Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Kikuchi, Haruka; Hirano, Hiroshi*; Kitamura, Akihiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 21(1), p.50 - 63, 2022/03
The air fed suit is a kind of personal protective equipment that provides purified air through a hose and that protects a worker from radiation hazards. In the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of the JAEA, the suit is used for size reduction and dismantlement of radioactively contaminated, in particular with plutonium, gloveboxes and equipment. Although the suit has been widely adopted in the similar activities, there still exist potential hazards due to the limiting features of the suit itself and its supplemental system. In fact, we had faced with several unexpected problems regarding such restricted aspects during the dismantling activities. To address these failure potentials, we have implemented various countermeasures and improvements to enhance the workers safety. We describe the disadvantages of the air fed suit system and positive feedbacks we have implemented.
Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Takata, Takashi; Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 86(883), p.19-00366_1 - 19-00366_8, 2020/03
Sodium fire is one of key issues in sodium-cooled fast reactor plant. JAEA has developed sodium fire analysis codes, such as AQUA-SF and SPHINCS, to evaluate the consequence of sodium fire events. This paper describes the PIRT (Phenomena Identification and Ranking Table) process for sodium fire events. Ranking table for important phenomena and an assessment matrix are completed. As a part of comprehensive validation based on the assessment matrix, experimental analyses using the AQUA-SF and SPHINCS codes for a sodium spray fire experiment Run-E1 show good agreement with the experimental result.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Takata, Takashi; Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 353, p.110240_1 - 110240_10, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has developed sodium fire analysis codes to evaluate the consequences of sodium fire events. This paper describes a PIRT (Phenomena Identification and Ranking Table) process for such events. Because a sodium fire event involves complex phenomena, the FOMs are specified through a factor analysis. Associated phenomena in a sodium fire event are identified through both element- and sequence-based phenomena analyses. The importance of each phenomenon is evaluated by considering the sequence-based analysis of associated phenomena related to the FOMs. Then, a ranking table is established. An assessment matrix of important phenomena and experiments is completed to confirm the sufficiency of experimental data for the validation of the models in the sodium fire analysis codes. Additional assessments are discussed specifically for the aerosol module and the CFD module in three-dimensional codes from a perspective of careful validation.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Takata, Takashi; Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/06
The present PIRT process is aimed to identify key phenomena involved in sodium fire accidents that involve complex phenomena in sodium-cooled fast reactor plants. In this PIRT process, the figures of merit (FOMs) are specified through factor analysis. Associated phenomena are identified through the element- and sequence-based phenomena analyses. Importance of each associated phenomenon is evaluated by considering the sequence-based analysis of associated phenomena correlated with the FOMs. Then, we complete the ranking table through the factor and phenomenon analyses. An assessment matrix of important phenomena and experiments is completed finally for model validation.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Takata, Takashi; Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 10th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-10) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/11
The present PIRT process was aimed to identify key phenomena involved in sodium fire accidents that involve complex phenomena in sodium-cooled fast reactor plants. In this PIRT process, the figures of merit (FOMs) were specified through factor analysis. Associated phenomena were identified through the element- and sequence-based phenomena analyses. Importance of each associated phenomenon was evaluated by considering the sequence-based analysis of associated phenomena correlated with the FOMs. Then, we complete the ranking table through the factor and phenomenon analyses.
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Aoki, Kazufumi; Okamoto, Akiko; Kawakami, Takeshi; Kume, Nobuhide; Nakanishi, Chika; Koie, Masahiro; Kawamata, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-048, 69 Pages, 2015/02
JAEA was assigned as a designated public institution under the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and under the Armed Attack Situations Response Act. Based on these Acts, the JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the national government and/or local governments in case of disaster responses or response in the event of a military attack, etc. In order to fulfill the tasks, the JAEA has established the Emergency Action Plan and the Civil Protection Action Plan. In case of a nuclear emergency, NEAT dispatches specialists of JAEA, supplies the national government and local governments with emergency equipment and materials, and gives technical advice and information. In normal time, NEAT provides various exercises and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response institutions of the national and local governments, police, fire fighters, self-defense forces, etc. in addition to the JAEA itself. The NEAT also researches nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and cooperates with international organizations. In the FY2013, the NEAT accomplished the following tasks: (1) Technical support activities as a designated public institution in cooperation with the national and local governments, etc. (2) Human resource development, exercise and training of nuclear emergency response personnel for the national and local governments, etc. (3) Researches on nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and sending useful information (4) International contributions to Asian countries on nuclear disaster preparedness and response in collaboration with the international organizations
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Okuno, Hiroshi; Katagiri, Hiromi; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Okamoto, Akiko; Koie, Masahiro; Ikeda, Takeshi; Nemotochi, Toshimasa; Saito, Toru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-046, 65 Pages, 2014/02
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire stations and nuclear operators etc., because the JAEA has been designated as the Designated Public Institution under the Basic Act on Disaster Control Measures and the Act on Response to Armed Attack Situations, etc.. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, dispatches specialists as required, and supplies the National Government and local governments with emergency equipments and materials. NEAT provides various exercise and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal times. The tasks of NEAT, with its past experiences as a designated public institution including the responses to TEPCO's Fukushima Accident, have been shifted to technical supports to the national government for strengthening its abilities to emergency responses; the NEAT therefore focused on maintenance and operation of its functions, and strengthening its response abilities in cooperation with the national government. This annual report summarized these activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2012.
Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Kurihara, Akikazu; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 79(808), p.2635 - 2639, 2013/12
Multi-physics analysis system for a heat transfer tube failure event in a steam generator of sodium-cooled fast reactors has been developed. In this study, applicability of the newly constructed numerical models in the analysis system was investigated. The droplet entrainment / transport model which was incorporated into the SERAPHIM code was verified through the analysis of the related experiment. The experimental data about the pressure variation when the droplet entrainment occurs was reproduced by our model successfully. The TACT code is integrated by the numerical models of fluid-structure thermal coupling, stress evaluation and failure judgment of the structure. The fluid-structure thermal coupling model could predict the temperature distribution formed by the flow around the circular cylinder. About the failure judgment model, the predicted time of failure occurrence showed good agreement with the results of the tube rupture simulation experiment.
Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Kurihara, Akikazu; Hamada, Hirotsugu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-21) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2013/07
Multiphysics analysis system was newly developed to evaluate possibility of failure propagation occurrence under tube failure accident in a steam generator of sodium cooled fast reactors. The system consists of the computer codes, SERAPHIM, TACT, RELAP5, which are based on the mechanistic numerical models. The SERAPHIM codes calculates multicomponent multiphase flow involving sodium-water chemical reaction. In this study, a numerical model for chemical reaction about production of a sodium monoxide and its transport process were constructed. We also developed the numerical models of the TACT code for evaluation of shell-side flow around an adjacent tube, heat transfer from the fluid to the tube and occurrence of tube failure. In our analysis system, thermal hydraulic behavior of water inside the tube is evaluated by the RELAP5 code. The original heat transfer correlations were corrected for the rapidly heated tube in the present work.
Onishi, Yuki*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 8th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-8) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2012/12
In the steam generator of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), self-wastage phenomena is a crack enlargement on the heat transfer tube itself caused by sodium-water reaction, a quantification of the self-wastage phenomenon is of importance from the viewpoint of safety assessment. In this study, we propose a numerical approach to evaluate the self-wastage phenomena and investigate a crack enlargement using SERAPHIM code. In the analysis, two-dimensional initial crack is assumed based on SWAT-4 experiment. The wastage rate was estimated by Arrhenius type equation, and re-meshing arrangement was performed by cut down from a part of tube in the initial model with the wastage amount. After simulated again using the re-meshing models, the resulting SWR products were distributed not only circumferential direction but also radial direction.
Katagiri, Hiromi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Okamoto, Akiko; Ikeda, Takeshi; Tamura, Kenichi; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Chika; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Abe, Minako; Sato, Sohei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-033, 70 Pages, 2012/08
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, etc., by the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. NEAT of JAEA gives technical advice and information, dispatch specialists as required, supplies with the National Government and local governments emergency equipment and materials. NEAT provides various lectures and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention for emergency response organizations at normal time. Concerning the assistance to the Accident of Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on 11 March, 2011, JAEA assisted activities including environmental radiation monitoring, environmental radioactivity analyses, resident public consulting etc., with its the utmost effort. This annual report summarized these activities of NEAT in the fiscal year 2011.
Katagiri, Hiromi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Sawahata, Masayoshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Chika; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-037, 66 Pages, 2011/12
When a Nuclear emergency occurs, Nuclear Emergency Assistance & Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA gives technical advice and information, dispatch specialists as required, supplies emergency equipment and materials to the National Government and local governments. NEAT provides various lectures and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. NEAT also researches on nuclear disaster prevention and cooperates with international organizations. Concerning about the assistance to the Accident of Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake at 11 March, 2011, JAEA assisted activities including environmental radiation monitoring, environmental radioactivity analyses, resident public consulting etc., with its full scale effort. NEAT served as the center of these supporting activities of JAEA.
 Al cable-in-conduit conductor
Al cable-in-conduit conductorKoizumi, Norikiyo; Matsui, Kunihiro; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Nakajima, Hideo; Takeuchi, Takao*; Banno, Nobuya*; Kikuchi, Akihiro*
Teion Kogaku, 46(8), p.495 - 499, 2011/08
JAEA and NIMS has been collaborating in development of high performance Rapid-Heating-Quenching-Transformation (RHQT) Nb Al CIC conductor, aiming at the application of this conductor to DEMO plant. The technical issue of the RHQT Nb
Al CIC conductor, aiming at the application of this conductor to DEMO plant. The technical issue of the RHQT Nb Al strand in the application to a fusion magnet is stabilization against perturbation. NIMS developed technique to attach copper stabilizer by using electroplating and a sub-scale CIC conductor is developed using this conductor. JAEA performed stability test of the developed CIC conductor to demonstrate efficiency of this copper stabilization technique. The measured stability margin is sufficiently high compared to the one of similar NbTi CIC conductor previously tested by the authors. Then, it can be concluded that the copper stabilizer works efficiently from view point of stability, resulting in solving the remained technical issues in the RHQT CIC conductor. Therefore, we can say that the RHQT Nb
Al strand in the application to a fusion magnet is stabilization against perturbation. NIMS developed technique to attach copper stabilizer by using electroplating and a sub-scale CIC conductor is developed using this conductor. JAEA performed stability test of the developed CIC conductor to demonstrate efficiency of this copper stabilization technique. The measured stability margin is sufficiently high compared to the one of similar NbTi CIC conductor previously tested by the authors. Then, it can be concluded that the copper stabilizer works efficiently from view point of stability, resulting in solving the remained technical issues in the RHQT CIC conductor. Therefore, we can say that the RHQT Nb Al CIC conductor is the most promising candidate for application to magnet in DEMO plant.
Al CIC conductor is the most promising candidate for application to magnet in DEMO plant.
 Ru
Ru )
) Sb
Sb and Pr
and Pr La
La Os
Os Sb
Sb
Shu, L.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Aoki, Yuji*; Hillier, A. D.*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Ishida, Kenji*; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Koda, Akihiro*; Bernal, O. O.*; MacLaughlin, D. E.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 83(10), p.100504_1 - 100504_4, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:77.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments have been carried out in the Pr(Os Ru
Ru )
) Sb
Sb and Pr
and Pr La
La Os
Os Sb
Sb alloy systems to investigate broken time-reversal symmetry (TRS) in the superconducting state, signaled by the onset of a spontaneous static local magnetic field B
alloy systems to investigate broken time-reversal symmetry (TRS) in the superconducting state, signaled by the onset of a spontaneous static local magnetic field B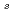 . In both alloy series B
. In both alloy series B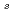 initially decreases linearly with solute concentration. Ru doping is considerably more efficient than La doping, with a 50% faster initial decrease. The data suggest that broken TRS is suppressed for Ru concentration
initially decreases linearly with solute concentration. Ru doping is considerably more efficient than La doping, with a 50% faster initial decrease. The data suggest that broken TRS is suppressed for Ru concentration 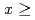 0.6 but persists for essentially all La concentrations. Our data support a crystal-field excitonic cooper pairing mechanism for TRS-breaking superconductivity.
0.6 but persists for essentially all La concentrations. Our data support a crystal-field excitonic cooper pairing mechanism for TRS-breaking superconductivity.
Kanamori, Masashi; Shirakawa, Yusuke; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Okuno, Hiroshi; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Sato, Sohei; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-037, 60 Pages, 2010/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are designated public organizations conforming to the basic law on emergency preparedness and the basic plan for disaster countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance & Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an off-site center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the national government and municipal office. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2009.
Kikuchi, Hirohiko*; Mochida, Haruo*; Ide, Akihiro*; Iitsuka, Toru*; Hayafune, Hiroki
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2010/05
Kanamori, Masashi; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro; Terunuma, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Takeshi; Omura, Akiko; Terakado, Naoya; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Watanabe, Fumitaka; Yamamoto, Kazuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-023, 61 Pages, 2009/09
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) provides technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire station and license holder etc. They are Designated Public Organizations conforming to the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, provides for the dispatch of specialist as required, supplies emergency equipments and materials to the Joint Council of Nuclear Disaster Countermeasures, which meets at the Off-Site Center. NEAT provide various lectures and training course concerning nuclear disaster prevention for those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal time. And NEAT researches on nuclear disaster prevention and also cooperate with international organizations. This annual report summarized the activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2008.
 Al strands subjected to an axial-strain for fusion DEMO reactor
Al strands subjected to an axial-strain for fusion DEMO reactorHemmi, Tsutomu; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Okui, Yoshio*; Matsui, Kunihiro; Nabara, Yoshihiro; Isono, Takaaki; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Banno, Nobuya*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 19(3), p.1540 - 1543, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:61.18(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Nb Al cable-in-conduit (CIC) conductors have been developed as one of candidates for the fusion DEMO reactor. The performances of superconducting strands in the CIC conductor are affected by transverse electromagnetic force and thermal strain at reaction heat treatment. In order to accurately design the conductors for the fusion DEMO reactor, the performance evaluation of the Nb
Al cable-in-conduit (CIC) conductors have been developed as one of candidates for the fusion DEMO reactor. The performances of superconducting strands in the CIC conductor are affected by transverse electromagnetic force and thermal strain at reaction heat treatment. In order to accurately design the conductors for the fusion DEMO reactor, the performance evaluation of the Nb Al strands, which is processed by a rapid heating, quenching and transformation (RHQT) method, was performed under various temperature, magnetic field and axial-strain conditions. The measured and parameterized results of the Nb
Al strands, which is processed by a rapid heating, quenching and transformation (RHQT) method, was performed under various temperature, magnetic field and axial-strain conditions. The measured and parameterized results of the Nb Al strands are presented.
Al strands are presented.