Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Takata, Takashi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.82(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) M
M O
O cathode materials for aqueous photo-rechargeable batteries
cathode materials for aqueous photo-rechargeable batteriesShimokawa, Kohei*; Matsubara, Shogo*; Kawaguchi, Tomoya*; Okamoto, Akihiro*; Ichitsubo, Tetsu
Chemical Communications, 59(51), p.7947 - 7950, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Iwase, Akihiro*; Fukuda, Kengo*; Saito, Yuichi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Amekura, Hiroshi*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(16), p.163902_1 - 163902_10, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Amorphous SiO samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO
samples were implanted with 380 keV Fe ions at room temperature. After implantation, some of the samples were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions. magnetic properties were investigated using a SQUID magnetometer, and the morphology of the Fe-implanted SiO samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic
samples was examined using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (EXAFS and XANES), which showed that the size of Fe nanoparticles was increasing The size of Fe nanoparticles increased with increasing Fe implantation amount; some of the Fe nanoparticles consisted of Fe oxides, and the valence and structure of Fe atoms became closer to that of metallic  -Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
-Fe with increasing Fe injection amount. The magnetization-field curve of the sample implanted with a small amount of Fe was reproduced by Langevin's equation, suggesting that the Fe nanoparticles behave in a superparamagnetic manner. In addition, when a large amount of Fe was implanted, the magnetization-magnetic field curve shows a ferromagnetic state. These magnetic property results are consistent with the X-ray absorption results. Subsequent 16 MeV Au irradiation crushed the Fe nanoparticles, resulting in a decrease in magnetization.
 O
O /TiO
/TiO in a water-in-salt electrolyte for photo-rechargeable batteries
in a water-in-salt electrolyte for photo-rechargeable batteriesShimokawa, Kohei*; Matsubara, Shogo*; Okamoto, Akihiro*; Ichitsubo, Tetsu
Chemical Communications, 58(69), p.9634 - 9637, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:74.08(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)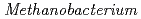 strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe
strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe under a freshwater environment
under a freshwater environmentHirano, Shinichi*; Ihara, Sota*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Dotsuta, Yuma; Otani, Kyohei; Kitagaki, Toru; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Microorganisms (Internet), 10(2), p.270_1 - 270_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:78.86(Microbiology)To understand the role of methanogens in corrosion under anoxic conditions in freshwater, we investigated the corrosion activities of methanogens in samples collected from groundwater and rivers. We enriched microorganisms that can grow with CO /NaHCO
/NaHCO and Fe
and Fe as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that
as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that 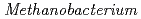 strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe
strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
Wakai, Satoshi*; Hirano, Shinichi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.491 - 496, 2021/12
After Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, various corrosion mitigating activities have been treated, and severe corrosion incident have never taken placed. On the other hand, the facilities were exposed sea water, and some of them have continuously exposed to ground water. The exposure of metal materials to environmental water has a risk of microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC). In this paper, we summarize the latest knowledge of MIC and the task of MIC in the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Li, C.-Y.; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Dai-25-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/07
The capability of stable cooling and avoiding re-criticality on the debris bed are the main issues for achieving IVR (In-Vessel Retention). In the actual situation, the debris bed is composed of mixed-density debris particles. Hence, when these mixed-density debris particles were launched to re-distribute, the debris bed would possibly form a density-stratified distribution. For the proper evaluation of this scenario, the multi-physics model of CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics is established to investigate the coolability and re-criticality on the heterogeneous density-stratified debris bed with considering the particle relocation. The CFD-DEM model has been verified by utilizing water injection experiments on the mixed-density particle bed in the first portion of this research. In the second portion, the coupled system of the CFD-DEM-Monte-Carlo based neutronics model is applied to reactor cases. Afterward, the debris particles' movement, debris particles' and coolant's temperature, and the k-eff eigenvalue are successfully tracked. Ultimately, the relocation and stratification effects on debris bed's coolability and re-criticality had been quantitatively confirmed.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Sekimoto, Shun*
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 257, 2020/08
To understand the influence of glass structural change by neutron irradiation and boron isotope composition, glass samples were made from enrichment boric acid reagents and neutron irradiation of those samples was carried out in Pn-2 of KUR. The structural change of glass sample after the irradiation will be estimated in 2020FY. Before neutron irradiation test of glass samples, the Si-O bridging structure difference by boron isotope composition compared by using a Raman spectrometry.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Sekimoto, Shun*
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 105, 2019/08
To understand this structural change of a borosilicate glass by a neutron irradiation in detail, the irradiation test was carried out in KUR in 2017FY. The glass structure was estimated by using Raman spectrometry in 2018FY. Comparing with the Raman spectra of glass samples before and after irradiation, it could be observed the change of peak height of Si-O bridging structure by the irradiation.
Booth, S. G.*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Chang, S.-Y.*; La Fontaine, C.*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Imai, Takahito*; Schroeder, S. L. M.*; Dryfe, R. A. W.*
Chemical Science, 8(12), p.7954 - 7962, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:72.1(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The two-phase Brust-Schiffrin synthesis of alkane thiol protected metal nanoparticles has been shown to undergo significantly different processes dependent on the precursor species and reactant conditions. In this work X-ray absorption spectroscopy is used in conjunction with liquid/liquid electrochemistry in order to highlight the significance of B r; to the reaction mechanism. We propose that the observed behavior of [AuBr
r; to the reaction mechanism. We propose that the observed behavior of [AuBr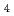 ]
] ; species described herein explain a deviation in reported behavior present in the current literature. The reported mechanistic understanding should enable a nanoparticle synthesis with a higher yield and reduce size polydispersity.
; species described herein explain a deviation in reported behavior present in the current literature. The reported mechanistic understanding should enable a nanoparticle synthesis with a higher yield and reduce size polydispersity.
 Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds
Ta intermetallic compoundsKojima, Hiroshi*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Ochi, Masaaki*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Saito, Yuichi*; Ishikawa, Norito; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*
Materials Transactions, 58(5), p.739 - 748, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Bulk samples of Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds were irradiated with 16 MeV Au, 4.5 MeV Ni, 4.5 MeV Al, 200 MeV Xe and 1.0 MeV He ions, and the change in near-surface lattice structure was investigated by means of the grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXD)and EXAFS. The Ni
Ta intermetallic compounds were irradiated with 16 MeV Au, 4.5 MeV Ni, 4.5 MeV Al, 200 MeV Xe and 1.0 MeV He ions, and the change in near-surface lattice structure was investigated by means of the grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXD)and EXAFS. The Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta lattice structures transform from the ordered structures (orthorhombic and monoclinic structures for Ni
Ta lattice structures transform from the ordered structures (orthorhombic and monoclinic structures for Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta, respectively) to the amorphous state by the Au, Ni, Al and Xe ion irradiations. Irrespective of such heavy ion species or energies, the lattice structure transformation to the amorphous state almost correlate with the density of energy deposited through elastic collisions.
Ta, respectively) to the amorphous state by the Au, Ni, Al and Xe ion irradiations. Irrespective of such heavy ion species or energies, the lattice structure transformation to the amorphous state almost correlate with the density of energy deposited through elastic collisions.
Mayumi, Ren*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Saito, Yuichi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 42(1), p.9 - 14, 2017/02
AlCu binary alloys were irradiated with 16 MeV Au, 4.5 MeV Ni or 4.5 MeV Al ions at room temperature. Changes in surface hardness and the local atomic structure around Cu atoms were examined by using the Vickers hardness measurement and the EXAFS measurements, respectively. Some specimens were aged at 453 K and Vickers hardness was measured. The computer simulation was also performed by using the rate equation method. The hardness of irradiated specimens increased much faster than that of the aged specimens and it became larger than the maximum value of the hardness for the aged specimens. The comparison of the experimental EXAFS result with that of FEFF simulation suggests that the ion irradiation produced small Cu precipitates in the specimens. The computer simulation visualized the growth process of Cu precipitates during the irradiation, and the result qualitatively corresponds to the experimental result.
Terunuma, Akihiro; Mimura, Ryuji; Nagashima, Hisao; Aoyagi, Yoshitaka; Hirokawa, Katsunori*; Uta, Masato; Ishimori, Yuu; Kuwabara, Jun; Okamoto, Hisato; Kimura, Yasuhisa; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-008, 98 Pages, 2016/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency formulated the plan to achieve the medium-term target in the period of April 2010 to March 2015(hereinafter referred to as "the second medium-term plan"). JAEA determined the plan for the business operations of each year (hereinafter referred to as "the year plan"). This report is that the Sector of Decommissioning and Radioactive Waste Management has summarized the results of the decommissioning technology development and decommissioning of nuclear facilities which were carried out in the second medium-term plan.
 Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiation
Ta intermetallic compounds induced by energetic ion beam irradiationKojima, Hiroshi*; Yoshizaki, Hiroaki*; Kaneno, Yasuyuki*; Semboshi, Satoshi*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Saito, Yuichi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 372, p.72 - 77, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.39(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ni Nb and Ni
Nb and Ni Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au
Ta intermetallic compounds, which show the complicated lattice structures were irradiated with 16 MeV Au ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni
ions at room temperature. The X-ray diffraction measurement revealed that the lattice structure of these intermetallic compounds changed from the ordered structures to the amorphous state by the ion irradiation. The irradiation-induced amorphization caused the increase in Vickers hardness. The result was compared with our previous results for Ni Al and Ni
Al and Ni V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.
V, and was discussed in terms of the intrinsic lattice structures of the samples.
 , and NaCO
, and NaCO solutions
solutionsUehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Yamana, Hajimu*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Radiochimica Acta, 104(1), p.1 - 9, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:54.81(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The spectroelectrochemical cell was fabricated for in-situ X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement. The XAFS spectra of U L -edge were monitored in electrolyte solutions during the electrochemical reduction. Tetravalent uranium was electrochemically prepared from hexavalent uranium and the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) was analyzed. The U
-edge were monitored in electrolyte solutions during the electrochemical reduction. Tetravalent uranium was electrochemically prepared from hexavalent uranium and the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) was analyzed. The U formed in 0.1M HNO
formed in 0.1M HNO was partially re-oxidized to UO
was partially re-oxidized to UO
 by NO
by NO
 in the solution. The UO
in the solution. The UO
 carbonates were prepared during electrolysis.
carbonates were prepared during electrolysis.
Nagai, Takayuki; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2015, Part B, 2 Pages, 2016/00
To investigate the characterization damage of a borosilicate glass by a neutron irradiation, the glass sample after neutron irradiation was estimated by using the Raman spectrophotometry and the synchrotron XAFS measurement. As a result, we confirmed that the Si-O bridge structure of a borosilicate glass and the containing element valence in the glass were changed by the neutron irradiation.
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Aoki, Kazufumi; Okamoto, Akiko; Kawakami, Takeshi; Kume, Nobuhide; Nakanishi, Chika; Koie, Masahiro; Kawamata, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-048, 69 Pages, 2015/02
JAEA was assigned as a designated public institution under the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and under the Armed Attack Situations Response Act. Based on these Acts, the JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the national government and/or local governments in case of disaster responses or response in the event of a military attack, etc. In order to fulfill the tasks, the JAEA has established the Emergency Action Plan and the Civil Protection Action Plan. In case of a nuclear emergency, NEAT dispatches specialists of JAEA, supplies the national government and local governments with emergency equipment and materials, and gives technical advice and information. In normal time, NEAT provides various exercises and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response institutions of the national and local governments, police, fire fighters, self-defense forces, etc. in addition to the JAEA itself. The NEAT also researches nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and cooperates with international organizations. In the FY2013, the NEAT accomplished the following tasks: (1) Technical support activities as a designated public institution in cooperation with the national and local governments, etc. (2) Human resource development, exercise and training of nuclear emergency response personnel for the national and local governments, etc. (3) Researches on nuclear disaster preparedness and response, and sending useful information (4) International contributions to Asian countries on nuclear disaster preparedness and response in collaboration with the international organizations
Sato, Takeshi; Muto, Shigeo; Okuno, Hiroshi; Katagiri, Hiromi; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Okamoto, Akiko; Koie, Masahiro; Ikeda, Takeshi; Nemotochi, Toshimasa; Saito, Toru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-046, 65 Pages, 2014/02
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, police, fire stations and nuclear operators etc., because the JAEA has been designated as the Designated Public Institution under the Basic Act on Disaster Control Measures and the Act on Response to Armed Attack Situations, etc.. The Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) of JAEA provides a comprehensive range of technical support activities to an Off-Site Center in case of a nuclear emergency. Specifically, NEAT gives technical advice and information, dispatches specialists as required, and supplies the National Government and local governments with emergency equipments and materials. NEAT provides various exercise and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention to those personnel taking an active part in emergency response organizations at normal times. The tasks of NEAT, with its past experiences as a designated public institution including the responses to TEPCO's Fukushima Accident, have been shifted to technical supports to the national government for strengthening its abilities to emergency responses; the NEAT therefore focused on maintenance and operation of its functions, and strengthening its response abilities in cooperation with the national government. This annual report summarized these activities of JAEA/NEAT in the fiscal year 2012.
Katagiri, Hiromi; Okuno, Hiroshi; Okamoto, Akiko; Ikeda, Takeshi; Tamura, Kenichi; Nagakura, Tomohiro; Nakanishi, Chika; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Abe, Minako; Sato, Sohei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-033, 70 Pages, 2012/08
When a nuclear emergency occurs in Japan, JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the National government, local governments, etc., by the Basic Law on Emergency Preparedness and the Basic Plan for Disaster Countermeasures. NEAT of JAEA gives technical advice and information, dispatch specialists as required, supplies with the National Government and local governments emergency equipment and materials. NEAT provides various lectures and training courses concerning nuclear disaster prevention for emergency response organizations at normal time. Concerning the assistance to the Accident of Fukushima No.1 Nuclear Power Station caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake on 11 March, 2011, JAEA assisted activities including environmental radiation monitoring, environmental radioactivity analyses, resident public consulting etc., with its the utmost effort. This annual report summarized these activities of NEAT in the fiscal year 2011.
 O
O -doped CeO
-doped CeO by means of synchrotron radiation X-ray spectroscopy
by means of synchrotron radiation X-ray spectroscopyTahara, Yuki*; Shimizu, Hirotaka*; Ishikawa, Norito; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Hori, Fuminobu*; Matsui, Toshiyuki*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 277, p.53 - 57, 2012/04
In this study, to simulate such an environment, Gd O
O -doped CeO
-doped CeO samples were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe
samples were irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions at room temperature using an ion beam accelerator at JAEA-Tokai. As CeO
ions at room temperature using an ion beam accelerator at JAEA-Tokai. As CeO has the same fluorite structure as that of UO
has the same fluorite structure as that of UO and several properties of CeO
and several properties of CeO are similar to UO
are similar to UO , in this study CeO
, in this study CeO was used as a simulation material of UO
was used as a simulation material of UO . To study the effects of the ion irradiation on Gd
. To study the effects of the ion irradiation on Gd O
O -doped CeO
-doped CeO , extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used at the Photon Factory of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) as well as conventional X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurement. The EXAFS and XRD spectra show that the effects of the ion irradiation are more pronounced for higher amount of Gd
, extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used at the Photon Factory of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) as well as conventional X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurement. The EXAFS and XRD spectra show that the effects of the ion irradiation are more pronounced for higher amount of Gd O
O dopant.
dopant.