Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; 森 隆人*; Golovin, D.*; 早川 岳人*; 岩田 夏弥*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:88.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutrons are powerful tools for investigating the structure and properties of materials used in science and technology. Recently, laser-driven neutron sources (LDNS) have attracted the attention of different communities, from science to industry, in a variety of applications, including radiography, spectroscopy, security, and medicine. However, the laser-driven ion acceleration mechanism for neutron generation and for establishing the scaling law on the neutron yield is essential to improve the feasibility of LDNS. In this paper, we report the mechanism that accelerates ions with spectra suitable for neutron generation. We show that the neutron yield increases with the fourth power of the laser intensity, resulting in the neutron generation of 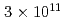 in
in 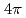 at a maximum, with
at a maximum, with 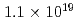 Wcm
Wcm , 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub-
, 900 J, 1.5 ps lasers. By installing a "hand-size" moderator, which is specially designed for the LDNS, it is demonstrated that the efficient generation of epithermal (0.1-100 eV) neutrons enables the single-shot analysis of composite materials by neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). We achieve the energy resolution of 2.3% for 5.19-eV neutrons 1.8 m downstream of the LDNS. This leads to the analysis of elements and isotopes within sub- s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
s times and allows for high-speed nondestructive inspection.
瀬戸 慧大*; Zhang, S.*; Koga, J. K.; 長友 英夫*; 中井 光男*; 三間 圀興*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2014(4), p.043A01_1 - 043A01_10, 2014/04
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:55.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)From the development of the electron theory by H. A. Lorentz in 1906, many authors have tried to reformulate this model. P. A. M. Dirac derived the relativistic-classical electron model in 1938, which is now called the Lorentz-Abraham-Dirac model. But this model has the big difficulty of the run-away solution. Recently, this equation has become important for ultra-intense laser-electron (plasma) interactions. For simulations in this research field, it is desirable to stabilize this model of the radiation reaction. In this paper, we will discuss this ability for radiation reaction with the inclusion of vacuum polarization.
藤岡 慎介*; 西村 博明*; 西原 功修*; 佐々木 明; 砂原 淳*; 奥野 智晴*; 上田 修義*; 安藤 強史*; Tao, Y.*; 島田 義則*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 95(23), p.235004_1 - 235004_4, 2005/12
被引用回数:147 パーセンタイル:95.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)レーザー生成スズプラズマからの極端紫外(EUV)発光へのオパシティの効果を実験的に解析した。X線放射によって電子温度30-40eVの均一なスズプラズマを生成することにより、EUV波長域(10-20nm)におけるオパシティを初めて測定した。測定されたオパシティは理論計算とほぼ一致した。理論計算で求めたオパシティを用いた輻射流体シミュレーションと実験の比較の結果は、EUV光源としての効率を高めるためには、13.5nm領域でプラズマの光学的厚みが1程度以上になることが必要だが、反面オパシティが大きすぎると吸収の効果によって効率が低下することを示し、オパシティの制御が重要なことを示す。
島田 義則*; 西村 博明*; 中井 光男*; 橋本 和久*; 山浦 道照*; Tao, Y.*; 重森 啓介*; 奥野 智晴*; 西原 功修*; 河村 徹*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 86(5), p.051501_1 - 051501_3, 2005/01
被引用回数:113 パーセンタイル:94.26(Physics, Applied)EUV光源として用いられるSnプラズマの基本的な輻射流体力学的な特性を明らかにするために、阪大レーザー研の激光XII号レーザーで球状のSnターゲットを照射し、生成したプラズマからのEUV光のスペクトル,発光強度分布,波長13.5nm領域の2%帯域中の発光強度とその時間変化,変換効率の測定を行った。照射強度5 10
10 W/cm
W/cm において最大効率3%が得られた。変換効率のレーザー強度依存性を等温膨張プラズマを仮定した理論モデルと比較した。
において最大効率3%が得られた。変換効率のレーザー強度依存性を等温膨張プラズマを仮定した理論モデルと比較した。
越智 義浩; Golovkin, I.*; Mancini, R.*; Uschmann, I.*; 砂原 淳*; 西村 博明*; 藤田 和久*; Louis, S.*; 中井 光男*; 白神 宏之*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 74(3), p.1683 - 1687, 2003/03
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:49.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)高強度レーザー光を重水素を充填した燃料球に照射することにより生成されるレーザー爆縮コアプラズマ中の、電子温度,電子密度勾配の時間変化を、時間・空間分解X線分光法により明らかにした。実験においてX線分光ストリークラスターカメラによる時間分解X線スペクトルデータと単色X線駒取りカメラによる特定のラインX線に対応する単色のX線エネルギーの時間分解二次元画像データを同時に取得した。これらのデータをもとに遺伝的アルゴリズムを用いた自己無頓着な解析手法により、爆縮コア内部の電子温度,電子密度勾配を求めることに成功した。得られた成果と流体コードによるシミュレーションとを比較し、爆縮コアプラズマ形成の動的過程の診断を進めている。
匂坂 明人; 小倉 浩一; 錦野 将元; Pirozhkov, A. S.; 河内 哲哉; 西内 満美子; 神門 正城; 近藤 公伯; 有川 安信*; 小島 完興*; et al.
no journal, ,
高強度レーザーと薄膜との相互作用により、高エネルギーの粒子,硬X線などが発生する。特にレーザー駆動陽子線については、医療やその他への応用が期待されている。今回、大阪大学設置のLFEXレーザーを用い、高エネルギーレーザーと薄膜ターゲットとの相互作用実験を行なった。レーザーは、3ビームをターゲットに照射した。3ビームの照射により、高エネルギー陽子を測定した。また、プラズマミラーの予備実験を開始した。
匂坂 明人; 小倉 浩一; Pirozhkov, A. S.; 錦野 将元; 今 亮; 西内 満美子; Esirkepov, T. Z.; 神門 正城; 河内 哲哉; 近藤 公伯; et al.
no journal, ,
高強度レーザーと薄膜との相互作用により、高エネルギーの粒子, 硬X線などが発生する。特にレーザー駆動陽子線については、医療やその他への応用が期待されている。今回、大阪大学設置のLFEXレーザーを用い、高エネルギーレーザーと薄膜ターゲットとの相互作用実験を行なった。レーザーは、4ビームをターゲットに照射した。4ビームを合計したレーザーエネルギー 1kJにおいて、陽子の最大エネルギーとして
1kJにおいて、陽子の最大エネルギーとして 40MeVが得られた。また、プラズマミラーを用いた陽子加速実験を開始した。
40MeVが得られた。また、プラズマミラーを用いた陽子加速実験を開始した。
匂坂 明人; 小倉 浩一; 錦野 将元; Pirozhkov, A. S.; 河内 哲哉; 西内 満美子; 今 亮; 神門 正城; 近藤 公伯; 有川 安信*; et al.
no journal, ,
高強度レーザーと物質との相互作用により生成される高エネルギーのイオン、電子、X線等は、量子ビーム源として注目されている。特に高エネルギーイオンについては、医療への応用が期待されている。レーザーの強度やエネルギーに対する加速イオンのエネルギー等を調べるため、超短パルスレーザーや高エネルギーレーザーを用いて、薄膜ターゲットからの陽子発生実験を進めている。超短パルスレーザーを用いた実験では、原子力機構設置のJ-KARENレーザーを用いて、実験を進めている。高エネルギーレーザーを用いた実験として、大阪大学レーザーエネルギー学研究センター設置のLFEXレーザーを照射し、陽子発生実験を行った。
小泉 光生; Lee, J.; 伊藤 史哲*; 高橋 時音; 鈴木 敏*; Omer, M.*; 瀬谷 道夫*; 羽島 良一; 静間 俊行; 余語 覚文*; et al.
no journal, ,
Along with the global increase of use of nuclear materials (NMs), growing requirements are development for new effective characterization methods for nuclear material accountancy and technologies to cope with the threat of nuclear terrorism. Non-destructive Assay (NDA) methods are an efficient, quick, and remote way to detect and quantify nuclear materials (NMs). Passive NDA techniques, which are based on radiation measurement, are conventionally used in accountancy for quantification of NMs and in security for detection and identification of NMs. However, they could not be applied to an object with strong radioactivity or in shielding materials. Active NDA techniques are, therefore, considered to be a breakthrough technique to measure such NMs samples by utilizing interrogation particles (such as photons and neutrons). Induced signals by the incident particles (for example, transmitted neutrons) are measured to deduce sample properties. This report overviews two research programs that utilize nuclear photonics technologies for nuclear non-proliferation and security. The research programs carried out by JAEA under collaborations are supported by MEXT (the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of the Japanese government) under the subsidy for "promotion of strengthening nuclear security and the like".
高橋 時音; 小泉 光生; 伊藤 史哲*; Lee, J.; 鈴木 敏*; 弘中 浩太; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 西村 博明*; et al.
no journal, ,
The technique of NRTA is based on a neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method. Collimated pulsed neuron beams passing through a sample arrive a neutron detector placed at a distance from the neutron source. The neutron kinetic energy is deduced from the flight time between the neutron generator and the detector. Since the neutron reaction cross section of a nuclide has a characteristic resonance structure, neutrons having the resonance energy are strongly absorbed or scattered by the nuclide in a sample. Resonance dips appeared in the transmission spectrum are analyzed to deduce each nuclide areal density. The resolution of the observed dip strongly depends on the flight path length and the neutron pulse width. To realize a compact NRTA system by shortening the flight path length, a short-pulsed neutron generation is required. A laser-driven neutron source (LDNS), which can generate extremely short pulse neutron beams, is considered to potentially be such a short pulse neutron generator for a compact NRTA system. In addition, because laser light can be transported by mirrors, the laser system of the LDNS can be installed in separated place from an NRTA system which has to be in the nuclear controlled area. This enables maintenance of a laser system to be easy. Also, several analyzing system can be operated parallelly by switching laser path. In this presentation, we will overview a proposal of an application of the LDNS to an NRTA system for nuclear non-proliferation.
余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 岩本 晃史*; 早川 岳人*; 小泉 光生; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Lan, Z.*; et al.
no journal, ,
大阪大学のLFEXレーザー施設において、大強度レーザーを用いたパルス中性子源(LDNS)の開発およびそれを利用した応用研究を進めている。レーザーは、パルス巾が1.5psで、最大出力は、1kJ(1.5 10
10 Wcm
Wcm である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10
である。開発した中性子源は1cm程度の大きさで、数十マイクロメータに収束したレーザーをターゲットに照射し、それによって生成したMeVもの高速イオン(水素や重水素粒子)を直径5mmのベリリウムに当てて、核反応により中性子を生成するものである。中性子の生成量は、1ショットあたり10 で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
で、この生成量は、入射エネルギーの4乗で増加することが分かった。さらに、生成した中性子を数cmの大きさのモデレータで減速させ、離れた位置に設置した中性子検出器により、中性子発生から検出までの飛行時間を測定するTOF測定を行った。試料を透過させて中性子の減衰を調べる実験を行った結果、核反応の共鳴による減衰の観測に成功した。
余語 覚文*; Lan, Z.*; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; 藤岡 慎介*; et al.
no journal, ,
レーザー駆動中性子源は、高強度レーザーパルスを薄膜の1次ターゲットに集光して、プラズマの作る瞬間的な電場でMeVエネルギーイオン(陽子・重陽子)を発生し、それを2次ターゲット(ベリリウム等)に照射して、短パルスの高速中性子を発生する。2次ターゲットに小型の減速材を取り付けて、パルス熱外中性子を発生し、1.8mのビームラインで飛行時間法によるエネルギースペクトルを分析した。ビームラインに銀(Ag),タンタル(Ta),インジウム(In)の合板を設置したところ、3.81eV ( In), 4.28eV (
In), 4.28eV ( Ta), 5.19eV (
Ta), 5.19eV ( Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Ag)に共鳴吸収によるディップを計測した。これらの共鳴吸収スペクトルは、レーザー1パルスで発生する中性子で計測されたものである。講演では、実験結果の詳細と、将来的なシングルショット分析への応用可能性について議論する。
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 早川 岳人*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; Golovin, D.*; 森 隆人*; Wei, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance diagnosis technology has been developed on reactors and accelerators for over ten years. By employing neutron beams with high transmittance, it is possible to analyse elementary composition, internal temperature and shock waves of thick objects in a non-destructive way. We developed a new approach to generate short-pulse epithermal neutron beams using relativistic intensity laser for the neutron resonance spectral diagnosis, which is known as Laser-driven Epithermal Neutron Source (LDENS). The neutron resonance measuring experiment was implemented at ILE, Osaka Univ. with peta-watt laser LFEX. The experimental results in 2020 demonstrated that LDENS is applicable for neutron resonance measurement. In 2021 experiments, we developed the system to record neutron spectrum with higher quality. Multiple resonance peaks of various isotopes with different temperature were clearly measured. The presentation will introduce the experimental results and discussions including characteristic evaluation of LDENS and temperature dependency of neutron resonance peaks.
Lan, Z.*; 余語 覚文*; 早川 岳人*; Wei, T.*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron resonance diagnosis technology has been developed worldwide for over ten years. By employing neutron beams with high transmittance, it is possible to measure the resonance spectral of samples in the neutron beam-line. We developed a new approach to generate short pulse epithermal neutron beams using relativistic intensity laser for the neutron resonance spectral diagnosis, which is known as Laser-Driven Epithermal Neutron Source (LDENS). Benefit from highly focused laser, the LDENS can provide high temporal accuracy with a compact volume of the source. Therefore, the minimal change of neutron resonance peaks caused by Doppler broadening effect of atom temperature could be detected via single pulse of LDENS. In experiment, we measured resonance at 4.28eV of a 0,1mm Ta plate with serial temperature points (300K-600K) and another resonance at 5.18eV of an Ag plate was recorded as a reference of the neutron signal. The experimental data shows the feasibility of isotope-discriminating atomic thermometer using a single shot of LDENS. More results will be reported in the presentation.
小泉 光生; 弘中 浩太; Lee, J.; 余語 覚文*; 有川 安信*; 安部 勇輝*; 中井 光男*
no journal, ,
本研究では、レーザー駆動中性子源(LDNS)を用いた中性子共鳴透過分析(NRTA)技術開発の一環として、大阪大学の超高強度レーザーLFEXから発生したパルス中性子に適用できる中性子モデレータ、中性子検出器及び飛行時間測定・分析システムの開発を進めており、開発に関する打ち合わせ、議論、情報交換などを行った。本発表では、今までの研究会から得られた成果を報告する。
Lan, Z.*; Wei, T.*; 早川 岳人*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; Morace, A.*; et al.
no journal, ,
A Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) is a novel neutron that provides neutron beam of ultra-short pulse duration and high flux. This technique would be useful for neutron resonance non-destructive diagnosis application. A demonstration experiment was carried out using an LDNS developed for the LFEX laser of Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. A neutron resonance spectrum was observed with a single laser shot. The technique can be used as a "nuclear thermometer" because the resonance shape is broadened as a function of the sample material temperature.
Lan, Z.*; 早川 岳人*; Wei, T.*; 加美山 隆*; 佐藤 博隆*; 有川 安信*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; 小泉 光生; 安部 勇輝*; 森 隆人*; et al.
no journal, ,
As a new approach of neutron generation with the ultra-short pulse duration and high flux, a Laser-Driven Neutron Source (LDNS) has been studied. A demonstration experiment of neutron resonance spectroscopy using a LDNS has been performed using the petawatt laser LFEX at the Institute of Laser Engineering, Osaka University. A CD foil target was used for an high-density plasma generation. Neutrons were produced by the impact of the high energy ions on a boron converter. A high-density polyethylene surrounding the boron converter slowed down neutron energy to epithermal temperature. A single shot neutron resonance experiment was carried out at a neutron beam line of 1.8m. The neutron resonance peak at 4.28 eV of Ta was measured with different temperature.