Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kameo, Yutaka; Sato, Soichi; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Nagai, Takayuki; Niibori, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masayuki; et al.
Introduction to Dismantling and Decommissioning Chemistry, 251 Pages, 2024/09
This book focuses on the dismantling and decommissioning of nuclear facilities and reactors that have suffered severe accidents. In Part 1, we introduce basic aspects ranging from fuel chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiation chemistry, corrosion, and decontamination chemistry to waste treatment and disposal. Then, Part 2 covers the chemistry involved in the decommissioning of various nuclear facilities, and discusses what chemical approaches are necessary and possible for the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, how decommissioning should be carried out, and what kind of research and development and also human resource development are required for this.
Kinase, Akari; Goto, Katsunori*; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-004, 60 Pages, 2024/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3 and stored at the waste storage facility L. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc, 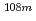 Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2024-006, 48 Pages, 2024/06
In the future, radioactive waste which generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. It is necessary to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of the radioactive wastes. In this work, we studied the evaluation methodology of the radioactivity concentrations in concrete waste generated from JPDR. In order to construct the evaluation methodology of the radioactivity concentration, the validity of the evaluation methods was confirmed by mainly theoretical calculation and using the result of radiochemical analysis. Correcting the theoretical calculations using results of nuclide analysis, it is possible to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of nuclides preliminary selected.
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsuchida, Daiki; Konda, Miki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-002, 81 Pages, 2023/05
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2020.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-004, 87 Pages, 2022/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until by the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed samples generated from JPDR, JRR-3 and JRR-4. In this report, radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) were determined based on radiochemical analysis and summarized as basic data for the study of evaluation method of radioactive concentration.
Cm) were determined based on radiochemical analysis and summarized as basic data for the study of evaluation method of radioactive concentration.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Endo, Tsubasa*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-013, 30 Pages, 2021/12
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JPDR facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 21 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2018-2019.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2018-2019.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Haraga, Tomoko; Tobita, Minoru*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Omori, Takeshi*; Murakami, Hideaki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-022, 34 Pages, 2021/03
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3 and JPDR. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 22 radionuclides( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Ba,
Ba,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Murata, Chinatsu; Kitahara, Masaru; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Amazawa, Hiroya; Takebe, Shinichi; Yamada, Osamu*; Kameo, Yutaka
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (62), p.20 - 31, 2020/09
On the basis of Act on Special Measures, municipalities stripped surface soil off the playground of park to decontaminate the soil which had been contaminated with radionuclides released from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. To minimize the exposure dose of the residents, it was essential to decide safe disposal of the contaminated soil which has been stored at temporary storage areas. Therefore, the ministry of the Environment and Tokai-mura office required Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to perform demonstration project of burying the contaminated soil generated by decontamination of public facilities in order to provide decision on the enforcement ordinance and guidelines of burying it. In this project, we acquired data of air dose rate and the personal exposure dose during transporting, burying, and storing the contaminated soil. In addition, we measured radioactivity concentration of dust collected from surroundings of the landfill and seepage water through contaminated soil.
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-006, 70 Pages, 2020/08
Radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried at the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JPDR and JRR-4. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Tobita, Minoru*; Haraga, Tomoko; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Seki, Kotaro*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Kochiyama, Mami; Shimomura, Yusuke; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-016, 72 Pages, 2020/02
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2, JRR-3 and Hot laboratory facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 25 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Mo,
Mo,  Tc,
Tc, 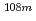 Ag,
Ag,  Sn,
Sn,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-012, 70 Pages, 2020/02
It is necessary to establish practical evaluation methods to determine radioactivity concentration of radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from Post Irradiation Examination Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Sato, Yoshiyuki; Aono, Ryuji; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Testing 2019-003, 20 Pages, 2019/12
In the Radioactive Waste Management Technology Section, the radioactive liquid waste generated in the test using natural uranium in the past has been stored based on the contents of permission. Although we decided to perform solidification treatment in order to reduce the risk in storage, no rational treatment method has been established so far. Therefore, we examined adsorption treatment of natural uranium using uranium adsorbent (Tannix), and finally stabilized treatment by cement solidification. The treatment methods and findings obtained for a series of operations in waste liquid treatment are summarized in this report for reference when treating similar liquid waste.
Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2019-015, 52 Pages, 2019/11
In the future, radioactive waste which generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. It is necessary to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of the radioactive wastes. In this work, we studied the evaluation method of radioactivity concentration based on radiochemical analysis data (H-3, C-14, Cl-36, Co-60, Ni-63, Sr-90, Mo-93, Nb-94, Tc-99, Ag-108m, Sn-126, I-129, Cs-137, Eu-152, Eu-154, U-233+234, U-238, Pu-238, Pu-239+240, Pu-241, Am-241, Am-243, Cm-244) which was generated from research facility Hot Laboratory. As a result of examining the application of the scaling factor method, the correlation with Key-nuclide in some nuclides which are Sr-90, I-129, Eu-154, U-233+234, Pu-238, Pu-239+240, Am-241, Cm-244 confirmed by the correlation coefficient and t-test. In the present radiochemical analysis data, the mean activity concentration method can be applied to all nuclides which could not be applied to the scaling factor method H-3, C-14, Cl-36, Ni-63, Mo-93, Nb-94, Tc-99, Ag-108m, Sn-126, Eu-152, U-238, Pu-241 and Am-243. Ni-63, Tc-99, Eu-152 and U-238 could be applied to the scaling factor method with getting several additional data, this study will be continued to review for the practical evaluation method.
Haraga, Tomoko; Shimomura, Yusuke; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-004, 48 Pages, 2019/10
In the future, radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried for the near surface disposal. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Haraga, Tomoko; Ouchi, Kazuki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Hoshino, Hitoshi*; Tanana, Rei*; Fujihara, Takashi*; Kurokawa, Hideki*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1032, p.188 - 196, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:46.22(Chemistry, Analytical)The development of safe, rapid and highly sensitive analytical methods for radioactive samples, especially actinide (An) ions, represents an important challenge. Here we propose a methodology for selecting appropriate emissive probes for An ions with very low consumption and emission of radioactivity by capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence detection (CE-LIF), using a small chemical library of probes with eight different chelating moieties. It was found that the emissive probe, which possesses the tetradentate chelating moiety, was suitable for detecting uranyl ions. The detection limit for the uranyl-probe complex using CE-LIF combined with dynamic ternary complexation and on-capillary concentration techniques was determined to be 0.7 ppt. This method was successfully applied to real radioactive liquid samples collected from nuclear facilities.
 Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
Sn analytical methods for radioactive waste from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationAono, Ryuji; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shimada, Asako; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Ueno, Takashi; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Technology 2017-025, 32 Pages, 2017/11
We have developed analytical methods for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for
Sn, which are considered important in terms of the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The methods are specialized for the wastes left after Fukushima accident. As the main analytical sample, we assumed accumulated water / treated water collected at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. As for  Zr,
Zr,  Mo,
Mo,  Pd and
Pd and  Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
Sn contained in this accumulated water / treated water, we have worked on the development of separation and purification method of target nuclide and improvement of recovery, and summarized these results in this report.
 Mo content in metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor
Mo content in metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration ReactorShimada, Asako; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Kameo, Yutaka
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 314(2), p.1361 - 1365, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.44(Chemistry, Analytical)A separation method of Mo from Nb, Zr, and the matrix elements of rubble waste was modified to determine the content of  Mo in metal waste. A separation scheme to treat 1 g of metal waste was established by optimizing the amount of ascorbic acid, the rinsing solution, and repeating of the procedure. A thin-layer source was prepared using direct drop deposition and evaporation to measure
Mo in metal waste. A separation scheme to treat 1 g of metal waste was established by optimizing the amount of ascorbic acid, the rinsing solution, and repeating of the procedure. A thin-layer source was prepared using direct drop deposition and evaporation to measure  Mo content. Finally,
Mo content. Finally,  Mo content in the metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor was analyzed using the developed method.
Mo content in the metal waste generated at the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor was analyzed using the developed method.
Takagai, Yoshitaka*; Furukawa, Makoto*; Kameo, Yutaka; Matsueda, Makoto; Suzuki, Katsuhiko*
Bunseki Kagaku, 66(4), p.223 - 231, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.53(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Haraga, Tomoko; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Kameo, Yutaka; Saito, Shingo*
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (55), p.22 - 27, 2017/03
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 311(3), p.1613 - 1618, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.50(Chemistry, Analytical)Separation method of Zr using trans uranium resin (TRU resin) was developed. Approximately 100% of Zr, Nb, Bi, Th, and U and a part of Mo and Hg were extracted on the TRU resin from 3 M HNO  solution and separated from Li, Be, Mg, Al, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ga, As, Se, Rb, Sr,Ag, Cd, In, Cs, Ba. Approximately 100% of Zr, Nb, and U were striped from the TRU resin with 0.01 M HF and 10% of Mo, 7.1% of Hg, 77% of Bi, and 20% of Th were also included in the stripping solution. In order to measure
solution and separated from Li, Be, Mg, Al, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ga, As, Se, Rb, Sr,Ag, Cd, In, Cs, Ba. Approximately 100% of Zr, Nb, and U were striped from the TRU resin with 0.01 M HF and 10% of Mo, 7.1% of Hg, 77% of Bi, and 20% of Th were also included in the stripping solution. In order to measure  Zr with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), Zr has to be separated from Nb and Mo to avoid isobaric interference. Therefore, further purification of Zr using tetra valent actinide resin (TEVA resin) was applied. The developed method was evaluated with the simulated rubble sample solution. Although a part of Zr was eluted during sample loading, most of Zr was extracted on the TRU resin and separated major elements of the rubble sample. Finally, Zr was separated from Nb and Mo with the TEVA resin.
Zr with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), Zr has to be separated from Nb and Mo to avoid isobaric interference. Therefore, further purification of Zr using tetra valent actinide resin (TEVA resin) was applied. The developed method was evaluated with the simulated rubble sample solution. Although a part of Zr was eluted during sample loading, most of Zr was extracted on the TRU resin and separated major elements of the rubble sample. Finally, Zr was separated from Nb and Mo with the TEVA resin.