Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
和田 有希*; 森本 健志*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; 菊池 博史*; 中村 佳敬*; 吉川 英一*; 牛尾 知雄*; 土屋 晴文
Science Advances (Internet), 11(21), p.eads6906_1 - eads6906_10, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Lightning discharges can produce transient gamma-ray emissions called terrestrial gamma-ray flashes (TGFs), which originates from electrons accelerated to relativistic energies in strong electric fields. However, it is not yet understood how lightning produces an enormous number of relativistic electrons in dense atmospheres. We present that, thanks to a ground-based observation with optical, radio frequency and high-energy measurements focused on television transmission towers in Kanazawa, Japan, a TGF and a cloud-to-ground discharge of 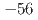 kA occurred when a downward negative leader was colliding with an upward positive leader from the tower. Because the cloud-to-ground current followed the TGF by 30
kA occurred when a downward negative leader was colliding with an upward positive leader from the tower. Because the cloud-to-ground current followed the TGF by 30  s, the TGF started when two leaders approached each other. Our results indicate that an immense number of electrons were produced and accelerated to relativistic energies in a strong and compact electric-field region between the two leaders.
s, the TGF started when two leaders approached each other. Our results indicate that an immense number of electrons were produced and accelerated to relativistic energies in a strong and compact electric-field region between the two leaders.
和田 有希*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中澤 知洋*; 森本 健志*; 中村 佳敬*; 篠田 太郎*; 土屋 晴文
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 128(15), p.e2023JD038606_1 - e2023JD038606_9, 2023/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:28.82(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)A gamma-ray glow, a minute-lasting burst of high-energy photons from a thundercloud, was detected by ground-based apparatus at Kanazawa University, Japan, in a winter thunderstorm on 18 December 2018. The gamma-ray glow was quenched by a lightning flash within a brief time window of 40 ms. The lightning flash produced several low-frequency (LF) E-change pulses that were temporally coincident withthe termination of the gamma-ray glow, and that were located within 0.5 km from the observation site by the Fast Antenna Lightning Mapping Array. The LF pulses had the same polarity as a positive cloud-to-ground current and a normal-polarity in-cloud current. Since this polarity is against the upward electric field for producing the gamma-ray glow (accelerating electrons to the ground), we infer that the glow was terminated by a normal-polarity in-cloud discharge activity between a middle negative layer and an upper positive layer.
鶴見 美和*; 榎戸 輝掲*; 一方井 祐子*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; 篠田 太郎*; 中澤 知洋*; 辻 直樹*; Diniz, G.*; 片岡 淳*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 50(13), p.e2023GL103612_1 - e2023GL103612_9, 2023/07
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:71.62(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Gamma-ray glows are observational evidence of relativistic electron acceleration due to the electric field in thunderclouds. However, it is yet to be understood whether such relativistic electrons contribute to the initiation of lightning discharges. To tackle this question, we started the citizen science "Thundercloud Project," where we map radiation measurements of glows from winter thunderclouds along Japan's sea coast area. We developed and deployed 58 compact gamma-ray monitors at the end of 2021. On 30 December 2021, five monitors simultaneously detected a glow with its radiation distribution horizontally extending for 2 km. The glow terminated coinciding with a lightning flash at 04:08:34 JST, which was recorded by the two radio-band lightning mapping systems, FALMA and DALMA. The initial discharges during the preliminary breakdown started above the glow, that is, in vicinity of the electron acceleration site. This result provides one example of possible connections between electron acceleration and lightning initiation.
久富 章平*; 中澤 知洋*; 和田 有希*; 辻 結菜*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 篠田 太郎*; 森本 健志*; 中村 佳敬*; 湯浅 孝行*; 土屋 晴文
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 126(18), p.e2021JD034543_1 - e2021JD034543_12, 2021/09
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:77.30(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)Around 17:00 on January 12, 2020 (UTC), radiation detectors installed at two locations with a 1.35 km separation in Kanazawa City, Japan, captured a total of four gamma-ray enhancements. The first pair was simultaneously observed at the two locations at 17:03 and were abruptly terminated by a lightning discharge. The remaining two enhancements were also nearly simultaneously observed  3 min later, and one of them was also terminated by another lightning discharge. At the last termination, a downward terrestrial gamma-ray flash and a negative energetic in-cloud pulse were observed. Both pairs were associated with thundercloud cells. In the first pair, simultaneous detection in two locations 1.35 km apart suggests either a gamma-ray glow emerged in-between and time variability of its intensity were directly observed or there were two (or more) gamma-ray glows in the cell which reached the two detectors coincidentally. In the latter pair, the peak time in the downwind detector was
3 min later, and one of them was also terminated by another lightning discharge. At the last termination, a downward terrestrial gamma-ray flash and a negative energetic in-cloud pulse were observed. Both pairs were associated with thundercloud cells. In the first pair, simultaneous detection in two locations 1.35 km apart suggests either a gamma-ray glow emerged in-between and time variability of its intensity were directly observed or there were two (or more) gamma-ray glows in the cell which reached the two detectors coincidentally. In the latter pair, the peak time in the downwind detector was  40 s later than that of the upwind detector. If the irradiation region moved with the cell, it would have taken
40 s later than that of the upwind detector. If the irradiation region moved with the cell, it would have taken  110 s. The discrepancy suggests either the glow moved 2.5 times faster than the cell or there were two (or more) glows in the cell. Also, the fact that the thunderstorm cell hosting the latter glows experienced the lightning discharge
110 s. The discrepancy suggests either the glow moved 2.5 times faster than the cell or there were two (or more) glows in the cell. Also, the fact that the thunderstorm cell hosting the latter glows experienced the lightning discharge  3 min before suggests that the strong electric field in the cell can develop within a few minutes.
3 min before suggests that the strong electric field in the cell can develop within a few minutes.
和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中村 佳敬*; 森本 健志*; 佐藤 光輝*; 牛尾 知雄*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; 米徳 大輔*; 澤野 達也*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 125(4), p.e2019JD031730_1 - e2019JD031730_11, 2020/02
被引用回数:30 パーセンタイル:79.18(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)During 2017-2018 winter operation of the Gamma-Ray Observation of Winter Thunderclouds experiment in Japan, two downward terrestrial gamma-ray flashes (TGFs) that triggered atmospheric photonuclear reactions were detected. They took place during winter thunderstorms on 5 December 2017 and 9 January 2018 at Kanazawa, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. Each event coincided with an intracloud/intercloud discharge, which had a negative-polarity peak current higher than 150 kA. Their radio waveforms in the low-frequency band are categorized as a distinct lightning type called energetic in-cloud pulse (EIP). Negative-polarity EIPs have been previously suggested to be highly associated with downward TGFs, and the present observations provide evidence of the correlation between them for the first time. Furthermore, both of the downward TGFs followed gamma-ray glows, minute-lasting high-energy emissions from thunderclouds. It is suggested that the negative EIPs took place with downward propagating negative leaders or upward positive ones developed in highly electrified regions responsible for the gamma-ray glows.
和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中澤 知洋*; 古田 禄大; 湯浅 孝行*; 中村 佳敬*; 森本 健志*; 松元 崇弘*; 牧島 一夫*; 土屋 晴文
Physical Review Letters, 123(6), p.061103_1 - 061103_6, 2019/08
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:88.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)During a winter thunderstorm on 2017 November 24, a strong burst of gamma-rays with energies up to  10 MeV was detected coincident with a lightning discharge, by scintillation detectors installed at Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant at sea level in Japan. The burst had a sub-second duration, which is suggestive of photoneutron productions. The leading part of the burst was resolved into four intense gamma-ray bunches, each coincident with a low-frequency radio pulse. These bunches were separated by 0.7
10 MeV was detected coincident with a lightning discharge, by scintillation detectors installed at Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant at sea level in Japan. The burst had a sub-second duration, which is suggestive of photoneutron productions. The leading part of the burst was resolved into four intense gamma-ray bunches, each coincident with a low-frequency radio pulse. These bunches were separated by 0.7 1.5 ms, with a duration of
1.5 ms, with a duration of  1 ms each. Thus, the present burst may be considered as a "downward" terrestrial gamma-ray flash (TGF), which is analogous to up-going TGFs observed from space. Although the scintillation detectors were heavily saturated by these bunches, the total dose associated with them was successfully measured by ionization chambers, employed by nine monitoring posts surrounding the power plant. From this information and Monte Carlo simulations, the present downward TGF is suggested to have taken place at an altitude of 2500
1 ms each. Thus, the present burst may be considered as a "downward" terrestrial gamma-ray flash (TGF), which is analogous to up-going TGFs observed from space. Although the scintillation detectors were heavily saturated by these bunches, the total dose associated with them was successfully measured by ionization chambers, employed by nine monitoring posts surrounding the power plant. From this information and Monte Carlo simulations, the present downward TGF is suggested to have taken place at an altitude of 2500 500 m, involving
500 m, involving 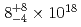 avalanche electrons with energies above 1 MeV which is comparable to those in up-going TGFs.
avalanche electrons with energies above 1 MeV which is comparable to those in up-going TGFs.
和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中村 佳敬*; 古田 禄大; 湯浅 孝行*; 中澤 知洋*; 森本 健志*; 佐藤 光輝*; 松元 崇弘*; 米徳 大輔*; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.67_1 - 67_9, 2019/06
被引用回数:62 パーセンタイル:92.52(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two types of high-energy events have been detected from thunderstorms. One is "terrestrial gamma-ray flashes" (TGFs), sub-millisecond emissions coinciding with lightning discharges. The other is minute-lasting "gamma-ray glows". Although both phenomena are thought to originate from relativistic runaway electron avalanches in strong electric fields, the connection between them is not well understood. Here we report unequivocal simultaneous detection of a gamma-ray glow termination and a downward TGF, observed from the ground. During a winter thunderstorm in Japan on 9 January 2018, our detectors caught a gamma-ray glow, which moved for 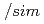 100 s with ambient wind, and then abruptly ceased with a lightning discharge. Simultaneously, the detectors observed photonuclear reactions triggered by a downward TGF, whose radio pulse was located within
100 s with ambient wind, and then abruptly ceased with a lightning discharge. Simultaneously, the detectors observed photonuclear reactions triggered by a downward TGF, whose radio pulse was located within  1 km from where the glow ceased. It is suggested that the highly-electrified region producing the glow was related to the initiation of the downward TGF.
1 km from where the glow ceased. It is suggested that the highly-electrified region producing the glow was related to the initiation of the downward TGF.
和田 有希*; Bowers, G. S.*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 鴨川 仁*; 中村 佳敬*; 森本 健志*; Smith, D.*; 古田 禄大*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 45(11), p.5700 - 5707, 2018/06
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:75.69(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)An on-ground observation program for high energy atmospheric phenomena in winter thunderstorms along Japan Sea has been performed via lightning measurements of  -ray radiation, atmospheric electric field and low-frequency radio band. On February 11, 2017, the radiation detectors recorded
-ray radiation, atmospheric electric field and low-frequency radio band. On February 11, 2017, the radiation detectors recorded  -ray emission lasting for 75 sec. The
-ray emission lasting for 75 sec. The  -ray spectrum extended up to 20 MeV and was reproduced by a cutoff power-law model with a photon index of 1.36
-ray spectrum extended up to 20 MeV and was reproduced by a cutoff power-law model with a photon index of 1.36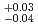 , being consistent with a Bremsstrahlung radiation from a thundercloud (as known as a
, being consistent with a Bremsstrahlung radiation from a thundercloud (as known as a  -ray glow). Then the
-ray glow). Then the  -ray glow was abruptly terminated with a nearby lightning discharge. The low-frequency radio monitors, installed
-ray glow was abruptly terminated with a nearby lightning discharge. The low-frequency radio monitors, installed  50 km away from Noto School, recorded intra/inter-cloud discharges spreading over
50 km away from Noto School, recorded intra/inter-cloud discharges spreading over  60km area with a
60km area with a  300 ms duration. The timing of the
300 ms duration. The timing of the  -ray termination coincided with the moment when a sequence of intra/inter-cloud discharges passed 0.7 km horizontally away from the radiation monitors. The atmospheric electric-field measurement presented that negative charge was located in the cloud base and not neutralized by the lightning discharge. This indicates that the
-ray termination coincided with the moment when a sequence of intra/inter-cloud discharges passed 0.7 km horizontally away from the radiation monitors. The atmospheric electric-field measurement presented that negative charge was located in the cloud base and not neutralized by the lightning discharge. This indicates that the  -ray source was located at an higher region than the cloud base.
-ray source was located at an higher region than the cloud base.
 single-crystal substrates irradiated with electrons
single-crystal substrates irradiated with electrons宮崎 尚*; 守本 純*; 戸田 耕司*; 小野田 忍; 大島 武
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(7), p.07HB07_1 - 07HB07_4, 2011/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:4.51(Physics, Applied)Electron irradiation effects on lithium niobate (LiNbO ) single crystals have been investigated by photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and Raman scattering spectroscopy. As a result of PAS and FT-IR, it was found that the oxygen vacancies are generated in LiNbO
) single crystals have been investigated by photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and Raman scattering spectroscopy. As a result of PAS and FT-IR, it was found that the oxygen vacancies are generated in LiNbO by electron irradiation. The Raman signal intensity observed from as-sliced surface decreases with increasing electron fluence, although the signal intensity observed from mirror-polished surface is not changed. The differences in these results are related to surface composition. Therefore the control of the composition is the most important to avoid the effects of electron irradiation to LiNbO
by electron irradiation. The Raman signal intensity observed from as-sliced surface decreases with increasing electron fluence, although the signal intensity observed from mirror-polished surface is not changed. The differences in these results are related to surface composition. Therefore the control of the composition is the most important to avoid the effects of electron irradiation to LiNbO .
.
阿部 浩之; 青根 茂雄*; 森本 亮*; 内田 裕久*; 大島 武
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 36(1), p.133 - 135, 2011/03
これまでに、パラジウム(水素吸蔵材料)について、重イオン照射により欠陥導入させることで表面構造が乱れ、それにより表面改質効果が生じ、水素吸蔵能向上が見込まれることを見いだしている。本研究ではその表面状態についてさらに詳細な知見を得るため、表面仕事関数測定により電子状態を調べ、初期水素吸蔵反応速度との相関関係を調べた。照射イオンはNイオン,Crイオン,Agイオン,Xeイオン照射を実施し、ドーズ量は10
 10
10 cm
cm とした。水素吸蔵反応速度測定により、イオン照射したPdは未照射Pdに比べ反応速度が3
とした。水素吸蔵反応速度測定により、イオン照射したPdは未照射Pdに比べ反応速度が3 10倍速くなることを確認し、仕事関数測定ではイオン照射のドーズ量の増加に伴い、仕事関数値が負側へシフトすることが判明した。これより、イオン照射により表面構造が乱され、表面電子状態が不安定になった結果、水素原子が取り込まれやすい状態となり、初期水素吸蔵反応速度が速くなったと結論できる。
10倍速くなることを確認し、仕事関数測定ではイオン照射のドーズ量の増加に伴い、仕事関数値が負側へシフトすることが判明した。これより、イオン照射により表面構造が乱され、表面電子状態が不安定になった結果、水素原子が取り込まれやすい状態となり、初期水素吸蔵反応速度が速くなったと結論できる。

宮崎 尚*; 守本 純*; 戸田 耕司*; 小野田 忍; 大島 武
Proceedings of 9th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-9), p.226 - 229, 2010/10
LiNO has several advantages for opto-electronic and acousto-optic applications including waveguides, modulators, second harmonic generators and surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices. In this study, we characterized the defects in electron irradiated LiNbO
has several advantages for opto-electronic and acousto-optic applications including waveguides, modulators, second harmonic generators and surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices. In this study, we characterized the defects in electron irradiated LiNbO single crystal substrates using Raman. The Raman peak of symmetrical O-Nb-O bending mode drastically decreased with increasing electron irradiation. It is thought that the electron irradiation gives the biggest influence on the Nb-O bond.
single crystal substrates using Raman. The Raman peak of symmetrical O-Nb-O bending mode drastically decreased with increasing electron irradiation. It is thought that the electron irradiation gives the biggest influence on the Nb-O bond.
米田 安宏; 田村 和久; 阿部 浩之; 大島 武; 森本 亮*; 内田 裕久*; 水木 純一郎
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(4), p.1053 - 1056, 2008/12
水素吸蔵合金であるパラジウムの特性を改変するためにN イオン照射を行い、エッチングなどによる表面改変に比べ大幅に改善されることがわかった。このしくみを理解するために表面構造を電子顕微鏡で、またミクロスコピックな構造を放射光X線を用いて調べた。N
イオン照射を行い、エッチングなどによる表面改変に比べ大幅に改善されることがわかった。このしくみを理解するために表面構造を電子顕微鏡で、またミクロスコピックな構造を放射光X線を用いて調べた。N イオンはパラジウム金属中に留まることはないため、イオン照射時に生じる格子欠陥が水素吸蔵過程に変化をもたらしていると考えられる。SEM観察からは金属パラジウムの表面自体は照射前から圧延時の痕跡が見られ、照射による表面積の拡大が水素吸蔵に影響を与えているとは考えられない。したがって、X線によって明らかとなった格子欠陥によるミクロ構造の変化が本質的に水素吸蔵量と関係していると考えられる。
イオンはパラジウム金属中に留まることはないため、イオン照射時に生じる格子欠陥が水素吸蔵過程に変化をもたらしていると考えられる。SEM観察からは金属パラジウムの表面自体は照射前から圧延時の痕跡が見られ、照射による表面積の拡大が水素吸蔵に影響を与えているとは考えられない。したがって、X線によって明らかとなった格子欠陥によるミクロ構造の変化が本質的に水素吸蔵量と関係していると考えられる。
南出 賢司*; 萩原 健司*; 名合 牧人*; 小川 弘之*; 宇山 幹紀*; 傳馬 啓輔*; 木須 芳男*; 森本 勤*; 工藤 元; 津坂 仁和
no journal, ,
立坑掘削では、断層破砕帯やブレイクアウト現象の影響による地山の崩落に起因する、「高抜け」と呼ばれる現象を抑制しなければならない。北海道天塩郡幌延町において建設を進めている幌延地下研究施設の立坑において、高抜け誘発する断層破砕帯やブレイクアウトを抑制する対策工の検討を行い、ステップ長の変更、及び増しロックボルトを実施した結果、崩落対策として有効であり、覆工の健全性が確保されることが明らかとなった。
 Es region by Coulomb excitation
Es region by Coulomb excitation  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopy柳原 陸斗; 井手口 栄治*; 西尾 勝久; Orlandi, R.; 牧井 宏之; 浅井 雅人; 廣瀬 健太郎; 塚田 和明; 豊嶋 厚史; 佐藤 哲也; et al.
no journal, ,
What is the limit of high Z nucleus, where is the island of stability, is one of the focus of nuclearphysics. Key ingredient to stabilize nucleus in this super-heavy region is shell structure and Z=114,120, N=184 are predicted to be new magic numbers. However, it is not easy to produce such nucleus and study the shell structure. In order to access such shell structure, we are focusing on the deformed nucleus of the heavy mass region including Es isotopes. By studying the excited states, spin and parity, and deformation, we will be able to access the single-particle orbital which is supposed to generate new shell structure at Z=114, 120, N=184 and try to investigate nuclear shell structure in the super-heavy mass region. Coulomb excitation experiment at the Tokai Tandem Accelerator Laboratory of JAEA is planned to measure B(E2) values of low-lying states in  Es and to deduce the deformation. Unknown high-lying states of
Es and to deduce the deformation. Unknown high-lying states of  Es will be also investigated for further understanding of nuclear structure in this region. We obtained
Es will be also investigated for further understanding of nuclear structure in this region. We obtained  Es via an international collaboration with ORNL. CAGRA will be used to measure the
Es via an international collaboration with ORNL. CAGRA will be used to measure the  rays from
rays from  Es. Experimental plan and preparation progress will be presented.
Es. Experimental plan and preparation progress will be presented.
阿部 浩之; 森本 亮*; 青根 茂雄*; 内田 裕久*; 大島 武
no journal, ,
Pdは水素吸収(吸蔵)する単体金属である。また実用材料としての水素吸蔵合金はニッケル水素電池の負極材やそのほかさまざまな用途に用いられている。これら材料の水素吸蔵性能を大幅向上させることは実用上重要である。そこでわれわれはイオン照射による吸蔵能向上を検討するため、PdへのCrイオン及びXeイオン照射を実施し、水素吸収初期反応速度や水素吸放出前後の仕事関数測定をして評価した。その結果、未照射に比べ、照射量変化による水素吸収初期反応速度の向上,表面仕事関数の負方向へのシフトや水素吸収速度が最大で10倍程度の向上を示した。
若林 啓美*; 宮崎 尚*; 岡本 庸一*; 守本 純*; 小野田 忍; 大島 武
no journal, ,
単結晶6H-SiCに電子線を照射し、生成された欠陥等を光音響分光法(PAS)により評価した。360nmから410nmと480nm以上でブロードなピークが確認された。さらに5 10
10 /cm
/cm の試料には620nmから660nmに大きなピークが確認された。同様の実験をLiNbO
の試料には620nmから660nmに大きなピークが確認された。同様の実験をLiNbO に行っているが、SiCのほうが電子線を照射したことによる変化は小さいことがわかった。PAS測定の結果から、6H-SiCのほうがLiNbO
に行っているが、SiCのほうが電子線を照射したことによる変化は小さいことがわかった。PAS測定の結果から、6H-SiCのほうがLiNbO よりもはるかに放射線に対し耐性があることが示された。
よりもはるかに放射線に対し耐性があることが示された。
萩原 健司*; 名合 牧人*; 南出 賢司*; 小川 弘之*; 宇山 幹紀*; 傳馬 啓輔*; 木須 芳男*; 森本 勤*; 工藤 元; 津坂 仁和
no journal, ,
北海道天塩郡幌延町において建設を進めている地下研究施設の立坑においては、「高抜け」を誘発する可能性のある、断層破砕帯やブレイクアウトに起因する地山の崩落が発生している。これらの崩落を抑制する対策工を検討した結果、通常2m(無支保区間最大3m)の掘削長を1m(無支保区間最大2m)として、1mの掘削と1mの覆工を繰り返す、1覆工長を短縮する案が最も有効であることが明らかとなった。
若林 啓美*; 宮崎 尚*; 岡本 庸一*; 守本 純*; 小野田 忍; 大島 武
no journal, ,
電子線照射した炭化ケイ素(SiC: Silicon Carbide)中の照射欠陥を光音響分光法(PAS:Photoacoustic Spectroscopy)にて測定した。PASは、通常行われるフォトルミネッセンス法による測定と異なり、非発光の欠陥を評価することができる。電子線照射した後、PASにより欠陥を評価したところ、シリコン(Si)空孔もしくはSi関連欠陥と考えられるピークを検出することができた。以上のように、通常の発光を用いた評価方法では検出することのできなかった電子線誘起欠陥をPAS法により検出することができた。
萩原 健司*; 南出 賢司*; 名合 牧人*; 小川 弘之*; 宇山 幹紀*; 木須 芳男*; 森本 勤*; 工藤 元; 津坂 仁和
no journal, ,
北海道天塩郡幌延町において建設を進めている地下研究施設の立坑では、発破掘削を採用している影響により発生したと考えられる地山の割れ目(以下、掘削性割れ目という)が壁面観察時に多く確認されている。これらの掘削性割れ目は、覆工コンクリートの変位を誘発し、圧縮応力の増加が懸念されるため、対策として先受けボルト工を行い、掘削性割れ目を抑制することができた。
南出 賢司*; 萩原 健司*; 名合 牧人*; 小川 弘之*; 宇山 幹紀*; 木須 芳男*; 森本 勤*; 矢吹 義生*; 工藤 元; 稲垣 大介; et al.
no journal, ,
北海道天塩郡幌延町において建設を進めている幌延地下研究施設の立坑において、覆工コンクリートの東西方向にひび割れが発生する事象が確認されている。本発表はその覆工コンクリートのひび割れの発生メカニズムを分析した結果とこれまでに行ったひび割れ抑制対策について報告するものである。