Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mori, Tetsuya; Hazama, Taira; Katagiri, Hiroki*; Ohgama, Kazuya
Nuclear Technology, 211(1), p.143 - 160, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reliability and usefulness of the reaction rate distribution data measured in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju were examined through a comparison with a calculation using JENDL-4.0, mainly focusing on shielding regions around the reactor core. The  U(n,f) and
U(n,f) and  Ni(n,p) reaction rates sensitive to high-energy neutrons were all judged reliable. The calculation-to-experiment values are slightly worse in the shielding regions, where those for the
Ni(n,p) reaction rates sensitive to high-energy neutrons were all judged reliable. The calculation-to-experiment values are slightly worse in the shielding regions, where those for the  Ni(n,p) reaction rates were improved by employing JEFF-3.3 instead of JENDL-4.0. A different tendency was observed between the two reactions, probably due to the
Ni(n,p) reaction rates were improved by employing JEFF-3.3 instead of JENDL-4.0. A different tendency was observed between the two reactions, probably due to the  U(n,f) cross section in the energy range of around 700 eV. The reaction rates of
U(n,f) cross section in the energy range of around 700 eV. The reaction rates of  U(n,f),
U(n,f),  Pu(n,f),
Pu(n,f),  U(n,
U(n, ), and
), and  Au(n,
Au(n, ) sensitive to the lower energy neutrons were mostly judged reliable. The data in the lower shielding region are less reliable but acceptable for the shielding calculation.
) sensitive to the lower energy neutrons were mostly judged reliable. The data in the lower shielding region are less reliable but acceptable for the shielding calculation.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hazama, Taira; Taninaka, Hiroshi; Oki, Shigeo
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-007, 41 Pages, 2024/10
The third version of the versatile reactor analysis code system, MARBLE3, has been developed. In the development of the former version of MARBLE, object-oriented scripting language Python (Python2) had been used and then the latest version of Python (Python3) was released. However, due to its backward incompatibility, MARBLE no longer worked with Python3. For this reason, MARBLE3 has been fully modified and maintained to work with Python3. In MARBLE3, newly developed analysis codes and newly proposed calculation methods were incorporated, and the user interface was extended and solvers were reimplemented for maintainability, extensibility, and flexibility. In MARBLE3, the three-dimensional hexagonal/triangular transport code MINISTRI Ver.7 (MINISTRI7) and the three-dimensional hexagonal/triangular diffusion code D-MINISTRI are available as the new analysis codes. These codes can be used in the neutronics analysis system SCHEME and the fast reactor burnup analysis system OPRHEUS, which are the subsystems of MARBLE. In addition, the user interface of CBG, a core analysis system embedded in MARBLE, was extended so that the diffusion and transport calculation solvers for the 2-dimensional RZ system of CBG can be used on SCHEME. On the other hand, MARBLE3 has extended the functionality of the burnup calculation solver so that it can use the numerical methods proposed in the papers on the improvement of the Chebyshev rational function approximation method and the minimax polynomial approximation method. From the viewpoint of maintainability, the point reactor kinetics solver POINTKINETICS, which was introduced in MARBLE2, has been newly reworked as the KINETICS solver in MARBLE3.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Hazama, Taira; Katagiri, Hiroki*; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Mori, Tetsuya
Nuclear Technology, 210(8), p.1336 - 1353, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju, reaction rate distributions of fission reaction rates of  Pu,
Pu,  U and
U and  U, and capture reaction rate of
U, and capture reaction rate of  U were measured by using activation foils during its system startup test. The measurements in the core and radial blanket regions were evaluated in detail, and their reliability and usefulness as the validation data for fast reactor neutronics design methodologies were examined through a comparison with calculations. The reaction rate data measured in Monju were confirmed all reliable and useful as the validation data. The fission reactions of
U were measured by using activation foils during its system startup test. The measurements in the core and radial blanket regions were evaluated in detail, and their reliability and usefulness as the validation data for fast reactor neutronics design methodologies were examined through a comparison with calculations. The reaction rate data measured in Monju were confirmed all reliable and useful as the validation data. The fission reactions of  Pu,
Pu,  U, and
U, and  U can be validated with an accuracy of a few percent in the core and blanket regions. The capture reaction of
U can be validated with an accuracy of a few percent in the core and blanket regions. The capture reaction of  U in the core region also can be validated with a similar accuracy, whereas a precise calculation of the foil cross section is necessary to consider resonance shielding effects of surrounding fuel pins and a foil.
U in the core region also can be validated with a similar accuracy, whereas a precise calculation of the foil cross section is necessary to consider resonance shielding effects of surrounding fuel pins and a foil.
Mori, Tetsuya; Ohgama, Kazuya; Hazama, Taira
Nuclear Technology, 209(7), p.1008 - 1023, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, the sodium radioactivity of  Na and
Na and  Na in the primary system measured in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju was evaluated, and the reliability of measurements and calculations was examined. The calculated-to-experiment (C/E) values and their uncertainties for
Na in the primary system measured in the prototype fast breeder reactor Monju was evaluated, and the reliability of measurements and calculations was examined. The calculated-to-experiment (C/E) values and their uncertainties for  Na and
Na and  Na radioactivities were 0.97-1.07 and 8.1%-11.0% and 1.03-1.16 and 23.3%-24.1%, respectively, using JENDL-4.0 nuclear data library. The
Na radioactivities were 0.97-1.07 and 8.1%-11.0% and 1.03-1.16 and 23.3%-24.1%, respectively, using JENDL-4.0 nuclear data library. The  Na radioactivity calculated with ENDF/B-VIII.0 was larger by 40% than those calculated with JENDL-4.0 and JEFF-3.3 due to the
Na radioactivity calculated with ENDF/B-VIII.0 was larger by 40% than those calculated with JENDL-4.0 and JEFF-3.3 due to the  Na(n,2n) cross-section discrepancy. The importance of the
Na(n,2n) cross-section discrepancy. The importance of the  Na neutron capture effect was also confirmed herein for the accurate evaluation of the
Na neutron capture effect was also confirmed herein for the accurate evaluation of the  Na radioactivity. The experimental data was judged to be useful for validating the calculation method for improving the reliability of the future designs of sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Na radioactivity. The experimental data was judged to be useful for validating the calculation method for improving the reliability of the future designs of sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Katagiri, Hiroki; Hazama, Taira
Nuclear Technology, 208(10), p.1619 - 1633, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Hazama, Taira
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, p.87 - 161, 2022/07
Ohgama, Kazuya; Katagiri, Hiroki; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Hazama, Taira
Nuclear Technology, 207(12), p.1810 - 1820, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)Mitsumoto, Rika; Hazama, Taira; Takahashi, Keita; Kondo, Satoru
JAEA-Technology 2019-020, 167 Pages, 2020/03
The prototype fast breeder reactor Monju has produced valuable technological achievements through design, construction, operation and maintenance over half a century since 1968. This report compiles the reactor technologies developed for Monju, including the areas: history and major achievements, design and construction, commissioning, safety, reactor physics, fuel, systems and components, sodium technology, materials and structures, operation and maintenance, and accidents and failures.
Sotsu, Masutake; Hazama, Taira
Journal of Energy and Power Engineering, 13(11), p.393 - 403, 2019/11
This paper describes methods and results of the uncertainty evaluation of the significant plant response analysis of the reactor trip failure event, i.e. anticipated transient without scram of the Japanese prototype fast breeder reactor Monju. Unprotected loss of heat sink has a relatively large contribution to the core damage frequency due to reactor trip failure. The uncertainty of the allowable time to core damage in this event by plant transient response analysis, so far, has been estimated with considering the range of reactivity coefficients. There are some cases where core damage is considered to be avoided. Specifically, it is assumed that the core damage due to the ULOHS event would be avoided if the sodium temperature at the pump inlet stays below 650 C for 1 h; otherwise the possibility of cavitation occurring in the hydrostatic bearing increases. In this study, a method is developed to search for a solution as an inverse problem of multiple input variables that satisfy the temperature condition. This paper, as a first step, describes input conditions and probability to satisfy the temperature are evaluated through analyses treating input parameters, reactivity coefficients and kinetic parameters, as variables within the design range.
C for 1 h; otherwise the possibility of cavitation occurring in the hydrostatic bearing increases. In this study, a method is developed to search for a solution as an inverse problem of multiple input variables that satisfy the temperature condition. This paper, as a first step, describes input conditions and probability to satisfy the temperature are evaluated through analyses treating input parameters, reactivity coefficients and kinetic parameters, as variables within the design range.
Ohgama, Kazuya; Takegoshi, Atsushi; Katagiri, Hiroki*; Hazama, Taira
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
Takano, Kazuya; Maruyama, Shuhei; Hazama, Taira; Usami, Shin
Proceedings of Reactor Physics Paving the Way Towards More Efficient Systems (PHYSOR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), p.1725 - 1735, 2018/04
Irradiation dependence of the core excess reactivity was investigated for the Monju system startup tests at zero-power carried out in 2010. The excess reactivity basically decreases with the  decay of
decay of  Pu in zero-power operation. However, the excess reactivity little changed in the two month period of the startup tests, which suggests a positive reactivity insertion during the period. The investigated irradiation dependence shows that the positive reactivity increases with reactor operation and mostly saturates by the fission-dose attained during the Monju zero-power operation in a month (
Pu in zero-power operation. However, the excess reactivity little changed in the two month period of the startup tests, which suggests a positive reactivity insertion during the period. The investigated irradiation dependence shows that the positive reactivity increases with reactor operation and mostly saturates by the fission-dose attained during the Monju zero-power operation in a month ( 10
10 fissions/cm
fissions/cm ). The saturated positive reactivity is equivalent to approximately 47% of the initially accumulated self-irradiation damage recovery assuming the defects were recovered by the fission-fragment irradiation in the reactor operation.
). The saturated positive reactivity is equivalent to approximately 47% of the initially accumulated self-irradiation damage recovery assuming the defects were recovered by the fission-fragment irradiation in the reactor operation.
Kitano, Akihiro; Takegoshi, Atsushi*; Hazama, Taira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(7), p.992 - 1008, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:63.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)A feedback reactivity measurement technique was developed based on a reactivity model featuring components that depend on the reactivity coefficients, denoted as reactor power (K ) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K
) and reactor vessel inlet temperature (K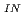 ). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K
). This technique was applied to the feedback reactivity experiment conducted in the Monju system start-up test in May 2010. A thorough evaluation considering all possible biases and uncertainties revealed that the reactivity coefficients can be evaluated with a measurement uncertainty smaller than 3%. The evaluated reactivity coefficients were simulated considering the temperature distribution in the core. The C/E value of K showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K
showed good agreement between calculated and measured values within the established uncertainty, and the value of K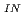 was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2
was consistent with that reported in a previous isothermal temperature coefficient experiment. The measured and calculated fuel subassembly outlet temperatures also agreed well within 0.2 C.
C.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Jin, Tomoyuki; Hirai, Yasushi*; Hazama, Taira
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-009, 120 Pages, 2015/07
The second version of the versatile reactor analysis code system, MARBLE2, has been developed. A lot of new functions have been added inMARBLE2 by using the base technology developed in the first version (MARBLE1). Introducing the remaining functions of the conventional code system (JOINT-FR and SAGEP-FR), MARBLE2 enables one to execute almost all analysis functions of the conventional code system with the unified user interfaces of its subsystem, SCHEME. In particular, the sensitivity analysis functionality is available in MARBLE2. On the other hand, new built-in solvers have been developed, and existing ones have been upgraded. Furthermore, some other analysis codes and libraries developed in JAEA have been consolidated and prepared in SCHEME. In addition, several analysis codes developed in the other institutes have been additionally introduced as plug-in solvers. Consequently,  -ray transport calculation and heating evaluation become available. As for another subsystem, ORPHEUS, various functionality updates and speed-up techniques have been applied based on user experience of MARBLE1 to enhance its usability.
-ray transport calculation and heating evaluation become available. As for another subsystem, ORPHEUS, various functionality updates and speed-up techniques have been applied based on user experience of MARBLE1 to enhance its usability.
Hazama, Taira
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.26 - 31, 2015/02
Various nuclear data have been applied to the reactor physics test analyses in Monju. Good accuracy is confirmed with JENDL-3.3 for the analysis of reactor physics tests performed in 1994-1995. On the other hand, a clear discrepancy is observed for the reactivity loss caused by the  Pu decay from 1994 to 2010. The discrepancy is resolved with JEDNL-4.0, where the revision of the
Pu decay from 1994 to 2010. The discrepancy is resolved with JEDNL-4.0, where the revision of the  Pu fission cross section and
Pu fission cross section and  Am capture cross section contributes. Use of covariance data is promising application in the future design calculation. Based on the reactor physics test analyses, the reliability of the covariance data is investigated and covariance data that needs improvement are extracted. It is suggested that data on the average cosine of the scattering angle of
Am capture cross section contributes. Use of covariance data is promising application in the future design calculation. Based on the reactor physics test analyses, the reliability of the covariance data is investigated and covariance data that needs improvement are extracted. It is suggested that data on the average cosine of the scattering angle of  Na need to be improved.
Na need to be improved.
Kitano, Akihiro; Kishimoto, Yasufumi; Misawa, Tsuyoshi*; Hazama, Taira
KURRI Progress Report 2013, 1 Pages, 2014/10
The approach to criticality is conventionally performed by the inverse multiplication method. The method uses neutron count rate at a steady state attained in a certain waiting time after a reactivity insertion; thus it requires long time (for example, several hours from the startup in Monju reactor). We have developed a more efficient method based on Critical Index (CI) featuring the time behavior of delayed neutrons.
Takeda, Toshikazu*; Hazama, Taira; Fujimura, Koji*; Sawada, Shusaku*
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; The Role of Reactor Physics toward a Sustainable Future (PHYSOR 2014) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2014/09
A national project started in 2013 in Japan entitled "technology development for the environmental burden reduction". The present study is one of the studies adopted as the national project. We are aiming to develop MA transmutation core concepts harmonizing MA transmutation performance with core safety and to improve design accuracy related to MA transmutation performance. To validate and improve design accuracy of the high safety and high MA transmutation performance of SFR cores, we develop methods for calculating the transmutation rate of individual MA nuclides and estimating uncertainty of MA transmutation by using burnup sensitivity. Also we develop reliable reactor physics database to reduce the uncertainty of MA transmutation calculations. The overall consistency of the measured data is investigated by evaluating the usefulness of conventional static data as well as those related to MA transmutation obtained from various facilities like Monju, Joyo, FCA, BFS and PFR.
Takano, Kazuya; Mori, Tetsuya; Kishimoto, Yasufumi; Hazama, Taira
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors; The Role of Reactor Physics toward a Sustainable Future (PHYSOR 2014) (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2014/09
This paper describes details of the IAEA/CRP benchmark calculation by JAEA on the control rod withdrawal test in the Phenix End-of-Life Experiments. The power distribution deviation by the control rod insertion/withdrawal, which is the major target of the benchmark, is well simulated by calculation. In addition to the CRP activities, neutron and photon transport effect is evaluated in the nuclear heating calculation of the benchmark analysis. It is confirmed that the neutron and photon transport effect contributes to the improvement of the absolute power calculation results in the breeder blanket region.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Hazama, Taira; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Jin, Tomoyuki*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 66, p.51 - 60, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)A comprehensive and versatile reactor analysis code system, MARBLE, has been developed. MARBLE is designed as a software development frame-work for reactor analysis, which offers reusable and extendible functions and data models based on physical concepts, rather than a reactor analysis code system. From a viewpoint of the code system, it provides a set of functionalities utilized in a detailed reactor analysis scheme for fast criticality assemblies and power reactors, and nuclear data related uncertainty quantication such as cross-section adjustment. MARBLE covers all phases required in fast reactor core design prediction and improvement procedures, i.e. integral experiment database management, nuclear data processing, fast criticality assembly analysis, uncertainty quantication, and power reactor analysis. In the present paper, these functionalities are summarized and system validation results are described.
Hazama, Taira; Yokoyama, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(5), p.525 - 533, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)A versatile nuclear heating calculation system is developed in MARBLE, a neutronics calculation platform based on the object-oriented language. The system provides a variety of heating calculation methods from the conventional simple methods based on energy-independent Q-values, to a detailed method based on NJOY. A particular feature is in hybrid methods that consider energy dependence employed in NJOY in the system. The hybrid methods provide tools to assess errors in the simple methods and to evaluate the heat transport property by neutrons and photons precisely. The accuracy of the hybrid methods and the errors in the simple methods are investigated in a Monju design calculation. It is confirmed that the hybrid methods realize the nuclear heating by the detailed method within an accuracy of 0.1%. The neglect of incident energy dependence of the fission Q-value in the simple methods causes clear overestimation in the Q-value but its influence on the total heating is less than 1%.