Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimizu, Mayuko; Amano, Kenji; Mizuno, Takashi; Hama, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Review 2021-004, 92 Pages, 2021/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting research and development (R&D) on geological disposal technology in order to establish a scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of HLW. "Debriefing Session on JAEA's Underground Research Laboratory" was held online on December 1, 2020 by live stream on YouTube, in order to widely disseminate the results of R&D themes ("Important issues") that we have been focusing on from fiscal year 2015 to 2019 and the plans for 2020 and beyond, and to further enhance the research plan. This document summarizes the overview of the debriefing session and the presentation materials.
Tateishi, Ryo*; Shimada, Koji; Shimizu, Mayuko; Ueki, Tadamasa*; Niwa, Masakazu; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishimaru, Tsuneari
Oyo Chishitsu, 62(2), p.104 - 112, 2021/06
We attempted to discriminate between active and non-active faults by linear discriminant analysis using the chemical composition data of fault gouges in Japan, and then examined the elements that represent the difference between them and better discriminants. As a result, the multiple discriminants obtained could discriminate between them with high probability. In addition, the generalization performance of these discriminants is discussed, and the discriminants that can be expected to have high discriminant performance for unknown samples are presented. Also, from the combination of elements common to these discriminants, we narrowed down the number of elements that represent the difference between active and non-active faults to 6, and showed that the combination of TiO and Sr contributing the most to the discrimination. The method applied in this study is an innovative one that can discriminate the activity by chemical analysis of fault rocks that are universally present in the bedrock.
and Sr contributing the most to the discrimination. The method applied in this study is an innovative one that can discriminate the activity by chemical analysis of fault rocks that are universally present in the bedrock.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-011, 67 Pages, 2020/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 5th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Nishio, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Mayuko; Iyatomi, Yosuke; Hama, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Review 2020-013, 59 Pages, 2020/08
The Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting geoscientific study in order to establish a scientific and technological basis for the geological disposal of HLW. Technical information of the result on the geoscientific study conducted at TGC is provided at the annual Information and Opinion Exchange Conference on Geoscientific Study of TGC for exchanging opinions among researchers and engineers from universities, research organizations and private companies. This document compiles the research presentations and posters of the conference in Mizunami on November 20, 2019.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Koji; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-010, 46 Pages, 2020/07
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2020. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2020 are described in detail based on the JAEA 3rd Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-006, 66 Pages, 2019/11
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 4th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Review 2019-010, 46 Pages, 2019/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2019. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2019 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-015, 89 Pages, 2019/03
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 3rd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this report, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Shimizu, Mayuko; Sano, Naomi; Ueki, Tadamasa; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yasue, Kenichi*; Niwa, Masakazu
Island Arc, 28(2), p.e12295_1 - e12295_13, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.28(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2018-020, 46 Pages, 2019/01
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2018. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2018 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Yasue, Kenichi*; Asamori, Koichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Saiga, Atsushi; Shimizu, Mayuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-008, 83 Pages, 2018/12
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 2nd fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Yonaga, Yusuke; Shimizu, Mayuko; Sano, Naomi; Ueki, Tadamasa; Yoshikawa, Kiyotaka*; Niwa, Masakazu
JAEA-Testing 2018-001, 29 Pages, 2018/07
Study on the formation process of mountains provides important clues for evaluating the uplift and erosion related to long-term changes of geological environment for geological disposal. Provenance analysis of detrital sediments is often be effective to understand the process. In the Tono Geoscience Center, quick and efficient mineralogical and chemical analyses for heavy minerals in basement rocks and sediments have been developed using the electron probe microanalyzer (JEOL JXA-8530F EPMA), as one of the promising tool for provenance analysis. To contribute evaluation of the analyses, sample preparation and EPMA analyses of heavy minerals were shown in this paper.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Akiomi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Saiga, Atsushi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2017-022, 45 Pages, 2017/12
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, in fiscal year 2017. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2017 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
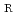 =100 mm spectrometer and correction of interferences between Th, U, and Pb with natural monazite
=100 mm spectrometer and correction of interferences between Th, U, and Pb with natural monaziteShimizu, Mayuko; Shibata, Kenji*; Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Niwa, Masakazu
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 112(2), p.88 - 96, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.19(Mineralogy)This paper outlines an advanced procedure involving the chemical Th-U-total Pb isochron method (CHIME) dating of monazite using a field-emission electron probe microanalyzer (FE-EPMA) equipped with spectrometers of 100 mm Rowland circle (R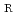 ) radius. The higher count rate of R
) radius. The higher count rate of R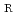 = 100 mm wavelength dispersive spectrometer (WDS) compared to R
= 100 mm wavelength dispersive spectrometer (WDS) compared to R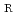 = 140 mm WDS enables measurements to be taken in a shorter time. CHIME dating using R
= 140 mm WDS enables measurements to be taken in a shorter time. CHIME dating using R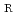 = 100 mm WDS had previously been difficult because of lower resolution compared to that of R
= 100 mm WDS had previously been difficult because of lower resolution compared to that of R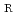 = 140 mm WDS. This problem has been overcome by a new interference correction method using natural monazites.
= 140 mm WDS. This problem has been overcome by a new interference correction method using natural monazites.
Shimizu, Mayuko; Sano, Naomi; Suzuki, Kazuhiro
Nagoya Daigaku Nendai Sokutei Kenkyu, 1, p.36 - 43, 2017/03
We established a CHIME monazite dating method using R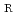 = 100 mm spectrometers and a provenance analysis method using heavy minerals for the dating and analysis of minerals. CHIME dating has traditionally been performed with conventional R
= 100 mm spectrometers and a provenance analysis method using heavy minerals for the dating and analysis of minerals. CHIME dating has traditionally been performed with conventional R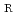 = 140 mm spectrometers for measurement of U, Th, and Pb. These spectrometers, however, have low count rates in measurements of Pb. We used a JEOL JXA-8530F FE-EPMA equipped with R
= 140 mm spectrometers for measurement of U, Th, and Pb. These spectrometers, however, have low count rates in measurements of Pb. We used a JEOL JXA-8530F FE-EPMA equipped with R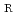 = 100 mm spectrometers, a system installed at Tono Geoscience Center in 2014, for the CHIME dating of monazite. We corrected the spectral interferences peculiar to R
= 100 mm spectrometers, a system installed at Tono Geoscience Center in 2014, for the CHIME dating of monazite. We corrected the spectral interferences peculiar to R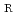 = 100 mm spectrometers by the method of AA mli and Griffin (1975) for monazite analyses. We calculated the correction factors by a new interference correction method using natural monazites. We also established a quick quantitative analysis and identification method for heavy minerals using the EPMA.
= 100 mm spectrometers by the method of AA mli and Griffin (1975) for monazite analyses. We calculated the correction factors by a new interference correction method using natural monazites. We also established a quick quantitative analysis and identification method for heavy minerals using the EPMA.
Shimizu, Mayuko; Sano, Naomi; Shibata, Kenji*
JAEA-Testing 2016-004, 40 Pages, 2017/02
X-ray fluorescence analysis is one of the methods commonly used to reveal whole-rock chemical composition, which is basic information of rock samples. This report shows methods to prepare glass beads of fused samples and to use the X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (Rigaku ZSX Primus II) housed in Tono Geoscience Center, and the evaluation of precision and accuracy of the measurement.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-023, 91 Pages, 2017/02
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. In this paper, the current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Hama, Yuki
JAEA-Review 2016-016, 44 Pages, 2016/08
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in JAEA, in fiscal year 2016. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2016 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Kameda, Jun*; Shimizu, Mayuko
Nendo Kagaku, 54(3), p.105 - 113, 2016/00
Umeda, Koji; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Fujita, Natsuko; Shimizu, Mayuko; Matsubara, Akihiro; Tamura, Hajimu; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2015-019, 42 Pages, 2015/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in JAEA, in fiscal year 2015. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2015 are described in detail based on the outline of 7 years plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). Background of this research is clarified with the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress in this report. In addition, the plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.