Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
神谷 潤一郎; 阿部 一英; 藤森 伸一; 福田 竜生; 小畠 雅明; 諸橋 裕子; 津田 泰孝; 山田 逸平; 吉越 章隆
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 22(4), p.316 - 326, 2024/08
真空容器内壁にゲッター機能を持たせることで、超高真空を実現する新しい技術であるNEGコーティングについて、その活性化と劣化のメカニズムの理解は、NEGコーティングの高性能化に不可欠である。本研究では代表的なNEGコーティング材料Ti-Zr-Vについて、SPring-8放射光光電子分光(SRPES)およびX線光電子分光(XPS)による測定を行った。実験ではNEGコーティング試料温度を250 Cに昇温させる過程をSRPESにより分析し、その後、酸素ガスを導入して表面酸化過程を同手法により分析した。これらは、NEGコーティング表面の活性化、酸化過程の初めてのオペランド測定である。さらに、試料の深さ方向をXPSにより分析することで、活性化によりZrがTi酸化物、V酸化物から酸素を受け取り、内部へ酸素が拡散すること、および内部では主にZrが酸化物となっていることを観測し、コーティング内部におけるZr酸化物の増加が、NEGコーティングの繰り返しの活性化と飽和による寿命を決定する大きな要素であることを解明した。このことは、今後のNEGコーティングの性能高度化につながる新しい事実である。
Cに昇温させる過程をSRPESにより分析し、その後、酸素ガスを導入して表面酸化過程を同手法により分析した。これらは、NEGコーティング表面の活性化、酸化過程の初めてのオペランド測定である。さらに、試料の深さ方向をXPSにより分析することで、活性化によりZrがTi酸化物、V酸化物から酸素を受け取り、内部へ酸素が拡散すること、および内部では主にZrが酸化物となっていることを観測し、コーティング内部におけるZr酸化物の増加が、NEGコーティングの繰り返しの活性化と飽和による寿命を決定する大きな要素であることを解明した。このことは、今後のNEGコーティングの性能高度化につながる新しい事実である。
矢板 毅; 藤森 伸一
放射光, 37(1), p.3 - 12, 2024/01
現在、原子力機構(JAEA)のビームラインは、SPring-8のRI実験棟に設置された2本のビームライン(BL22XUおよびBL23SU)で運用されており、試料は密封を原則として運用しているが、RI棟建屋は負圧管理された施設であり、このような規模の放射光実験施設は世界でも他に例を見ない。原子力機構は、この2本のビームラインで、アクチノイドなどの重元素の基礎科学、環境エネルギー材料の開発、福島原子力発電所事故(1F)に関連した研究開発を進めている。さらに、2022年に新たに核燃料物質使用認可が規制庁より下りたことに伴い、JAEAでは、重元素科学と1F関連の研究開発を大きく推進する計画である。本稿では、放射性物質を扱うビームラインの世界的動向と原子力機構ビームラインの最近の成果を紹介する。
 FeSi
FeSi角田 一樹; 藤田 裕一*; Zhou, W.*; 増田 啓介*; 川崎 郁斗; 藤森 伸一; 木村 昭夫*; 桜庭 裕弥*
Physical Review B, 108(24), p.L241101_1 - L241101_6, 2023/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:34.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the element-specific electronic structure of a half-metallic Weyl ferromagnet candidate Co FeSi film by utilizing soft-X-ray resonant photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculations with/without considering on-site Coulomb interaction. Fe 2
FeSi film by utilizing soft-X-ray resonant photoelectron spectroscopy and first-principles calculations with/without considering on-site Coulomb interaction. Fe 2 -3
-3 resonant photoelectron experiment revealed that the Fe 3
resonant photoelectron experiment revealed that the Fe 3 states exist around 2 and 4 eV below the Fermi energy. Our calculations, based on the generalized gradient approximation without considering Coulomb interaction at the Fe site, successfully reproduced the experimentally observed Fe 3
states exist around 2 and 4 eV below the Fermi energy. Our calculations, based on the generalized gradient approximation without considering Coulomb interaction at the Fe site, successfully reproduced the experimentally observed Fe 3 partial density of states. Our findings shed light on the highly controversial correlation effect of Co
partial density of states. Our findings shed light on the highly controversial correlation effect of Co FeSi, offering valuable insights into its half-metallicity and Weyl semi-metallicity.
FeSi, offering valuable insights into its half-metallicity and Weyl semi-metallicity.
大槻 太毅*; Ishida, Tatsuhiro*; Tsutsumi, Naoya*; 小林 正起*; Inagaki, Kodai*; 吉田 鉄平*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 保井 晃*; 北川 彩貴*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(12), p.124601_1 - 124601_6, 2023/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:21.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In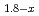 Mn
Mn Sn
Sn O
O is a diluted magnetic semiconductor combining transparent, ferromagnetism, and semiconducting properties. We report the electronic structure of In
is a diluted magnetic semiconductor combining transparent, ferromagnetism, and semiconducting properties. We report the electronic structure of In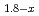 Mn
Mn Sn
Sn O
O (x = 0.0, 0.2, and 0.3) by means of hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES), soft X-ray resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES), and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The spectral shape of the Mn
(x = 0.0, 0.2, and 0.3) by means of hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES), soft X-ray resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES), and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The spectral shape of the Mn  -
-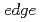 XAS spectra indicates that the valence of the substitutional Mn ions is divalent. The In 3
XAS spectra indicates that the valence of the substitutional Mn ions is divalent. The In 3 and O
and O 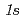 core-level shifts with Mn substitution suggest the hole doping due to the Mn
core-level shifts with Mn substitution suggest the hole doping due to the Mn ions. The valence-band spectra exhibit the well-defined features associated with the donor states across the Fermi level (EF) and the valence-band edge. The valence-band maximum (VBM) shifts to higher binding energy and the spectral weight near EF decreases with increasing Mn concentration, which is consistent with the hole doping nature observed in the core-level shift. The Mn
ions. The valence-band spectra exhibit the well-defined features associated with the donor states across the Fermi level (EF) and the valence-band edge. The valence-band maximum (VBM) shifts to higher binding energy and the spectral weight near EF decreases with increasing Mn concentration, which is consistent with the hole doping nature observed in the core-level shift. The Mn 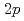 -3
-3 RPES reveals that the hump structure around 1.9 eV above the VBM is originating from the Mn 3
RPES reveals that the hump structure around 1.9 eV above the VBM is originating from the Mn 3 impurity band and the valence-band state consists of the O 2
impurity band and the valence-band state consists of the O 2 band strongly hybridized with the Mn 3
band strongly hybridized with the Mn 3 orbital. Furthermore, there is no contribution of the Mn 3
orbital. Furthermore, there is no contribution of the Mn 3 orbital to the spectral weight close to
orbital to the spectral weight close to 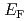 . Based on our results, we argue the possible mechanism of the ferromagnetism for In
. Based on our results, we argue the possible mechanism of the ferromagnetism for In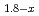 Mn
Mn Sn
Sn O
O .
.
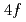 states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
states in the electronic structure of the intermediate-valence superconductor CeIr
藤森 伸一; 川崎 郁斗; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; 雀部 矩正*; 佐藤 芳樹*; 清水 悠晴*; 仲村 愛*; Maruya, A.*; 本間 佳哉*; et al.
Electronic Structure (Internet), 5(4), p.045009_1 - 045009_7, 2023/11
The electronic structure of the  -based superconductor
-based superconductor 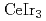 was studied by photoelectron spectroscopy. The energy distribution of the
was studied by photoelectron spectroscopy. The energy distribution of the 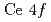 state was revealed by the
state was revealed by the 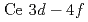 resonant photoelectron spectroscopy. The
resonant photoelectron spectroscopy. The 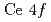 state was mostly distributed in the vicinity of the Fermi energy, suggesting the itinerant character of the
state was mostly distributed in the vicinity of the Fermi energy, suggesting the itinerant character of the 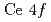 state. The contribution of the
state. The contribution of the 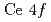 state to the density of states (DOS) at the Fermi energy was estimated to be nearly half of that of the
state to the density of states (DOS) at the Fermi energy was estimated to be nearly half of that of the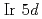 states, implying that the
states, implying that the 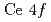 state has aconsiderable contribution to the DOS at the Fermi energy. The
state has aconsiderable contribution to the DOS at the Fermi energy. The 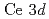 core-level and
core-level and 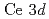 X-ray absorption spectra were analyzed based on a single-impurity Anderson model. The number of the
X-ray absorption spectra were analyzed based on a single-impurity Anderson model. The number of the 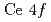 state in the ground state was estimated to be 0.8-0.9, which is much larger than the values obtained in the previous studies (i.e., 0-0.4).
state in the ground state was estimated to be 0.8-0.9, which is much larger than the values obtained in the previous studies (i.e., 0-0.4).

川崎 郁斗; 竹内 一陽*; 藤森 伸一; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; 山本 悦嗣; 芳賀 芳範
Physical Review B, 108(16), p.165127_1 - 165127_9, 2023/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:13.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We performed angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) experiments using soft X rays to investigate the electronic structure of the heavy-fermion superconductor UPt . The overall band structure revealed by the present ARPES measurements is compared with density-functional calculations for UPt
. The overall band structure revealed by the present ARPES measurements is compared with density-functional calculations for UPt and the non-
and the non-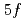 reference compound ThPt
reference compound ThPt . We showed that the calculation for ThPt
. We showed that the calculation for ThPt gives a better description of the experimental band structure, except for the
gives a better description of the experimental band structure, except for the 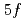 -derived heavy quasiparticle bands. This situation is reminiscent of Ce-based heavy-fermion systems, whose band structures are often very similar to those of non-
-derived heavy quasiparticle bands. This situation is reminiscent of Ce-based heavy-fermion systems, whose band structures are often very similar to those of non-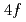 La-based compounds. The narrow heavy quasiparticle bands are located just below the Fermi level (
La-based compounds. The narrow heavy quasiparticle bands are located just below the Fermi level (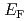 ), and their band structure could not be resolved by the present energy resolution. We also showed that most of the U
), and their band structure could not be resolved by the present energy resolution. We also showed that most of the U 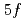 spectral weight exists not as the coherent heavy-fermion bands but as incoherent components that distribute over a wide energy range, spanning from near
spectral weight exists not as the coherent heavy-fermion bands but as incoherent components that distribute over a wide energy range, spanning from near 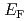 to approximately 2 eV. This result indicates that the heavy quasiparticle bands are enormously renormalized by the electron correlation effect. Additionally, we showed that the spectral intensity of the heavy-fermion bands is almost temperature independent, at least up to 100 K, where the magnetic susceptibility follows a Curie-Weiss behavior.
to approximately 2 eV. This result indicates that the heavy quasiparticle bands are enormously renormalized by the electron correlation effect. Additionally, we showed that the spectral intensity of the heavy-fermion bands is almost temperature independent, at least up to 100 K, where the magnetic susceptibility follows a Curie-Weiss behavior.
 localized ferromagnet CeRu
localized ferromagnet CeRu Ge
Ge studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy川崎 郁斗; 藤森 伸一; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; 大貫 惇睦*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(6), p.064709_1 - 064709_8, 2023/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The electronic state of 4 localized ferromagnet CeRu
localized ferromagnet CeRu Ge
Ge has been investigated by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (APRES) experiments using soft X rays. The band structure and Fermi surfaces consisting of non-4
has been investigated by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (APRES) experiments using soft X rays. The band structure and Fermi surfaces consisting of non-4 bands are almost consistent with a calculation based on the density-functional theory for LaRu
bands are almost consistent with a calculation based on the density-functional theory for LaRu Ge
Ge , thus confirming a localized character of the 4
, thus confirming a localized character of the 4 electrons. On the other hand, the Ce 3
electrons. On the other hand, the Ce 3 -4
-4 resonant ARPES experiments demonstrated that the 4
resonant ARPES experiments demonstrated that the 4 spectral function is dominated by
spectral function is dominated by 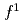 components in the vicinity of the Fermi level and thus is different from that expected for a localized electron system. We also revealed that the intensities of the
components in the vicinity of the Fermi level and thus is different from that expected for a localized electron system. We also revealed that the intensities of the 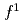 components have almost no temperature dependence up to at least 100 K, which is two orders of magnitude larger than the Kondo temperature of CeRu
components have almost no temperature dependence up to at least 100 K, which is two orders of magnitude larger than the Kondo temperature of CeRu Ge
Ge .
.
 Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
岩佐 和晃*; Suyama, Kazuya*; 河村 聖子; 中島 健次; Raymond, S.*; Steffens, P.*; Yamada, Akira*; 松田 達磨*; 青木 勇二*; 川崎 郁斗; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_11, 2023/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:42.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The spin dynamics, crystalline-electric-field (CEF) level scheme, specific heat, and X-ray photoemission spectra (XPS) of Ce Rh
Rh Sn
Sn were investigated, which exhibits anomalous semimetal transport in the chiral crystallographic phase. CEF excitations observed at approximately 7 and 39 meV are consistent with the two inequivalent Ce-ion cites in the chiral structure. Because of broader CEF excitations and a strong 4
were investigated, which exhibits anomalous semimetal transport in the chiral crystallographic phase. CEF excitations observed at approximately 7 and 39 meV are consistent with the two inequivalent Ce-ion cites in the chiral structure. Because of broader CEF excitations and a strong 4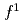 peak at the Fermi level in the Ce 4
peak at the Fermi level in the Ce 4 on-resonance spectrum, the hybridized Ce 4
on-resonance spectrum, the hybridized Ce 4 electrons contribute to the semimetal carriers. In addition, the spin fluctuation associated with the Kramers doublet ground state is characterized by the peak located at 0.15 meV. The electronic state involving the spin fluctuation causes the
electrons contribute to the semimetal carriers. In addition, the spin fluctuation associated with the Kramers doublet ground state is characterized by the peak located at 0.15 meV. The electronic state involving the spin fluctuation causes the 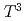 behavior of specific heat below 0.6 K, which is attributed to linear dispersion relations of electrons of the Weyl Kondo semimetal in the chiral-lattice symmetry.
behavior of specific heat below 0.6 K, which is attributed to linear dispersion relations of electrons of the Weyl Kondo semimetal in the chiral-lattice symmetry.
 Al
Al ; Impact of the U
; Impact of the U 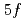 states on the electronic structure of UPd
states on the electronic structure of UPd Al
Al
藤森 伸一; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; Posp
 il, J.*; 山本 悦嗣; 芳賀 芳範
il, J.*; 山本 悦嗣; 芳賀 芳範
Physical Review B, 105(11), p.115128_1 - 115128_6, 2022/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:7.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structure of 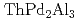 , which is isostructural to the heavy fermion superconductor
, which is isostructural to the heavy fermion superconductor 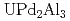 , was investigated by photoelectron spectroscopy. The band structure and Fermi surfaces of
, was investigated by photoelectron spectroscopy. The band structure and Fermi surfaces of 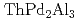 were obtained by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES), and the results were well-explained by the band-structure calculation based on the local density approximation. The comparison between the ARPES spectra and the band-structure calculation suggests that the Fermi surface of
were obtained by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES), and the results were well-explained by the band-structure calculation based on the local density approximation. The comparison between the ARPES spectra and the band-structure calculation suggests that the Fermi surface of 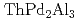 mainly consists of the
mainly consists of the 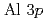 and
and 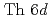 states with a minor contribution from the
states with a minor contribution from the 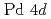 states. The comparison of the band structures between
states. The comparison of the band structures between 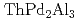 and
and 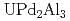 argues that the
argues that the 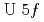 states form Fermi surfaces in
states form Fermi surfaces in 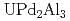 through hybridization with the
through hybridization with the 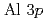 state in the
state in the 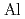 layer, suggesting that the Fermi surface of
layer, suggesting that the Fermi surface of 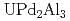 has a strong three-dimensional nature.
has a strong three-dimensional nature.
 layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O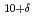 studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy出田 真一郎*; Johnston, S.*; 吉田 鉄平*; 田中 清尚*; 森 道康; 安齋 太陽*; 井野 明洋*; 有田 将司*; 生天目 博文*; 谷口 雅樹*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(21), p.217004_1 - 217004_6, 2021/11
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:67.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hybridization of Bogoliubov quasiparticles (BQPs) between the CuO layers in the triple-layer cuprate high-temperature superconductor Bi
layers in the triple-layer cuprate high-temperature superconductor Bi Sr
Sr Ca
Ca Cu
Cu O
O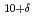 is studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). In the superconducting state, an anti-crossing gap opens between the outer- and inner-BQP bands, which we attribute primarily to interlayer single-particle hopping with possible contributions from interlayer Cooper pairing. We find that the
is studied by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). In the superconducting state, an anti-crossing gap opens between the outer- and inner-BQP bands, which we attribute primarily to interlayer single-particle hopping with possible contributions from interlayer Cooper pairing. We find that the  -wave superconducting gap of both BQP bands smoothly develops with momentum without abrupt jump in contrast to a previous ARPES study. Hybridization between the BQPs also gradually increases in going from the off-nodal to the anti-nodal region, which is explained by the momentum-dependence of the interlayer single-particle hopping. As possible mechanisms for the enhancement of the superconducting transition temperature, the hybridization between the BQPs, as well as the combination of phonon modes of the triple CuO
-wave superconducting gap of both BQP bands smoothly develops with momentum without abrupt jump in contrast to a previous ARPES study. Hybridization between the BQPs also gradually increases in going from the off-nodal to the anti-nodal region, which is explained by the momentum-dependence of the interlayer single-particle hopping. As possible mechanisms for the enhancement of the superconducting transition temperature, the hybridization between the BQPs, as well as the combination of phonon modes of the triple CuO layers and spin fluctuations are discussed.
layers and spin fluctuations are discussed.
 P
P studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy川崎 郁斗; 小畠 雅明; 藤森 伸一; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; 辺土 正人*; 仲間 隆男*; 大貫 惇睦*
Physical Review B, 104(16), p.165124_1 - 165124_8, 2021/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We carried out angle-resolved photoemission (ARPES) experiments using soft X rays to investigate the electronic structure of the intermediate valence compound EuNi P
P . Both the Eu
. Both the Eu and Eu
and Eu components arising from the 4
components arising from the 4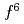 and 4
and 4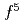 final states were observed in the valence spectra, directly confirming an intermediate character of Eu ions. The three-dimensional band structure was studied by ARPES measurements, and we found that the ARPES spectra up to just below the Fermi level can well be explained by a calculation based on the density-functional theory for the non-4
final states were observed in the valence spectra, directly confirming an intermediate character of Eu ions. The three-dimensional band structure was studied by ARPES measurements, and we found that the ARPES spectra up to just below the Fermi level can well be explained by a calculation based on the density-functional theory for the non-4 reference compound SrNi
reference compound SrNi P
P . The heavy-fermion bands in EuNi
. The heavy-fermion bands in EuNi P
P are thus considered to be formed through the hybridization between the dispersive valence bands, which resemble those for SrNi
are thus considered to be formed through the hybridization between the dispersive valence bands, which resemble those for SrNi P
P , and the Eu
, and the Eu components located at the very vicinity of the Fermi level.
components located at the very vicinity of the Fermi level.
 Si
Si in paramagnetic phase; Three-dimensional angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy study
in paramagnetic phase; Three-dimensional angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy study藤森 伸一; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; 山本 悦嗣; 芳賀 芳範
Electronic Structure (Internet), 3(2), p.024008_1 - 024008_8, 2021/06
The three-dimensional (3D) electronic structure of the hidden order compound 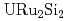 in a paramagnetic phase was revealed using a 3D angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy where the electronic structure of the entire Brillouin zone is obtained by scanning both incident photon energy and detection angles of photoelectrons. The quasi-particle bands with enhanced contribution from the
in a paramagnetic phase was revealed using a 3D angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy where the electronic structure of the entire Brillouin zone is obtained by scanning both incident photon energy and detection angles of photoelectrons. The quasi-particle bands with enhanced contribution from the 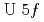 state were observed near
state were observed near 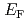 , formed by the hybridization with the
, formed by the hybridization with the 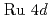 states. The energy dispersion of the quasi-particle band is significantly depend on
states. The energy dispersion of the quasi-particle band is significantly depend on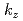 , indicating that they inherently have a 3D nature. The band-structure calculation qualitatively explain the characteristic features of the band structure and Fermi surface although the electron correlation effect strongly renormalizes the quasi-particle bands. The 3D and strongly-correlated nature of the quasi-particle bands in
, indicating that they inherently have a 3D nature. The band-structure calculation qualitatively explain the characteristic features of the band structure and Fermi surface although the electron correlation effect strongly renormalizes the quasi-particle bands. The 3D and strongly-correlated nature of the quasi-particle bands in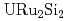 is an essential ingredient for modeling its hidden-order transition.
is an essential ingredient for modeling its hidden-order transition.
小林 正起*; Anh, L. D.*; 鈴木 雅弘*; 金田-高田 真悟*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 芝田 悟朗*; 田中 新*; 田中 雅明*; 大矢 忍*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 15(6), p.064019_1 - 064019_10, 2021/06
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:47.11(Physics, Applied)A fundamental understanding of the interfacial magnetic properties in ferromagnetic heterostructures is essential for utilizing ferromagnetic materials for spintronic device applications. Here, we investigate the interfacial magnetic and electronic structures of epitaxial single-crystalline LaAlO (LAO)/La
(LAO)/La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (LSMO)/Nb:SrTiO
(LSMO)/Nb:SrTiO (Nb:STO) heterostructures with varying LSMO layer thicknesses, in which the magnetic anisotropy strongly changes with the LSMO thickness due to the delicate balance between strains originating from both the Nb:STO and LAO layers, using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and photoemission spectroscopy. We successfully detect the clear change of the magnetic behavior of the Mn ions concomitant with the thickness-dependent metal-insulator transition. Our results suggest that the double-exchange interaction induces ferromagnetism in the metallic LSMO film under tensile strain caused by the STO substrate, while the superexchange interaction determines the magnetic behavior in the insulating LSMO film under compressive strain originating from the top LAO layer. The change in strain, depending on LSMO layer thickness, is confirmed by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Based on those findings, the formation of a magnetic dead layer near the LAO/LSMO interface is attributed to competition between the superexchange interaction via Mn
(Nb:STO) heterostructures with varying LSMO layer thicknesses, in which the magnetic anisotropy strongly changes with the LSMO thickness due to the delicate balance between strains originating from both the Nb:STO and LAO layers, using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and photoemission spectroscopy. We successfully detect the clear change of the magnetic behavior of the Mn ions concomitant with the thickness-dependent metal-insulator transition. Our results suggest that the double-exchange interaction induces ferromagnetism in the metallic LSMO film under tensile strain caused by the STO substrate, while the superexchange interaction determines the magnetic behavior in the insulating LSMO film under compressive strain originating from the top LAO layer. The change in strain, depending on LSMO layer thickness, is confirmed by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Based on those findings, the formation of a magnetic dead layer near the LAO/LSMO interface is attributed to competition between the superexchange interaction via Mn 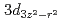 orbitals under compressive strain and the double-exchange interaction via the
orbitals under compressive strain and the double-exchange interaction via the 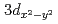 orbitals. These findings provide key aspects of ferromagnetic oxide heterostructures for the development of spintronic device applications.
orbitals. These findings provide key aspects of ferromagnetic oxide heterostructures for the development of spintronic device applications.
 ; A Nearly insulating half-filled
; A Nearly insulating half-filled 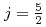 5
5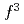 heavy-fermion metal
heavy-fermion metalShick, A. B.*; 藤森 伸一; Pickett, W. E.*
Physical Review B, 103(12), p.125136_1 - 125136_12, 2021/03
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:82.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Correlated band theory implemented as a combination of density functional theory with exact diagonalization [DFT+ (ED)] of the Anderson impurity term with Coulomb repulsion U in the open 14-orbital 5f shell is applied to UTe
(ED)] of the Anderson impurity term with Coulomb repulsion U in the open 14-orbital 5f shell is applied to UTe . The small gap for
. The small gap for  =0, evidence of the half-filled
=0, evidence of the half-filled 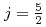 subshell of 5
subshell of 5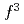 uranium, is converted for
uranium, is converted for  = 3 eV to a flat band semimetal with small heavy-carrier Fermi surfaces that will make properties sensitive to pressure, magnetic field, and off stoichiometry, as observed experimentally. Two means of identification from the Green's function give a mass enhancement of the order of 12 for already heavy (flat) bands, consistent with the common heavy-fermion characterization of UTe
= 3 eV to a flat band semimetal with small heavy-carrier Fermi surfaces that will make properties sensitive to pressure, magnetic field, and off stoichiometry, as observed experimentally. Two means of identification from the Green's function give a mass enhancement of the order of 12 for already heavy (flat) bands, consistent with the common heavy-fermion characterization of UTe . The predicted Kondo temperature around 100 K matches the experimental values from resistivity. The electric field gradients for the two Te sites are calculated by DFT+
. The predicted Kondo temperature around 100 K matches the experimental values from resistivity. The electric field gradients for the two Te sites are calculated by DFT+ (ED) to differ by a factor of seven, indicating a strong site distinction, while the anisotropy factor
(ED) to differ by a factor of seven, indicating a strong site distinction, while the anisotropy factor  = 0.18 is similar for all three sites. The calculated uranium moment
= 0.18 is similar for all three sites. The calculated uranium moment 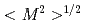 of 3.5
of 3.5 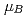 is roughly consistent with the published experimental Curie-Weiss values of 2.8
is roughly consistent with the published experimental Curie-Weiss values of 2.8 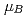 and 3.3
and 3.3 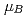 , and the calculated separate spin and orbital moments are remarkably similar to Hund's rule values for an
, and the calculated separate spin and orbital moments are remarkably similar to Hund's rule values for an 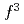 ion. The
ion. The  =3 eV spectral density is compared with angle-integrated and angle-resolved photoemission spectra, with agreement that there is strong 5f character at, and for several hundred meV below, the Fermi energy. Our results support the picture that the underlying ground state of UTe
=3 eV spectral density is compared with angle-integrated and angle-resolved photoemission spectra, with agreement that there is strong 5f character at, and for several hundred meV below, the Fermi energy. Our results support the picture that the underlying ground state of UTe is that of a half-filled
is that of a half-filled 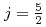 subshell with two half-filled
subshell with two half-filled 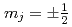 orbitals forming a narrow gap by hybridization, then driven to a conducting state by configuration mixing (spin-charge fluctuations). UTe
orbitals forming a narrow gap by hybridization, then driven to a conducting state by configuration mixing (spin-charge fluctuations). UTe displays similarities to UPt
displays similarities to UPt with its 5f dominated Fermi surfaces rather than a strongly localized Kondo lattice system.
with its 5f dominated Fermi surfaces rather than a strongly localized Kondo lattice system.
Kataoka, Noriyuki*; Tanaka, Masashi*; Hosoda, Wataru*; Taniguchi, Takumi*; 藤森 伸一; Wakita, Takanori*; Muraoka, Yuji*; Yokoya, Takashi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 33(3), p.035501_1 - 035501_6, 2021/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:22.53(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have performed soft X-ray spectroscopy in order to study thephotoirradiation time dependence of the valence band structure and chemicalstates of layered transition metal nitride chloride TiNCl. Under the soft X-ray irradiation, the intensities of the states near the Fermi level (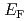 )and the Ti
)and the Ti component increased, while the Cl 2
component increased, while the Cl 2 intensity decreased. Ti2
intensity decreased. Ti2 -3
-3 resonance photoemission spectroscopy confirmed a distinctive Fermiedge with Ti 3
resonance photoemission spectroscopy confirmed a distinctive Fermiedge with Ti 3 character. These results indicate the photo-inducedmetallization originates from deintercalation due to Cl desorption, and thusprovide a new carrier doping method that controls the conducting propertiesof TiNCl.
character. These results indicate the photo-inducedmetallization originates from deintercalation due to Cl desorption, and thusprovide a new carrier doping method that controls the conducting propertiesof TiNCl.

藤森 伸一; 川崎 郁斗; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; 仲村 愛*; 本間 佳哉*; 青木 大*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(1), p.015002_1 - 015002_2, 2021/01
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:82.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
 impurity band state as the origin of high Curie temperature in the
impurity band state as the origin of high Curie temperature in the  -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb武田 崇仁*; 坂本 祥哉*; 荒木 恒星*; 藤澤 唯太*; Anh, L. D.*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 藤森 淳*; 田中 雅明*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(24), p.245203_1 - 245203_8, 2020/12
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:35.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)(Ga ,Fe
,Fe )Sb is one of the promising ferromagnetic semiconductors for spintronic device applications because its Curie temperature (Tc) is above 300 K when the Fe concentration
)Sb is one of the promising ferromagnetic semiconductors for spintronic device applications because its Curie temperature (Tc) is above 300 K when the Fe concentration  is equal to or higher than 0.20. However, the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb remains to be elucidated. To address this issue, we use resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES) and first-principles calculations to investigate the x dependence of the Fe 3
is equal to or higher than 0.20. However, the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb remains to be elucidated. To address this issue, we use resonant photoemission spectroscopy (RPES) and first-principles calculations to investigate the x dependence of the Fe 3 states in (Ga
states in (Ga ,Fe
,Fe )Sb (
)Sb ( = 0.05, 0.15, and 0.25) thin films. The observed Fe 2
= 0.05, 0.15, and 0.25) thin films. The observed Fe 2 -3
-3 RPES spectra reveal that the Fe-3
RPES spectra reveal that the Fe-3 impurity band (IB) crossing the Fermi level becomes broader with increasing
impurity band (IB) crossing the Fermi level becomes broader with increasing  , which is qualitatively consistent with the picture of double-exchange interaction. Comparison between the obtained Fe-3
, which is qualitatively consistent with the picture of double-exchange interaction. Comparison between the obtained Fe-3 partial density of states and the first-principles calculations suggests that the Fe-3
partial density of states and the first-principles calculations suggests that the Fe-3 IB originates from the minority-spin (
IB originates from the minority-spin (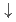 )
) 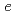 states. The results indicate that enhancement of the double-exchange interaction between
states. The results indicate that enhancement of the double-exchange interaction between 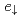 electrons with increasing
electrons with increasing  is the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb.
is the origin of the high Tc in (Ga,Fe)Sb.
 -based materials; A View on valence-fluctuating EuIr
-based materials; A View on valence-fluctuating EuIr Si
Si
Usachov, D. Yu*; Tarasov, A. V.*; Schulz, S.*; Bokai, K. A.*; Tupitsyn, I. I.*; Poelchen, G.*; Seiro, S.*; Caroca-Canales, N.*; Kliemt, K.*; Mende, M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(20), p.205102_1 - 205102_11, 2020/11
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:50.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using photoelectron diffraction (PED) and magnetic dichroism measurements, we explore the electronic and magnetic properties of the near-surface region of the valence-fluctuating material EuIr Si
Si . We present and discuss the methodology for modeling of the 4
. We present and discuss the methodology for modeling of the 4 photoemission spectra, PED patterns and magnetic dichroism for rare-earth-based materials. For the Eu-terminated surface we found that the topmost Eu layer is divalent and exhibits a ferromagnetic order below 10 K. The valency of the next Eu layer, that is the 5th atomic layer, is about 2.8 at low temperature that is close to the valency in the bulk. The properties of the Si-terminated surface are drastically different. The first subsurface Eu layer (4th atomic layer below the surface) behaves divalently and orders ferromagnetically at much higher temperature. Experimental data indicate, however, that there is an admixture of trivalent Eu in this layer, resulting in its valency of about 2.1. The next deeper lying Eu layer (8th atomic layer below the surface) behaves mixed-valently, but the estimated valency of 2.4 is notably lower than the value in the bulk. The obtained results create a background for further studies of exotic surface properties of 4
photoemission spectra, PED patterns and magnetic dichroism for rare-earth-based materials. For the Eu-terminated surface we found that the topmost Eu layer is divalent and exhibits a ferromagnetic order below 10 K. The valency of the next Eu layer, that is the 5th atomic layer, is about 2.8 at low temperature that is close to the valency in the bulk. The properties of the Si-terminated surface are drastically different. The first subsurface Eu layer (4th atomic layer below the surface) behaves divalently and orders ferromagnetically at much higher temperature. Experimental data indicate, however, that there is an admixture of trivalent Eu in this layer, resulting in its valency of about 2.1. The next deeper lying Eu layer (8th atomic layer below the surface) behaves mixed-valently, but the estimated valency of 2.4 is notably lower than the value in the bulk. The obtained results create a background for further studies of exotic surface properties of 4 -based materials, and allow to derive information related to valency and magnetism of individual rare-earth layers in a rather extended area near the surface.
-based materials, and allow to derive information related to valency and magnetism of individual rare-earth layers in a rather extended area near the surface.
明午 伸一郎; 大井 元貴; 藤森 寛*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(6), p.062802_1 - 062802_24, 2020/06
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:37.19(Physics, Nuclear)加速器駆動の核変換システム(ADS)や核破砕中性子源に用いられる陽子加速器のビーム出力増強につれ、ビーム窓や標的の損傷は深刻な問題となり、損傷緩和のためにビーム電流密度の均一化が重要となる。密度均一化のため比較的よく用いられるラスター磁石には、故障時のビーム集束の重大な問題がある。一方、非線形光学を用いたビーム平坦化にはビーム拡大の問題があることが指摘され、これまで非線形効果導入の八極磁石におけるビームの角度の広がりを無視したフィラメント近似模型による検討が行われた。フィラメント近似模型では、非線形収斂作用を適切に評価できないため、本研究では一般化した非線形モデルの適用により非線形ビーム光学における収斂および発散作用を詳細に検討した。正規化した八極強度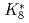 と位相進行
と位相進行 における
における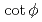 の2つのパラメータ導入により、非線形効果を特定な条件によらず一般化できることを明確にした。ビームのピーク密度低減と損失最小化という拮抗する問題の解決には、
の2つのパラメータ導入により、非線形効果を特定な条件によらず一般化できることを明確にした。ビームのピーク密度低減と損失最小化という拮抗する問題の解決には、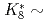 1および
1および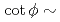 3とすることにより解決できることが判明した。J-PARCの陽子ビーム輸送系(3NBT)に本検討結果を適用し、核破砕中性子源の水銀標的入口のビーム形状の比較検討した結果、モデル計算によるビーム分布は実験データとよい一致を示し、線形光学においてピーク電流密度を約50%にできることを示した。
3とすることにより解決できることが判明した。J-PARCの陽子ビーム輸送系(3NBT)に本検討結果を適用し、核破砕中性子源の水銀標的入口のビーム形状の比較検討した結果、モデル計算によるビーム分布は実験データとよい一致を示し、線形光学においてピーク電流密度を約50%にできることを示した。
 studied by soft X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy
studied by soft X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy川崎 郁斗; 小畠 雅明; 藤森 伸一; 竹田 幸治; 山上 浩志; 仲村 愛*; 伊覇 航*; 辺土 正人*; 仲間 隆男*; 大貫 惇睦*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(4), p.044704_1 - 044704_6, 2020/04
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)EuPd is a rare Eu-based compound, whose Eu ions are in a trivalent state. The electronic structure of EuPd
is a rare Eu-based compound, whose Eu ions are in a trivalent state. The electronic structure of EuPd was investigated by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) using soft X rays. Eu
was investigated by angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) using soft X rays. Eu components arising from the 4f
components arising from the 4f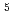 final state multiplet were clearly observed in the valence spectra, and no Eu
final state multiplet were clearly observed in the valence spectra, and no Eu components were observed within an experimental accuracy, confirming a robust Eu
components were observed within an experimental accuracy, confirming a robust Eu state. The band structure and Fermi surfaces revealed by ARPES measurements were compared to the band structure calculations based on the density-functional theory for LaPd
state. The band structure and Fermi surfaces revealed by ARPES measurements were compared to the band structure calculations based on the density-functional theory for LaPd andYPd
andYPd . We found that the calculation for LaPd
. We found that the calculation for LaPd provides a better description for our ARPES results. The effective electron masses estimated from the ARPES spectra near the Fermi level are in good agreement with the corresponding cyclotron effective masses in previous de Haas-van Alphen experiments.
provides a better description for our ARPES results. The effective electron masses estimated from the ARPES spectra near the Fermi level are in good agreement with the corresponding cyclotron effective masses in previous de Haas-van Alphen experiments.