered the energy barriers associated with dynamic transformation, facilitating the activation of dynamic transformation more readily than in the equilibrium state before deformation.
 complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transition
complex exhibiting intermolecular proton shifting coupled spin transitionJi, T.*; Su, S.*; Wu, S.*; 堀 優太*; 重田 育照*; Huang, Y.*; Zheng, W.*; Xu, W.*; Zhang, X.*; 鬼柳 亮嗣; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 63(25), p.e202404843_1 - e202404843_6, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we investigated reversible intermolecular proton shifting (IPS) coupled with spin transition (ST) in a novel Fe complex. The host Fe
complex. The host Fe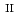 complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
complex and the guest carboxylic acid anion were connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonds (IHBs). We extended the intramolecular proton transfer coupled ST phenomenon to the intermolecular system. The dynamic phenomenon was confirmed by variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, neutron crystallography, and infrared spectroscopy.
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; 徐 平光; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:79.11(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The quasi-static superelastic responses and hierarchical martensite transformation from body-centered cubic (BCC) to face-centered cubic (FCC) under dynamic impact in Fe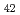 Mn
Mn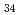 Al
Al Ni
Ni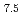 Ti
Ti alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC
alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC  FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:23.52(Chemistry, Physical)The grain orientation-dependent lattice strain evolution of a (TiZrHfNb)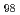
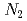 refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using
refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using  neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary
neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary 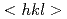 -oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
-oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
 TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Kang, Y.-G.*; Avdeev, M.*; Sibille, R.*; 飯田 一樹*; 梶本 亮一; Lee, K. H.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.8346_1 - 8346_9, 2023/12
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:86.45(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The triangular lattice antiferromagnet (TLAF) has been the standard paradigm of frustrated magnetism for several decades. The most common magnetic ordering in insulating TLAFs is the 120 structure. However, a new triple-
structure. However, a new triple-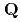 chiral ordering can emerge in metallic TLAFs, representing the short wavelength limit of magnetic skyrmion crystals. We report the metallic TLAF Co
chiral ordering can emerge in metallic TLAFs, representing the short wavelength limit of magnetic skyrmion crystals. We report the metallic TLAF Co TaS
TaS as the first example of tetrahedral triple-
as the first example of tetrahedral triple-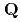 magnetic ordering with the associated topological Hall effect (non-zero
magnetic ordering with the associated topological Hall effect (non-zero 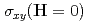 ). We also present a theoretical framework that describes the emergence of this magnetic ground state, which is further supported by the electronic structure measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Additionally, our measurements of the inelastic neutron scattering cross section are consistent with the calculated dynamical structure factor of the tetrahedral triple-
). We also present a theoretical framework that describes the emergence of this magnetic ground state, which is further supported by the electronic structure measured by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Additionally, our measurements of the inelastic neutron scattering cross section are consistent with the calculated dynamical structure factor of the tetrahedral triple-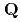 state.
state.
Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; 梶本 亮一; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:92.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnon polarons are novel elementary excitations possessing hybrid magnonic and phononic signatures, and are responsible for many exotic spintronic and magnonic phenomena. Despite long-term sustained experimental efforts in chasing for magnon polarons, direct spectroscopic evidence of their existence is hardly observed. Here, we report the direct observation of magnon polarons using neutron spectroscopy on a multiferroic Fe Mo
Mo O
O possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling. Specifically, below the magnetic ordering temperature, a gap opens at the nominal intersection of the original magnon and phonon bands, leading to two separated magnon-polaron bands. Each of the bands undergoes mixing, interconverting and reversing between its magnonic and phononic components. We attribute the formation of magnon polarons to the strong magnon-phonon coupling induced by Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Intriguingly, we find that the band-inverted magnon polarons are topologically nontrivial. These results uncover exotic elementary excitations arising from the magnon-phonon coupling, and offer a new route to topological states by considering hybridizations between different types of fundamental excitations.
Esser, S. P.*; Rahlff, J.*; Zhao, W.*; Predl, M.*; Plewka, J.*; Sures, K.*; Wimmer, F.*; Lee, J.*; Adam, P. S.*; McGonigle, J.*; et al.
Nature Microbiology (Internet), 8(9), p.1619 - 1633, 2023/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:74.53(Microbiology)CRISPR-Cas systems defend prokaryotic cells from viruses, plasmids, and other mobile genetic elements. Capitalizing on multi-omics approaches, we show here that the CRISPR-Cas systems of uncultivated archaea also play an integral role in mitigating potentially detrimental interactions with episymbionts. A comprehensive analysis of CRISPR-Cas-based infection histories revealed that uncultivated deep-subsurface archaeal primary-producers defend themselves from archaeal episymbionts of the DPANN superphylum of archaea, some of which are known to fuse their membranes with their host. We show that host cells counter these attacks by deploying one of two CRISPR-Cas systems (type I-B and type III-A) to target and disrupt essential genes in the episymbiont. However, genome-scale modeling of metabolic interactions between two deep subsurface host-symbiont systems revealed that host cells also benefit from the symbionts via metabolic complementation. We speculate that populations of these uncultivated archaeal episymbionts are currently transitioning from a parasitic lifestyle to one of mutualism, as must have occurred in countless mutualistic systems known today. By expanding our analysis to thousands of archaeal genomes, we conclude that CRISPR-Cas mediated resistance to archaeal episymbiosis evolved independently in various archaeal lineages and may be a wide-spread evolutionary phenomenon.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetization of a quantum magnet can be pinned at a fraction of its saturated value by collective effects. One example of such a plateau phase is found in spin-1/2 triangular-lattice antiferromagnets. They feature strong geometrical frustration and the plateau phase therein is often interpreted as arising from an order-by-disorder mechanism driven by quantum fluctuations. Here we observe a one-third magnetization plateau under an applied magnetic field in the spin-1 antiferromagnet Na Ni
Ni BiO
BiO with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
 neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag
neutron diffraction study on the deformation behavior of the plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag S
SWang, Y.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Zhang, K.*; Zhang, Z. D.*; Li, B.*
Applied Physics Letters, 123(1), p.011903_1 - 011903_6, 2023/07
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:47.87(Physics, Applied)Bulk Ag S is a plastic inorganic semiconductor at room temperature. It exhibits a compressive strain greater than 50%, which is highly different from brittle conventional counterparts, such as silicon. Here, we present the experimental investigation of the deformation behavior in a plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag
S is a plastic inorganic semiconductor at room temperature. It exhibits a compressive strain greater than 50%, which is highly different from brittle conventional counterparts, such as silicon. Here, we present the experimental investigation of the deformation behavior in a plastic inorganic semiconductor Ag S using
S using  neutron diffraction during compressive deformation at room and elevated temperatures. At room temperature, the lattice strain partitioning among
neutron diffraction during compressive deformation at room and elevated temperatures. At room temperature, the lattice strain partitioning among 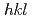 -orientated grain families could be responsible for the significant work-hardening behavior in the bulk Ag
-orientated grain families could be responsible for the significant work-hardening behavior in the bulk Ag S with a monoclinic structure. The rapid accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable development of the deformation texture suggest that dislocation slip promotes plasticity. At 453 K, a monoclinic phase transforms into a body-centered cubic phase. A stress plateau appears at
S with a monoclinic structure. The rapid accumulation of lattice defects and remarkable development of the deformation texture suggest that dislocation slip promotes plasticity. At 453 K, a monoclinic phase transforms into a body-centered cubic phase. A stress plateau appears at  -4.8 MPa, followed by a rehardening state. The deformation mode of bulk Ag
-4.8 MPa, followed by a rehardening state. The deformation mode of bulk Ag S at the initial stage is likely attributable to the migration of silver ions, and as strain increases, it is closer to that of room temperature, leading to rehardening.
S at the initial stage is likely attributable to the migration of silver ions, and as strain increases, it is closer to that of room temperature, leading to rehardening.
Zhang, T.*; Yao, Y.*; 守田 幸路*; Liu, X.*; Liu, W.*; 今泉 悠也; 神山 健司
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The in-pile EAGLE ID1 test was conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency to demonstrate the effectiveness of the fuel assembly with an internal duct structure during a core disruptive accident in a sodium-cooled fast reactor. In this study, a new computational fluid dynamics code based on the fully Lagrangian particle method was developed for the purpose of clarifying the failure mechanism of the inner duct wall of FAIDUS. The three-dimensional simulation of the ID1 test was performed to analyze a series of thermal hydraulic behaviors leading up to duct wall failure for a computational domain that included six fuel pins. The simulations reasonably reproduced the heat transfer characteristics observed in the test, showing that the local contact of liquid steel with high thermal conductivity with the duct wall greatly enhances the heat transfer from the nuclear heating fuel to the duct wall. The results support the validity of the conclusions of our analytical study regarding the molten pool-to-duct wall heat transfer mechanism that caused the thermal failure of the duct wall.
Lam, T.-N.*; Chin, H.-H.*; Zhang, X.*; Feng, R.*; Wang, H.*; Chiang, C.-Y.*; Lee, S. Y.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Liaw, P. K.*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 245, p.118585_1 - 118585_9, 2023/02
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:88.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The present study investigates the crystallographic-texture effects on the improved fatigue resistance in the CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys (HEAs) with the full-size geometry of the ASTM Standards E647-99. We exploited X-ray nano-diffraction mapping to characterize the crystal-deformation levels ahead of the crack tip after stress unloading under both constant- and tensile overloaded-fatigue conditions. The crack-tip blunting-induced much higher deformation level was concentrated surrounding the crack-tip which delays the fatigue-crack growth immediately after a tensile overload. The predominant deformation texture orientation in the Paris regime was investigated, using electron backscatter diffraction and orientation distribution function analyses. The twinning formation-driven shear deformation gave rise to the development of the Goss-type texture within the plastic deformation regime under a tensile-overloaded-fatigue condition, which was attributed to enhance the crack deflection and thus the tensile induced crack-growth-retardation period in the CoCrFeMnNi HEA.
Chong, Y.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; 都留 智仁; Zhang, R.*; 井上 耕治*; Gao, W.*; Godfrey, A.*; 光原 昌寿*; Morris, J. W. Jr.*; Minor, A. M.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.404_1 - 404_11, 2023/02
被引用回数:49 パーセンタイル:96.50(Multidisciplinary Sciences)チタンは格子間酸素によって脆化する。特に極低温では顕著な脆化挙動を示すため、チタンやその合金の製造において酸素含有量を厳しく管理する必要がある。この問題を解決するために、我々は結晶粒の微細化という構造戦略を提案した。77Kで非常に脆い粗粒の組織と比較して、Ti-0.3wt.%Oの超微細粒(UFG)組織(粒径 2.0
2.0 m)は、UFG組織特有の超高降伏強度を維持したまま均一延びを1桁上昇させることに成功した。UFG Ti-0.3wt.%Oにおけるこの特異な強度-延性相乗効果は、粒界凝集エネルギー向上に寄与する希薄な酸素の粒界偏析と優れたひずみ硬化能に寄与する
m)は、UFG組織特有の超高降伏強度を維持したまま均一延びを1桁上昇させることに成功した。UFG Ti-0.3wt.%Oにおけるこの特異な強度-延性相乗効果は、粒界凝集エネルギー向上に寄与する希薄な酸素の粒界偏析と優れたひずみ硬化能に寄与する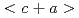 転位の活性化の複合効果によって達成された。この方法は、低温での高強度Ti-O合金の応用の可能性を高めるだけでなく、格子間固溶硬化による延性の低下を生じる他の合金系にも適用できる可能性がある。
転位の活性化の複合効果によって達成された。この方法は、低温での高強度Ti-O合金の応用の可能性を高めるだけでなく、格子間固溶硬化による延性の低下を生じる他の合金系にも適用できる可能性がある。
Chen, J.*; 山本 慧; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; Yu, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:62.75(Physics, Applied)Coherent coupling in magnon based hybrid system has many potential applications in quantum information processing. Magnons can propagate in magnetically ordered materials without any motion of electrons, offering a unique method to build low-power-consumption devices and information channels free of heat dissipation. In this article, we demonstrate the coherent propagation of hybridized modes between spin waves and Love surface acoustic waves in a multiferroic BiFeO and ferromagnetic La
and ferromagnetic La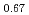 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO based heterostructure. The magneto-elastic coupling enables a giant enhancement of strength of the hybridized mode by a factor of 26 compared to that of the pure spin waves. A short wavelength down to 250 nm is demonstrated for the hybridized mode, which is desirable for nanoscale acousto-magnonic applications. Our combined experimental and theoretical analyses represent an important step towards the coherent control in hybrid magnonics, which may inspire the study of magnon-phonon hybrid systems for coherent information processing and manipulation.
based heterostructure. The magneto-elastic coupling enables a giant enhancement of strength of the hybridized mode by a factor of 26 compared to that of the pure spin waves. A short wavelength down to 250 nm is demonstrated for the hybridized mode, which is desirable for nanoscale acousto-magnonic applications. Our combined experimental and theoretical analyses represent an important step towards the coherent control in hybrid magnonics, which may inspire the study of magnon-phonon hybrid systems for coherent information processing and manipulation.
Zhang, H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Ao, N.*; Zhang, J. W.*; Li, H.*; Zhou, L.*; 徐 平光; Su, Y. H.
International Journal of Fatigue, 166, p.107296_1 - 107296_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:84.17(Engineering, Mechanical)Abnormal damages in railway axles can lead to a significant hazard to running safety and reliability. To this end, a surface treatment was selected to effectively inhibit fatigue crack initiation and growth. In this study, a single edge notch bending fatigue test campaign with artificial notches was conducted to elucidate the fatigue crack non-propagation behavior in railway S38C axles subjected to an induction hardening process. The fatigue cracking behavior in the gradient structure was revealed by optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction, and fractography. The microhardness distribution was measured using a Vickers tester. The obtained results show that the microhardness of the strengthening layer is nearly triple that of the matrix. Owing to the gradient microstructures and hardness, as well as compressive residual stress, the fatigue long crack propagates faster once it passes through the hardened zone (approximately 2.0 mm in the radial depth). Thereafter, local retarding (including deflection, branching, and blunting) of the long crack occurs because of the relatively coarse ferrite and pearlite in the transition region and matrix. Totally, this fatigue cracking resistance is reasonably believed to be due to the gradient microstructure and residual stress. These findings help to tailor a suitable detection strategy for maximum defects or cracks in railway axles.
Wu, P.*; 村井 直樹; Li, T.*; 梶本 亮一; 中村 充孝; 古府 麻衣子; 中島 健次; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The understanding of the lattice dynamics is essential for engineering the thermal transport properties in quantum materials. Based on the canonical point of view, acoustic phonons are believed to be the principal thermal carriers in heat flow. Here, in this work, optical phonons are elucidated to play a pivotal role in determining the lattice thermal conductivity in thermoelectric material SnS by using the state-of-the-art inelastic neutron scattering technique combined with first-principles calculations. Additionally, in contrast to acoustic phonons, optical phonons are observed to exhibit pronounced softening and broadening with temperature. Our observations not only shed light on the significance of the optical phonons in thermal transport but also provide a vital clue to suppress the propagation of optical phonons to optimize the thermoelectric performance of SnS.